
Acta Horticulturae Sinica ›› 2022, Vol. 49 ›› Issue (6): 1213-1232.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2021-0331
• Research Papers • Previous Articles Next Articles
ZHANG Kai, MA Mingying, WANG Ping, LI Yi, JIN Yan, SHENG Ling, DENG Ziniu, MA Xianfeng( )
)
Received:2021-12-14
Revised:2022-02-25
Online:2022-06-25
Published:2022-07-04
Contact:
MA Xianfeng
E-mail:ma8006@hunau.edu.cn
CLC Number:
ZHANG Kai, MA Mingying, WANG Ping, LI Yi, JIN Yan, SHENG Ling, DENG Ziniu, MA Xianfeng. Identification of HSP20 Family Genes in Citrus and Their Expression in Pathogen Infection Responses Citrus Canker[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(6): 1213-1232.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.ahs.ac.cn/EN/10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2021-0331
| 目的基因引物 Primer | 上游引物序列(5′-3′) Forward primer sequence | 下游引物序列(5′-3′) Reverse primer sequence |
|---|---|---|
| EF-1α(qRT-PCR) | GTAACCAAGTCTGCTGCCAAG | GACCCAAACACCCAACACATT |
| CsHSP17.9(qRT-PCR) | TGGTACGAAAGCAAACCCCT | TCAGACTTACAATTGCAAACACACA |
| CmHSP17.9(qRT-PCR) | TGGGCCATAGAAGAAGCAGC | AGCATCCGTAACGACACCAA |
| CsHSP23.3(qRT-PCR) | CTTCCGGGTGCTAGAGCAAA | CGTTTCCTCTCTCCGCTCAC |
| CsHSP18.5(qRT-PCR) | TTTTCCATCTGCGGTGTCCT | CCTTAGCCCCGGAAGATCAG |
| CsHSP18.0(qRT-PCR) | AAGCATTTCCGAAGTTGTTGAG | TTGGGATGTTTCCCTAGCCG |
| CmHSP18.0(qRT-PCR) | TGGGCCATAGAAGAAGCAGC | AGCATCCGTAACGACACCAA |
| CsHSP17.9(ORF) | TAGGTACCATGTCACTCATTCCAAGCATCT | TAGGTACCGCCAGAGATCTCAATAGCCTTA |
| CmHSP17.9(ORF) | GGGAGCTCATGTCACTCATTCCAAGCATCT | AAGAGCTCAGAGCTGGCATCTGTTCCAGG |
| CsHSP23.3(ORF) | TAGGTACCATGAGGCAGCAACAACAAACA | TAGGTACCAAGCTCTTGCCTAGCCTCGCTC |
| CmHSP23.3(ORF) | TAGGTACCATGAGACAGCAACAACGAACAC | AAGGTACCAAGCTCTTGCCTAGCCTCGCTC |
| CsHSP18.5(ORF) | TAGGTACCATGTCGCTGATTCCAAGCTTCT | TAGGTACCGCCAGAGATTTGAATAGCCCTG |
Table 1 Primer sequences used in this study
| 目的基因引物 Primer | 上游引物序列(5′-3′) Forward primer sequence | 下游引物序列(5′-3′) Reverse primer sequence |
|---|---|---|
| EF-1α(qRT-PCR) | GTAACCAAGTCTGCTGCCAAG | GACCCAAACACCCAACACATT |
| CsHSP17.9(qRT-PCR) | TGGTACGAAAGCAAACCCCT | TCAGACTTACAATTGCAAACACACA |
| CmHSP17.9(qRT-PCR) | TGGGCCATAGAAGAAGCAGC | AGCATCCGTAACGACACCAA |
| CsHSP23.3(qRT-PCR) | CTTCCGGGTGCTAGAGCAAA | CGTTTCCTCTCTCCGCTCAC |
| CsHSP18.5(qRT-PCR) | TTTTCCATCTGCGGTGTCCT | CCTTAGCCCCGGAAGATCAG |
| CsHSP18.0(qRT-PCR) | AAGCATTTCCGAAGTTGTTGAG | TTGGGATGTTTCCCTAGCCG |
| CmHSP18.0(qRT-PCR) | TGGGCCATAGAAGAAGCAGC | AGCATCCGTAACGACACCAA |
| CsHSP17.9(ORF) | TAGGTACCATGTCACTCATTCCAAGCATCT | TAGGTACCGCCAGAGATCTCAATAGCCTTA |
| CmHSP17.9(ORF) | GGGAGCTCATGTCACTCATTCCAAGCATCT | AAGAGCTCAGAGCTGGCATCTGTTCCAGG |
| CsHSP23.3(ORF) | TAGGTACCATGAGGCAGCAACAACAAACA | TAGGTACCAAGCTCTTGCCTAGCCTCGCTC |
| CmHSP23.3(ORF) | TAGGTACCATGAGACAGCAACAACGAACAC | AAGGTACCAAGCTCTTGCCTAGCCTCGCTC |
| CsHSP18.5(ORF) | TAGGTACCATGTCGCTGATTCCAAGCTTCT | TAGGTACCGCCAGAGATTTGAATAGCCCTG |
| 基因名称 Gene name | CAP登录号 CAP ID | 染色体 Chr. | 基因位置 Genomic position | 开放阅读框 ORF | 外显子数 Exon number | 氨基酸数 Amino acid number | 分子量/ kD MW | 等电点 pI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CsHSP20-01 | Cs1g12560 | 1 | 15649712 ~ 15650511 (-) | 800 | 2 | 235 | 26.81 | 9.08 |
| CsHSP20-02 | Cs1g16780 | 1 | 20054644 ~ 20057349 (-) | 539 | 3 | 135 | 15.17 | 9.01 |
| CsHSP20-03 | Cs2g07920 | 2 | 4751770 ~ 4753509 (-) | 490 | 3 | 136 | 15.44 | 4.94 |
| CsHSP20-04 | Cs2g24040 | 2 | 22865474 ~ 22866152 (+) | 417 | 1 | 138 | 15.65 | 5.79 |
| CsHSP20-05 | Cs2g24360 | 2 | 23415680 ~ 23417091 (-) | 865 | 2 | 229 | 25.80 | 6.77 |
| CsHSP20-06 | Cs2g28910 | 2 | 28489066 ~ 28490856 (+) | 1 630 | 2 | 308 | 34.20 | 9.26 |
| CsHSP20-07 | Cs3g07660 | 3 | 10958719 ~ 10959189 (-) | 471 | 1 | 156 | 18.08 | 5.70 |
