
Acta Horticulturae Sinica ›› 2023, Vol. 50 ›› Issue (1): 188-196.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2021-0502
• New Methods • Previous Articles Next Articles
LI Zhenxi, PAN Ruixuan, XU Meirong, ZHENG Zheng, DENG Xiaoling*( )
)
Received:2022-04-25
Revised:2022-06-17
Online:2023-01-25
Published:2023-01-18
Contact:
*(E-mail:CLC Number:
LI Zhenxi, PAN Ruixuan, XU Meirong, ZHENG Zheng, DENG Xiaoling. Development of Duplex Real-time PCR Assay of‘Candidatus Liberibacter asiatics’[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(1): 188-196.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.ahs.ac.cn/EN/10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2021-0502
| 引物名称 Primer | 引物序列(5′-3′) Primer sequence | 参考文献 Reference |
|---|---|---|
| HLBas/HLBr | TCGAGCGCGTATGCAATACG/GCGTTATCCCGTAGAAAAAGGTAG | Li et al., |
| CQULA04F/CQULA04R | TGGAGGTGTAAAAGTTGCCAAA/CCAACGAAAAGATCAGATATTCCTCTA | Wang et al., |
| f-rplLAs/r-rplLAs | CGCCCGTTTCCGTTGT/AGCCTCTTTAAGCCCTAAATCAG | Teixeira et al., |
| LJ900f/LJ900r | GCCGTTTTAACACAAAAGATGAATATC/ATAAATCAATTTGTTCTAGTTTACGAC | Morgan et al., |
| RNRf/RNRr | CATGCTCCATGAAGCTACCC/GGAGCATTTAACCCCACGAA | Zheng et al., |
| CLas-4G/HLBr | AGTCGAGCGCGTATGCGAAT/GCGTTATCCCGTAGAAAAAGGTAG | Bao et al., |
| 4CPf/4CPr | GCCAAAAGTCTTGCACGTAA/GCGAAAACTTACCGCCTCTA |
Table 1 Primers used in the experiments
| 引物名称 Primer | 引物序列(5′-3′) Primer sequence | 参考文献 Reference |
|---|---|---|
| HLBas/HLBr | TCGAGCGCGTATGCAATACG/GCGTTATCCCGTAGAAAAAGGTAG | Li et al., |
| CQULA04F/CQULA04R | TGGAGGTGTAAAAGTTGCCAAA/CCAACGAAAAGATCAGATATTCCTCTA | Wang et al., |
| f-rplLAs/r-rplLAs | CGCCCGTTTCCGTTGT/AGCCTCTTTAAGCCCTAAATCAG | Teixeira et al., |
| LJ900f/LJ900r | GCCGTTTTAACACAAAAGATGAATATC/ATAAATCAATTTGTTCTAGTTTACGAC | Morgan et al., |
| RNRf/RNRr | CATGCTCCATGAAGCTACCC/GGAGCATTTAACCCCACGAA | Zheng et al., |
| CLas-4G/HLBr | AGTCGAGCGCGTATGCGAAT/GCGTTATCCCGTAGAAAAAGGTAG | Bao et al., |
| 4CPf/4CPr | GCCAAAAGTCTTGCACGTAA/GCGAAAACTTACCGCCTCTA |
