
Acta Horticulturae Sinica ›› 2022, Vol. 49 ›› Issue (9): 1967-1976.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2021-0784
• Research Papers • Previous Articles Next Articles
GUO Lina1, WANG Lu1, HAO Xinyuan1, QI Meng2, LI Xiaoman1,3, WANG Xinchao1, ZENG Jianming1( )
)
Received:2022-05-25
Revised:2022-08-09
Online:2022-09-25
Published:2022-10-08
CLC Number:
GUO Lina, WANG Lu, HAO Xinyuan, QI Meng, LI Xiaoman, WANG Xinchao, ZENG Jianming. Physiological Characteristics of Selenium Uptake in Tea Plant Root[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(9): 1967-1976.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.ahs.ac.cn/EN/10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2021-0784
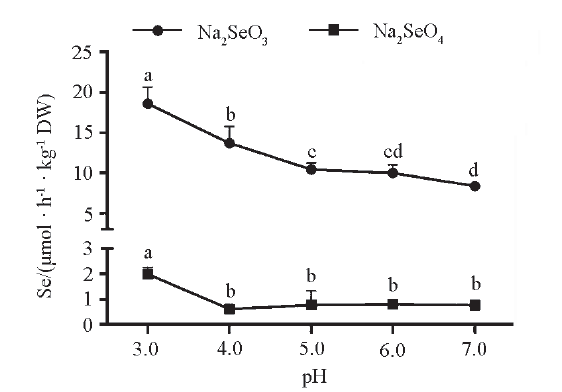
Fig. 1 Uptake of selenite and selenate by roots of tea plants in response to different pH levels The statistical analyses of Na2SeO3 and Na2SeO4 treatments were independent,different small letters represent significant differences at 0.05 level. The same below.

Fig. 3 Uptake of selenite and selenate by roots of tea plants at various Se concentrations The error bars represent the standard deviation of four replicates.
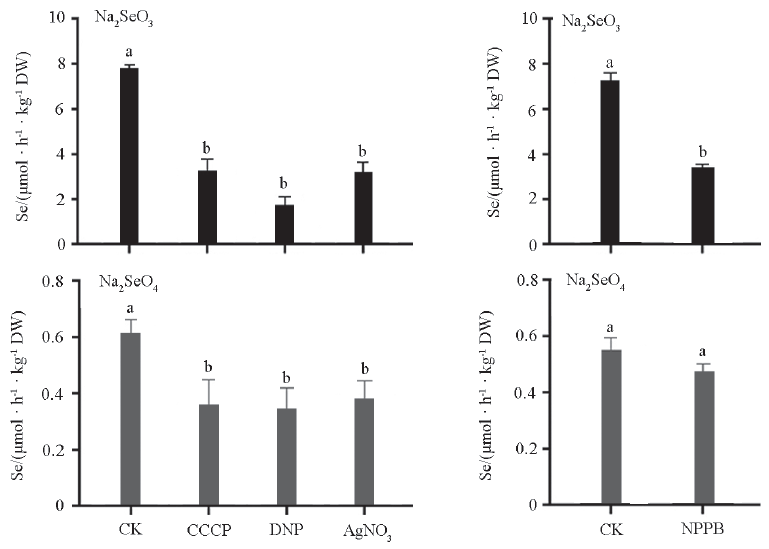
Fig. 4 Uptake of selenium by roots of tea plants at energy metabolism inhibitors,the aquaporin inhibitor and anion-channel inhibitor Different small letters represent significant differences at 0.05 level.
| [1] |
Arvy M P. 1993. Selenate and selenite uptake and translocation in bean plants(Phaseolus vulgaris). Journal of Experimental Botany, 44:1083-1087.
doi: 10.1093/jxb/44.6.1083 URL |
| [2] |
Cao D, Liu Y, Ma L, Jin X, Guo G, Tan R, Liu Z, Zheng L, Ye F, Liu W. 2018. Transcriptome analysis of differentially expressed genes involved in selenium accumulation in tea plant(Camellia sinensis). PLoS ONE, 13:e0197506.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0197506 URL |
| [3] |
Combs G F. 2007. Selenium in global food systems. British Journal of Nutrition, 85:517-547.
