
Acta Horticulturae Sinica ›› 2022, Vol. 49 ›› Issue (5): 1060-1072.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2021-0673
• Research Papers • Previous Articles Next Articles
GONG Mingxia1, ZHAO Hu1, WANG Meng1, WU Xing1, ZHAO Zengjing1, HE Zhi1, HUANG Jinmei1, MENG Shengde2, WANG Risheng1,*( )
)
Received:2022-03-02
Revised:2022-04-22
Online:2022-05-25
Published:2022-05-25
Contact:
WANG Risheng
E-mail:shengriwang@126.com
CLC Number:
GONG Mingxia, ZHAO Hu, WANG Meng, WU Xing, ZHAO Zengjing, HE Zhi, HUANG Jinmei, MENG Shengde, WANG Risheng. Identification of Viruses Infecting Peppers in Guangxi by Small RNA Deep Sequencing and RT-PCR[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(5): 1060-1072.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.ahs.ac.cn/EN/10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2021-0673

Fig. 1 Field symptoms on pepper leaves caused by viruses A,B:Chlorosis mottled mosaic leaves;C:Yellow leaves;D:Fern leaves;E:Linear leaves;F:Arbuscule.
| 病毒 Virus | 引物序列(5′-3′) Sequence | 片段大小/bp Product | 退火温度/℃ Tm |
|---|---|---|---|
| ChiVMV | F:ATAATTTGTCCCAACCACCTGA;R:CTCACAAGCATTAACACAGAGC | 923 | 51 |
| CMV | F:GGTTCTGGAAAACACAGGTTCA;R:GAGTCATGGACAAATCTGAATCAAC | 682 | 56 |
| PVMV | F:AGGTGTGTAAATGATTTCGGC;R:GAAAAAGTGAGAGCCAGTTAGT | 825 | 50 |
| PMMoV | F:TCCGAGAAGTGCCGACA;R:TCAATTTGTCTGCCGCTGAG | 992 | 52 |
| ChiRSV | F:ATGAACTGTACGCCGAAGGG;R:AGTCCGATCGCCTATGAGGA | 897 | 56 |
| PeVYV | F:GACGACGAAATGGAGGC;R:CATTAATCTGCGAAGCCCG | 361 | 51 |
| CFEV 1 | F:TGTGCGTGAAGGGTGTTTCT;R:GCGGTCATGCGAGTAGTGAA | 568 | 56 |
| PCV 2 | F:CACGTGTGAGGGCATTTGAC;R:GTCCGACACCGTATGCCTTT | 717 | 57 |
| TMGMV | F:TTCCGCTTATGCAGATCCTGT;R:GACGAACAACCACTGCTGAT | 523 | 54 |
| PepMoV | F:GGACTTCTGTTTGTCGGTGAT;R:AGATGTCTGAAGTGAGTCATCAG | 385 | 50 |
| PVY | F:AGCAAAGCAGCATCCAGTCA;R:GTACTGATGCCACCGTCCAA | 670 | 56 |
| TMV | F:GTTCTTGTCATCTGCGTGGG;R:GCTCTCGAAAGAGCTCCGAT | 406 | 57 |
Table 1 Primers used for RT-PCR
| 病毒 Virus | 引物序列(5′-3′) Sequence | 片段大小/bp Product | 退火温度/℃ Tm |
|---|---|---|---|
| ChiVMV | F:ATAATTTGTCCCAACCACCTGA;R:CTCACAAGCATTAACACAGAGC | 923 | 51 |
| CMV | F:GGTTCTGGAAAACACAGGTTCA;R:GAGTCATGGACAAATCTGAATCAAC | 682 | 56 |
| PVMV | F:AGGTGTGTAAATGATTTCGGC;R:GAAAAAGTGAGAGCCAGTTAGT | 825 | 50 |
| PMMoV | F:TCCGAGAAGTGCCGACA;R:TCAATTTGTCTGCCGCTGAG | 992 | 52 |
| ChiRSV | F:ATGAACTGTACGCCGAAGGG;R:AGTCCGATCGCCTATGAGGA | 897 | 56 |
| PeVYV | F:GACGACGAAATGGAGGC;R:CATTAATCTGCGAAGCCCG | 361 | 51 |
| CFEV 1 | F:TGTGCGTGAAGGGTGTTTCT;R:GCGGTCATGCGAGTAGTGAA | 568 | 56 |
| PCV 2 | F:CACGTGTGAGGGCATTTGAC;R:GTCCGACACCGTATGCCTTT | 717 | 57 |
| TMGMV | F:TTCCGCTTATGCAGATCCTGT;R:GACGAACAACCACTGCTGAT | 523 | 54 |
| PepMoV | F:GGACTTCTGTTTGTCGGTGAT;R:AGATGTCTGAAGTGAGTCATCAG | 385 | 50 |
| PVY | F:AGCAAAGCAGCATCCAGTCA;R:GTACTGATGCCACCGTCCAA | 670 | 56 |
| TMV | F:GTTCTTGTCATCTGCGTGGG;R:GCTCTCGAAAGAGCTCCGAT | 406 | 57 |
| 采样地 Sampling site | sRNA 原始读数 Number of sRNA raw reads | 高质量sRNA读数 Number of sRNA clean reads | 重叠群Contigs | 高质量siRNA序列 siRNA clean reads | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 重叠群N50/bp Contigs_N50 | 重叠群数 Number of contigs | 数量 Number | 占比/% Percentage | |||
| 横县Hengxian | 20 895 583 | 20 380 089 | 135 | 738 | 8 630 968 | 42.35 |
| 钦州Qinzhou | 20 275 068 | 19 860 840 | 108 | 576 | 7 688 131 | 38.71 |
| 五塘Wutang | 19 934 894 | 19 044 126 | 92 | 953 | 6 328 363 | 33.23 |
