
Acta Horticulturae Sinica ›› 2021, Vol. 48 ›› Issue (12): 2385-2402.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2020-1063
Previous Articles Next Articles
ZHANG Jingya, LEI Lei, SHANG Qingmao, XIE Lulu, DONG Chunjuan( )
)
Received:2021-04-19
Revised:2021-07-21
Published:2022-01-04
Contact:
DONG Chunjuan
E-mail:dongchunjuan@caas.cn
CLC Number:
ZHANG Jingya, LEI Lei, SHANG Qingmao, XIE Lulu, DONG Chunjuan. Expression Patterns of Tomato SlIAMT1 and SlIAMT2 and Their Functions During Hypocotyl and Root Development[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2021, 48(12): 2385-2402.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.ahs.ac.cn/EN/10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2020-1063
| 用途Use | 基因Gene | 引物序列(5′-3′)Sequence |
|---|---|---|
| 基因克隆 Gene clone | SlIAMT1 | F:CACTAGCAAAACAATAGAGACA;R:TCTAATACATGAGAGACATATAGACTT |
| SlIAMT2 | F:TCTACTTTTATGGTTAGATTCTG;R:TATCCCAAATGTTGCTTAA | |
| qRT-PCR | SlIAMT1 | F:CTCAAGCTCAGGGGCAACAT;R:ATCTCCGGCGAGTTTAGCTG |
| SlIAMT2 | F:CTCAAGCCCAGGGACAACAT;R:CGAAGGGGATGTCGTCGTTAT | |
| SlActin41 | F:CTTCCAGCAGATGTGGATTGC;R:GCATCTCTGGTCCAGTAGGAAA | |
| AtIAMT1 | F:CGGTCTACTCTTCGGCACTC;R:GGTGCGTACACCGGGATATT | |
| AtActin2 | F:ACACTGTGCCAATCTACGAGGGTT;R:ACAATTTCCCGCTCTGCTGTTGTG | |
| 载体构建 Transgenic vector construction | 35S:SlIAMT1 | F:CGGTACCCGGGGATCCATGGCACCTTTAGGAGACAA; R:CGACTCTAGAGGATCCCTACACAAGAGAAAGTGAAGCAACA |
Table 1 Primers used in this study
| 用途Use | 基因Gene | 引物序列(5′-3′)Sequence |
|---|---|---|
| 基因克隆 Gene clone | SlIAMT1 | F:CACTAGCAAAACAATAGAGACA;R:TCTAATACATGAGAGACATATAGACTT |
| SlIAMT2 | F:TCTACTTTTATGGTTAGATTCTG;R:TATCCCAAATGTTGCTTAA | |
| qRT-PCR | SlIAMT1 | F:CTCAAGCTCAGGGGCAACAT;R:ATCTCCGGCGAGTTTAGCTG |
| SlIAMT2 | F:CTCAAGCCCAGGGACAACAT;R:CGAAGGGGATGTCGTCGTTAT | |
| SlActin41 | F:CTTCCAGCAGATGTGGATTGC;R:GCATCTCTGGTCCAGTAGGAAA | |
| AtIAMT1 | F:CGGTCTACTCTTCGGCACTC;R:GGTGCGTACACCGGGATATT | |
| AtActin2 | F:ACACTGTGCCAATCTACGAGGGTT;R:ACAATTTCCCGCTCTGCTGTTGTG | |
| 载体构建 Transgenic vector construction | 35S:SlIAMT1 | F:CGGTACCCGGGGATCCATGGCACCTTTAGGAGACAA; R:CGACTCTAGAGGATCCCTACACAAGAGAAAGTGAAGCAACA |
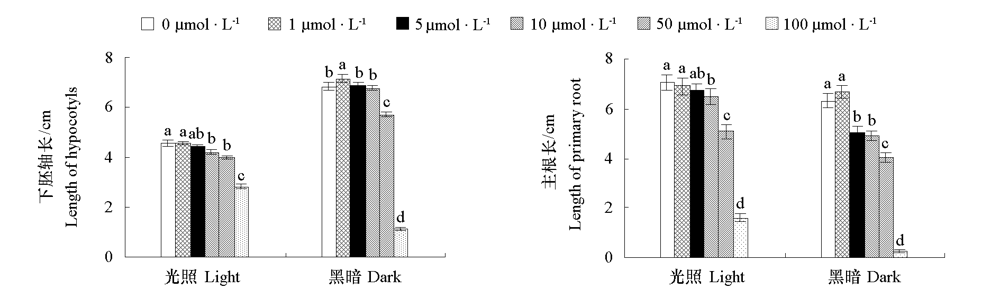
Fig. 1 Effects of exogenous MeIAA application on growth of hypocotyls and roots in tomato seedlings under light and dark conditions Different lowercases indicate significant differences between groups under same culture condition(P < 0.05).