doi: 10.1079/BJN2000280 URL |
| [4] |
de Souza M P, Pilon-Smits E A H, Lytle C M, Hwang S, Tai J, Honma T S U, Yeh L, Terry N. 1998. Rate-limiting steps in selenium assimilation and volatilization by Indian mustard. Plant Physiology, 117:1487-1494.
pmid: 9701603 |
| [5] |
Dinh Q T, Cui Z, Huang J, Tran T A T, Wang D, Yang W, Zhou F, Wang M, Yu D, Liang D. 2018. Selenium distribution in the Chinese environment and its relationship with human health:a review. Environment International, 112:294-309.
doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2017.12.035 URL |
| [6] | Du Qi-zhen, Fang Xing-han, Shen Xing-rong. 1991. Dynamic distribution and main forms of selenium accumulation in tea plants. China Tea, 3:8-9. (in Chinese) |
| 杜琪珍, 方兴汉, 沈星荣. 1991. 茶树累积硒的动态分布和主要形态. 中国茶叶, 3:8-9. | |
| [7] | Fairweather-Tait S, Bao Y, Broadley M, Collings R, Ford D, Hesketh J, Hurst R. 2011. Selenium in human health and disease. Antioxidants & Redox Signaling, 14:1337-1383. |
| [8] |
Goh K H, Lim T T. 2004. Geochemistry of inorganic arsenic and selenium in a tropical soil:effect of reaction time,pH,and competitive anions on arsenic and selenium adsorption. Chemosphere, 55:849-859.
doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2003.11.041 URL |
| [9] |
Guo L, Gao L, Ma X, Guo F, Ruan H, Bao Y, Xia T, Wang Y. 2019. Functional analysis of flavonoid 3′-hydroxylase and flavonoid 3′,5′-hydroxylases from tea plant(Camellia sinensis),involved in the B-ring hydroxylation of flavonoids. Gene, 717:144046.
doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2019.144046 URL |
| [10] | Gupta M, Gupta S. 2017. An overview of selenium uptake,metabolism,and toxicity in plants. Frontiers in Plant Science, 7:2074. |
| [11] | Hatfield D, Berry M, Gladyshev V. 2011. Selenium:its molecular biology and role in human health. New York: Springer. |
| [12] |
Hu Q, Xu J, Pang G. 2003. Effect of selenium on the yield and quality of green tea leaves harvested in early spring. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 51:3379-3381.
pmid: 12744670 |
| [13] | Hu Yu-rong. 2016. Identification and expression analysis of genes related with selenium accumulation in tea plant[M. D. Dissertation]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Agricutural Sciences. (in Chinese) |
| 胡玉荣. 2016. 茶树根系硒吸收和代谢的关键基因发掘与分析[硕士论文]. 北京: 中国农业科学院. | |
| [14] |
Ip C, El-Bayoumy K, Upadhyaya P, Ganther H, Vadhanavikit S, Thompson H. 1994. Comparative effect of inorganic and organic selenocyanate derivatives in mammary cancer chemoprevention. Carcinogenesis, 15:187-192.
pmid: 8313507 |
| [15] |
Li H F, McGrath S P, Zhao F J. 2008. Selenium uptake,translocation and speciation in wheat supplied with selenate or selenite. New Phytologist, 178:92-102. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8137.2007.02343.x URL |
| [16] | Li Jun,Zhang Zhong-cheng. 2011. Microelement selenium and human health. Studies of Trace Elements and Health, 28:59-63. |
| 李军, 张忠诚. 2011. 微量元素硒与人体健康. 微量元素与健康研究, 28:59-63. | |
| [17] | Marschner P. 2012. Marschner’s mineral nutrition of higher plants. Third Edition. London:Academic. |
| [18] |
Milne J. 1987. Haloselenate(IV)formation and selenous acid dissociation equilibria in hydrochloric and hydrofluoric acids. Canadian Journal of Chemistry, 65:316-321.
