
Acta Horticulturae Sinica ›› 2024, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (5): 1137-1150.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2023-0146
• Plant Protection • Previous Articles Next Articles
WANG Qing1,3, HU Yan2, CHEN Shan1, LU Jingwei2, ZHENG Yang2, TAO Weilin2, SUN Xianchao1, ZHOU Na2,**( ), CHEN Guokang1,**(
), CHEN Guokang1,**( )
)
Received:2023-10-08
Revised:2024-02-10
Online:2024-05-25
Published:2024-05-29
WANG Qing, HU Yan, CHEN Shan, LU Jingwei, ZHENG Yang, TAO Weilin, SUN Xianchao, ZHOU Na, CHEN Guokang. Biocontrol Efficacy and Mechanisms of Streptomyces purpeofuscus CC2-6 Against Chinese Cabbage Clubroot Caused by Plasmodiophora brassicae[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(5): 1137-1150.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.ahs.ac.cn/EN/10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2023-0146
| 病原菌 Target pathogen | 抑制率 Inhibition rate | 病原菌 Target pathogen | 抑制率 Inhibition rate |
|---|---|---|---|
| 棉花枯萎病菌Fusarium oxysporum | 50.30 ± 1.50 | 油菜菌核病菌Sclerotinia sclerotiorum | 76.19 ± 1.19 |
| 甘薯软腐病菌Rhizopus stolonifer | 51.67 ± 0.78 | 棉花立枯病菌Thanatepehorus cucumeris | 52.79 ± 1.51 |
| 茄褐纹病菌Phomopsis vexans | 55.58 ± 1.24 | 辣椒疫霉病菌Phytophthora capsici | 66.67 ± 1.67 |
| 烟草灰霉病菌Botrytis cinerea | 53.95 ± 0.63 | 黄瓜猝倒病菌Pythium delicense | 72.31 ± 0.96 |
| 烟草炭疽病菌Colletotrichum micotianae | 47.20 ± 5.21 | 烟草叶斑病菌Pestalotiopsis nicotiae | 59.71 ± 0.75 |
Table 1 Inhibitory effect of actinomycete CC2-6 on ten pathogens %
| 病原菌 Target pathogen | 抑制率 Inhibition rate | 病原菌 Target pathogen | 抑制率 Inhibition rate |
|---|---|---|---|
| 棉花枯萎病菌Fusarium oxysporum | 50.30 ± 1.50 | 油菜菌核病菌Sclerotinia sclerotiorum | 76.19 ± 1.19 |
| 甘薯软腐病菌Rhizopus stolonifer | 51.67 ± 0.78 | 棉花立枯病菌Thanatepehorus cucumeris | 52.79 ± 1.51 |
| 茄褐纹病菌Phomopsis vexans | 55.58 ± 1.24 | 辣椒疫霉病菌Phytophthora capsici | 66.67 ± 1.67 |
| 烟草灰霉病菌Botrytis cinerea | 53.95 ± 0.63 | 黄瓜猝倒病菌Pythium delicense | 72.31 ± 0.96 |
| 烟草炭疽病菌Colletotrichum micotianae | 47.20 ± 5.21 | 烟草叶斑病菌Pestalotiopsis nicotiae | 59.71 ± 0.75 |

Fig. 1 Biocontrol efficiency of antagonistic strains CC2-6 against clubroot on Chinese cabbage A. Observation on root incidence of potted Chinese cabbage under microscope;B. Root disease phenotype. Student’s t-test(*** P < 0.001).
| 处理 Treatment | 防治效果/% Indoor control effect |
|---|---|
| 同时接菌 Strain CC2-6 was simultaneously inoculated with P. brassicae | 27.46 ± 2.37 b |
| 提前7 d接种菌株CC2-6 Strain CC2-6 was inoculated 7 d in advance | 53.20 ± 1.82 a |
Table 2 Control effect of strain CC2-6 on Chinese cabbage clubroot in pot trials
| 处理 Treatment | 防治效果/% Indoor control effect |
|---|---|
| 同时接菌 Strain CC2-6 was simultaneously inoculated with P. brassicae | 27.46 ± 2.37 b |
| 提前7 d接种菌株CC2-6 Strain CC2-6 was inoculated 7 d in advance | 53.20 ± 1.82 a |

Fig. 2 Morphological features of actinomycete strain CC2-6 on GS-1 A:Culture morphology;B:Single colonies;C:Mycelia growing on a glass slide placed on GS-1 culture.