| 基因 Gene | 序列号 Accession No. | 基因全长/bp Gene length | 外显子数 Number of exons | 内含子数 Number of introns | ORF/ bp | 蛋白长度/aa Protein length | 分子量/ kD MW | 等电点 pI | 亚细胞定位 Subcellular localization |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SlIAMT1 | Solyc07G064990 | 2 510 | 4 | 3 | 1 173 | 390 | 42.92 | 5.58 | 细胞质Cytoplasm |
| SlIAMT2 | Solyc12G014500 | 4 620 | 4 | 3 | 1 173 | 390 | 43.28 | 5.90 | 细胞质Cytoplasm |
Table 2 Sequence characteristics of SlIAMT1 and SlIAMT2 genes in tomato
| 基因 Gene | 序列号 Accession No. | 基因全长/bp Gene length | 外显子数 Number of exons | 内含子数 Number of introns | ORF/ bp | 蛋白长度/aa Protein length | 分子量/ kD MW | 等电点 pI | 亚细胞定位 Subcellular localization |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SlIAMT1 | Solyc07G064990 | 2 510 | 4 | 3 | 1 173 | 390 | 42.92 | 5.58 | 细胞质Cytoplasm |
| SlIAMT2 | Solyc12G014500 | 4 620 | 4 | 3 | 1 173 | 390 | 43.28 | 5.90 | 细胞质Cytoplasm |

Fig. 2 Homology alignment of SlIAMT1 and SlIAMT2 with Arabidopsis AtIAMT1 protein sequences ▼:SAM/SAH-binding site;*:Interaction site with carboxyl moiety of IAA;†:Interaction site with aromatic moiety of IAA.
| 调控元件 Cis-element | 核心序列 Core sequence | 元件功能描述 Functional description of cis-element | 位置Positions* | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SlIAMT1 | SlIAMT2 | |||
| ABRE | CACGTG | ABA响应元件 cis-Acting element involved in the abscisic acid responsiveness | -1 547 | -552、 -1 129、 -1 921 |
| TCA-element | CCATCTTTTT | 水杨酸响应元件 cis-Acting element involved in salicylic acid responsiveness | -1 513 | / |
| TGA-element | AACGAC | 生长素响应元件 Auxin-responsive element | / | -791 |
| TGACG-motif | TGACG | 茉莉酸甲酯响应元件 cis-Acting regulatory element involved in the methyl jasmonate responsiveness | / | -367 |
| MBS | CAACTG | 参与干旱诱导的MYB结合位点 MYB binding site involved in drought-inducibility | / | -712 |
| ACE | CTAACGTATT | 光响应元件cis-Acting element for light responsive | -1 754 | / |
| G-box | TACGTG | 光响应元件cis-Acting element for light responsive | -1 546,-1 981 | / |