doi: 10.1139/v87-053 URL |
| [19] | Papp L, Lu J, Holmgren A, Khanna K. 2007. From selenium to selenoproteins:synthesis,identity,and their role in human health. Antioxidants & Redox Signaling, 9:775-806. |
| [20] | Qin Xiao-min, Wei Jin-jian, Nong Yu-qin, Chen Hai-sheng, Li Jin-ting, Chen Yuan-quan, Wei Chi-zhang. 2018. Effects of exogenous selenium on chemical quality and selenium content of tea. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Science, 46:31-33. (in Chinese) |
| 覃潇敏, 韦锦坚, 农玉琴, 陈海生, 李金婷, 陈远权, 韦持章. 2018. 外源硒肥对茶叶化学品质及硒含量的影响. 安徽农业科学, 46:31-33. | |
| [21] | Sha Ji-qin, Zheng Da-xian. 1996. Analysis on the factors influencing selenium content of tea fresh leaves. Journal of Tea Science, 16:25-30. (in Chinese) |
| 沙济琴, 郑达贤. 1996. 茶树鲜叶含硒量影响因素分析. 茶叶科学, 16:25-30. | |
| [22] |
Shrift A, Ulrich J M. 1969. Transport of selenate and selenite into Astragalus roots. Plant Physiology, 44:893-896.
pmid: 5799050 |
| [23] |
Sors T G, Ellis D R, Salt D E. 2005. Selenium uptake,translocation,assimilation and metabolic fate in plants. Photosynthesis Research, 86:373-389.
pmid: 16307305 |
| [24] | Tong Zong-xi, Kang Shi-liang, Wu Rui. 2002. Advances of researches on biological effects of selenium and selenoproteins. Progress in Veterinary Medicine, 6:17-19. (in Chinese) |
| 仝宗喜, 康世良, 武瑞. 2002. 硒及硒蛋白生物学作用的研究进展. 动物医学进展, 6:17-19. | |
| [25] |
Vadgama J V, Wu Y, Shen D, Hsia S, Block J. 2000. Effect of selenium in combination with Adriamycin or Taxol on several different cancer cells. Anticancer Research, 20:1391-1414.
pmid: 10928049 |
| [26] | Wan Yanan, Wang Xiaofang, Luo Zhang, Yu Yao, Wang Qi, Guo Yanbin, Li Huafen. 2017. Effects of soil-applied selenite and selenate on accumulation in Chinese leek and retention in soil of selenium. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 44 (4):703-711. (in Chinese) |
| 万亚男, 王晓芳, 罗章, 余垚, 王琪, 郭岩彬, 李花粉. 2017. 不同形态硒对韭菜吸收富集及土壤累积硒的影响. 园艺学报, 44 (4):703-711. | |
| [27] |
Wang M, Yang W, Zhou F, Du Z, Xue M, Chen T, Liang D. 2019. Effect of phosphate and silicate on selenite uptake and phloem-mediated transport in tomato(Solanum lycopersicum L.). Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 26:20475-20484.
doi: 10.1007/s11356-019-04717-x URL |
| [28] |
White P J, Bowen H C, Parmaguru P, Fritz M, Spracklen W P, Spiby R E, Meacham M C, Mead A, Harriman M, Trueman L J, Smith B M, Thomas B, Broadley M R. 2004. Interactions between selenium and sulphur nutrition in Arabidopsis thaliana. Journal of Experimental Botany, 55:1927-1937.
pmid: 15258164 |
| [29] |
Winkel L H E, Vriens B, Jones G D, Schneider L S, Pilon-Smits E, Bañuelos G S. 2015. Selenium cycling across soil-plant-atmosphere interfaces:a critical review. Nutrients, 7:4199-4239.