| CsHSP20-08 | Cs3g13530 | 3 | 17951675 ~ 17954257 (+) | 2 280 | 3 | 208 | 22.15 | 4.81 |
| CsHSP20-09 | Cs3g21390 | 3 | 24314830 ~ 24316680 (-) | 1 232 | 2 | 373 | 41.71 | 4.80 |
| CsHSP20-10 | Cs4g04260 | 4 | 2440105 ~ 2443442 (-) | 453 | 1 | 150 | 16.84 | 4.53 |
| CsHSP20-11 | Cs4g05780 | 4 | 3542671 ~ 3543153 (-) | 483 | 1 | 160 | 17.87 | 5.57 |
| CsHSP20-12 | Cs4g05800 | 4 | 3545945 ~ 3546616 (-) | 489 | 1 | 162 | 18.39 | 6.45 |
| CsHSP20-13 | Cs4g05880 | 4 | 3592334 ~ 3593451 (-) | 477 | 1 | 158 | 17.80 | 5.37 |
| CsHSP20-14 | Cs4g12260 | 4 | 9326064 ~ 9327838 (+) | 773 | 2 | 198 | 22.48 | 5.48 |
| CsHSP20-15 | Cs5g04230 | 5 | 2361326 ~ 2362866 (+) | 819 | 2 | 180 | 20.34 | 4.73 |
| CsHSP20-16 | Cs5g18500 | 5 | 18849146 ~ 18850530 (+) | 612 | 1 | 203 | 23.26 | 5.77 |
| CsHSP20-17 | Cs5g26930 | 5 | 29657216 ~ 29657893 (+) | 630 | 2 | 182 | 20.96 | 10.07 |
| CsHSP20-18 | Cs5g26940 | 5 | 29661034 ~ 29661937 (+) | 715 | 2 | 207 | 23.08 | 9.10 |
| CsHSP20-19 | Cs6g07310 | 6 | 9164497 ~ 9165164 (-) | 471 | 1 | 156 | 17.78 | 7.93 |
| CsHSP20-20 | Cs6g07320 | 6 | 9166603 ~ 9167820 (+) | 438 | 1 | 145 | 16.34 | 7.92 |
| CsHSP20-21 | Cs6g17370 | 6 | 17879116 ~ 17880307 (-) | 1 192 | 2 | 148 | 16.55 | 6.92 |
| CsHSP20-22 | Cs7g10040 | 7 | 6437870 ~ 6438966 (-) | 779 | 2 | 224 | 25.41 | 8.67 |
| CsHSP20-23 | Cs7g23870 | 7 | 22776659 ~ 22778441 (-) | 1 597 | 2 | 339 | 37.75 | 5.30 |
| CsHSP20-24 | Cs7g23890 | 7 | 22813654 ~ 22814811 (-) | 1 062 | 2 | 309 | 34.41 | 8.20 |
| CsHSP20-25 | Cs7g32260 | 7 | 31935895 ~ 31936951 (-) | 471 | 1 | 156 | 17.64 | 5.55 |
| CsHSP20-26 | Cs8g13310 | 8 | 16029454 ~ 16030281 (+) | 828 | 1 | 275 | 30.11 | 5.68 |
| CsHSP20-27 | Cs8g13370 | 8 | 16132947 ~ 16133375 (+) | 429 | 1 | 142 | 15.91 | 5.84 |
| CsHSP20-28 | Cs8g13450 | 8 | 16211348 ~ 16212457 (+) | 1 110 | 1 | 369 | 40.91 | 5.97 |
| CsHSP20-29 | Cs8g13500 | 8 | 16261568 ~ 16262230 (+) | 663 | 1 | 220 | 23.89 | 8.02 |
| CsHSP20-30 | Cs8g13560 | 8 | 16334995 ~ 16335974 (+) | 980 | 1 | 224 | 24.62 | 5.75 |
| CsHSP20-31 | Cs8g18020 | 8 | 20763153 ~ 20764015 (+) | 477 | 1 | 158 | 17.98 | 5.84 |
| CsHSP20-32 | Cs8g18360 | 8 | 20993803 ~ 20994946 (-) | 477 | 1 | 158 | 17.89 | 6.77 |
| CsHSP20-33 | Cs8g19490 | 8 | 21656820 ~ 21657642 (-) | 486 | 1 | 161 | 18.28 | 6.17 |
| CsHSP20-34 | Cs8g19510 | 8 | 21667991 ~ 21668854 (-) | 486 | 1 | 161 | 18.22 | 6.76 |
| CsHSP20-35 | Cs8g19520 | 8 | 21670200 ~ 21671498 (+) | 489 | 1 | 162 | 18.47 | 5.79 |
| CsHSP20-36 | Cs8g19530 | 8 | 21674289 ~ 21675349 (+) | 492 | 1 | 163 | 18.46 | 6.76 |
| CsHSP20-37 | Cs8g19540 | 8 | 21677280 ~ 21677985 (-) | 453 | 1 | 150 | 17.15 | 6.18 |
| CsHSP20-38 | Cs9g14690 | 9 | 14093289 ~ 14096486 (-) | 1 036 | 2 | 207 | 23.37 | 5.43 |
| CsHSP20-39 | orange1.1t01849 | Un | 29239328 ~ 29242931 (+) | 939 | 1 | 312 | 34.78 | 8.56 |
| CsHSP20-40 | orange1.1t03235 | Un | 49911150 ~ 49912086 (+) | 489 | 1 | 162 | 17.98 | 7.13 |
| CsHSP20-41 | orange1.1t03877 | Un | 59580055 ~ 59580573 (-) | 519 | 1 | 172 | 19.78 | 7.93 |
| CsHSP20-42 | orange1.1t03881 | Un | 59667559 ~ 59668167 (-) | 609 | 1 | 202 | 23.10 | 6.61 |
Table 2 Features of HSP20 family genes in Citrus sinensis
| 基因名称 Gene name | CAP登录号 CAP ID | 染色体 Chr. | 基因位置 Genomic position | 开放阅读框 ORF | 外显子数 Exon number | 氨基酸数 Amino acid number | 分子量/ kD MW | 等电点 pI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CsHSP20-01 | Cs1g12560 | 1 | 15649712 ~ 15650511 (-) | 800 | 2 | 235 | 26.81 | 9.08 |
| CsHSP20-02 | Cs1g16780 | 1 | 20054644 ~ 20057349 (-) | 539 | 3 | 135 | 15.17 | 9.01 |
| CsHSP20-03 | Cs2g07920 | 2 | 4751770 ~ 4753509 (-) | 490 | 3 | 136 | 15.44 | 4.94 |
| CsHSP20-04 | Cs2g24040 | 2 | 22865474 ~ 22866152 (+) | 417 | 1 | 138 | 15.65 | 5.79 |
