
Acta Horticulturae Sinica ›› 2024, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (2): 411-422.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2023-0484
• Plant Protection • Previous Articles Next Articles
ZHU Jie1,2, LU Dingyihui2, ZHANG Deyong2, ZHANG Zhanhong3, ZHANG Zhuo2, SHI Xiaobin2,*( ), LIU Yong1,2,*(
), LIU Yong1,2,*( )
)
Received:2023-09-22
Revised:2024-01-06
Online:2024-02-25
Published:2024-02-27
Contact:
SHI Xiaobin, LIU Yong
ZHU Jie, LU Dingyihui, ZHANG Deyong, ZHANG Zhanhong, ZHANG Zhuo, SHI Xiaobin, LIU Yong. Effect of ToCV and TYLCV Infection on Detoxification Enzymes of Bemisia tabaci[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(2): 411-422.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.ahs.ac.cn/EN/10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2023-0484
| 目的 Purpose | 引物名称 Primer name | 引物序列(5′-3′) Primer sequence |
|---|---|---|
| ToCV RT-PCR | ToCV-3F | GGTTTGGATTTTGGTACTACATTCAGT |
| ToCV-3R | AAACTGCCTGCATGAAAAGTCTC | |
| TYLCV RT-PCR | TYLCV-F | GTTCACGGATTTCGTTGTATG |
| TYLCV-R | AGAGGGACTGGCAAAGCAACA | |
| Bemisia tabaci 参考基因 Bemisia tabaci reference genes | Actin-F | CGCTGCCTCCACCTCATT |
| Actin-R | ACCGCAAGATTCCATACCC | |
| EF-1α-F | AGCCTTGTGCCAATTTCCG | |
| EF-1α-R | CCTTCAGCATTACCGTCC | |
| CarE-F | CCCTCTCGAGCAGCAAAGAA | |
| CarE-R | GGCCTTCAAGAGAACGGACA | |
| GST-F | GAGCCGGTTCGTTTCATCCT | |
| GST-R | TCCCAAATGGTGTGGTTGGT | |
| AchE-F | CCACGAGGATTGCCTCTACC | |
| AchE-R | GAGAGCGGAACCATCCCAAA | |
| P450-F | CAACAATGCTGGTTCGGAGC | |
| P450-R | CCAAGTGAGCTGTGATGGGT | |
| UDP-F | CGGCGTAAATTTGCAGCGTA | |
| UDP-R | TGCAACCCGCCTATCAAACT |
Table 1 Primer list used in the experiment
| 目的 Purpose | 引物名称 Primer name | 引物序列(5′-3′) Primer sequence |
|---|---|---|
| ToCV RT-PCR | ToCV-3F | GGTTTGGATTTTGGTACTACATTCAGT |
| ToCV-3R | AAACTGCCTGCATGAAAAGTCTC | |
| TYLCV RT-PCR | TYLCV-F | GTTCACGGATTTCGTTGTATG |
| TYLCV-R | AGAGGGACTGGCAAAGCAACA | |
| Bemisia tabaci 参考基因 Bemisia tabaci reference genes | Actin-F | CGCTGCCTCCACCTCATT |
| Actin-R | ACCGCAAGATTCCATACCC | |
| EF-1α-F | AGCCTTGTGCCAATTTCCG | |
| EF-1α-R | CCTTCAGCATTACCGTCC | |
| CarE-F | CCCTCTCGAGCAGCAAAGAA | |
| CarE-R | GGCCTTCAAGAGAACGGACA | |
| GST-F | GAGCCGGTTCGTTTCATCCT | |
| GST-R | TCCCAAATGGTGTGGTTGGT | |
| AchE-F | CCACGAGGATTGCCTCTACC | |
| AchE-R | GAGAGCGGAACCATCCCAAA | |
| P450-F | CAACAATGCTGGTTCGGAGC | |
| P450-R | CCAAGTGAGCTGTGATGGGT | |
| UDP-F | CGGCGTAAATTTGCAGCGTA | |
| UDP-R | TGCAACCCGCCTATCAAACT |

Fig. 1 The results of healthy(A),TYLCV-infected(B),ToCV-infected(C),ToCV and TYLCV-infected(D,E)Bemisia tabaci M:DNA marker;1-12:B. tabaci sample;N:Negative control;P:Positive control.

Fig. 2 Detoxification activity of Bemisia tabaci 48h after feeding on healthy and virus-carrying (ToCV + TYLCV,ToCV,TYLCV)tomatoes Different lowercase letters indicate significant difference at 0.05 level. The same below.