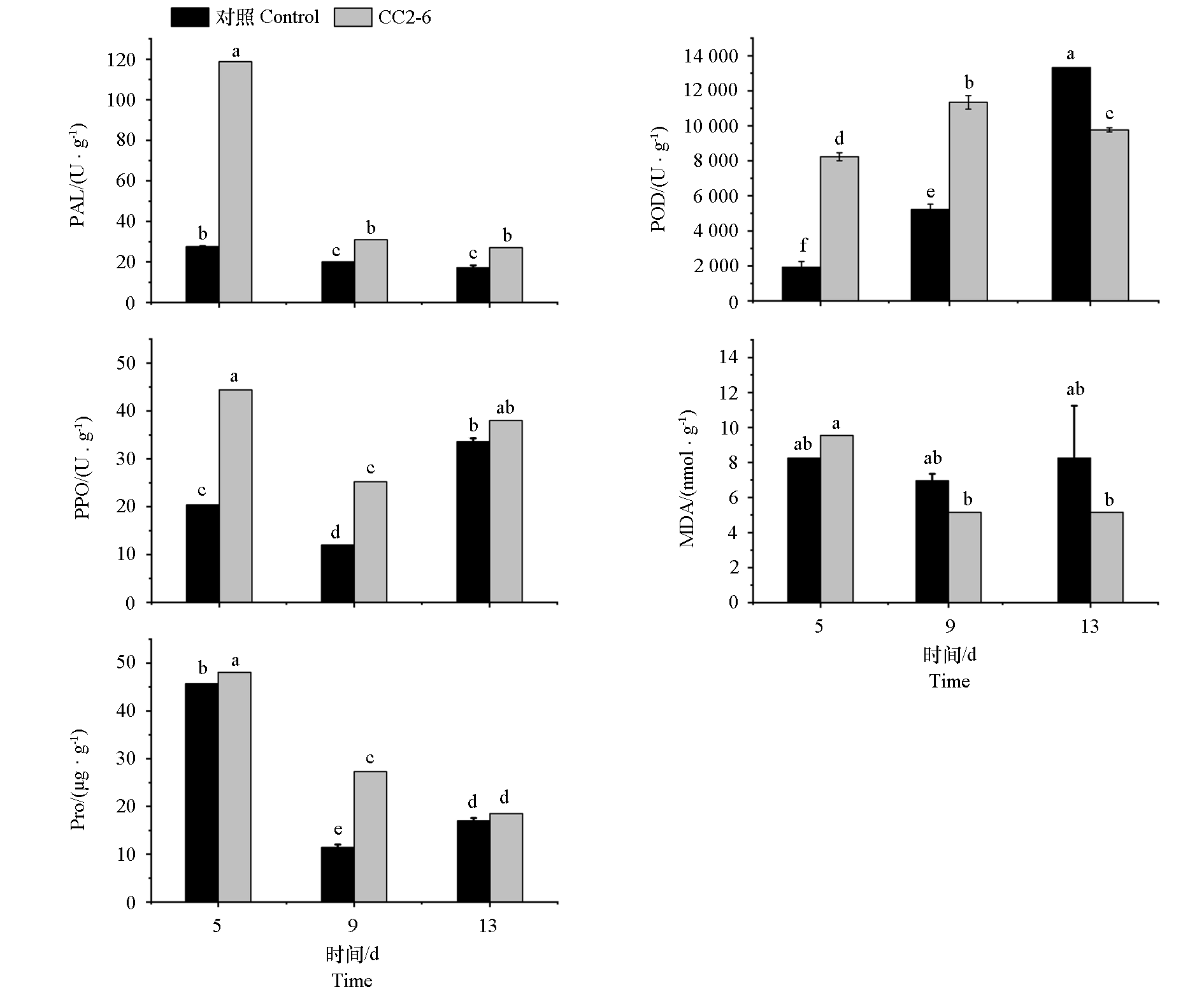
Fig. 5 Effects of fermentation broth of antagonistic actinomycetes CC2-6 on activities of PAL,POD,PPO,MDA and Pro in Chinese cabbage LSD’s test,P < 0.05.