| CsHSP20-05 | Cs2g24360 | 2 | 23415680 ~ 23417091 (-) | 865 | 2 | 229 | 25.80 | 6.77 |
| CsHSP20-06 | Cs2g28910 | 2 | 28489066 ~ 28490856 (+) | 1 630 | 2 | 308 | 34.20 | 9.26 |
| CsHSP20-07 | Cs3g07660 | 3 | 10958719 ~ 10959189 (-) | 471 | 1 | 156 | 18.08 | 5.70 |
| CsHSP20-08 | Cs3g13530 | 3 | 17951675 ~ 17954257 (+) | 2 280 | 3 | 208 | 22.15 | 4.81 |
| CsHSP20-09 | Cs3g21390 | 3 | 24314830 ~ 24316680 (-) | 1 232 | 2 | 373 | 41.71 | 4.80 |
| CsHSP20-10 | Cs4g04260 | 4 | 2440105 ~ 2443442 (-) | 453 | 1 | 150 | 16.84 | 4.53 |
| CsHSP20-11 | Cs4g05780 | 4 | 3542671 ~ 3543153 (-) | 483 | 1 | 160 | 17.87 | 5.57 |
| CsHSP20-12 | Cs4g05800 | 4 | 3545945 ~ 3546616 (-) | 489 | 1 | 162 | 18.39 | 6.45 |
| CsHSP20-13 | Cs4g05880 | 4 | 3592334 ~ 3593451 (-) | 477 | 1 | 158 | 17.80 | 5.37 |
| CsHSP20-14 | Cs4g12260 | 4 | 9326064 ~ 9327838 (+) | 773 | 2 | 198 | 22.48 | 5.48 |
| CsHSP20-15 | Cs5g04230 | 5 | 2361326 ~ 2362866 (+) | 819 | 2 | 180 | 20.34 | 4.73 |
| CsHSP20-16 | Cs5g18500 | 5 | 18849146 ~ 18850530 (+) | 612 | 1 | 203 | 23.26 | 5.77 |
| CsHSP20-17 | Cs5g26930 | 5 | 29657216 ~ 29657893 (+) | 630 | 2 | 182 | 20.96 | 10.07 |
| CsHSP20-18 | Cs5g26940 | 5 | 29661034 ~ 29661937 (+) | 715 | 2 | 207 | 23.08 | 9.10 |
| CsHSP20-19 | Cs6g07310 | 6 | 9164497 ~ 9165164 (-) | 471 | 1 | 156 | 17.78 | 7.93 |
| CsHSP20-20 | Cs6g07320 | 6 | 9166603 ~ 9167820 (+) | 438 | 1 | 145 | 16.34 | 7.92 |
| CsHSP20-21 | Cs6g17370 | 6 | 17879116 ~ 17880307 (-) | 1 192 | 2 | 148 | 16.55 | 6.92 |
| CsHSP20-22 | Cs7g10040 | 7 | 6437870 ~ 6438966 (-) | 779 | 2 | 224 | 25.41 | 8.67 |
| CsHSP20-23 | Cs7g23870 | 7 | 22776659 ~ 22778441 (-) | 1 597 | 2 | 339 | 37.75 | 5.30 |
| CsHSP20-24 | Cs7g23890 | 7 | 22813654 ~ 22814811 (-) | 1 062 | 2 | 309 | 34.41 | 8.20 |
| CsHSP20-25 | Cs7g32260 | 7 | 31935895 ~ 31936951 (-) | 471 | 1 | 156 | 17.64 | 5.55 |
| CsHSP20-26 | Cs8g13310 | 8 | 16029454 ~ 16030281 (+) | 828 | 1 | 275 | 30.11 | 5.68 |
| CsHSP20-27 | Cs8g13370 | 8 | 16132947 ~ 16133375 (+) | 429 | 1 | 142 | 15.91 | 5.84 |
| CsHSP20-28 | Cs8g13450 | 8 | 16211348 ~ 16212457 (+) | 1 110 | 1 | 369 | 40.91 | 5.97 |
| CsHSP20-29 | Cs8g13500 | 8 | 16261568 ~ 16262230 (+) | 663 | 1 | 220 | 23.89 | 8.02 |
| CsHSP20-30 | Cs8g13560 | 8 | 16334995 ~ 16335974 (+) | 980 | 1 | 224 | 24.62 | 5.75 |
| CsHSP20-31 | Cs8g18020 | 8 | 20763153 ~ 20764015 (+) | 477 | 1 | 158 | 17.98 | 5.84 |
| CsHSP20-32 | Cs8g18360 | 8 | 20993803 ~ 20994946 (-) | 477 | 1 | 158 | 17.89 | 6.77 |
| CsHSP20-33 | Cs8g19490 | 8 | 21656820 ~ 21657642 (-) | 486 | 1 | 161 | 18.28 | 6.17 |
| CsHSP20-34 | Cs8g19510 | 8 | 21667991 ~ 21668854 (-) | 486 | 1 | 161 | 18.22 | 6.76 |
| CsHSP20-35 | Cs8g19520 | 8 | 21670200 ~ 21671498 (+) | 489 | 1 | 162 | 18.47 | 5.79 |
| CsHSP20-36 | Cs8g19530 | 8 | 21674289 ~ 21675349 (+) | 492 | 1 | 163 | 18.46 | 6.76 |
| CsHSP20-37 | Cs8g19540 | 8 | 21677280 ~ 21677985 (-) | 453 | 1 | 150 | 17.15 | 6.18 |
| CsHSP20-38 | Cs9g14690 | 9 | 14093289 ~ 14096486 (-) | 1 036 | 2 | 207 | 23.37 | 5.43 |
| CsHSP20-39 | orange1.1t01849 | Un | 29239328 ~ 29242931 (+) | 939 | 1 | 312 | 34.78 | 8.56 |
| CsHSP20-40 | orange1.1t03235 | Un | 49911150 ~ 49912086 (+) | 489 | 1 | 162 | 17.98 | 7.13 |
| CsHSP20-41 | orange1.1t03877 | Un | 59580055 ~ 59580573 (-) | 519 | 1 | 172 | 19.78 | 7.93 |
| CsHSP20-42 | orange1.1t03881 | Un | 59667559 ~ 59668167 (-) | 609 | 1 | 202 | 23.10 | 6.61 |
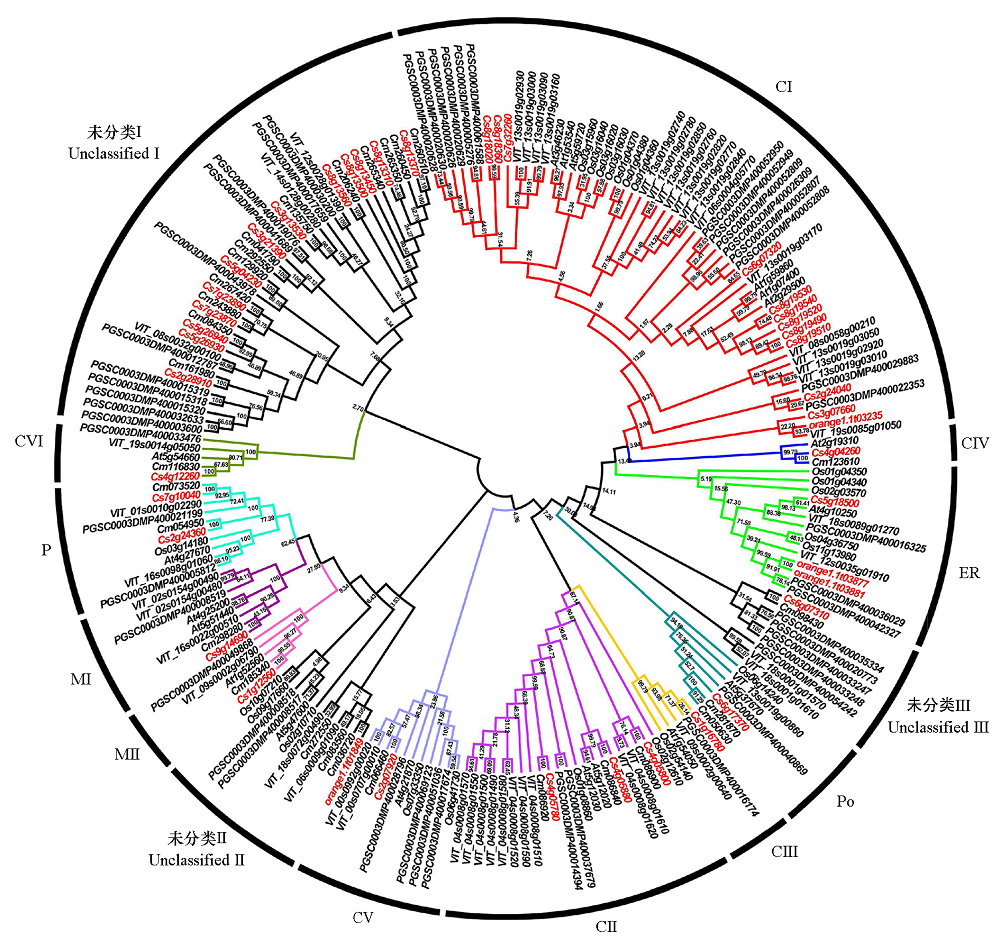
Fig. 2 The phylogenetic relationships of HSP20 genes in different species Cs:C. sinensis;Cm:C. medica;At:Arabidopsis thaliana;Os:Oryza sativa;PGSC:Solanum tuberosum;VIT:Vitis vinifera. The numbers on the branch are bootstrap value(%),the larger the value,the higher the confidence of the evolutionary branch.