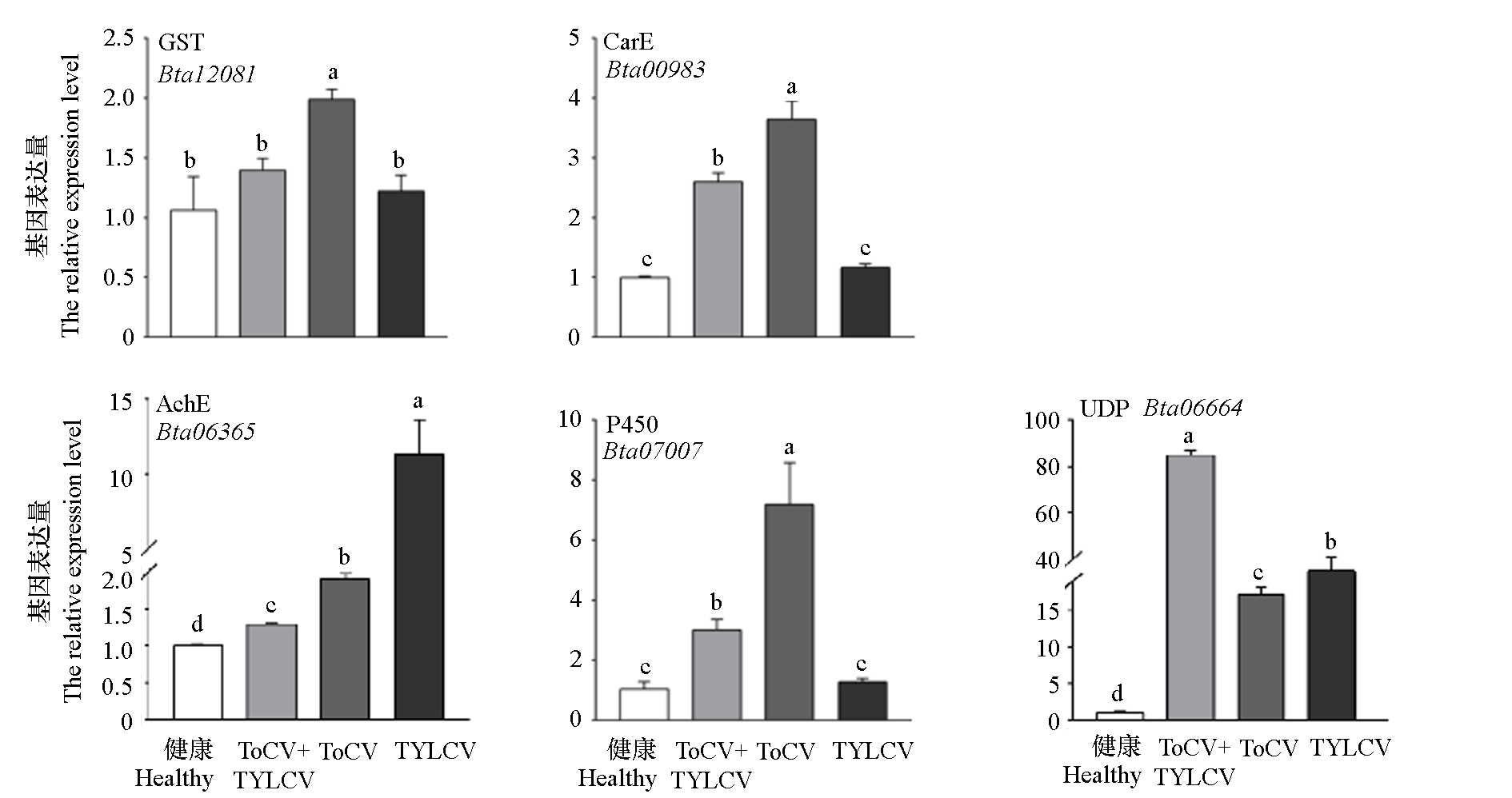
Fig. 3 Changes of detoxification enzyme related gene expression in healthy and virus-carrying tomatoes (ToCV + TYLCV,ToCV,TYLCV)for 48 h in Bemisia tabaci
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
|
曹增, 王金娜, 张友军, 谢文, 王少丽. 2015. 烟粉虱取食感染TYLCV番茄对其解毒酶和保护酶活性的影响. 植物保护, 41 (6):103-108,112.
|
|
| [3] |
|
|
褚栋, 张友军. 2018. 近10年我国烟粉虱发生为害及防治研究进. 植物保护, 44 (5):51-55.
|
|
| [4] |
|
|
代惠洁. 2018. Q烟粉虱对番茄褪绿病毒的传播特性及其转录组分析[博士论文]. 泰安: 山东农业大学.