| GT1-motif | GGTTAA | 光响应元件Light responsive element | -263,-170, -1 500,-1 810 | / |
| AE-box | AGAAACAA | 光响应元件的一部分 Part of a module for light response | -1 867 | / |
| AT1-motif | AATTATTTTTTATT | 光响应元件的一部分 Part of a light responsive module | -1 711、-698 | / |
| I-box | TGATAATGT | 光响应元件的一部分 Part of a light responsive element | -1 331 | / |
| MRE | AACCTAA | 参与光响应的MYB结合位点 MYB binding site for light responsive | / | -1 614、 -1 079 |
Table 3 Some important cis-acting regulatory elements in the promoters of SlIAMT1 and SlIAMT2
| 调控元件 Cis-element | 核心序列 Core sequence | 元件功能描述 Functional description of cis-element | 位置Positions* | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SlIAMT1 | SlIAMT2 | |||
| ABRE | CACGTG | ABA响应元件 cis-Acting element involved in the abscisic acid responsiveness | -1 547 | -552、 -1 129、 -1 921 |
| TCA-element | CCATCTTTTT | 水杨酸响应元件 cis-Acting element involved in salicylic acid responsiveness | -1 513 | / |
| TGA-element | AACGAC | 生长素响应元件 Auxin-responsive element | / | -791 |
| TGACG-motif | TGACG | 茉莉酸甲酯响应元件 cis-Acting regulatory element involved in the methyl jasmonate responsiveness | / | -367 |
| MBS | CAACTG | 参与干旱诱导的MYB结合位点 MYB binding site involved in drought-inducibility | / | -712 |
| ACE | CTAACGTATT | 光响应元件cis-Acting element for light responsive | -1 754 | / |
| G-box | TACGTG | 光响应元件cis-Acting element for light responsive | -1 546,-1 981 | / |
| GT1-motif | GGTTAA | 光响应元件Light responsive element | -263,-170, -1 500,-1 810 | / |
| AE-box | AGAAACAA | 光响应元件的一部分 Part of a module for light response | -1 867 | / |
| AT1-motif | AATTATTTTTTATT | 光响应元件的一部分 Part of a light responsive module | -1 711、-698 | / |
| I-box | TGATAATGT | 光响应元件的一部分 Part of a light responsive element | -1 331 | / |
| MRE | AACCTAA | 参与光响应的MYB结合位点 MYB binding site for light responsive | / | -1 614、 -1 079 |
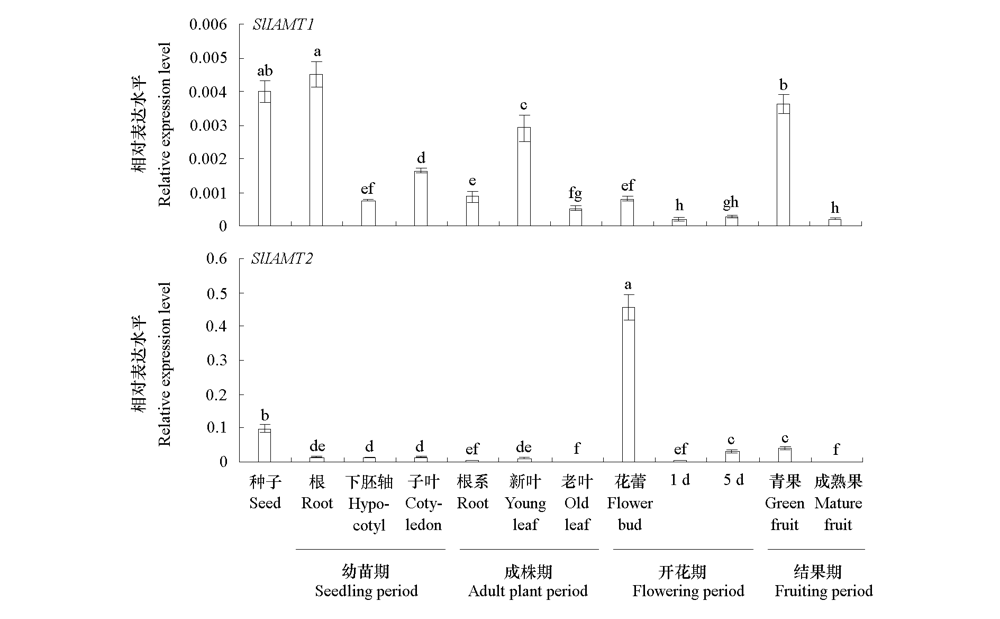
Fig. 4 Expression levels of SlIAMT1 and SlIAMT2 in different tissues of tomato The different lowercases indicate significant differences between groups(P < 0.05).