| 柳江Liujiang | 19 576 663 | 19 207 270 | 132 | 685 | 6 088 705 | 31.70 |
| 桂林Guilin | 19 742 187 | 19 083 857 | 86 | 505 | 2 383 574 | 12.49 |
| 北海Beihai | 20 170 123 | 18 339 543 | 196 | 400 | 9 448 533 | 51.52 |
| 武鸣Wuming | 17 175 774 | 16 804 826 | 141 | 433 | 10 212 293 | 60.77 |
| 百色Baise | 20 390 152 | 19 925 555 | 84 | 609 | 7 884 542 | 39.57 |
| 凭祥Pingxiang | 19 234 300 | 18 607 934 | 116 | 474 | 3 232 198 | 17.37 |
Table 2 Preliminary statistics and analysis of virus sequencing data of nine pepper mixed diseased samples
| 采样地 Sampling site | sRNA 原始读数 Number of sRNA raw reads | 高质量sRNA读数 Number of sRNA clean reads | 重叠群Contigs | 高质量siRNA序列 siRNA clean reads | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 重叠群N50/bp Contigs_N50 | 重叠群数 Number of contigs | 数量 Number | 占比/% Percentage | |||
| 横县Hengxian | 20 895 583 | 20 380 089 | 135 | 738 | 8 630 968 | 42.35 |
| 钦州Qinzhou | 20 275 068 | 19 860 840 | 108 | 576 | 7 688 131 | 38.71 |
| 五塘Wutang | 19 934 894 | 19 044 126 | 92 | 953 | 6 328 363 | 33.23 |
| 柳江Liujiang | 19 576 663 | 19 207 270 | 132 | 685 | 6 088 705 | 31.70 |
| 桂林Guilin | 19 742 187 | 19 083 857 | 86 | 505 | 2 383 574 | 12.49 |
| 北海Beihai | 20 170 123 | 18 339 543 | 196 | 400 | 9 448 533 | 51.52 |
| 武鸣Wuming | 17 175 774 | 16 804 826 | 141 | 433 | 10 212 293 | 60.77 |
| 百色Baise | 20 390 152 | 19 925 555 | 84 | 609 | 7 884 542 | 39.57 |
| 凭祥Pingxiang | 19 234 300 | 18 607 934 | 116 | 474 | 3 232 198 | 17.37 |
| 病毒 Virus | 横县 Hengxian | 钦州 Qinzhou | 五塘 Wutang | 柳江 Liujiang | 桂林 Guilin | 北海 Beihai | 武鸣 Wuming | 百色 Baise | 凭祥Pingxiang |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ChiVMV | 56 | 131 | 93 | 111 | 60 | 39 | - | 54 | 62 |
| CMV | - | 19 | - | 49 | 6 | 50 | 22 | 52 | 26 |
| PVMV | 76 | 51 | 72 | - | 3 | 50 | - | - | 66 |
| CFEV 1 | 46 | - | 33 | 37 | - | 46 | - | - | - |
| PMMoV | 32 | - | 17 | 22 | 33 | - | - | - | - |
| ChiRSV | 37 | - | - | 64 | - | - | 17 | - | - |
| PeVYV | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | - | 51 | 1 |
| PCV 2 | 1 | - | - | - | 11 | - | 1 | - | - |
| PepMoV | - | - | 56 | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| TMGMV | 4 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
Table 3 The number of viral contigs in mixed diseased samples from nine major pepper growing areas in Guangxi analyzed by sRNA deep sequencing
| 病毒 Virus | 横县 Hengxian | 钦州 Qinzhou | 五塘 Wutang | 柳江 Liujiang | 桂林 Guilin | 北海 Beihai | 武鸣 Wuming | 百色 Baise | 凭祥Pingxiang |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ChiVMV | 56 | 131 | 93 | 111 | 60 | 39 | - | 54 | 62 |
| CMV | - | 19 | - | 49 | 6 | 50 | 22 | 52 | 26 |
| PVMV | 76 | 51 | 72 | - | 3 | 50 | - | - | 66 |
| CFEV 1 | 46 | - | 33 | 37 | - | 46 | - | - | - |
| PMMoV | 32 | - | 17 | 22 | 33 | - | - | - | - |
| ChiRSV | 37 | - | - | 64 | - | - | 17 | - | - |
| PeVYV | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | - | 51 | 1 |
| PCV 2 | 1 | - | - | - | 11 | - | 1 | - | - |
| PepMoV | - | - | 56 | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| TMGMV | 4 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
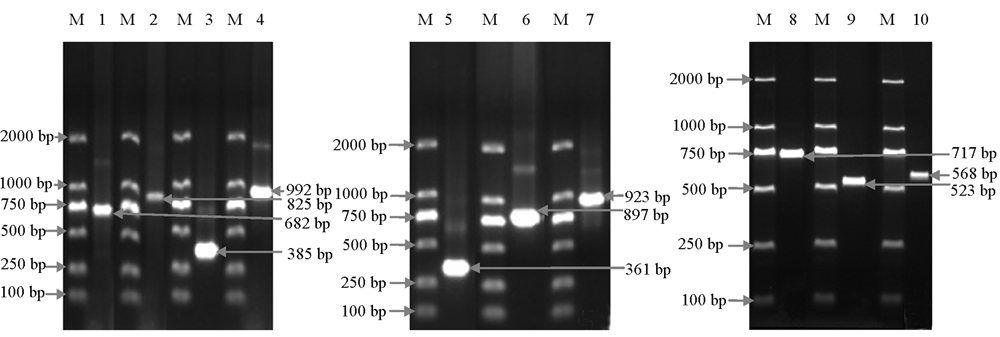
Fig. 2 Positive amplification products by PCR of ten pairs of virus primers M:DL2000 Marker;1:CMV;2:PVMV;3:PepMoV;4:PMMoV;5:PeVYV;6:ChiVMV;7:ChiRSV;8:PCV 2;9:TMGMV;10:CFEV 1.