|
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2010.01.002 pmid: 20093154 |
| [7] |
|
|
丁天波, 周雪, 杨楠, 杨炀, 唐瑶, 褚栋. 2021. ToCV单独侵染和TYLCV & ToCV复合侵染番茄植株上烟粉虱寄主适应性及寄主植物营养成分含量和防御反应变化. 昆虫学报, 64 (3):384-391.
|
|
| [8] |
|
|
杜田华, 危学高, 殷城, 杨静, 黄明娇, 桂连友, 杨鑫, 张友军. 2022. Q型烟粉虱UDP-糖基转移酶UGT354A1基因克隆及其在噻虫嗪抗性中的作用. 应用昆虫学报, 59 (2):257-267.
|
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
|
何超, 谢文, 张友军. 2017. 谷胱甘肽S-转移酶基因在B型烟粉虱寄主转换中的差异比较. 植物保护, 43 (6):72-77.
|
|
| [12] |
|
|
胡荣, 冯丽肖, 张宇, 张松柏, 张德咏, 刘勇. 2020. 我国6个省份番茄褪绿病毒和番茄黄化曲叶病毒复合侵染率及序列系统发育分析. 中国蔬菜,(9):31-35.
|
|
| [13] |
doi: 10.1016/j.ibmb.2008.03.008 pmid: 18510975 |
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
|
廖锦钰. 2020. 组织蛋白酶影响Q烟粉虱传播番茄褪绿病毒的机制[硕士论文]. 长沙: 湖南大学.
|
|
| [16] |
|
|
刘国霞, 李娇娇, 张安盛. 2021. 番茄褪绿病毒对Q型烟粉虱重要生物学参数及保护酶和解毒酶活力的影响. 环境昆虫学报, 43 (5):1237-1243.
|
|
| [17] |
|
|
刘微. 2019. 番茄褪绿病毒对烟粉虱直接和间接的影响[硕士论文]. 长沙: 湖南大学.
|
|
| [18] |
|
|
刘微, 史晓斌, 唐鑫. 2018. 云南番茄褪绿病毒和番茄黄化曲叶病毒复合侵染的分子鉴定. 园艺学报, 45 (3):552-560.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2017-0735 |
|
| [19] |
doi: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2019.02.005 |
|
刘勇, 李凡, 李月月, 张松柏, 高希武, 谢艳, 燕飞, 张安盛, 戴良英, 程兆榜, 丁铭, 牛颜冰, 王升吉, 车海彦, 江彤, 史晓斌, 何自福, 吴云锋, 张德咏, 青玲, 严婉荣, 杨学辉, 汤亚飞, 郑红英, 唐前君, 章松柏, 章东方, 蔡丽, 陶小荣. 2019. 侵染我国主要蔬菜作物的病毒种类、分布与发生趋势. 中国农业科学, 52 (2):239-261.
doi: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2019.02.005 |
|
| [20] |
doi: 10.1006/meth.2001.1262 pmid: 11846609 |
| [21] |
doi: 10.1111/imb.12048 pmid: 23889516 |
| [22] |
|
|
罗瑞雪, 赵丹, 潘求一, 曾颖, 史晓斌, 张德咏, 史彩华, 刘勇. 2022. 番茄黄化曲叶病毒与番茄褪绿病毒复合侵染对番茄黄化曲叶病毒传播的影响. 植物保护, 48 (5):116-121,128.
|
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2583.1999.00146.x pmid: 10620045 |
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
|
王海鸿, 李雪, 张妮. 2007. 寄主转换后B型烟粉虱羧酸酯酶和乙酰胆碱酯酶活力的变化// 植物保护与现代农业. 北京: 中国农业科学技术出版社:41-46.
|
|
| [31] |
|
|
王建军, 韩召军, 王荫长. 2001. 新烟碱类杀虫剂毒理学研究进展. 植物保护学报,(2):178-182.
|
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
|
吴青君, 张文吉, 张友军, 徐宝云, 朱国仁. 2001. 解毒酶系在小菜蛾对阿维菌素抗性中的作用寄主转换后B型烟粉虱羧酸酯酶. 农药学学报, 3 (3):23-28.
|
|
| [34] |
|
|
张爱红, 杨菲, 潘阳, 孙祥瑞, 张尚卿, 苗洪芹. 2019. 河北省番茄黄化曲叶病毒和番茄褪绿病毒复合侵染及分布. 植物病理学报, 49 (2):271-275.
|
|
| [35] |
|
|
周涛, 杨普云, 赵汝娜, 师迎春, 原锴, 范在丰. 2014. 警惕番茄褪绿病毒在我国的传播和危害. 植物保护, 40 (5):196-200.
|
|
| [36] |
|
|
周雪平, 崔晓峰, 陶小荣. 2003. 双生病毒—— 一类值得重视的植物病毒. 植物病理学报,(6):487-492.