| 保守基序名称 Motif name | 氨基酸序列 Amino acid sequence | 起始位点 Site | 序列长度/aa Width |
|---|---|---|---|
| Motif 1 | WKETPEAHVFKADLPGLRKEEVKVE | 32 | 25 |
| Motif 2 | KMDQIKASMENGVLTVTVPK | 33 | 20 |
| Motif 3 | SSGMFSRRFRLPENA | 31 | 15 |
| Motif 4 | VEDDRVLQISGQRKIEKEDKN | 27 | 21 |
| Motif 5 | MSLIPSFFGNRRSSVFDPFSLDVWDPFRDF | 8 | 30 |
| Motif 6 | DTWHRVER | 16 | 8 |
| Motif 7 | LSFLKKNEGDTTSPIGPMEFNLPAGLNTNDFETAIDDEGLLTLTFKKLVP | 5 | 50 |
| Motif 8 | MCLGNNPYQCSVFWYEDVNLVHFKYPLPPGAKQEDVKVEID | 7 | 41 |
| Motif 9 | EEEKKPEVKAIEISG | 11 | 15 |
| Motif 10 | QFPQETSAFVNTRVD | 9 | 15 |
Table 3 Conserved structural motifs built from the primary sequences
| 保守基序名称 Motif name | 氨基酸序列 Amino acid sequence | 起始位点 Site | 序列长度/aa Width |
|---|---|---|---|
| Motif 1 | WKETPEAHVFKADLPGLRKEEVKVE | 32 | 25 |
| Motif 2 | KMDQIKASMENGVLTVTVPK | 33 | 20 |
| Motif 3 | SSGMFSRRFRLPENA | 31 | 15 |
| Motif 4 | VEDDRVLQISGQRKIEKEDKN | 27 | 21 |
| Motif 5 | MSLIPSFFGNRRSSVFDPFSLDVWDPFRDF | 8 | 30 |
| Motif 6 | DTWHRVER | 16 | 8 |
| Motif 7 | LSFLKKNEGDTTSPIGPMEFNLPAGLNTNDFETAIDDEGLLTLTFKKLVP | 5 | 50 |
| Motif 8 | MCLGNNPYQCSVFWYEDVNLVHFKYPLPPGAKQEDVKVEID | 7 | 41 |
| Motif 9 | EEEKKPEVKAIEISG | 11 | 15 |
| Motif 10 | QFPQETSAFVNTRVD | 9 | 15 |
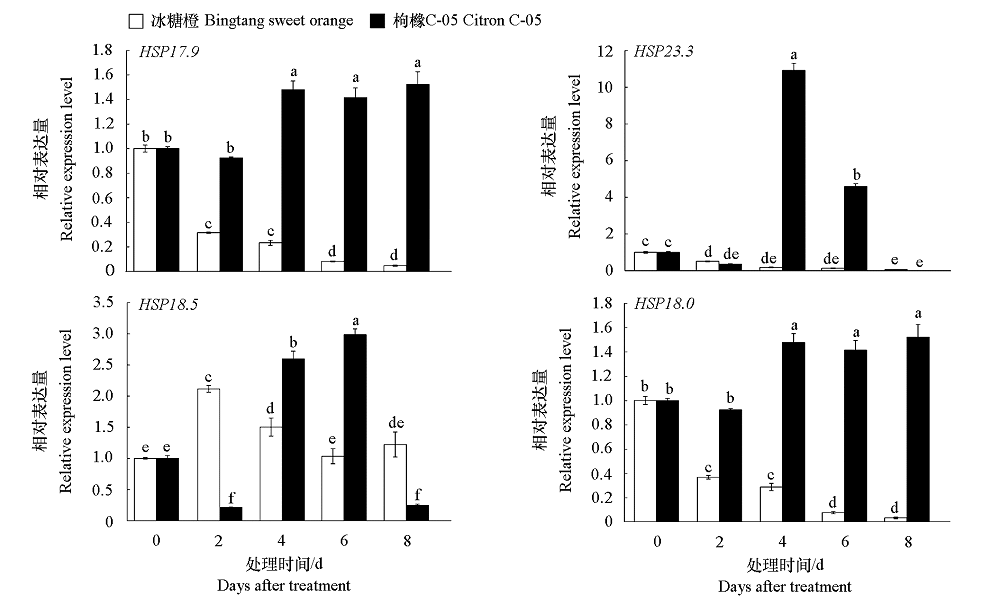
Fig. 5 Expression analysis of HSP20 candidate genes in response to 105 CFU · mL-1 Xcc Different letters indicate significant differences(P < 0.05). The same below.

Fig. 8 Symptoms in resistance identification of sweet orange leaves A:Buffer control;B:HSP20 candidate genes overexpression vector Agrobacterium;C:Buffer + Xcc;D:HSP20 candidate genes overexpression vector agrobacterium + Xcc。1:CsHSP23.3;2:CmHSP23.3;3:CsHSP17.9;4:CmHSP17.9;5:CsHSP18.5;6:CmHSP18.5;P:pCAMIBA1300 vector control.