| 采样地 Sampling site | 检测方式 Detection method | 病毒Virus | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ChiVMV | CMV | PVMV | PMMoV | ChiRSV | PeVYV | CFEV 1 | TMGMV | PepMoV | PCV 2 | ||
| 横县Hengxian | sRNA | + | - | + | + | + | + | + | + | - | + |
| RT-PCR | + | - | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | |
| 钦州Qinzhou | sRNA | + | + | + | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| RT-PCR | + | + | + | + | - | - | + | - | - | - | |
| 五塘Wutang | sRNA | + | - | + | + | - | - | + | - | + | - |
| RT-PCR | + | + | + | + | - | - | + | - | + | + | |
| 柳江Liujiang | sRNA | + | + | - | + | + | - | + | - | - | - |
| RT-PCR | + | + | - | + | + | - | + | - | - | - | |
| 桂林Guilin | sRNA | + | + | + | + | - | - | - | - | - | + |
| RT-PCR | + | + | + | + | - | - | - | - | - | + | |
| 北海Beihai | sRNA | + | + | + | - | - | - | + | - | - | - |
| RT-PCR | + | + | + | - | - | + | + | - | - | - | |
| 武鸣Wuming | sRNA | - | + | - | - | + | - | - | - | - | + |
| RT-PCR | + | + | + | - | + | + | - | - | - | + | |
| 百色Baise | sRNA | + | + | - | - | - | + | - | - | - | - |
| RT-PCR | + | + | - | + | + | + | + | - | - | + | |
| 凭祥Pingxiang | sRNA | + | + | + | - | - | + | - | - | - | - |
| RT-PCR | + | + | + | - | - | + | + | - | - | - | |
Table 4 Comparison of results between small RNA deep sequencing and RT-PCR
| 采样地 Sampling site | 检测方式 Detection method | 病毒Virus | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ChiVMV | CMV | PVMV | PMMoV | ChiRSV | PeVYV | CFEV 1 | TMGMV | PepMoV | PCV 2 | ||
| 横县Hengxian | sRNA | + | - | + | + | + | + | + | + | - | + |
| RT-PCR | + | - | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | |
| 钦州Qinzhou | sRNA | + | + | + | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| RT-PCR | + | + | + | + | - | - | + | - | - | - | |
| 五塘Wutang | sRNA | + | - | + | + | - | - | + | - | + | - |
| RT-PCR | + | + | + | + | - | - | + | - | + | + | |
| 柳江Liujiang | sRNA | + | + | - | + | + | - | + | - | - | - |
| RT-PCR | + | + | - | + | + | - | + | - | - | - | |
| 桂林Guilin | sRNA | + | + | + | + | - | - | - | - | - | + |
| RT-PCR | + | + | + | + | - | - | - | - | - | + | |
| 北海Beihai | sRNA | + | + | + | - | - | - | + | - | - | - |
| RT-PCR | + | + | + | - | - | + | + | - | - | - | |
| 武鸣Wuming | sRNA | - | + | - | - | + | - | - | - | - | + |
| RT-PCR | + | + | + | - | + | + | - | - | - | + | |
| 百色Baise | sRNA | + | + | - | - | - | + | - | - | - | - |
| RT-PCR | + | + | - | + | + | + | + | - | - | + | |
| 凭祥Pingxiang | sRNA | + | + | + | - | - | + | - | - | - | - |
| RT-PCR | + | + | + | - | - | + | + | - | - | - | |
| 病毒 Virus | 桂南Southern Guangxi | 桂中 Central Guangxi | 桂西 Western Guangxi | 桂北 Northern Guangxi | 总检出率 Total detection rate | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 横县 Hengxian | 钦州 Qinzhou | 五塘 Wutang | 北海 Beihai | 武鸣 Wuming | 凭祥 Pingxiang | 柳江 Liujiang | 百色 baise | 桂林 Guilin | ||
| ChiVMV | 28.57 | 25.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 75.00 | 83.33 | 100.00 | 50.00 | 33.33 | 66.67 |
| PVMV | 100.00 | 100.00 | 90.00 | 100.00 | 75.00 | 33.33 | - | - | 16.67 | 62.67 |
| CMV | - | 50.00 | 20.00 | 100.00 | 75.00 | 100.00 | 16.67 | 100.00 | 16.67 | 41.33 |
| CFEV 1 | 14.29 | 25.00 | 20.00 | 28.57 | - | 33.33 | 100.00 | 50.00 | - | 32.00 |
| PCV 2 | 71.43 | - | 20.00 | - | 50.00 | - | - | 25.00 | 50.00 | 26.67 |
| PMMoV | 28.57 | 25.00 | 40.00 | - | - | - | 33.33 | 50.00 | 50.00 | 22.67 |
| PeVYV | 42.86 | - | - | 28.57 | 25.00 | 33.33 | - | 100.00 | - | 21.33 |
| CHiRSV | 28.57 | - | - | - | 25.00 | - | 66.67 | 50.00 | - | 21.33 |
| PepMoV | 28.57 | - | 80.00 | - | - | - | - | - | - | 16.00 |
| TMGMV | 42.86 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 8.00 |
| PVY | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0.00 |
| TMV | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0.00 |
Table 5 RT-PCR detection results of viruses in different major pepper-growing areas in Guangxi %
| 病毒 Virus | 桂南Southern Guangxi | 桂中 Central Guangxi | 桂西 Western Guangxi | 桂北 Northern Guangxi | 总检出率 Total detection rate | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 横县 Hengxian | 钦州 Qinzhou | 五塘 Wutang | 北海 Beihai | 武鸣 Wuming | 凭祥 Pingxiang | 柳江 Liujiang | 百色 baise | 桂林 Guilin | ||