| 引物名称 Primer name | 曲线下面积 Area under curve | 约登指数 Youden index | 临界Ct值 Cut-off Ct value | 敏感性/% Sensitivity | 特异性/% Specificity | 似然比 Likelihood ratio | 预测值/% Predictive value | 检出率/% Detection rate | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 阳性 Positive | 阴性 Negative | 阳性 Positive | 阴性 Negative | |||||||
| HLBas/HLBr | 0.957 | 0.8006 | 32.08 | 83.02 | 97.04 | 28.02 | 0.17 | 91.7 | 93.6 | 25.53 |
| CQULA04F/ CQULA04R | 0.963 | 0.8572 | 33.36 | 88.68 | 97.04 | 29.93 | 0.12 | 92.2 | 92.2 | 27.13 |
| f-rplLAs/ r-rplLAs | 0.933 | 0.8498 | 36.74 | 88.68 | 96.30 | 23.94 | 0.12 | 90.4 | 95.6 | 27.66 |
| LJ900f/LJ900r | 0.954 | 0.8194 | 33.00 | 84.91 | 97.04 | 28.66 | 0.16 | 91.8 | 94.2 | 26.06 |
| RNRf/RNRr | 0.971 | 0.8498 | 30.19 | 88.68 | 96.30 | 23.94 | 0.12 | 90.4 | 95.6 | 28.19 |
| CLas-4G/HLBr | 0.966 | 0.8349 | 32.44 | 88.68 | 94.81 | 17.10 | 0.12 | 87.0 | 95.5 | 28.72 |
| 4CPf/4CPr | 0.964 | 0.8457 | 30.96 | 86.79 | 97.78 | 39.06 | 0.14 | 93.9 | 93.9 | 26.06 |
Table 2 ROC curve analysis of different single primer set qPCR assays
| 引物名称 Primer name | 曲线下面积 Area under curve | 约登指数 Youden index | 临界Ct值 Cut-off Ct value | 敏感性/% Sensitivity | 特异性/% Specificity | 似然比 Likelihood ratio | 预测值/% Predictive value | 检出率/% Detection rate | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 阳性 Positive | 阴性 Negative | 阳性 Positive | 阴性 Negative | |||||||
| HLBas/HLBr | 0.957 | 0.8006 | 32.08 | 83.02 | 97.04 | 28.02 | 0.17 | 91.7 | 93.6 | 25.53 |
| CQULA04F/ CQULA04R | 0.963 | 0.8572 | 33.36 | 88.68 | 97.04 | 29.93 | 0.12 | 92.2 | 92.2 | 27.13 |
| f-rplLAs/ r-rplLAs | 0.933 | 0.8498 | 36.74 | 88.68 | 96.30 | 23.94 | 0.12 | 90.4 | 95.6 | 27.66 |
| LJ900f/LJ900r | 0.954 | 0.8194 | 33.00 | 84.91 | 97.04 | 28.66 | 0.16 | 91.8 | 94.2 | 26.06 |
| RNRf/RNRr | 0.971 | 0.8498 | 30.19 | 88.68 | 96.30 | 23.94 | 0.12 | 90.4 | 95.6 | 28.19 |
| CLas-4G/HLBr | 0.966 | 0.8349 | 32.44 | 88.68 | 94.81 | 17.10 | 0.12 | 87.0 | 95.5 | 28.72 |
| 4CPf/4CPr | 0.964 | 0.8457 | 30.96 | 86.79 | 97.78 | 39.06 | 0.14 | 93.9 | 93.9 | 26.06 |
| 串联检测引物 Tandem assay primer | 曲线下面积 Area under curve | 敏感性/% Sensitivity | 特异性/% Specificity | 似然比 Likelihood ratio | 预测值/% Predictive value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 阳性 Positive | 阴性 Negative | 阳性 Positive | 阴性 Negative | ||||