| 编号 | 代谢物 | 归一化后的代谢物丰度 Metabolic abundance after normalization | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Code | Metabolite components | CC2-6-1 | CC2-6-2 | CC2-6-3 |
| pos_628 | 诺氟沙星 Norfloxacin | 0.001539502 | 0.000906463 | 0.001681919 |
| pos_695 | 四环素 Tetracycline | 2.28324E-05 | 6.55759E-06 | 2.04925E-05 |
| pos_690 | 潮霉素B Hygromycin B | 3.22625E-05 | 1.30073E-07 | 3.03196E-05 |
| pos_664 | 托普霉素 Tobramycin | 0.000110993 | 6.0012E-05 | 6.48009E-05 |
| pos_683 | 盐霉素 Salinomycin | 0.023219173 | 0.022620707 | 0.022703959 |
| pos_474 | 2-苯乙醇 2-Phenylethanol | 6.18249E-06 | 5.00147E-06 | 4.44714E-06 |
| pos_445 | 莽草酸 Shikimic acid | 3.38127E-06 | 3.21205E-06 | 4.07632E-06 |
| pos_708 | 紫杉醇 Paclitaxel | 2.47289E-05 | 3.74363E-05 | 3.1205E-05 |
| pos_482 | 熊果苷 Arbutin | 0.000933082 | 0.00089494 | 0.00096134 |
| pos_236 | L-岩藻糖 L-Fucose | 5.18191E-06 | 3.25384E-06 | 3.57858E-06 |
| pos_26 | 麦芽四糖Maltotetraose | 0.006656552 | 0.006144853 | 0.007064496 |
| pos_345 | 乙酰丁香酮 Acetosyringone | 0.000384261 | 0.001579729 | 0.000450847 |
| pos_54 | 姜油酮 Zingerone | 2.82372E-05 | 2.29699E-05 | 3.25111E-05 |
| pos_250 | 香豆酸 Coutaric acid | 0.000821003 | 0.001010641 | 0.000847733 |
| pos_469 | 阿斯特酚苷 Astringin | 5.47227E-05 | 5.21228E-06 | 4.92987E-05 |
Table 3 Analysis of metabolites of CC2-6 fermentation broth with antibacterial activity in positive ion mode
| 编号 | 代谢物 | 归一化后的代谢物丰度 Metabolic abundance after normalization | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Code | Metabolite components | CC2-6-1 | CC2-6-2 | CC2-6-3 |
| pos_628 | 诺氟沙星 Norfloxacin | 0.001539502 | 0.000906463 | 0.001681919 |
| pos_695 | 四环素 Tetracycline | 2.28324E-05 | 6.55759E-06 | 2.04925E-05 |
| pos_690 | 潮霉素B Hygromycin B | 3.22625E-05 | 1.30073E-07 | 3.03196E-05 |
| pos_664 | 托普霉素 Tobramycin | 0.000110993 | 6.0012E-05 | 6.48009E-05 |
| pos_683 | 盐霉素 Salinomycin | 0.023219173 | 0.022620707 | 0.022703959 |
| pos_474 | 2-苯乙醇 2-Phenylethanol | 6.18249E-06 | 5.00147E-06 | 4.44714E-06 |
| pos_445 | 莽草酸 Shikimic acid | 3.38127E-06 | 3.21205E-06 | 4.07632E-06 |
| pos_708 | 紫杉醇 Paclitaxel | 2.47289E-05 | 3.74363E-05 | 3.1205E-05 |
| pos_482 | 熊果苷 Arbutin | 0.000933082 | 0.00089494 | 0.00096134 |
| pos_236 | L-岩藻糖 L-Fucose | 5.18191E-06 | 3.25384E-06 | 3.57858E-06 |