| ChiVMV | 28.57 | 25.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 75.00 | 83.33 | 100.00 | 50.00 | 33.33 | 66.67 |
| PVMV | 100.00 | 100.00 | 90.00 | 100.00 | 75.00 | 33.33 | - | - | 16.67 | 62.67 |
| CMV | - | 50.00 | 20.00 | 100.00 | 75.00 | 100.00 | 16.67 | 100.00 | 16.67 | 41.33 |
| CFEV 1 | 14.29 | 25.00 | 20.00 | 28.57 | - | 33.33 | 100.00 | 50.00 | - | 32.00 |
| PCV 2 | 71.43 | - | 20.00 | - | 50.00 | - | - | 25.00 | 50.00 | 26.67 |
| PMMoV | 28.57 | 25.00 | 40.00 | - | - | - | 33.33 | 50.00 | 50.00 | 22.67 |
| PeVYV | 42.86 | - | - | 28.57 | 25.00 | 33.33 | - | 100.00 | - | 21.33 |
| CHiRSV | 28.57 | - | - | - | 25.00 | - | 66.67 | 50.00 | - | 21.33 |
| PepMoV | 28.57 | - | 80.00 | - | - | - | - | - | - | 16.00 |
| TMGMV | 42.86 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 8.00 |
| PVY | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0.00 |
| TMV | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0.00 |
| 侵染病毒种数 Number of infection viruses | 横县 Hengxian | 钦州 Qinzhou | 五塘 Wutang | 柳江 Liujiang | 桂林 Guilin | 北海 Beihai | 武鸣 Wuming | 百色 Baise | 凭祥 Pingxiang | 合计 Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | - | - | - | - | 33.33 | - | - | - | - | 2.67 |
| 1 | - | 25.00 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 2.67 |
| 2 | - | 25.00 | 0 | 16.67 | 50.00 | - | 25.00 | - | 33.33 | 14.67 |
| 3 | 50.00 | 50.00 | 40.00 | 66.67 | 16.67 | 57.14 | 25.00 | - | 33.33 | 42.67 |
| 4 | 14.29 | - | 50.00 | - | - | 28.57 | 50.00 | 75.00 | 33.33 | 24.00 |
| 5 | 35.17 | - | 10.00 | 16.67 | - | 14.29 | - | 25.00 | - | 13.33 |
Table 6 Incidence of single or mixed infection of viruses in different major pepper-growing areas in Guangxi %
| 侵染病毒种数 Number of infection viruses | 横县 Hengxian | 钦州 Qinzhou | 五塘 Wutang | 柳江 Liujiang | 桂林 Guilin | 北海 Beihai | 武鸣 Wuming | 百色 Baise | 凭祥 Pingxiang | 合计 Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | - | - | - | - | 33.33 | - | - | - | - | 2.67 |
| 1 | - | 25.00 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 2.67 |
| 2 | - | 25.00 | 0 | 16.67 | 50.00 | - | 25.00 | - | 33.33 | 14.67 |
| 3 | 50.00 | 50.00 | 40.00 | 66.67 | 16.67 | 57.14 | 25.00 | - | 33.33 | 42.67 |
| 4 | 14.29 | - | 50.00 | - | - | 28.57 | 50.00 | 75.00 | 33.33 | 24.00 |
| 5 | 35.17 | - | 10.00 | 16.67 | - | 14.29 | - | 25.00 | - | 13.33 |
| 复合侵染病毒种数 Number of viruses in mixed infection | 病毒复合侵染类型 Types of mixed infection of viruses | 比例/% Percentage |
|---|---|---|
| 2 | ChiVMV + CMV | 27.27 |
| ChiVMV + PVMV | 18.18 | |
| ChiVMV + PCV 2 | 18.18 | |
| ChiVMV + CFEV 1 | 18.18 | |
| PCV 2 + PMMoV | 18.18 | |
| 3 | ChiVMV + PVMV + CMV | 18.75 |
| ChiVMV + CFEV 1 + ChiRSV | 18.75 | |
| 其他Others | 62.50 | |
| 4 | ChiVMV + PVMV + CMV + CFEV 1 | 16.67 |
| ChiVMV + PVMV + CMV + ChiRSV | 11.11 | |
| PVMV + CMV+PCV 2 + PeVYV | 11.11 | |
| ChiVMV + PVMV + PCV 2 + PepMoV | 11.11 | |
| ChiVMV + PVMV + CFEV 1 + PepMoV | 11.11 | |
| 其他Others | 38.89 | |
| 5 | PVMV + PCV 2 + PeVYV + PepMoV + TMGMV | 30.00 |
| ChiVMV + CMV+ CFEV 1 + PMMoV + ChiRSV | 20.00 | |
| PVMV + PCV 2 + PMMoV + PeVYV + TMGMV | 20.00 | |
| 其他Others | 30.00 |
Table 7 Types and percentages of mixed infection of viruses in peppers
| 复合侵染病毒种数 Number of viruses in mixed infection | 病毒复合侵染类型 Types of mixed infection of viruses | 比例/% Percentage |
|---|---|---|
| 2 | ChiVMV + CMV | 27.27 |
| ChiVMV + PVMV | 18.18 | |
| ChiVMV + PCV 2 | 18.18 | |
| ChiVMV + CFEV 1 | 18.18 | |
| PCV 2 + PMMoV | 18.18 | |
| 3 | ChiVMV + PVMV + CMV | 18.75 |
| ChiVMV + CFEV 1 + ChiRSV | 18.75 | |
| 其他Others | 62.50 | |
| 4 | ChiVMV + PVMV + CMV + CFEV 1 | 16.67 |
| ChiVMV + PVMV + CMV + ChiRSV | 11.11 | |
| PVMV + CMV+PCV 2 + PeVYV | 11.11 | |
| ChiVMV + PVMV + PCV 2 + PepMoV | 11.11 | |
| ChiVMV + PVMV + CFEV 1 + PepMoV | 11.11 | |
| 其他Others | 38.89 | |
| 5 | PVMV + PCV 2 + PeVYV + PepMoV + TMGMV | 30.00 |
| ChiVMV + CMV+ CFEV 1 + PMMoV + ChiRSV | 20.00 | |
| PVMV + PCV 2 + PMMoV + PeVYV + TMGMV | 20.00 | |
| 其他Others | 30.00 |
| [1] |
Brunt A A, Kenten R H, Phillips S. 1978. Symptomatologically distinct strains of Pepper veinal mottle virus from four West Africa solanaceous crops. Annals of Applied Biology, 88:115-119.