| CQULA04F/CQULA04R + RNRf/RNRr | 0.957 | 81.48 | 99.25 | 109.19 | 0.19 | 97.8 | 93.0 |
| CQULA04F/CQULA04 + CLas-4G/HLBr | 0.958 | 81.48 | 98.51 | 54.59 | 0.19 | 95.7 | 93.0 |
| CQULA04F/CQULA04R + 4CPf/4CPr | 0.956 | 81.48 | 98.51 | 54.59 | 0.19 | 95.7 | 93.0 |
| RNRf/RNRr + CLas-4G/HLBr | 0.963 | 85.19 | 99.25 | 114.15 | 0.15 | 97.9 | 94.3 |
| RNRf/RNRr + 4CPf/4CPr | 0.961 | 83.33 | 99.25 | 111.67 | 0.17 | 97.8 | 93.7 |
| CLas-4G/HLBr + 4CPf/4CPr | 0.960 | 83.33 | 97.76 | 37.22 | 0.17 | 93.7 | 93.6 |
Table 3 ROC curve analysis of qPCR tandem assays
| 串联检测引物 Tandem assay primer | 曲线下面积 Area under curve | 敏感性/% Sensitivity | 特异性/% Specificity | 似然比 Likelihood ratio | 预测值/% Predictive value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 阳性 Positive | 阴性 Negative | 阳性 Positive | 阴性 Negative | ||||
| CQULA04F/CQULA04R + RNRf/RNRr | 0.957 | 81.48 | 99.25 | 109.19 | 0.19 | 97.8 | 93.0 |
| CQULA04F/CQULA04 + CLas-4G/HLBr | 0.958 | 81.48 | 98.51 | 54.59 | 0.19 | 95.7 | 93.0 |
| CQULA04F/CQULA04R + 4CPf/4CPr | 0.956 | 81.48 | 98.51 | 54.59 | 0.19 | 95.7 | 93.0 |
| RNRf/RNRr + CLas-4G/HLBr | 0.963 | 85.19 | 99.25 | 114.15 | 0.15 | 97.9 | 94.3 |
| RNRf/RNRr + 4CPf/4CPr | 0.961 | 83.33 | 99.25 | 111.67 | 0.17 | 97.8 | 93.7 |
| CLas-4G/HLBr + 4CPf/4CPr | 0.960 | 83.33 | 97.76 | 37.22 | 0.17 | 93.7 | 93.6 |
| 并联检测引物 Parallel assay primer | 曲线下面积 Area under curve | 敏感性/% Sensitivity | 特异性/% Specificity | 似然比 Likelihood ratio | 预测值/% Predictive value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 阳性 Positive | 阴性 Negative | 阳性 Positive | 阴性 Negative | ||||
| CQULA04F/CQULA04R + RNRf/RNRr | 0.966 | 92.59 | 94.03 | 15.51 | 0.079 | 86.2 | 96.9 |
| CQULA04F/CQULA04 + CLas-4G/HLBr | 0.971 | 92.59 | 93.28 | 13.79 | 0.079 | 86.2 | 96.9 |
| CQULA04F/CQULA04R + 4CPf/4CPr | 0.972 | 88.89 | 96.27 | 23.82 | 0.120 | 90.6 | 95.6 |
| RNRf/RNRr + CLas-4G/HLBr | 0.957 | 88.89 | 91.79 | 10.83 | 0.120 | 81.4 | 95.3 |
| RNRf/RNRr + 4CPf/4CPr | 0.959 | 87.04 | 94.78 | 16.66 | 0.140 | 87.0 | 94.8 |
| CLas-4G/HLBr + 4CPf/4CPr | 0.959 | 87.04 | 94.78 | 16.66 | 0.140 | 87.0 | 94.8 |