doi: 10.3390/nu7064199 pmid: 26035246 |
| [30] | Wu Xun. 1964. Talking about the soil condition of tea plant. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 1:59-60. (in Chinese) |
| 吴洵. 1964. 谈茶树的土壤条件. 土壤通报, 1:59-60. | |
| [31] | Zhang Hao-jie, Hao Xin-yuan, Zhou Chao, Wang Lu, Wang Xin-chao, Yang Ya-jun, Zeng Jian-ming, Sun Leng-xue, Dai Ju-hui, Xiang Jun, Luo Hong, Wang Chao-yang, Zhang Xian-gui, Liu Tao. 2020. Correlation analysis between selenium accumulation in tea leaves and soil factors in selenium-rich areas. Journal of Tea Science, 40:465-477. (in Chinese) |
| 张豪杰, 郝心愿, 周超, 王璐, 王新超, 杨亚军, 曾建明, 孙冷雪, 戴居会, 向俊, 罗鸿, 王朝阳, 张贤贵, 刘涛. 2020. 富硒区茶树鲜叶中硒累积与土壤因子的相关性分析. 茶叶科学, 40:465-477. | |
| [32] |
Zhang H, Hao X, Zhang J, Wang L, Wang Y, Li N, Guo L, Ren H, Zeng J. 2021. Genome-wide identification of SULTR genes in tea plant and analysis of their expression in response to sulfur and selenium. Protoplasma,doi: 10.1007/s00709-021-01643-z.
doi: 10.1007/s00709-021-01643-z URL |
| [33] | Zhang Jing-jing. 2018. Response of tea plant sulfate transporter genes to selenium and functional analysis of CsSULTR3.5[M. D. Dissertation]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Agricutural Sciences. (in Chinese) |
| 张晶晶. 2018. 茶树硫酸盐转运蛋白基因对硒的响应及CsSULTR3.5功能分析[硕士论文]. 北京: 中国农业科学院. | |
| [34] | Zhang Jingjing, Qian Wenjun, Hao Xinyuan, Wang Lu, Ding Changqing, Yao Lina, Wang Xinchao, Zeng Jianming. 2018. Cloning and expression analysis of CsSULTR3.1 implicated in sulfate and selenate treatments in tea plant(Camellia sinensis). Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 45 (2):321-332. (in Chinese) |
| 张晶晶, 钱文俊, 郝心愿, 王璐, 丁长庆, 姚利娜, 王新超, 曾建明. 2018. 茶树硫酸盐转运蛋白基因CsSULTR3.1的克隆及其对硫和硒的响应分析. 园艺学报, 45 (2):321-332. | |
| [35] |
Zhang L, Hu B, Li W, Che R, Deng K, Li H, Yu F, Ling H, Li Y, Chu C. 2014. OsPT2,a phosphate transporter,is involved in the active uptake of selenite in rice. New Phytologist, 201:1183-1191.
doi: 10.1111/nph.12596 URL |
| [36] |
Zhang L, Yu F, Shi W, Li Y, Miao Y. 2010. Physiological characteristics of selenite uptake by maize roots in response to different pH levels. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Soil Science, 173:417-422.
doi: 10.1002/jpln.200900260 URL |
| [37] |
Zhang Y, Pan G, Chen J, Hu Q. 2003. Uptake and transport of selenite and selenate by soybean seedlings of two genotypes. Plant and Soil, 253:437-443.
doi: 10.1023/A:1024874529957 URL |
| [38] |
Zhao X Q, Mitani N, Yamaji N, Shen R F, Ma J F. 2010. Involvement of silicon influx transporter OsNIP2;1 in selenite uptake in rice. Plant Physiology, 153:1871-1877.