doi: 10.1111/j.1744-7348.1978.tb00685.x URL |
| [2] | Chai Ali, Chen Lida, Cao Jinqiang, Kang Huajun, Shi Yanxia, Xie Xuewen, Li Baoju. 2019. Identification of viruses causing eggplant purple mottle flower disease by siRNA high-throughput sequencing and RT-PCR detection. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 46 (3):508-518. (in Chinese) |
| 柴阿丽, 陈利达, 曹金强, 康华军, 石延霞, 谢学文, 李宝聚. 2019. 利用siRNA高通量测序和RT-PCR技术鉴定引起茄子斑驳紫花病的病毒种类. 园艺学报, 46 (3):508-518. | |
| [3] | Chan P P, Lowe T M. 2009. GtRNAdb:a database of transfer RNA genes detected in genomic sequence. Nucleic Acids Research, 37 (suppl 1):93-97. |
| [4] | Chen Dao, Zhang Jie, Wu Zujian, Ding Xinlun. 2021. Genome sequence of strawberry pallidosis-associated virus isolated in China. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 48 (1):146-152. (in Chinese) |
| 陈道, 张洁, 吴祖建, 丁新伦. 2021. 草莓白化相关病毒中国分离物全基因组分析. 园艺学报, 48 (1):146-152. | |
| [5] | Chen Yahan, Ma Qiang, Sun Pingping, Zhang Lei, Li Zhengnan. 2020. Identification of viruses causing apricot decline and leaf chlorosis disease by siRNA high-throughput sequencing and RT-PCR detection. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 47 (4):725-733. (in Chinese) |
| 陈雅寒, 马强, 孙平平, 张磊, 李正男. 2020. 杏衰退萎黄病病毒的siRNA高通量测序和RT-PCR鉴定. 园艺学报, 47 (4):725-733. | |
| [6] | Cheng Y H, Wang R Y, Chen C C, Chang C A, Jan F J. 2009. First report of Pepper veinal mottle virus in tomato and pepper in Taiwan. Plant Disease, 93 (1):107. |
| [7] |
Ding M, Yang C, Zhang L, Jiang Z L, Fang Q, Qin X Y, Zhang Z K. 2011. Occurrence of Chilli veinal mottle virus in Nicotiana tabacum in Yunnan,China. Plant Disease, 95 (3):357.
doi: 10.1094/PDIS-09-10-0685 pmid: 30743508 |
| [8] | Feng Geng, Xin Min, Cao Meng-ji, Wang Li-shuang, Wang Xi-feng. 2017. Identification of multiple viruses infecting hot pepper in Guiyang by deep sequencing. Acta Phytopathologica Sinica, 47 (5):591-597. (in Chinese) |
| 冯耿, 辛敏, 曹孟籍, 王莉爽, 李莉, 王锡锋. 2017. 深度测序发现贵阳发生的辣椒病毒病由多种病毒复合侵染所致. 植物病理学报, 47 (5):591-597. | |
| [9] | Gong Ming-xia, Zhao Hu, Wang Meng, Wu Xing, Zhao Zeng-jing, Huang Jin-mei, He Zhi, Wang Ri-sheng. 2020. Investigation and pathogen preliminary identification of pepper virus disease in Guangxi. China Vegetables,(4):74-79. (in Chinese) |
| 龚明霞, 赵虎, 王萌, 吴星, 赵曾菁, 黄金梅, 何志, 王日升. 2020. 广西辣椒病毒病调查及病原种类初步鉴定. 中国蔬菜,(4):74-79. | |
| [10] | Griffiths-Jones S, Bateman A, Marshall M, Khanna A, Eddy S R. 2003. Rfam:an RNA family database. Nucleic Acids Research, 31 (1):439-441. |
| [11] | Grill L K, Garger S J. 1981. Identification and characterization of double-stranded RNA associated with cytoplasmic male sterility in Vicia faba. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 78 (11):R7043-7046. |
| [12] | Guo Si-yao, Tong Yan, Huang Ya, Luo Xin-fu, Qing Ling. 2015. Preliminary identification and analyses of viruses causing pepper virus disease in Chongqing,China. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 42 (2):263-270. (in Chinese) |
| 郭思瑶, 童艳, 黄娅, 罗信福, 青玲. 2015. 重庆辣椒病毒病病原初步鉴定和分析. 园艺学报, 42 (2):263-270. | |
| [13] | Jurka J, Kapitonov V V, Pavlicek A, Klonowski P, Kohany O, Walichiewicz J. 2005. Repbase update,a database of eukaryotic repetitive elements. Cytogenetic and Genome Research, 110 (1-4):462-467. |
| [14] | Kenyon L, Kumar S, Tsai W S, Hughes J. 2014. Virus diseases of peppers(Capsicum spp.)and their control. Advances in Virus Research, 90:297-354. |
| [15] |
Kreuze J F, Perez A, Untiveros M, Quispe D, Fuentes S, Barker L, Simon R. 2009. Complete viral genome sequence and discovery of novel viruses by deep sequencing of small RNAs:a generic method for diagnosis,discovery and sequencing of viruses. Virology, 388 (1):1-7.
doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2009.03.024 pmid: 19394993 |
| [16] |
Langmead B, Trapnell C, Pop M, Salzberg S L. 2009. Ultrafast and memory-efficient alignment of short DNA sequences to the human genome. Genome Biology, 10:R25.
doi: 10.1186/gb-2009-10-3-r25 URL |
| [17] | Li R, Gao S, Hernandez A G, Wechter W P, Fei Z, Ling K S. 2012. Deep sequencing of small RNAs in tomato for virus and viroid identification and strain differentiation. PLoS ONE, 7 (5):1-10. |
| [18] | Li Sang-sang, Hu Rong, Luo Xiang-wen, Li Shi-jun, Bu Shan, Zhang Yu, Liu Yong, Zhang Song-bai. 2020. Detection and genetic identity of Pepper veinal mottle virus in Hubei and Guangxi. Journal of Southern Agriculture, 51 (7):1693-1698. (in Chinese) |
| 李桑桑, 胡荣, 罗香文, 李诗君, 卜珊, 张宇, 刘勇, 张松柏. 2020. 湖北和广西辣椒脉斑驳病毒的检测及遗传多样性分析. 南方农业学报, 51 (7):1693-1698. | |
| [19] |
Li Y, Tan G, Xiao L, Zhou W, Lan P, Chen X, Liu Y, Li R, Li F. 2021. A multiyear survey and identification of pepper- and tomato-infecting viruses in Yunnan Province,China. Frontiers in Microbiology, 12:623875.
doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.623875 URL |
| [20] | Liang Jie. 2015. Diversity of the viruses infecting pepper in Hainan[M. D. Dissertation]. Haikou: Hainan University. (in Chinese) |
| 梁洁. 2015. 海南辣椒病毒病病原种类及株系多样性研究[硕士论文]. 海口: 海南大学. | |
| [21] | Liao Zhen, Zhao De-gang, Zhao Yi-chen. 2018. Detection and analysis of viruses from small yellow ginger(Zingiber officinale Rosc.)by small RNA deep sequencing technology. Genomics and Applied Biology, 37 (6):2417-2422. (in Chinese) |
| 廖震, 赵德刚, 赵懿琛. 2018. 利用小RNA深度测序技术检测分析小黄姜病毒. 基因组学与应用生物学, 37 (6):2417-2422. | |
| [22] |
Liu M Y, Liu X N, Li X, Zhang D Y, Dai L Y, Tang Q J. 2016. Complete genome sequence of a Chinese isolate of Pepper vein yellows virus and evolutionary analysis based on the CP,MP and RdRp coding regions. Archives of Virology, 161:677-683.
doi: 10.1007/s00705-015-2691-9 URL |
| [23] | Liu Yong, Li Fan, Li Yue-yue, Zhang Song-bai, Gao Xi-Wu, Xie Yan, Yan Fei, Zhang An-sheng, Dai Liang-ying, Cheng Zhao-bang, Ding Ming, Niu Yan-bing, Wang Sheng-ji, Che Hai-yan, Jiang Tong, Shi Xiao-bin, He Zi-fu, Wu Yun-feng, Zhang De-yong, Qing Ling, Yan Wan-rong, Yang Xue-hui, Tang Ya-fei, Zheng Hong-ying, Tang Qian-jun, Zhang Song-bai, Zhang Dong-fang, Cai Li, Tao Xiao-rong. 2019. Identification,distribution and occurrence of viruses in the main vegetables of China. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 52 (2):239-261. (in Chinese) |
| 刘勇, 李凡, 李月月, 张松柏, 高希武, 谢艳, 燕飞, 张安盛, 戴良英, 程兆榜, 丁铭, 牛颜冰, 王升吉, 车海彦, 江彤, 史晓斌, 何自福, 吴云锋, 张德咏, 青玲, 严婉荣, 杨学辉, 汤亚飞, 郑红英, 唐前君, 章松柏, 章东方, 蔡丽, 陶小荣. 2019. 侵染我国主要蔬菜作物的病毒种类、分布与发生趋势. 中国农业科学, 52 (2):239-261. | |
| [24] |
Martínez R T, Severo de Almeida M M, Rodriguez R, Silva de Oliveira A, Melo F L, Resende R O. 2018. Identification and genome analysis of Tomato chlorotic spot virus and dsRNA viruses from coinfected vegetables in the Dominican Republic by high-throughput sequencing. Virology Journal, 15 (1):24.
doi: 10.1186/s12985-018-0931-9 pmid: 29373979 |
| [25] | Ong C A, Varghese G, Ting W P. 1979. Aetiological investigations on a veinal mottle virus of chill(Capsicum annuum L.)newly recorded from peninsula Malaysia. Malaysian Agricultural Research and Development Institute Research Bulletin, 7:78-88. |
| [26] |
Pfeiffer P. 1998. Nucleotide sequence,genetic organization and expressionstrategy of the double-stranded RNA associated with the‘447’ cytoplasmicmale sterility trait inVicia faba. Journal of General Virology, 79:2349-2358.
doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-79-10-2349 URL |
| [27] | Poojari S, Alabi O J, Fofanov V Y, Naidu R A. 2013. A leafhopper-transmissible DNA virus with novel evolutionary lineage in the family geminiviridae implicated in grapevine redleaf disease by next-generation sequencing. PLoS ONE, 8 (6):1-17. |
| [28] |
Pruesse E, Quast C, Knittel K. 2007. SILVA:a comprehensive online resource for quality checked and aligned ribosomal RNA sequence data compatible with ARB. Nucleic Acids Research, 35 (21):7188-7196.
doi: 10.1093/nar/gkm864 pmid: 17947321 |
| [29] |
Safari M, Roossinck M J. 2018. Coevolution of a persistent plant virus and its pepper hosts. Molecular Plant-Microbe Interactions, 31 (7):776-786.
doi: 10.1094/MPMI-12-17-0312-R |
| [30] |
Souza J D, MÜller G, Perez W, Cuellar W, Kreuze J. 2017. Complete sequence and variability of a new subgroup B nepovirus infecting potato in central Peru. Archives of Virology, 162:885-889.
doi: 10.1007/s00705-016-3147-6 pmid: 27858290 |
| [31] | Tan Gen-tang, Shi Lian-lian, Shang Hui-lan, Gong Zhen-hui. 2003. Diagnosis of viruses in chilli pepper in Shanxi Province. Journal of China Capicum,(4):32-33. (in Chinese) |
| a谭根堂, 史联联, 尚惠兰, 巩振辉. 2003. 陕西线辣椒病毒病病原检测简报. 辣椒杂志,(4):32-33. | |
| [32] | Tang Ya-fei, Pei Fan, Li Zheng-gang, She Xiao-man, Yu Lin, Lan Guo-bing, Deng Ming-guang, He Zi-fu. 2019. Identification of viruses infecting peppers in Guangdong by small RNA deep sequencing. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 52 (13):2256-2267. |
| 汤亚飞, 裴凡, 李正刚, 佘小漫, 于琳, 蓝国兵, 邓铭光, 何自福. 2019. 基于小RNA深度测序技术鉴定侵染广东辣椒的病毒种类. 中国农业科学, 52 (13):2256-2267. | |
| [33] | Tang Yafei, Pei Fan, Yu Lin, He Zifu, She Xiaoman, Lan Guobing, Deng Mingguang. 2018. Molecular characterization of Chilli veinal mottle virus infecting pepper in Guangdong Province. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 45 (11):2209-2216. (in Chinese) |
| 汤亚飞, 裴凡, 于琳, 何自福, 佘小漫, 蓝国兵, 邓铭光. 2018. 侵染广东辣椒的辣椒脉斑驳病毒的分子特征. 园艺学报, 45 (11):2209-2216. | |
| [34] | Tsai W S, Abdourhamane I K, Kenyon L. 2010. First report of Pepper veinal mottle virus associated with mosaic and mottle diseases of tomato and pepper in Mali. Plant Disease, 94:378. |
| [35] |
Tsai W S, Huang Y C, Zhang D Y, Reddy K, Hidayat S H, Srithongchai W, Jan F J. 2008. Molecular characterization of the CP gene and 3'UTR of Chilli veinal mottle virus from South and Southeast Asia. Plant Pathology, 57 (3):408-416.
doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3059.2007.01780.x URL |
| [36] | Wang Da-xin, Wang Jian-hua, Zhao Huan-ge, Qiu Shi-ming, Liu Zhi-xin. 2007. Research progress in Chill veinal mottle virus(CHiVMV). Journal of South China University of Tropical Agriculture, 13 (2):32-36. (in Chinese) |
| 王达新, 王健华, 赵焕阁, 邱世明, 刘志昕. 2007. 辣椒叶脉斑驳病毒研究进展. 华南热带农业大学学报, 13 (2):32-36. | |
| [37] |
Wang J, Liu Z, Niu S, Niu S, Peng M, Wang D, Weng Z, Xiong Z. 2006. Natural occurrence of Chilli veinal mottle virus on Capsicum chinense in China. Plant Disease, 90 (3):377.
doi: 10.1094/PD-90-0377C pmid: 30786572 |
| [38] | Wang Li-hao, Ma Yan-qing, Zhang Bao-xi. 2019. Market demand and breeding trend of pepper varieties in China. China Vegetables,(8):1-4. (in Chinese) |
| 王立浩, 马艳青, 张宝玺. 2019. 我国辣椒品种市场需求与育种趋势. 中国蔬菜,(8):1-4. | |
| [39] | Wang Pei, Tang Lin-fei, Lei Yan, Xiong Xing-yao, Nie Xian-zhou, Hu Xin-xi. 2015. Research advances in hot pepper viral diseases. Hunan Agricultural Sciences,(7):151-154. (in Chinese) |
| 汪沛, 汤琳菲, 雷艳, 熊兴耀, 聂先舟, 胡新喜. 2015. 辣椒病毒病研究进展. 湖南农业科学,(7):151-154. | |
| [40] | Wang Shao-li, Tan Wei-ping, Yang Yuan-yuan, Dai Hui-jie, Sun Xiao-hui, Qiao Ning, Zhu Xiao-ping. 2017. Molecular detection and identification of main viruses on pepper in Shandong Province. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 50 (14):2728-2738. (in Chinese) |
| 王少立, 谭玮萍, 杨园园, 代惠洁, 孙晓辉, 乔宁, 竺晓平. 2017. 山东省辣椒主要病毒种类的分子检测与鉴定. 中国农业科学, 50 (14):2728-2738. | |
| [41] | Yao Yu-rong, Chen Guo-hua, Feng Lan-xiang, Xie Bing-yan. 2013. Molecular detection of pepper viruses in southern vegetable production bases. China Vegetables,(10):84-89. (in Chinese) |
| 姚玉荣, 陈国华, 冯兰香, 谢丙炎. 2013. 北运蔬菜基地辣椒病毒病病原种类的分子检测. 中国蔬菜,(10):84-89. | |
| [42] | Yu Hai-long, Jin Yuan, Liu Jing, Zhang Bao-xi, Zhang Zheng-hai, Cao Ya-cong, Wang Li-hao. 2020. Occurrence and development trend of pepper virus disease in China—based on main pepper producing areas investigation in 2018 and 2019. China Vegetables,(9):25-30. (in Chinese) |
| 于海龙, 靳远, 刘婧, 张宝玺, 张正海, 曹亚从, 王立浩. 2020. 我国辣椒病毒病发生情况及发展趋势——基于2018年和2019年辣椒主产区的调查. 中国蔬菜,(9):25-30. | |
| [43] |
Zerbino D R, Birney E. 2008. Velvet: algorithms for de novo short read assembly using de Bruijn graphs. Genome Research, 18 (5):821-829.