| pos_26 | 麦芽四糖Maltotetraose | 0.006656552 | 0.006144853 | 0.007064496 |
| pos_345 | 乙酰丁香酮 Acetosyringone | 0.000384261 | 0.001579729 | 0.000450847 |
| pos_54 | 姜油酮 Zingerone | 2.82372E-05 | 2.29699E-05 | 3.25111E-05 |
| pos_250 | 香豆酸 Coutaric acid | 0.000821003 | 0.001010641 | 0.000847733 |
| pos_469 | 阿斯特酚苷 Astringin | 5.47227E-05 | 5.21228E-06 | 4.92987E-05 |
| 编号 | 代谢物 | 归一化后的代谢物丰度 Metabolic abundance after normalization | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Code | metabolite components | CC2-6-1 | CC2-6-2 | CC2-6-3 |
| neg_575 | 土霉素 Oxytetracycline | 1.87E-05 | 6.75E-07 | 0.075964 |
| neg_51 | 放线酰胺素 actinonin | 0.023284 | 0.014191 | 0.000149 |
| neg_611 | 氟康唑Fluconazole | 0.00664 | 0.014538 | 0 |
| neg_511 | 印楝素A Azadirachtin A | 0.00039 | 0.000211 | 0.015373 |
| neg_569 | 柚皮苷 Naringin | 0.004988 | 0.005777 | 1.48E-05 |
| neg_372 | 硫乳霉素 Thiolactomycin | 2.64E-05 | 1.16E-05 | 0.003713 |
| neg_518 | 银杏内酯B Ginkgolide B | 0.001923 | 0.001084 | 0.000244 |
| neg_233 | 4-羟基苯甲酸 4-Hydroxybenzoic acid | 0.000101 | 0.000116 | 0.001317 |
| neg_510 | 喜树碱 Camptothecin | 0.000331 | 0.001183 | 1.92E-05 |
| neg_552 | 潮霉素B Hygromycin B | 0 | 0 | 0.001455 |
| neg_159 | 苯乙胺 Phenylethylamine | 0.000451 | 0.000677 | 0.000183 |
| neg_9 | 柠檬酸 Citric acid | 0.00079 | 0.000511 | 0 |
| neg_152 | 二羟丙酮 Dihydroxyacetone | 0.00047 | 0.000458 | 0.000222 |
| neg_446 | 噻苯咪唑 Thiabendazole | 0.00034 | 0.000636 | 0.000151 |
| neg_648 | 淫羊藿苷 Icariin | 0.000323 | 0.000301 | 0 |
| neg_354 | 对羟基肉桂酸 4-Hydroxycinnamic acid | 1.61E-05 | 1.5E-05 | 0.000363 |
| neg_320 | 新生霉素 Novobiocin | 0 | 0 | 0.000288 |
| neg_617 | 多球壳菌素 Myriocin | 0 | 0 | 0.00028 |
| neg_513 | 四环素 Tetracycline | 0.000129 | 0.000133 | 1.25E-06 |
| neg_667 | 依诺沙星 Enoxacin | 7.17E-06 | 5.7E-06 | 0.000149 |
Table 4 Analysis of metabolites of CC2-6 fermentation broth with antibacterial activity in negative ion mode
| 编号 | 代谢物 | 归一化后的代谢物丰度 Metabolic abundance after normalization | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Code | metabolite components | CC2-6-1 | CC2-6-2 | CC2-6-3 |
| neg_575 | 土霉素 Oxytetracycline | 1.87E-05 | 6.75E-07 | 0.075964 |
| neg_51 | 放线酰胺素 actinonin | 0.023284 | 0.014191 | 0.000149 |
| neg_611 | 氟康唑Fluconazole | 0.00664 | 0.014538 | 0 |