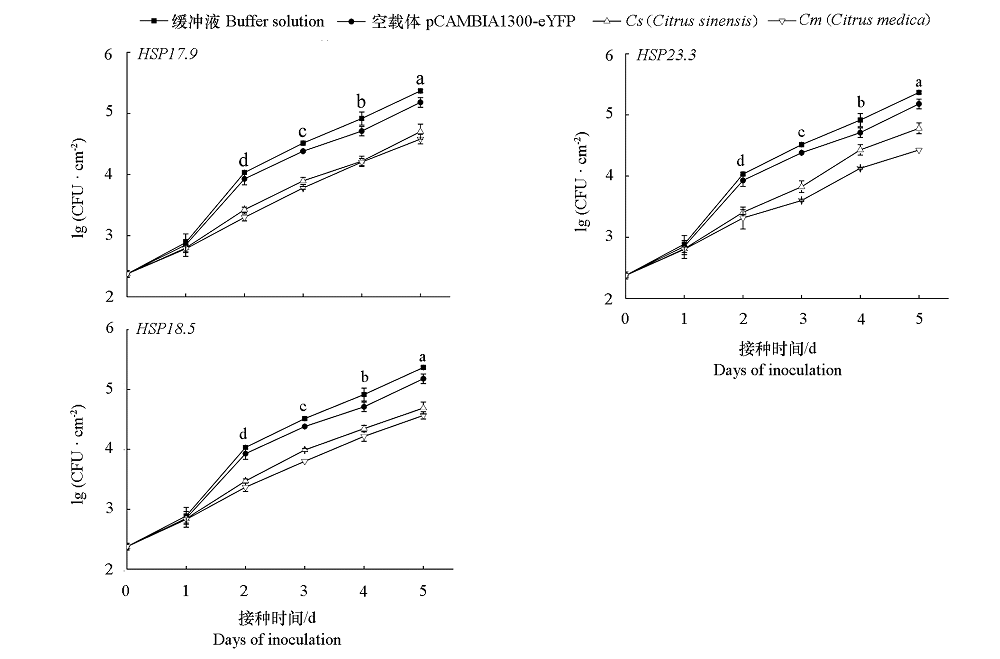
Fig. 9 Xcc quantitative analysis of overexpression of HSP20 candidate genes in sweet orange leaves Different letters indicate significant difference at 0.05 levels Xcc growth by buffer and overexpression of HSP20 candidate genes on the same day.
| [1] | Alshameri A, Al-Qurainy F, Gaafar A-R, Khan S, Nadeem M, Alansi S. 2020. Identification of heat-responsive genes in guar[Cyamopsis tetragonoloba(L.)Taub]. International Journal of Genomics, 2020:3126592. |
| [2] |
Basha E, O’Neill H, Vierling E. 2012. Small heat shock proteins and alpha-crystallins:dynamic proteins with flexible functions. Trends in Biochemical Sciences, 37 (3):106-117.
doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2011.11.005 pmid: 22177323 |
| [3] |
Behlau F, Gochez A M, Jones J B. 2020. Diversity and copper resistance of Xanthomonas affecting citrus. Tropical Plant Pathology, 45:200-212.
doi: 10.1007/s40858-020-00340-1 URL |
| [4] |
Bhaskar P B, Venkateshwaran M, Wu L, Ane J M, Jiang J. 2009. Agrobacterium-mediated transient gene expression and silencing:a rapid tool for functional gene assay in potato. PLoS ONE, 4 (6):e5812.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0005812 URL |
| [5] |
Bondino H G, Valle E M, Have A T. 2012. Evolution and functional diversification of the small heat shock protein/α-crystallin family in higher plants. Planta, 235 (6):1299-1313.
doi: 10.1007/s00425-011-1575-9 URL |
| [6] |
Boter M, Amigues B, Peart J, Breuer C, Kadota Y, Casais C, Moore G, Kleanthous C, Ochsenbein F, Shirasu K, Guerois R. 2007. Structural and functional analysis of SGT 1 reveals that its interaction with HSP90 is required for the accumulation of Rx,an R protein involved in plant immunity. Plant Cell, 19 (11):3791-3804.
doi: 10.1105/tpc.107.050427 URL |
| [7] | Canto T. 2016. Transient expression systems in plants:potentialities and constraints. Adv Exp Med Biol, 896:287-301. |
| [8] |
Deng Z N, Xu L, Li D Z, Long G Y, Liu L P, Fang F, Shu G P. 2010. Screening citrus genotypes for resistance to canker disease(Xanthomonas axonopodis pv. citri). Plant Breeding, 129 (3):341-345.
doi: 10.1111/j.1439-0523.2009.01695.x URL |
| [9] |
Eisenhardt B D. 2013. Small heat shock proteins:recent developments. Biomol Concepts, 4 (6):583-595.
doi: 10.1515/bmc-2013-0028 pmid: 25436758 |
| [10] |
Escandon M, Valledor L, Pascual J, Pinto G, Canal M J, Meijon M. 2017. System-wide analysis of short-term response to high temperature in Pinus radiata. Journal of Experimental Botany, 68 (13):3629-3641.
doi: 10.1093/jxb/erx198 URL |
| [11] |
Ference C M, Gochez A M, Behlau F, Wang N, Graham J H, Jones J B. 2018. Recent advances in the understanding of Xanthomonas citri ssp. citri pathogenesis and citrus canker disease management. Molecular Plant Pathology, 19 (6):1302-1318.
doi: 10.1111/mpp.12638 URL |
| [12] | Figueiredo J F, Romer P, Lahaye T, Graham J H, White F F, Jones J B. 2011. Agrobacterium-mediated transient expression in citrus leaves:a rapid tool for gene expression and functional gene assay. Plant Cell Report, 30 (7):1339-1345. |
| [13] |
Fu H, Zhao M, Xu J, Tan L, Han J, Li D, Wang M, Xiao S, Ma X, Deng Z. 2020. Citron C-05 inhibits both the penetration and colonization of Xanthomonas citri subsp. citri to achieve resistance to citrus canker disease. Horticulture Research, 7:58-70.
doi: 10.1038/s41438-020-0278-4 URL |
| [14] |
Gallegos J E, Rose A B. 2019. An intron-derived motif strongly increases gene expression from transcribed sequences through a splicing independent mechanism in Arabidopsis thaliana. Scientific Reports, 9 (1):13777.
doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-50389-5 pmid: 31551463 |
| [15] |
Gochez A M, Behlau F, Singh R, Ong K, Whilby L, Jones J B. 2020. Panorama of citrus canker in the United States. Tropical Plant Pathology, 45:192-199.
doi: 10.1007/s40858-020-00355-8 URL |
| [16] |
Gottwald T R, Graham J H, Schubert T S. 2002. Citrus canker:the pathogen and its impact. Plant Health Progress, 3 (1):15-49.
doi: 10.1094/PHP-2002-0812-01-RV URL |
| [17] |
Graham J H, Gottwald T R, Cubero J, Achor D S. 2004. Xanthomonas axonopodis pv. citri:factors affecting successful eradication of citrus canker. Molecular Plant Pathology, 5 (1):1-15.
doi: 10.1046/j.1364-3703.2004.00197.x pmid: 20565577 |
| [18] |
Green B J, Fujiki M, Mett V, Kaczmarczyk J, Shamloul M, Musiychuk K, Underkoffler S, Yusibov V, Mett V. 2009. Transient protein expression in three Pisum sativum(green pea)varieties. Biotechnol J, 4 (2):230-237.