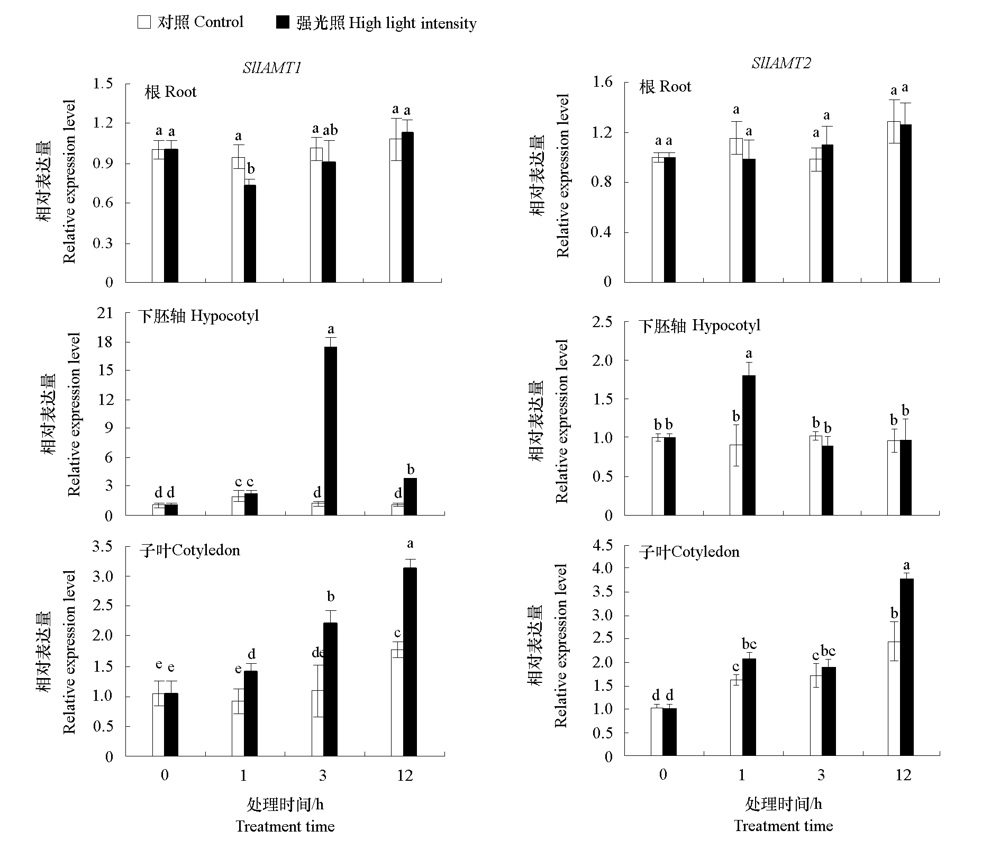
Fig. 5 Expression levels of SlIAMT1 and SlIAMT2 in root,hypocotyl,and cotyledon of tomato seedlings in response to high light intensity(150 μmol · m-2 · s -1 Different lowercases indicate significant differences between groups(P < 0.05).