Table 4 ROC curve analysis of qPCR parallel assays
| 并联检测引物 Parallel assay primer | 曲线下面积 Area under curve | 敏感性/% Sensitivity | 特异性/% Specificity | 似然比 Likelihood ratio | 预测值/% Predictive value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 阳性 Positive | 阴性 Negative | 阳性 Positive | 阴性 Negative | ||||
| CQULA04F/CQULA04R + RNRf/RNRr | 0.966 | 92.59 | 94.03 | 15.51 | 0.079 | 86.2 | 96.9 |
| CQULA04F/CQULA04 + CLas-4G/HLBr | 0.971 | 92.59 | 93.28 | 13.79 | 0.079 | 86.2 | 96.9 |
| CQULA04F/CQULA04R + 4CPf/4CPr | 0.972 | 88.89 | 96.27 | 23.82 | 0.120 | 90.6 | 95.6 |
| RNRf/RNRr + CLas-4G/HLBr | 0.957 | 88.89 | 91.79 | 10.83 | 0.120 | 81.4 | 95.3 |
| RNRf/RNRr + 4CPf/4CPr | 0.959 | 87.04 | 94.78 | 16.66 | 0.140 | 87.0 | 94.8 |
| CLas-4G/HLBr + 4CPf/4CPr | 0.959 | 87.04 | 94.78 | 16.66 | 0.140 | 87.0 | 94.8 |
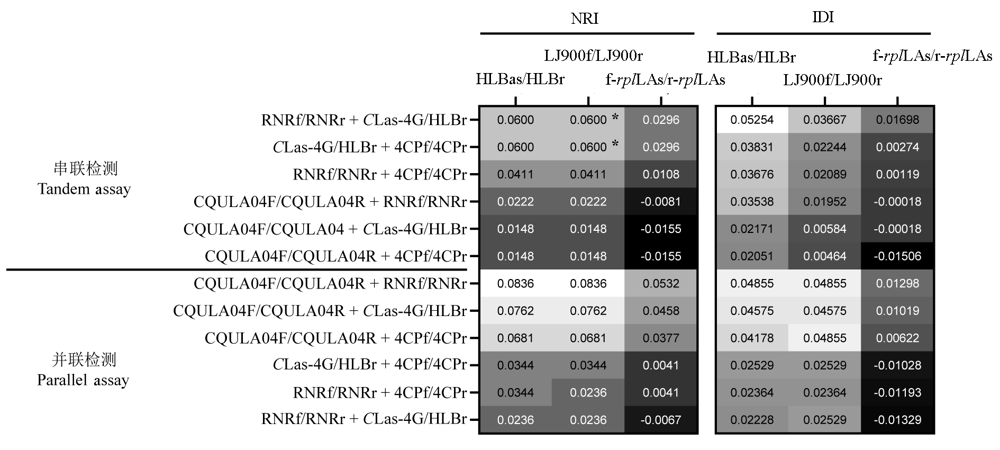
Fig. 1 NRI and IDI values between qPCR tandem and parallel assays of two primer sets and single primer set qPCR assays * The diagnostic effect of the two detection methods is significantly different in the Z test.
| 模板稀释倍数 Relative template concentration | RNRf/RNRr | CLas-4G/HLBr | RNRf/RNRr + CLas-4G/HLBr |
|---|---|---|---|
| 100 | 17.64 | 17.67 | 16.53 |
| 101 | 20.97 | 20.97 | 20.01 |
| 102 | 24.34 | 24.46 | 23.38 |
| 103 | 27.54 | 28.00 | 26.64 |
| 104 | 31.40 | 31.41 | 30.28 |
| 105 | 34.94 | 35.27 | 34.50 |
| 106 | N/A | N/A | 37.21 |
| ddH2O | N/A | N/A | N/A |
Table 5 Sensitivity(Ct)analysis of RNRf/RNRr + CLas-4G/HLBr duplex qPCR
| 模板稀释倍数 Relative template concentration | RNRf/RNRr | CLas-4G/HLBr | RNRf/RNRr + CLas-4G/HLBr |
|---|---|---|---|
| 100 | 17.64 | 17.67 | 16.53 |
| 101 | 20.97 | 20.97 | 20.01 |
| 102 | 24.34 | 24.46 | 23.38 |
| 103 | 27.54 | 28.00 | 26.64 |
| 104 | 31.40 | 31.41 | 30.28 |
| 105 | 34.94 | 35.27 | 34.50 |
| 106 | N/A | N/A | 37.21 |
| ddH2O | N/A | N/A | N/A |
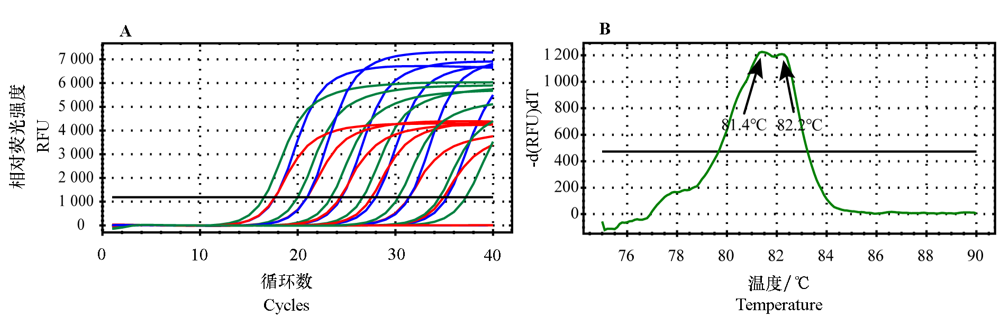
Fig. 2 Amplification curves and melting curves of single primer qPCR assays and the duplex primer qPCR assay Red curve:RNRf/RNRr-qPCR;Blue curve:CLas-4G/HLBr-qPCR;Green curve:RNRf/RNRr + CLas-4G/HLBr duplex qPCR.