|
|
| [37] |
|
|
朱昌亮, 吴观陵, 张兆松. 1999. 昆虫细胞色素P450分子生物学研究进展. 中国寄生虫学与寄生虫病杂志,(1):49-52.
|
| [1] | HAN Ying, DUAN Ying, NIU Yijie, LI Yansu, HE Chaoxing, SUN Mintao, WANG Jun, LI Qiang, CHEN Shuangchen, YAN Yan. Transcription Metabolic Mechanism of Humic Acid Biodegradable Plastic Film to Improving the Fruit Quality of Tomato in the Greenhouse [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(8): 1758-1772. |
| [2] | GONG Xiaoya, LI Xian, ZHOU Xingang, WU Fengzhi. Effect of Rhizosphere Microorganisms Induced by Potato-Onion on Tomato Root-Knot Nematode Disease [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(8): 1913-1926. |
| [3] | MENG Sida, HAN Leilei, XIANG Hengzuo, ZHU Meiyu, FENG Zhen, YE Yunzhu, SUN Meihua, LI Yanbing, ZHAO Liping, TAN Changhua, QI Mingfang, and LI Tianlai. Research Progress on the Mechanism of Regulating the Number of Tomato Locules [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(7): 1649-1664. |
| [4] | MA Xingyun, FAN Bingli, TANG Guangcai, JIA Zhiqi, LI Ying, XUE Dongqi, ZHANG Shiwen. Preliminary Study on the Mechanism of DXR Regulating Chloroplast Development Flower Color and Fruit Coloring in Tomato [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(6): 1241-1255. |
| [5] | ZHANG Wenjing, XU Dayong, WU Qianlin, YANG Fo, XIN Bingyue, ZENG Xin, LI Feng. Genome Analysis of Bacillus velezensis XDY66,an Antagonist of Tomato Botrytis cinerea [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(6): 1413-1425. |
| [6] | WANG Yongzhen, ZHANG Jianguo, LIU Caihong, LI Sibei, LÜ Tiantian. A New Tomato Hybrid Cultivar‘Yuanhong 212’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(6): 1435-1436. |
| [7] | LIU Zeying, SUN Shuai, LIU Zhiqiang, CUI Xia, LI Ren. Mapping of the Sharp Blossom-end Gene and Screening of Candidate Gene in Tomato [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(5): 982-992. |
| [8] | LI Pin, GAN Ning, CHEN Jiawei, XIANG Sixiang, SHEN Jingyi, OUYANG Bo, LU Yong’en. Analysis of Phosphorus Utilization Efficiency in Natural Population of Tomato and Screening of Low Phosphorus Tolerant Germplasm [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(5): 993-1004. |
| [9] | YANG Ting, XI Dehui, XIA Ming, LI Jianan. Studies on the Mechanism of α-Momordicin Gene Enhancing Tomato Resistance to Tobacco Mosaic Virus [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(5): 1126-1136. |
| [10] | HU Zhifeng, SHAO Jingcheng, ZHANG Li. A New Tomato Cultivar‘Longfan 15’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(4): 917-918. |
| [11] | LIU Genzhong, LI Fangman, GE Pingfei, TAO Jinbao, ZHANG Xingyu, YE Zhibiao, ZHANG Yuyang. QTL Mapping and Candidate Gene Identification Related to Ascorbic Acid Content in Tomato [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(2): 219-228. |
| [12] | DONG Shuchao, HONG Jun, LING Jiayi, XIE Zixin, ZHANG Shengjun, ZHAO Liping, SONG Liuxia, WANG Yinlei, ZHAO Tongmin. Genome-wide Association Studies of Drought Tolerance in Tomato [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(2): 229-238. |
| [13] | XU Qin, WANG Jiaying, ZHANG Mannan, XIAO Zhihao, ZHENG Hankai, LU Yong'en, WANG Taotao, ZHANG Yuyang, ZHANG Junhong, YE Zhibiao, YE Jie. Identification of Genetic Loci and Molecular Marker Development of Salt Tolerance in Tomato Seedlings [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(2): 239-252. |
| [14] | YANG Liang, LIU Huan, MA Yanqin, LI Ju, WANG Hai'e, ZHOU Yujie, LONG Haicheng, MIAO Mingjun, LI Zhi, CHANG Wei. Creating High Lycopene Fruit Using CRISPR/Cas9 Technology in Tomato [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(2): 253-265. |
| [15] | YAN Chaofan, SUN Xuemei, ZHONG Qiwen, SHAO Dengkui, DENG Changrong, WEN Junqin. Identification and Bioinformatics Analysis of 20S Proteasome Gene Family in Tomato [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2024, 51(2): 266-280. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2012 Acta Horticulturae Sinica 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
Tel: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
Support by: Beijing Magtech Co.Ltd