doi: 10.1002/biot.200800256 URL |
| [19] | Guo M, Liu J, Lu J, Zhai Y, Wang H, Gong Z, Wang S, Lu M. 2015. Genome-wide analysis of the CaHsp20 gene family in pepper:comprehensive sequence and expression profile analysis under heat stress. Frontiers in Plant Science, 6:806-812. |
| [20] |
Haq S U, Khan A, Ali M, Khattak A M, Gai W, Zhang H, Wei A, Gong Z. 2019. Heat shock proteins:dynamic biomolecules to counter plant biotic and abiotic stresses. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20 (21):5321-5352.
doi: 10.3390/ijms20215321 URL |
| [21] |
Haslbeck M, Vierling E. 2015. A first line of stress defense:small heat shock proteins and their function in protein homeostasis. Journal of Molecular Biology, 427 (7):1537-1548.
doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2015.02.002 pmid: 25681016 |
| [22] |
Hu T, Sun X, Zhang X, Nevo E, Fu J. 2014a. An RNA sequencing transcriptome analysis of the high-temperature stressed tall fescue reveals novel insights into plant thermotolerance. BMC Genomics 15:1147-1160.
doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-15-1147 URL |
| [23] | Hu Y, Zhang J, Jia H, Sosso D, Li T, Frommer W B, Yang B, White F F, Wang N, Jones J B. 2014b. Lateral organ boundaries 1 is a disease susceptibility gene for citrus bacterial canker disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci, 111 (4):E521-E529. |
| [24] |
Jacob P, Hirt H, Bendahmane A. 2017. The heat-shock protein/chaperone network and multiple stress resistance. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 15 (4):405-414.
doi: 10.1111/pbi.12659 URL |
| [25] |
Ji X, Yu Y, Ni P, Zhang G, Guo D. 2019. Genome-wide identification of small heat-shock protein(HSP20)gene family in grape and expression profile during berry development. BMC Plant Biology, 19 (1):433-448.
doi: 10.1186/s12870-019-2031-4 URL |
| [26] |
Joensuu J J, Conley A J, Lienemann M, Brandle J E, Linder M B, Menassa R. 2010. Hydrophobin fusions for high-level transient protein expression and purification in Nicotiana benthamiana. Plant Physiol, 152 (2):622-633.
doi: 10.1104/pp.109.149021 pmid: 20018596 |
| [27] |
Jones H D, Doherty A, Sparks C A. 2009. Transient transformation of plants. Methods Mol Biol, 513:131-152.
doi: 10.1007/978-1-59745-427-8_8 pmid: 19347644 |
| [28] |
Ju Y, Tian H, Zhang R, Zuo L, Jin G, Xu Q, Ding X, Li X, Chu Z. 2017. Overexpression of OsHSP18.0-CI enhances resistance to bacterial leaf streak in rice. Rice, 10 (1):12-23.
doi: 10.1186/s12284-017-0153-6 URL |
| [29] |
Kim J H, Lim S D, Jang C S. 2019. Oryza sativa heat-induced RING finger protein 1(OsHIRP1)positively regulates plant response to heat stress. Plant Molecular Biology, 99 (6):545-559.
doi: 10.1007/s11103-019-00835-9 URL |
| [30] |
Kotak S, Larkindale J, Lee U, Koskull-Doring P V, Vierling E, Scharf K. 2007. Complexity of the heat stress response in plants. Current Opinion in Plant Biology, 10 (3):310-316.
doi: 10.1016/j.pbi.2007.04.011 URL |
| [31] |
Krenek P, Samajova O, Luptovciak I, Doskocilova A, Komis G, Samaj J. 2015. Transient plant transformation mediated by Agrobacterium tumefaciens:Principles,methods and applications. Biotechnology Advances, 33 (6 Pt 2):1024-1042.
doi: 10.1016/j.biotechadv.2015.03.012 pmid: 25819757 |
| [32] |
Kuang J, Liu J, Mei J, Wang C, Hu H, Zhang Y, Sun M, Ning X, Xiao L, Yang L. 2017. A Class II small heat shock protein OsHsp18.0 plays positive roles in both biotic and abiotic defense responses in rice. Sci Rep, 7 (1):11333.
doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-11882-x pmid: 28900229 |
| [33] |
Li J, Xiang C Y, Yang J, Chen J P, Zhang H M. 2015. Interaction of HSP 20 with a viral RdRp changes its sub-cellular localization and distribution pattern in plants. Scientific Reports, 5:14016.
doi: 10.1038/srep14016 URL |
| [34] |
Li J, Zhang H, Hu J, Liu J, Liu K. 2012. A heat shock protein gene,CsHsp45.9,involved in the response to diverse stresses in cucumber. Biochemical Genetic, 50 (7-8):565-578.
doi: 10.1007/s10528-012-9501-9 URL |
| [35] | Li Qiang, Qi Jingjing, Dou Wanfu, Qin Xiujuan, He Yongrui, Chen Shanchun. 2020. Overexpression of CsNBS-LRR in citrus confers bacterial canker resistance by regulating SA signaling pathway. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 47 (5):817-826. (in Chinese) |
| 李强, 祁静静, 窦万福, 秦秀娟, 何永睿, 陈善春. 2020. 柑橘超量表达CsNBS-LRR通过SA信号途径增强对溃疡病抗性. 园艺学报 47 (5):817-826. | |
| [36] | Long Qin, Xie Yu, Lei Tiangang, He Yongrui, Xu Lanzhen, Zou Xiuping, Chen Shanchun. 2020a. Bioinformatics analysis of MAPK genes in citrus and their expression in response to canker disease. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 47 (11):2095-2106. (in Chinese) |
| 龙琴, 谢宇, 雷天刚, 何永睿, 许兰珍, 邹修平, 陈善春. 2020a. 柑橘MAPK基因的生物信息及其响应溃疡病菌侵染的表达分析. 园艺学报, 47 (11):2095-2106. | |
| [37] | Long Qin, Xie Yu, Xu Lanzhen, He Yongrui, Zou Xiuping, Chen Shanchun. 2020b. Characteristics and mechanism of programmed cell death in response to citrus canker pathogen in the early stage of infection. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 47 (6):1047-1058. (in Chinese) |
| 龙琴, 谢宇, 许兰珍, 何永睿, 邹修平, 陈善春. 2020b. 溃疡病菌侵染早期柑橘细胞程序性死亡的响应特征及机制. 园艺学报, 47 (6):1047-1058. | |
| [38] |
Lopes-Caitar V S, Carvalho M C D, Darben L M, Kuwahara M K, Nepomuceno A L, Dias W P, Abdelnoor R V, Marcelino-Guimarães F C. 2013. Genome-wide analysis of the Hsp20gene family in soybean:comprehensive sequence,genomic organization and expression profile analysis under abiotic and biotic stresses. BMC Genomics, 14:577-594.
doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-14-577 pmid: 23985061 |
| [39] |
Lozano R, Hamblin M T, Prochnik S, Jannink J L. 2015. Identification and distribution of the NBS-LRR gene family in the Cassava genome. BMC Genomics, 16:360-374.
doi: 10.1186/s12864-015-1554-9 URL |
| [40] |
MacRae T H. 2000. Structure and function of small heat shock/α-crystallin proteins:established concepts and emerging ideas. Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences, 57:899-913.