| [1] |
Armstrong C M, Doud M S, Luo W L, Raithore S, Baldwin E A, Zhao W, Plotto A, Bai J H, Manthey J A, Stover E, Duan Y P. 2021. Beneficial horticultural responses from the application of solar thermotherapy to mature huanglongbing-affected citrus trees. Horticultural Plant Journal, 7 (5):411-422.
doi: 10.1016/j.hpj.2021.04.008 URL |
| [2] |
Bao M, Zheng Z, Sun X, Chen J, Deng X. 2020. Enhancing PCR capacity to detect‘Candidatus Liberibacter asiaticus’utilizing whole genome sequence information. Plant Disease, 104 (2):527-532.
doi: 10.1094/PDIS-05-19-0931-RE URL |
| [3] |
Bendix C, Lewis J D. 2018. The enemy within:phloem-limited pathogens. Molecular Plant Pathology, 19 (1):238-254.
doi: 10.1111/mpp.12526 URL |
| [4] |
Bové J M. 2014. Huanglongbing or yellow shoot,a disease of Gondwanan origin:will it destroy citrus worldwide? Phytoparasitica, 42 (5):579-583.
doi: 10.1007/s12600-014-0415-4 URL |
| [5] | Bové J M, Barros A P D. 2006. Huanglongbing:a destructive,newly emerging,century-old disease of citrus. Journal of Plant Pathology, 88 (1):7-37. |
| [6] | Dominguez-Mirazo M, Jin R, Weitz J S. 2019. Functional and comparative genomic analysis of integrated prophage-like sequences in‘Candidatus Liberibacter asiaticus’. mSphere, 4 (6):e00409-19. |
| [7] | Guo Shuang, Yang Chun-xia, Tian Xiao-jun, Ren Yi, Gu Li. 2017. Clinical value of multiple quantitative PCR in the diagnosis of Pneumocystis pneumonia. Journal of Pathogen Biology, 12 (10):966-970. (in Chinese) |
| 郭爽, 杨春霞, 田小军, 任翊, 谷丽. 2017. 多重定量PCR在肺孢子菌肺炎诊断中的应用. 中国病原生物学杂志, 12 (10):966-970. | |
| [8] |
Jagoueix S, Bove J M, Garnier M. 1994. The phloem-limited bacterium of greening disease of citrus is a member of the alpha subdivision of the Proteobacteria. International Journal of Systematic Bacteriology, 44 (3):379.
doi: 10.1099/00207713-44-3-379 pmid: 7520729 |
| [9] | Li De-wang, Tang Wei-wen, Fan Huai-zhong. 1992. Preliminary study on serological detection and diagnosis of Citrus Huanglongbing. Journal of South China Agricultural University, 13 (2):16-22. (in Chinese) |
| 李德望, 唐伟文, 范怀忠. 1992. 柑桔黄龙病的血清学检测与诊断方法的初步研究. 华南农业大学学报, 13 (2):16-22. | |
| [10] | Li Jia-hui, Deng Xiao-ling. 2019. Population genetic structure of‘Candidatus Liberibacter asiaticus’in China based on the prophage types. Acta Phytopathologica Sinica, 49 (3):334-342. (in Chinese) |
| 李嘉慧, 郑正, 邓晓玲. 2019. 基于原噬菌体类型的我国柑橘黄龙病菌种群遗传结构分析. 植物病理学报, 49 (3):334-342. | |
| [11] |
Li W, Hartung J S, Levy L. 2006. Quantitative real-time PCR for detection and identification of‘Candidatus Liberibacter species’associated with Citrus Huanglongbing. Journal of Microbiological Methods, 66 (1):104-115.
doi: 10.1016/j.mimet.2005.10.018 URL |
| [12] |
Li W, Hartung J S, Levy L. 2007. Evaluation of DNA amplification methods for improved detection of‘Candidatus Liberibacter species’associated with Citrus Huanglongbing. Plant Disease, 91 (1):51-58.