| neg_511 | 印楝素A Azadirachtin A | 0.00039 | 0.000211 | 0.015373 |
| neg_569 | 柚皮苷 Naringin | 0.004988 | 0.005777 | 1.48E-05 |
| neg_372 | 硫乳霉素 Thiolactomycin | 2.64E-05 | 1.16E-05 | 0.003713 |
| neg_518 | 银杏内酯B Ginkgolide B | 0.001923 | 0.001084 | 0.000244 |
| neg_233 | 4-羟基苯甲酸 4-Hydroxybenzoic acid | 0.000101 | 0.000116 | 0.001317 |
| neg_510 | 喜树碱 Camptothecin | 0.000331 | 0.001183 | 1.92E-05 |
| neg_552 | 潮霉素B Hygromycin B | 0 | 0 | 0.001455 |
| neg_159 | 苯乙胺 Phenylethylamine | 0.000451 | 0.000677 | 0.000183 |
| neg_9 | 柠檬酸 Citric acid | 0.00079 | 0.000511 | 0 |
| neg_152 | 二羟丙酮 Dihydroxyacetone | 0.00047 | 0.000458 | 0.000222 |
| neg_446 | 噻苯咪唑 Thiabendazole | 0.00034 | 0.000636 | 0.000151 |
| neg_648 | 淫羊藿苷 Icariin | 0.000323 | 0.000301 | 0 |
| neg_354 | 对羟基肉桂酸 4-Hydroxycinnamic acid | 1.61E-05 | 1.5E-05 | 0.000363 |
| neg_320 | 新生霉素 Novobiocin | 0 | 0 | 0.000288 |
| neg_617 | 多球壳菌素 Myriocin | 0 | 0 | 0.00028 |
| neg_513 | 四环素 Tetracycline | 0.000129 | 0.000133 | 1.25E-06 |
| neg_667 | 依诺沙星 Enoxacin | 7.17E-06 | 5.7E-06 | 0.000149 |
| [1] |
|
|
陈亮, 陈年来. 2019. 西瓜叶片防御酶活性与枯萎病抗性的关系. 河南农业科学, 48 (1):77-83,114.
|
|
| [2] |
|
|
陈美云. 2019. 防控生姜茎基腐病的生防菌与杀菌剂协同施用研究[硕士论文]. 泰安: 山东农业大学.
|
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
|
董乔琳. 2017. 芸薹根肿菌近红外光谱检测体系及喜树碱抑菌机理的研究[博士论文]. 武汉: 华中农业大学.
|
|
| [5] |
|
|
杜蕙, 王春明, 郭建国, 漆永红, 蒋晶晶. 2019. 葡萄生单轴霉菌对葡萄几种防御酶活性的影响. 江苏农业科学, 47 (15):151-154.
|
|
| [6] |
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2561.2022.09.015 |
|
段雅婕, 杨宝明, 郭志祥, 尹可锁, 胡会刚, 曾莉, 白亭亭. 2022. 外源水杨酸诱导香蕉苯丙烷类代谢提高对枯萎病抗性. 热带作物学报, 43 (9):1870-1879.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2561.2022.09.015 |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
|
江彤, 杨建卿, 高明, 孔俊. 2006. 不同抗病性烟草罹黑胫病后几种酶的活性及丙二醛含量的变化. 安徽农业大学学报,(2):218-221.
|
|
| [9] |
|
|
李建, 黄琳丽. 2020. 乙烯在植物抗性反应中的作用. 生物化工, 6 (6):140-142.
|
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
|
李玉龙. 2019. 生防菌对两种作物病害的防治作用及机理[博士论文]. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学.
|
|
| [13] |
|
|
刘翠平. 2014. 甘蓝根肿病生防菌的筛选及防治效果测定[硕士论文]. 重庆: 西南大学.
|
|
| [14] |
|
|
刘会宁, 李从玉. 2015. 6个生理生化指标与葡萄抗白粉病的关系. 中国南方果树, 44 (5):79-82.
|
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
|
罗红春. 芸薹根肿菌生活史研究I—病原菌的侵染[硕士论文]. 重庆: 西南大学.