pmid: 10950306 |
| [41] |
Mu C, Zhang S, Yu G, Chen N, Li X, Liu H. 2013. Overexpression of small heat shock protein LimHSP16.45 in Arabidopsis enhances tolerance to abiotic stresses. PLoS ONE, 8 (12):e82264.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0082264 URL |
| [42] | Ong K, Alabi O J. 2016. Xanthomonas citri(citrus canker). Extension Plant Pathology. |
| [43] |
Ouyang Y, Chen J, Xie W, Wang L, Zhang Q. 2009. Comprehensive sequence and expression profile analysis of Hsp20 gene family in rice. Plant Molecular Biology, 70 (3):341-357.
doi: 10.1007/s11103-009-9477-y pmid: 19277876 |
| [44] | Park C, Seo Y. 2015. Heat shock proteins:a review of the molecular chaperones for plant immunity. Plant Pathology Journal, 31 (4):323-333. |
| [45] |
Pei Q Y, Yu T, Wu T, Yang Q H, Gong K, Zhou R, Cui C L, Yu Y, Zhao W, Kang X, Cao R, Song X M. 2021. Comprehensive identification and analyses of the Hsf gene family in the whole-genome of three Apiaceae species. Horticultural Plant Journal, 7 (5):457-458.
doi: 10.1016/j.hpj.2020.08.005 URL |
| [46] |
Qi W Q, Zhang C L, Wang W J, Cao Z, Li S, Li H, Zhu W, HuangY Q, Bao M Z, HeY H, Zheng R R. 2021. Comparative transcriptome analysis of different heat stress responses between self-root grafting line and heterogeneous grafting line in rose. Horticultural Plant Journal, 7 (3):243-255.
doi: 10.1016/j.hpj.2021.03.004 URL |
| [47] |
Sarkar N K, Kim Y, Grover A. 2009. Rice sHsp genes:genomic organization and expression profiling under stress and development. BMC Genomics, 10:393-411.
doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-10-393 URL |
| [48] |
Schaad N W, Postnikova E, Lacy G, Sechler A, Agarkova I, Stromberg P E, Stromberg V K, Vidaver A K. 2006. Emended classification of xanthomonad pathogens on citrus. Systematic and Applied Microbiology, 29 (8):690-695.
doi: 10.1016/j.syapm.2006.08.001 URL |
| [49] | Scharf K, Siddique M, Vierling E. 2001. The expanding family of Arabidopsis thaliana small heat stress proteins and a new family of proteins containing α-crystallin domains(Acd proteins). Cell Stress & Chaperones, 6 (3):225-237. |
| [50] |
Sewelam N, Kazan K, Hudig M, Maurino V G, Schenk P M. 2019. The AtHSP17.4C1 gene expression is mediated by diverse signals that link biotic and abiotic stress factors with ROS and can be a useful molecular marker for oxidative stress. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20 (13):3201-3218.
doi: 10.3390/ijms20133201 URL |
| [51] | Shiotani H, Ozaki K, Tsuyumu S. 2000. Pathogenic interactions between Xanthomonas axonopodis pv. citri and cultivars of pummelo(Citrus grandis). Phytopathology, 91 (12):1383-1389. |
| [52] |
Siddique M, Gernhard S, Koskull-Döring P V, Vierling E, Scharf K. 2008. The plant sHSP superfamily:five new members in Arabidopsis thaliana with unexpected properties. Cell Stress & Chaperones, 13 (2):183-197.
doi: 10.1007/s12192-008-0032-6 URL |
| [53] |
Sumares J A P, Morão L G, Martins P M M, Martins D A B, Gomes E, Jr J B, Ferreira H. 2016. Temperature stress promotes cell division arrest in Xanthomonas citri subsp. citri. Microbiologyopen, 5 (2):244-253.
doi: 10.1002/mbo3.323 pmid: 26663580 |
| [54] | Sun W, Montagu M V, Verbruggen N. 2002. Small heat shock proteins and stress tolerance in plants. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 1577:1-9. |
| [55] |
Vernière C J, Gottwald T R, Pruvost O. 2003. Disease Development and symptom expression of Xanthomonas axonopodis pv. citri in various citrus plant tissues. Phytopathology, 93 (7):832-843.
doi: 10.1094/PHYTO.2003.93.7.832 pmid: 18943164 |
| [56] | Wang J, Chen D, Lei Y, Chang J W, Hao B H, Xing F, Li S, Xu Q, Deng X X, Chen L L. 2014. Citrus sinensis annotation project(CAP):a comprehensive database for sweet orange genome. PLoS ONE, 9 (1):e87723. |
| [57] | Wang Jing, Tan Fangjun, Liang Chengliang, Zhang Xilu, Ou Lijun, Niran Juntawong, Wang Fei, Jiao Chunhai, Zou Xuexiao, Chen Wenchao. 2020. Genome-wide identification and analysis of HSP 90 gene family in pepper. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 47 (4):665-674. (in Chinese) |
| 王静, 谭放军, 梁成亮, 张西露, 欧立军, Niran Juntawong, 王飞, 焦春海, 邹学校, 陈文超. 2020. 辣椒热激蛋白HSP90家族基因鉴定及分析. 园艺学报, 47 (4):665-674. | |
| [58] |
Wang W, Vinocur B, Shoseyov O, Altman A. 2004. Role of plant heat-shock proteins and molecular chaperones in the abiotic stress response. TRENDS in Plant Science, 9 (5):244-252.
doi: 10.1016/j.tplants.2004.03.006 URL |
| [59] |
Waters E R. 2013. The evolution,function,structure,and expression of the plant sHSPs. Journal of Experimental Botany, 64 (2):391-403.
doi: 10.1093/jxb/ers355 URL |
| [60] | Xu Jing, Tan Limei, Fu Hongyan, Zhu Zhimei, Long Libing, Hu Zhe, Ma Xianfeng, Deng Ziniu. 2021. Genetic diversity analysis of 14 citron genotypes based on molecular markers. Molecular Plant Breeding, 19 (14):4726-4737. (in Chinese) |
| 徐静, 谭李梅, 符红艳, 朱志媚, 龙栎冰, 胡哲, 马先锋, 邓子牛. 2021. 利用分子标记对14份枸橼种质进行多样性分析. 分子植物育种, 19 (14):4726-4737. | |
| [61] |
Xu Q, Chen L L, Ruan X, Chen D, Zhu A, Chen C, Bertrand D, Jiao W B, Hao B H, Lyon M P, Chen J, Gao S, Xing F, Lan H, Chang J W, Ge X, Lei Y, Hu Q, Miao Y, Wang L, Xiao S, Biswas M K, Zeng W, Guo F, Cao H, Yang X, Xu X W, Cheng Y J, Xu J, Liu J H, Luo O J, Tang Z, Guo W W, Kuang H, Zhang H Y, Roose M L, Nagarajan N, Deng X X, Ruan Y. 2013. The draft genome of sweet orange(Citrus sinensis). Nature Genetics, 45 (1):59-66.