doi: 10.1094/PD-91-0051 URL |
| [13] | Liang Zi-ying, Liu Fang. 2020. Research progress on real-time quantitative PCR technology and its application. Modern Agricultural Science and Technology,(6):1-3. (in Chinese) |
| 梁子英, 刘芳. 2020. 实时荧光定量PCR技术及其应用研究进展. 现代农业科技,(6):1-3. | |
| [14] | Long Junhong, Zhao Ke, Du Meixia, Xie Zhu, Chen Shanchun, He Yongrui, Zou Xiuping. 2020. Expression characteristics and interacting proteins of the effector SDE 70 from‘Candidatus Liberibacter asiatics’in infected citrus. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 47 (8):1451-1462. (in Chinese) |
| 龙俊宏, 赵珂, 杜美霞, 谢竹, 陈善春, 何永睿, 邹修平. 2020. 柑橘中黄龙病菌效应子SDE70的表达特征及寄主互作蛋白解析. 园艺学报, 47 (8):1451-1462. | |
| [15] |
Morgan J K, Zhou L, Li W, Shatters R G, Keremane M, Duan Y. 2012. Improved real-time PCR detection of‘Candidatus Liberibacter asiaticus’from citrus and psyllid hosts by targeting the intragenic tandem-repeats of its prophage genes. Molecular and Cellular Probes, 26 (2):90-98.
doi: 10.1016/j.mcp.2011.12.001 pmid: 22245034 |
| [16] |
Nageswara-Rao M, Irey M, Garnsey S M, Gowda S. 2013. Candidate gene markers for‘Candidatus Liberibacter asiaticus’for detecting citrus greening disease. J Biosci, 38 (2):229-237.
doi: 10.1007/s12038-013-9315-x URL |
| [17] | Pencina M J, D'Agostino R B, Vasan R S. 2008. Evaluating the added predictive ability of a new marker: from area under the ROC curve to reclassification and beyond. Statistics in Medicine, 27 (2):157-172. |
| [18] |
Pitino M, Sturgeon K, Dorado C, Cano L M, Manthey J A, Shatters R G, Rossi L. 2020. Quercus leaf extracts display curative effects against Candidatus Liberibacter asiaticus that restore leaf physiological parameters in HLB-affected citrus trees. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 148:70-79.
doi: S0981-9428(20)30013-9 pmid: 31945669 |
| [19] | Qiao Tian-min, Zhang Jing, Ma Wen-jian, Zhu Tian-hui. 2015. The double gene-jointed PCR technique for detection of Cylindrocladium scoparium on rice. Journal of Nanjing Agricultural University, 38 (2):273-278. (in Chinese) |
| 谯天敏, 张静, 麻文建, 朱天辉. 2015. 双基因联合PCR检测水稻叶鞘网斑病菌. 南京农业大学学报, 38 (2):273-278. | |
| [20] | Shrestha S, Regmi C, Rana N, Rana P, Giri A, Sijapati J. 2003. Polymerase chain reaction-based diagnosis of citrus Huanglongbing disease in Nepal. Nepal Journal of Science and Technology, 5 (1):107-113. |
| [21] | Tang Li-hua, Guo Tang-xun, Li Qi-li, Huang Sui-ping, Mo Jian-you. 2018. Research progress on field diagnosis and detection techniques for Citrus Huanglongbing. China Plant Protection, 38 (8):81-87. (in Chinese) |
| 唐利华, 郭堂勋, 李其利, 黄穗萍, 莫贱友. 2018. 柑橘黄龙病田间诊断与检测技术研究进展. 中国植保导刊, 38 (8):81-87. | |
| [22] |
Teixeira D C, Saillard C, Couture C, Martins E C, Wulff N A, Eveillard-Jagoueix S, Yamamoto P T, Ayres A J, Bové J M. 2008. Distribution and quantification of‘Candidatus Liberibacter americanus’,agent of Huanglongbing disease of citrus in São Paulo State,Brasil,in leaves of an affected sweet orange tree as determined by PCR. Molecular and Cellular Probes, 22 (3):139-150.
doi: 10.1016/j.mcp.2007.12.006 pmid: 18400468 |
| [23] |
Wang N, Trivedi P. 2013. Citrus Huanglongbing:a newly relevant disease presents unprecedented challenges. Phytopathology, 103 (7):652-665.
doi: 10.1094/PHYTO-12-12-0331-RVW URL |
| [24] |
Wang Z, Yin Y, Hu H, Yuan Q, Peng G, Xia Y. 2006. Development and application of molecular-based diagnosis for‘Candidatus Liberibacter asiaticus’,the causal pathogen of Citrus Huanglongbing. Plant Pathology, 55 (5):630-638.
doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3059.2006.01438.x URL |
| [25] | Xie Zhu, Zhao Ke, Zheng Lin, Long Junhong, Du Meixia, He Yongrui, Chen Shanchun, Zou Xiuping. 2020. Cloning and expression analysis of alcohol dehydrogenase CsADH1gene responding to Huanglongbing infection in Citrus. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 47 (3):445-454. (in Chinese) |
| 谢竹, 赵珂, 郑林, 龙俊宏, 杜美霞, 何永睿, 陈善春, 邹修平. 2020. 响应黄龙病侵染的柑橘乙醇脱氢酶基因CsADH1的克隆与表达分析. 园艺学报, 47 (3):445-454. | |
| [26] | Xu Mei-rong, Chen Yan-ling, Deng Xiao-ling. 2016. Correlationships between symptoms of Citrus Huanglongbing and PCR detection of ‘Candidatus Liberibacter asiaticus’. 46 (3):367-373. (in Chinese) |
| 许美容, 陈燕玲, 邓晓玲. 2016. 柑橘黄龙病症状与“Candidatus Liberibacter asiaticus”PCR检测结果的相关性分析. 植物病理学报, 46 (3):367-373. | |
| [27] | Zhang Qingwen, Qi Jingjing, Xie Yu, Xie Zhu, Peng Yun, Li Qiang, Peng Aihong, Zou Xiuping, He Yongrui, Chen Shanchun, Yao Lixiao. 2021. Preliminary analysis of CsCalS5and callose deposition in Citrus sinensis infected with Candidatus Liberibacter asiaticus. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 48 (2):276-288. (in Chinese) |
| 张庆雯, 祁静静, 谢宇, 谢竹, 彭蕴, 李强, 彭爱红, 邹修平, 何永睿, 陈善春, 姚利晓. 2021. 黄龙病菌胁迫下‘锦橙’CsCalS5表达和胼胝质沉积的初步分析. 园艺学报, 48 (2):276-288. | |
| [28] |
Zheng Z, Bao M, Wu F, van Horn C, Chen J, Deng X. 2018. A type 3 prophage of‘Candidatus Liberibacter asiaticus’carrying a restriction-modification system. Phytopathology, 108 (4):454-461.
doi: 10.1094/PHYTO-08-17-0282-R pmid: 29192841 |
| [29] |
Zheng Z, Xu M, Bao M, Wu F, Chen J, Deng X. 2016. Unusual five copies and dual forms of nrdB in‘Candidatus Liberibacter asiaticus’:Biological implications and PCR detection application. Scientific Reports, 6 (1):1-9.
doi: 10.1038/s41598-016-0001-8 URL |
| [1] | WEI Zhuangmin, WEI Sijia, CHEN Peng, HU Jianbing, TANG Yuqing, YE Junli, LI Xianxin, DENG Xiuxin, CHAI Lijun. Identification of S-genotypes of 63 Pummelo Germplasm Resources [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(5): 1111-1120. |
| [2] | YANG Ting, XUE Zhenzhen, LI Na, LANG Xiaoan, LI Lingfei, ZHONG Chunmei. Reference Genes Selection and Validation in Begonia masoniana Leaves of Different Developmental Stages [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2021, 48(11): 2251-2261. |
| [3] | GUO Jun1,2,ZHU Jie1,2,XIE Shangqian1,3,ZHANG Ye1,2,YE Beilei1,2,ZHENG Liyan2,and LING Peng1,3,* . Development of SSR Molecular Markers Based on Transcriptome and Analysis of Genetic Relationship of Germplasm Resources in Avocado [J]. ACTA HORTICULTURAE SINICA, 2020, 47(8): 1552-1564. |
| [4] | HE Honghong1,LU Zhihao2,MA Zonghuan1,LIANG Guoping1,MA Lijuan1,WAN Peng1,and MAO Juan1,*. Genome-Wide Identification and Expression Analysis of the PP2C Gene Family in Vitis vinifera [J]. ACTA HORTICULTURAE SINICA, 2018, 45(7): 1237-1250. |