doi: 10.1101/gr.074492.107 pmid: 18349386 |
| [44] | Zhang S B, Zhao Z B, Zheng L M, Zhang D Y, Liu Y, Liu J, Du J, Peng J, Yan F, Li F, Xie Y, Cheng Z B. 2016. First report of Pepper veinal mottle virus infecting pepper in mainland China. Plant Disease, 100 (5):1025. |
| [45] |
Zhang Y L, Yu N T, Huang Q X, Yin G H, Guo A P, Wang X F, Xiong Z G, Liu Z X. 2014. Complete genome of Hainan Papaya ringspot virus using small RNA deep sequencing. Virus Genes, 48:502-508.
doi: 10.1007/s11262-014-1042-3 URL |
| [46] | Zhang Zhu-qing. 2009. Study on pepper virus disease [Ph. D. Dissertation]. Changsha: Hunan Agricultural University. (in Chinese) |
| 张竹青. 2009. 辣椒病毒病研究[博士论文]. 长沙: 湖南农业大学. |
| [1] | LUO Hailin, YUAN Lei, WENG Hua, YAN Jiahui, GUO Qingyun, WANG Wenqing, MA Xinming. Identification and Analysis of Complete Genomic Sequence of Broad Bean Wilt Virus 2 Pepper Isolate in Qinghai Province [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(1): 161-169. |
| [2] | CAO Yacong, ZHANG Zhenghai, YU Hailong, FENG Xigang, ZHANG Baoxi, and WANG Lihao. A New Spiral Pepper Cultivar‘Zhongjiao 409’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(S2): 111-112. |
| [3] | CAO Yacong, ZHANG Zhenghai, YU Hailong, FENG Xigang, ZHANG Baoxi, and WANG Lihao. A New Disease-resistant Spiral Hot Pepper Cultivar‘Zhongjiao 209’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(S2): 113-114. |
| [4] | WANG Yongping, HU Mingwen, ZHU Wenchao, LIAO Fangfang, BAI Liwei, and GAO Gang. A New Pepper Cultivar‘Hongla 3’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(S2): 115-116. |
| [5] | Liu Shujun, Hui Chengzhang, Zhao Lili, Sun Yongsheng, and Liu Aiqun . A New Mid-early Ripening Pepper Cultivar‘Meroka’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(S2): 117-118. |
| [6] | WANG Fei, LI Ning, YIN Yanxu, GAO Shenghua, XU Kai, and YAO Minghua. A New Pepper Cultivar‘Ejiao Hongyuanshuai’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(S2): 119-120. |
| [7] | LI Ning, YIN Yanxu, GAO Shenghua, XU Kai, WANG Fei, and YAO Minghua. A New Pepper Cultivar‘Jinxiuhong 117’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(S2): 121-122. |
| [8] | FANG Rong, CHEN Xuejun, ZHOU Kunhua, YUAN Xinjie, LEI Gang, and HUANG Yueqin. A New Pepper Cultivar‘Ganjiao 18’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(S1): 75-76. |
| [9] | HAN Shuai, WU Jie, ZHANG Heqing, XI Yadong. Identification and Sequence Analysis of Tomato Spotted Wilt Orthotospovirus Infecting Lettuce in Sichuan [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(9): 2007-2016. |
| [10] | DONG Sangjie, GE Shibei, LI Lan, HE Liqun, FAN Feijun, QI Zhenyu, YU Jingquan, ZHOU Yanhong. Effects of Supplemental Lighting on Growth,Root Colonization by Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungi and Phosphorus Uptake in Pepper Seedlings [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(8): 1699-1712. |
| [11] | LI Ying, WANG Hengming, XU Xiaowan, XU Xiaomei, HUANG Zhiwen. A New Pepper Cultivar‘Yuejiao 8’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(8): 1837-1838. |
| [12] | XIA Yan, HUANG Song, WU Xueli, LIU Yiqi, WANG Miaomiao, SONG Chunhui, BAI Tuanhui, SONG Shangwei, PANG Hongguang, JIAO Jian, ZHENG Xianbo. Identification and Analysis of Apple Viruses Diseases Based on Virome Sequencing Technology [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(7): 1415-1428. |
| [13] | ZHANG Qiuyue, LIU Changlai, YU Xiaojing, YANG Jiading, FENG Chaonian. Screening of Reference Genes for Differentially Expressed Genes in Pyrus betulaefolia Plant Under Salt Stress by qRT-PCR [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(7): 1557-1570. |
| [14] | ZOU Xuexiao, ZHU Fan. Origin,Evolution and Cultivation History of the Pepper [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(6): 1371-1381. |
| [15] | FU Hongfei, NIE Zhixing, CHEN Jianying. A New Pepper‘Hangjiao 12’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(6): 1395-1396. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2012 Acta Horticulturae Sinica 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
Tel: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
Support by: Beijing Magtech Co.Ltd