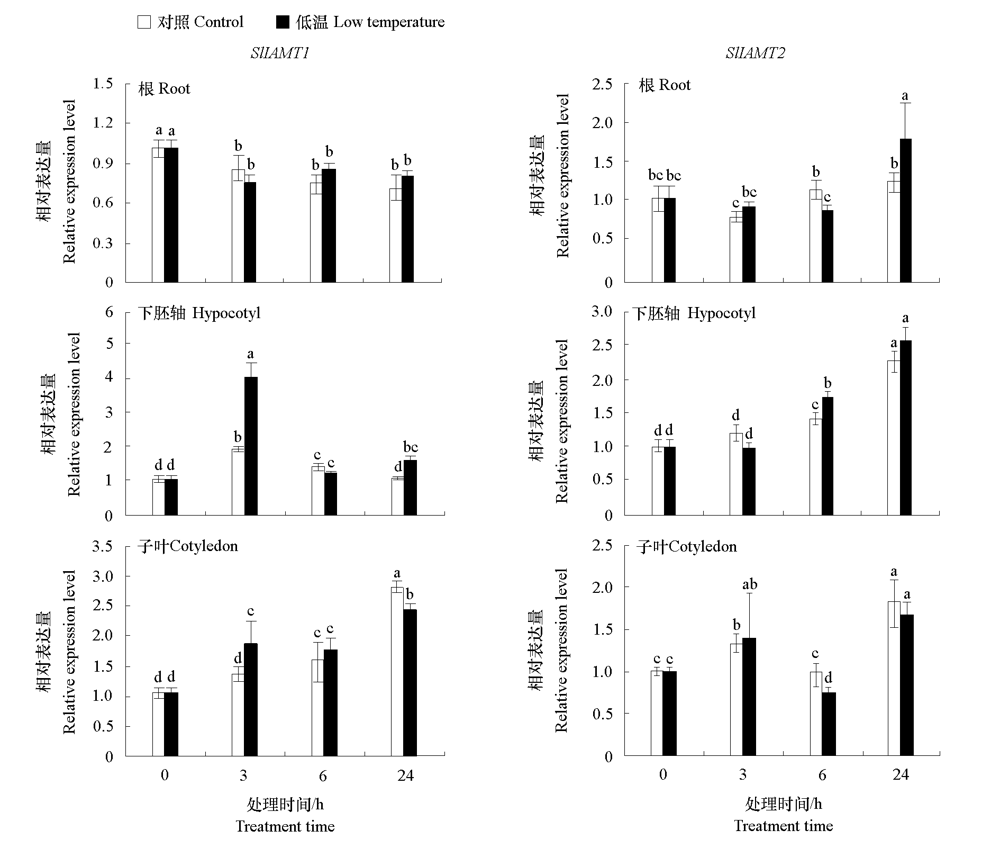
Fig. 6 Expression levels of SlIAMT1 and SlIAMT2 in root,hypocotyl,and cotyledon of tomato seedlings in response to low temperature(15 ℃/15 ℃) Different lowercases indicate significant differences between groups(P < 0.05).
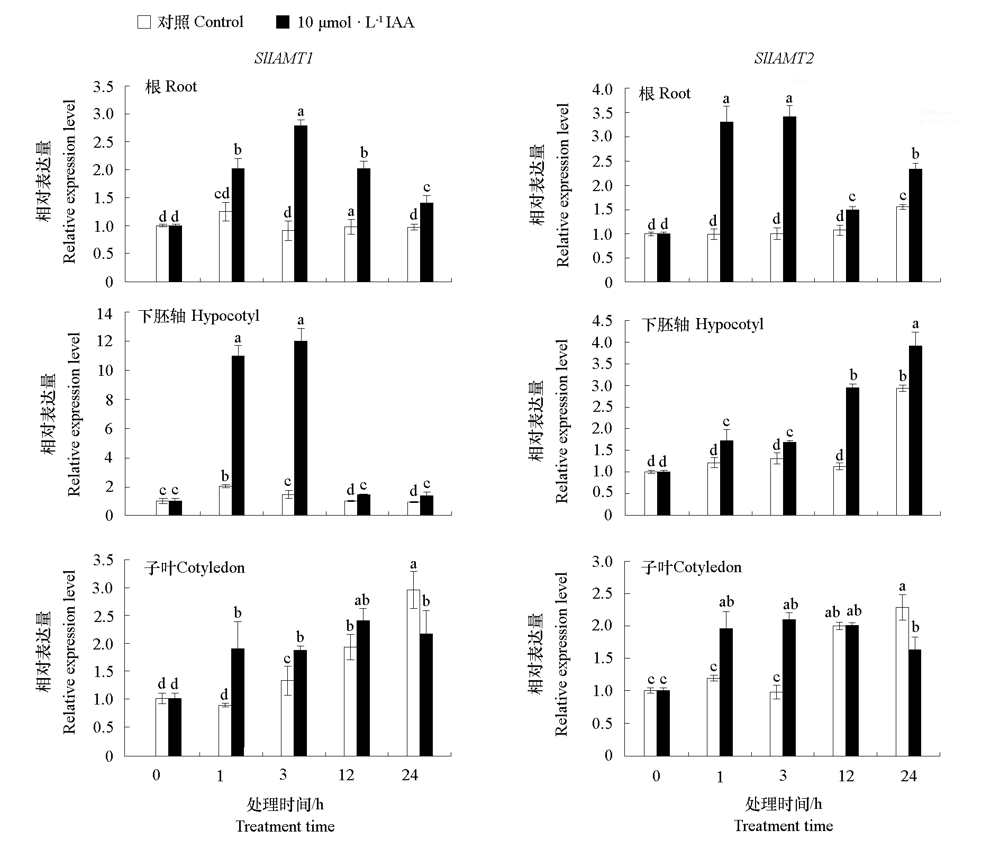
Fig. 7 Expression levels of SlIAMT1 and SlIAMT2 in root,hypocotyl,and cotyledonof tomato seedlings in response to IAA Different lowercases indicate significant differences between groups(P < 0.05).