|
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
|
彭飞飞. 2021. 外源茉莉酸及茉莉酸甲酯对日本落叶松防御蛋白活性的影响[硕士论文]. 恩施: 湖北民族大学.
|
|
| [20] |
|
|
彭海莹. 2020. 烟草黑胫病和根黑腐病的生物防治技术研究[硕士论文]. 泰安: 山东农业大学.
|
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
|
王靖, 黄云, 张艳, 姚佳. 2011. 油菜根肿病菌拮抗微生物的筛选及其防治效果测定. 中国油料作物学报, 33 (2):169-174.
|
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
|
吴道军. 2013. 十字花科根肿病室内接种标准化研究[硕士论文]. 重庆: 西南大学.
|
|
| [26] |
|
|
吴鑫燕, 姚雪琴, 李光庆, 刘春晴, 黄雷, 谢祝捷, 耿春女. 2020. 芸薹属植物根肿病的研究进展. 分子植物育种, 20 (16):5377-5385.
|
|
| [27] |
|
|
吴泽钰. 2020. 柚皮苷对主要致龋细菌及生物膜作用的实验研究[硕士论文]. 乌鲁木齐: 新疆医科大学.
|
|
| [28] |
|
|
杨晓琴, 马冠华, 周丹妮, 陈国康, 肖崇刚. 2015. 芸薹根肿菌次生游动孢子侵染致病分析. 植物保护学报, 42 (2):188-193.
|
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
|
张建. 2015. 生防木霉(Trichoderma guizhouense NJAU 4742)重寄生分子机理研究Ⅰ中性金属肽酶NMP1和活性氧的功能分析[博士论文]. 南京: 南京农业大学.
|
|
| [31] |
|
|
张立钦, 孙逸钊, 王品维, 童森淼, 马良进. 2008. 喜树碱对黄瓜白粉病和霜霉病及水稻纹枯病的抑菌活性. 浙江林学院学报,(6):681-684.
|
|
| [32] |
|
|
张莹莹, 郝文娟, 李宏玉, 马艳, 毛伟力. 2022. 一株多黏类芽胞杆菌Paenibacillus polymyxa菌株P1防治广东菜心根肿病的研究. 植物保护, 48 (1):291-296,304.
|
|
| [33] |
|
|
周东兴, 王恩泽, 刘多, 金聪敏, 李欣, 姜姗, 白皓天. 2020. 番茄枯萎病生防细菌的筛选及对植株防御酶活性的影响. 生态学杂志, 39 (5):1753-1760.
|
|
| [34] |
|
| [1] | CHEN Ming, ZHANG Jieru, YANG Hangyun, WANG Yinbao, ZHENG Zhiyuan, ZENG Jiaoke, CHEN Jinyin, FU Yongqi, and XIANG Miaolian. Induction Mechanism of Methyl Jasmonate on Postharvest Navel Orange Fruit Against Blue Mold [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(9): 2183-2194. |
| [2] | ZHENG Chuanqi, TANG Yuchao, YANG Panpan, PENG Fuhai, XU Leifeng, TANG Le, ZHI Yongming, and MING Jun, . Advances in Bitter Taste of the Horticultural Plants [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(7): 1529-1546. |
| [3] | QIAO Chengkui, ZHUANG Ming, TIAN Fajun, WANG Caixia, PANG Tao, CHEN Ruxia, LI Xiaoguang, CHENG Xin, and XIE Hanzhong, . Degradation Behaviors and Dietary Risk Assessment of Flonicamid and Spirotetramat in Kiwifruit Plantations [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(6): 1386-1402. |
| [4] | PENG Yulong, SUN Xiaofang, WANG Shuangshuang, HAN Chang, LIU Ting, HUANG Yun. Research Progress on the Resting Spore and Zoospore of Plasmodiophora brassicae [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(9): 1987-1996. |
| [5] | WANG Yu, ZHANG Xue, ZHANG Xueying, ZHANG Siyu, WEN Tingting, WANG Yingjun, GAN Caixia, PANG Wenxing. The Effect of Camalexin on Chinese Cabbage Resistance to Clubroot [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(8): 1689-1698. |
| [6] | RUI Tingting, GAO Qingyun, LI Xiaojing, SHI Yanxia, XIE Xuewen, LI Lei, ZHANG Hongjie, XU Wenjuan, CHAI Ali, LI Baoju. Methylene Blue Combined Agarose Assay for Single-spore Isolation of Plasmodiophora brassicae and Pathotype Differentiation [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(6): 1290-1300. |