doi: 10.1104/pp.110.157867 pmid: 20498338 |
| [39] | Zhou Chao, Hu Yu-rong, Zeng Jian-ming, Yang Jian, Chen Li-yan. 2015. Effects of soil factors on the selenium absorption characteristics of tea plant. Journal of Tea Science, 35:28-35. (in Chinese) |
| 周超, 胡玉荣, 曾建明, 杨坚, 陈利燕. 2015. 土壤因子对茶树硒吸收特性的影响. 茶叶科学, 35:28-35. |
| [1] | WANG Mengmeng, SUN Deling, CHEN Rui, YANG Yingxia, ZHANG Guan, LÜ Mingjie, WANG Qian, XIE Tianyu, NIU Guobao, SHAN Xiaozheng, TAN Jin, and YAO Xingwei, . Construction and Evaluation of Cauliflower Core Collection [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(2): 421-431. |
| [2] | CHENG Qinghua, ZHANG Zhipeng, WU Yanping, WAN Yuhe, and CHEN Yingjuan. Studies on the Antifungal Effect of Matrine on Colletotrichum Species on Tea Plant [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(2): 432-440. |
| [3] | YUAN Kejun, NIU Qinglin, QIN Zhihua, and WANG Peijiu. A New Early-ripening Apricot Cultivar‘Yinghua’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(S2): 27-28. |
| [4] | ZHANG Lei, ZHANG Lili, ZHANG Yuping, ZHU Shiyi, CHEN Ming, XIN Ling, WANG Yuelin, and BAO Xianxun, . A New Dictyophora rubrovalvata Cultivar‘Wansun 1’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(S2): 147-148. |
| [5] | WANG Huaxin, ZHANG Hai, LI Jun, MA Jiyao, GONG Jianying, AN Jiacheng, CHEN Pinxian, YANG Yanhua, TANG Qiuming, LI Hua, and ZHANG Yan. An Improved Podocarpus Cultivar‘Podocarpus macrophyllus LDW’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(S2): 277-278. |
| [6] | YUE Cuinan, WANG Zhihui, YANG Puxiang, LI Wenjin, PENG Hua, CHEN Luojun, and ZHOU Hanzhong. A New Tea Cultivar‘Ningzhouzao 1’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(S2): 281-282. |
| [7] | REN Zhihong, WU Huanhuan, XIAO Wenmin, ZHANG Hong, YANG Shengxiang, SUN Haiwei, WANG Jian, and GAO Wenxing. A New Cold Tolerant Tea Cultivar‘Daiding Yufeng’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(S2): 287-288. |
| [8] | LU Chuqiao, GAO Jie, XIE Qi, WEI Yonglu, JIN Jianpeng, YANG Fengxi, and ZHU Genfa. A New Phalaenopsis Cultivar‘Jinxiang’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(S1): 139-140. |
| [9] | JIANG Xionghui, LIU Xiaofei, ZHAN Qicheng, LI Dongmei, WANG Zhen, LIU Huiqing, HUANG Dan, LI Dongjun, CAI Guiqi, and ZHU Genfa, . A New Philodendron Cultivar‘Xiaopingguo’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(S1): 151-152. |
| [10] | JIANG Xionghui, LIU Xiaofei, ZHAN Qicheng, LI Dongmei, WANG Zhen, LIU Huiqing, HUANG Dan, LI Dongjun, CAI Guiqi, and ZHU Genfa, . A New Philodendron Cultivar‘Green Princess’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(S1): 153-155. |
| [11] | WANG Yan, LEI Jingyang, REN Jie, , and ZUO Meili. A New Phoebe zhennan Cultivar‘Wankang 1’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(S1): 177-178. |
| [12] | WANG Zhihui, YANG Puxiang, PENG Hua, LI Wenjin, WANG Shengli, BAO Runyuan, and JIANG Xinfeng. A New Tea Cultivar‘Fuliang Zhuye 1’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(S1): 191-192. |
| [13] | WANG Zhihui, PENG Hua, YUE Cuinan, LI Wenjin, YANG Puxiang, CHEN Niansheng, LI Yansheng, CAI Hailan, and JIANG Xinfeng. A New Tea Cultivar‘Gancha 4’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(S1): 195-196. |
| [14] | TAN Shanshan, QIU Liang, DUAN Aoqi, SHU Sheng, ZENG Xiaoping, ZHU Weimin, JIA Min, YAN Jun, LIU Yanhua, LIU Hui, XIONG Aisheng. Effects of Different Concentrations of Sodium Hypochlorite on Seeds Germination and Seedlings Quality of Celery [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(9): 1907-1921. |
| [15] | DING Zhijie, BAO Jinbo, ROUXIAN Guli, ZHU Tiantian, LI Xueli, MIAO Haoyu, TIAN Xinmin. Comparative Chloroplast Genome Study of Mallus servisii‘Red Delicious’and‘Golden Delicious’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(9): 1977-1990. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2012 Acta Horticulturae Sinica 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
Tel: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
Support by: Beijing Magtech Co.Ltd