doi: 10.1038/ng.2472 URL |
| [62] |
Yang M, Zhang Y, Zhang H, Wang H, Wei T, Che S, Zhang L, Hu B, Long H, Song W, Yu W, Yan G. 2017. Identification of MsHsp20 gene family in malus sieversii and functional characterization of MsHsp16.9 in heat tolerance. Frontiers in Plant Science, 8:1761-1778.
doi: 10.3389/fpls.2017.01761 URL |
| [63] | Yao Tingshan, Zhou Yan, Zhou Changyong. 2015. Research development of the differentiation and control of citrus bacterial canker disease. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 42 (9):1699-1706. (in Chinese) |
| 姚廷山, 周彦, 周常勇. 2015. 柑橘溃疡病菌分化及防治研究进展. 园艺学报, 42 (9):1699-1706. | |
| [64] |
Ye S, Yu S, Shu L, Wu J, Wu A, Luo L. 2012. Expression profile analysis of 9 heat shock protein genes throughout the life cycle and under abiotic stress in rice. Chinese Science Bulletin, 57 (4):336-343.
doi: 10.1007/s11434-011-4863-7 URL |
| [65] | Yu J, Cheng Y, Feng K, Li Z, Ruan M, Ye Q, Wang R, Zhou G, Yao Z, Yang Y, Wan H. 2016. Genome-wide identification and expression profiling of tomato Hsp20 gene family in response to biotic and abiotic stresses. Frontiers in Plant Science, 7:1215-1229. |
| [66] |
Zhao P, Wang D, Wang R, Kong N, Zhang C, Yang C, Wu W, Ma H, Chen Q. 2018. Genome-wide analysis of the potato Hsp20gene family:identification,genomic organization and expression profiles in response to heat stress. BMC Genomics, 19 (1):61-74.
doi: 10.1186/s12864-018-4443-1 URL |
| [67] | Zhao Xi, Zhang Tingting, Xing Wenting, Wang Jian, Song Xiqiang, Zhou Yang. 2021. Genome-wide identification and expression analysis under temperature stress of HSP 70 gene family in Dendrobium catenatum. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 48 (9):1743-1754. (in Chinese) |
| 赵溪, 张婷婷, 邢文婷, 王健, 宋希强, 周扬. 2021. 铁皮石斛热激蛋白HSP70基因家族鉴定及温度胁迫下的表达分析. 园艺学报, 48 (9):1743-1754. | |
| [68] | Zhu Zhimei, Tan Limei, Xu Jing, Fu Hongyan, Hu Zhe, Gong Lei, Yang Guibing, Wang Ping, Ma Xianfeng, Deng Ziniu. 2021. Evaluation of citron genotypes for the resistance to citrus canker. China Fruits,(1):43-49,110-111. (in Chinese) |
| 朱志媚, 谭李梅, 徐静, 符红艳, 胡哲, 龚蕾, 杨贵兵, 王萍, 马先锋, 邓子牛. 2021. 枸橼种质对柑橘溃疡病的抗性鉴定. 中国果树,(1):43-49,110-111. |
| [1] | YE Zimao, SHEN Wanxia, LIU Mengyu, WANG Tong, ZHANG Xiaonan, YU Xin, LIU Xiaofeng, and ZHAO Xiaochun, . Effect of R2R3-MYB Transcription Factor CitMYB21 on Flavonoids Biosynthesis in Citrus [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(2): 250-264. |
| [2] | JIANG Jingdong, WEI Zhuangmin, WANG Nan, ZHU Chenqiao, YE Junli, XIE Zongzhou, DENG Xiuxin, CHAI Lijun. Exploitation and Identification of Tetraploid Resources of Hongkong Kumquat(Fortunella hindsii) [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(1): 27-35. |
| [3] | DU Yuling, YANG Fan, ZHAO Juan, LIU Shuqi, LONG Chaoan. Antifungal Mechanisms of Sodium New Houttuyfonate Against Penicillium digitatum [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(1): 145-152. |
| [4] | ZHAO Xueyan, WANG Qi, WANG Li, WANG Fangyuan, WANG Qing, LI Yan. Comparative Transcriptome Analysis of Differential Expression in Different Tissues of Corydalis yanhusuo [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(1): 177-187. |
| [5] | LI Zhenxi, PAN Ruixuan, XU Meirong, ZHENG Zheng, DENG Xiaoling. Development of Duplex Real-time PCR Assay of‘Candidatus Liberibacter asiatics’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(1): 188-196. |
| [6] | SONG Fang, CHEN Qi, YUAN Yanliang, CHEN Sha, YIN Haijun, and JIANG Yingchun, . A New Yellow-fleshed Kiwifruit Cultivar‘Xianwo 1’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(S2): 47-48. |
| [7] | QI Yongjie, GAO Zhenghui, MA Na, WANG Qingming, KE Fanjun, CHEN Qian, and XU Yiliu, . A New Yellow Flesh and Resistant to Canker Disease Kiwifruit Cultivar ‘Wannong Jinguo’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(S2): 49-50. |
| [8] | ZHU Kaijie, ZHANG Zhehui, CAO Lixin, XIANG Shunde, YE Junli, XIE Zongzhou, CHAI Lijun, and DENG Xiuxin, . A New Brown Late-ripening Navel Orange Cultivar‘Zongcheng’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(S1): 41-42. |
| [9] | ZHU Shiping, WEN Rongzhong, WANG Yuanyuan, and ZENG Yang. A New Very Late Ripening Citrus Variety‘Jinlegan’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(S1): 43-44. |
| [10] | GAO Yanlong, WU Yuxia, ZHANG Zhongxing, WANG Shuangcheng, ZHANG Rui, ZHANG De, WANG Yanxiu. Bioinformatics Analysis of Apple ELO Gene Family and Its Expression Analysis Under Low Temperature Stress [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(8): 1621-1636. |
| [11] | QIU Ziwen, LIU Linmin, LIN Yongsheng, LIN Xiaojie, LI Yongyu, WU Shaohua, YANG Chao. Cloning and Functional Analysis of the MbEGS Gene from Melaleuca bracteata [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(8): 1747-1760. |
| [12] | ZHENG Lin, WANG Shuai, LIU Yunuo, DU Meixia, PENG Aihong, HE Yongrui, CHEN Shanchun, ZOU Xiuping. Gene Cloning and Expression Analysis of NAC Gene in Citrus in Response to Huanglongbing [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(7): 1441-1457. |
| [13] | YANG Haijian, ZHANG Yungui, ZHOU Xinzhi. A New Citrus Cultivar‘Yungui Cui Cheng’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(7): 1611-1612. |
| [14] | MA Weifeng, LI Yanmei, MA Zonghuan, CHEN Baihong, MAO Juan. Identification of Apple POD Gene Family and Functional Analysis of MdPOD15 Gene [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(6): 1181-1199. |
| [15] | LI Wenting, LI Cuixiao, LIN Xiaoqing, ZHENG Yongqin, ZHENG Zheng, DENG Xiaoling. Population Genetic Structure of Xanthomonas citri pv. citri in Guangdong Province Based on the STR Locus [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(6): 1233-1246. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2012 Acta Horticulturae Sinica 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
Tel: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
Support by: Beijing Magtech Co.Ltd