| [7] | XIANG Miaolian, WU Fan, LI Shucheng, MA Qiaoli, WANG Yinbao, XIAO Liuhua, CHEN Jinyin, CHEN Ming. Exogenous Melatonin Regulates Reactive Oxygen Metabolism to Induce Resistance of Postharvest Pear Fruit to Black Spot [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(5): 1102-1110. |
| [8] | WANG Hong, YANG Wangli, LIN Jing, YANG Qingsong, LI Xiaogang, SHENG Baolong, CHANG Youhong. Comparative Metabolic and Transcriptomic Analysis of Ripening Fruit in Pear Cultivars of‘Sucui 1’‘Cuiguan’and‘Huasu’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(3): 493-508. |
| [9] | LI Chunhong, WANG Kaituo, LEI Changyi, XU Feng, JI Nana, JIANG Yongbo. Identification of TGA Gene Family in Peach and Analysis of Expression Mode Involved in a BABA-Induced Disease Resistance [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(2): 265-280. |
| [10] | LIANG Qiaolan*,WEI Liexin,XU Bingliang,ZHANG Shuwu,and HAN Liang. Effect of the Trichoderma atroviride T2 Proteinaceous TraT2A Induction Treatment on Photoresponsive and Fluorescent Characteristics of Lily Leaves inoculated Botrytis cinerea [J]. ACTA HORTICULTURAE SINICA, 2020, 47(4): 769-778. |
| [11] | DOU Guoxia1,JIANG Chunhao2,GUO Hongna1,LIU Jia1,HE Qinyu1,and XIAO Hongmei1,*. Studies on the Resistance Induction of Hanseniaspora uvarum to Postharvest Gray Mold in Strawberry [J]. ACTA HORTICULTURAE SINICA, 2019, 46(7): 1290-1302. |
| [12] | SONG Xin,TAN Fengquan,ZHANG Miao,CAI Yuankang,GUO Dayong,XIE Kaidong,WU Xiaomeng,and GUO Wenwu*. Metabolic Characteristics of Interspecific Allotetraploid Somatic Hybrid Between‘Newhall’Navel Orange and‘Eureka’Lemon [J]. ACTA HORTICULTURAE SINICA, 2019, 46(1): 37-46. |
| [13] | FANG Xinsheng*,ZHOU Hongying,NING Anqi,SU Jie,and WANG Jianhua*. Comparison of Pollen Morphology and Chemical Components of Flower Between Long Style Typeand ShortStyle Type of Forsythia suspense [J]. ACTA HORTICULTURAE SINICA, 2017, 44(2): 373-380. |
| [14] | XIANG Miaolian1,ZHAO Xianyang1,CHEN Ming1,FU Yongqi1,and ZENG Xiaochun1,2,*. Involvement of Induced Resistance by Methyl Jasmonate to Bacterial Wilt and Reactive Oxygen Species Metabolism in Pepper Seedlings [J]. ACTA HORTICULTURAE SINICA, 2017, 44(10): 1985-1992. |
| [15] | SUN Ping-ping,JIA Xiao-hui,CUI Jian-chao,TONG Wei,and WANG Wen-hui *. Selection,Identification and Characterization of Actinomyces L-30 for the Biocontrol of Pear Gray Mold [J]. ACTA HORTICULTURAE SINICA, 2016, 43(12): 2335-2346. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2012 Acta Horticulturae Sinica 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
Tel: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
Support by: Beijing Magtech Co.Ltd