| [5] | LIU Xiaoting1,2,*,WANG Shunli2,*,XUE Jingqi2,XUE Yuqian2,Lü Yingmin1,**,and ZHANG Xiuxin2,**. Selection of Reference Genes for Quantitative Real-Time PCR in Different Tissue and Organ of Barbadoslily [J]. ACTA HORTICULTURAE SINICA, 2018, 45(5): 919-930. |
| [6] | WEN Qingli,XIE Zhu,WU Liu,HE Yongrui,CHEN Shanchun*,and ZOU Xiuping*. Clone and Expression Analysis of the Citrus Phloem Protein 2 Gene CsPP2B15 Responding to Huanglongbing Infection in Citrus [J]. ACTA HORTICULTURAE SINICA, 2018, 45(12): 2347-2357. |
| [7] | CHENG Yunqing,ZHANG Lina,ZHAO Yongbin,and LIU Jianfeng*. Analysis of SSR Markers Information and Primer Selection from Transcriptome Sequence of Hybrid Hazelnut Corylus heterophylla × C. avellana [J]. ACTA HORTICULTURAE SINICA, 2018, 45(1): 139-148. |
| [8] | HU Yan,WANG Xue-feng*,and ZHOU Chang-yong *. Recent Advances in Interactions Among‘Candidatus Liberibacter asiaticus’,Insect Vector and Plant Host [J]. ACTA HORTICULTURAE SINICA, 2016, 43(9): 1688-1698. |
| [9] | WANG An-jun1,2,LI Yu-dan2,3,HUANG He-xun2,LUO Shao-bo2,4,WU Ting-quan2,4,LI Ren-qiang1,*,and ZHONG Yu-juan2,4,*. Cloning and Characterization of Two Genes Encoding Myo-inositol Monophosphatase 1(CmIMP1)and 2(CmIMP2)from Pumpkin [J]. ACTA HORTICULTURAE SINICA, 2016, 43(7): 1315-1325. |
| [10] | XU Lan-zhen,HE Yong-rui,LEI Tian-gang,PENG Ai-hong,YAO Li-xiao,JIANG Guo-jin,LI Qiang,ZOU Xiu-ping*,and CHEN Shan-chun*. Identification of the Copy Number of Exogenous Gene in Transgenic Citrus by Quantitative Real-time PCR [J]. ACTA HORTICULTURAE SINICA, 2016, 43(6): 1186-1194. |
| [11] | YU Ying1,*,CHEN Dan1,*,SUN Jun2,Lü Shi-heng1,CHEN Gui-xin1,**,and YE Nai-xing1,**. Cloning and Expression Analysis of Terpene Synthase Gene from Jasminum sambac [J]. ACTA HORTICULTURAE SINICA, 2016, 43(2): 356-364. |
| [12] | SUN Jie,WANG Wan,RAO Xue-qin*,and LI Hua-ping*. Development of TaqMan Real-time PCR Assay of Banana bunchy top virus [J]. ACTA HORTICULTURAE SINICA, 2016, 43(12): 2473-2480. |
| [13] | BEN Hai-yan1,SHI Yan-xia2,XIE Xue-wen2,CHAI A-li2,and LI Bao-ju2,*. Studies of Soil Improvement Effect of Calcium Cyanamide and Its Control#br# Efficiency on Soil-borne Diseases of Vegetable Crops [J]. ACTA HORTICULTURAE SINICA, 2016, 43(11): 2173-2181. |
| [14] | FU Li-li,WU Ju-xun,and YI Hua-lin*. Expression Analysis of Citrate Metabolic Related Genes in Late-ripening Mutant of Navel Orange and Its Wild Type [J]. ACTA HORTICULTURAE SINICA, 2016, 43(1): 38-46. |
| [15] | LI Jia-wei*,LIN Ming*,HU Hong,WANG Xiao-xuan,GUO Yan-mei,HUANG Ze-jun,DU Yong-chen,and GAO Jian-chang**. The Combined Effects of Different TYLCV Resistant Genes and Temperatures on TYLCV Duplication [J]. ACTA HORTICULTURAE SINICA, 2016, 43(1): 71-79. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2012 Acta Horticulturae Sinica 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
Tel: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
Support by: Beijing Magtech Co.Ltd