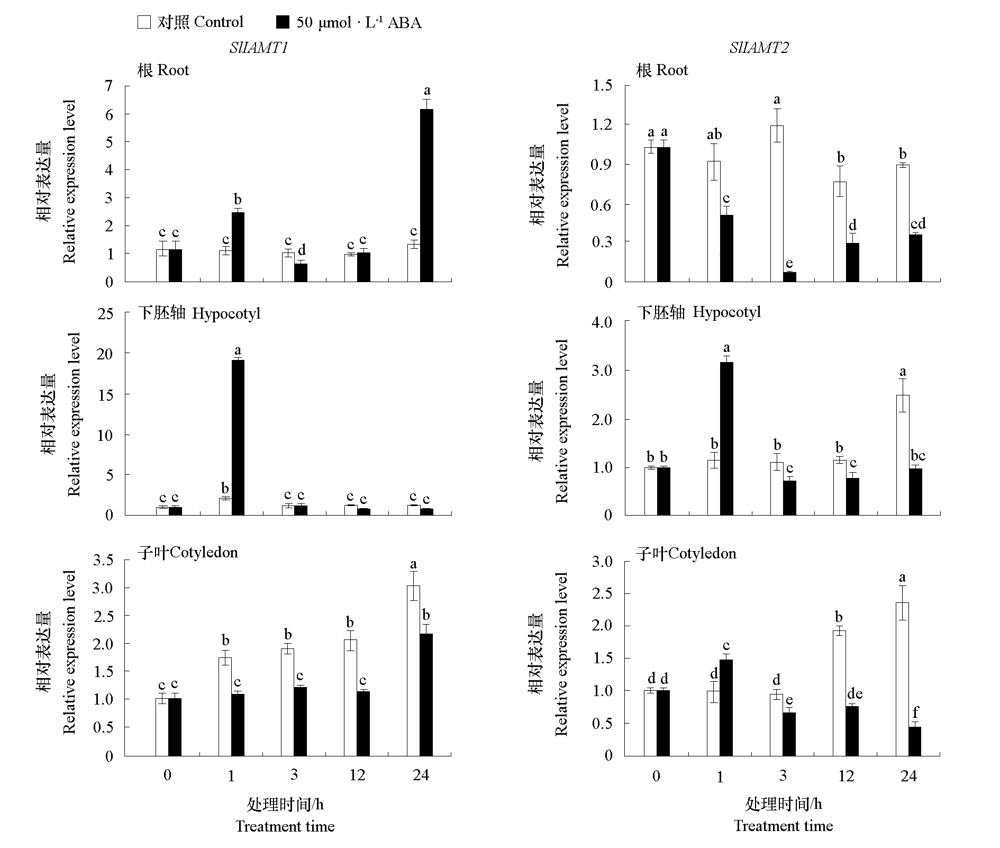
Fig. 8 Expression levels of SlIAMT1 and SlIAMT2 in root,hypocotyl,and cotyledon of tomato seedlings in response to ABA Different lowercases indicate significant differences between groups(P < 0.05).
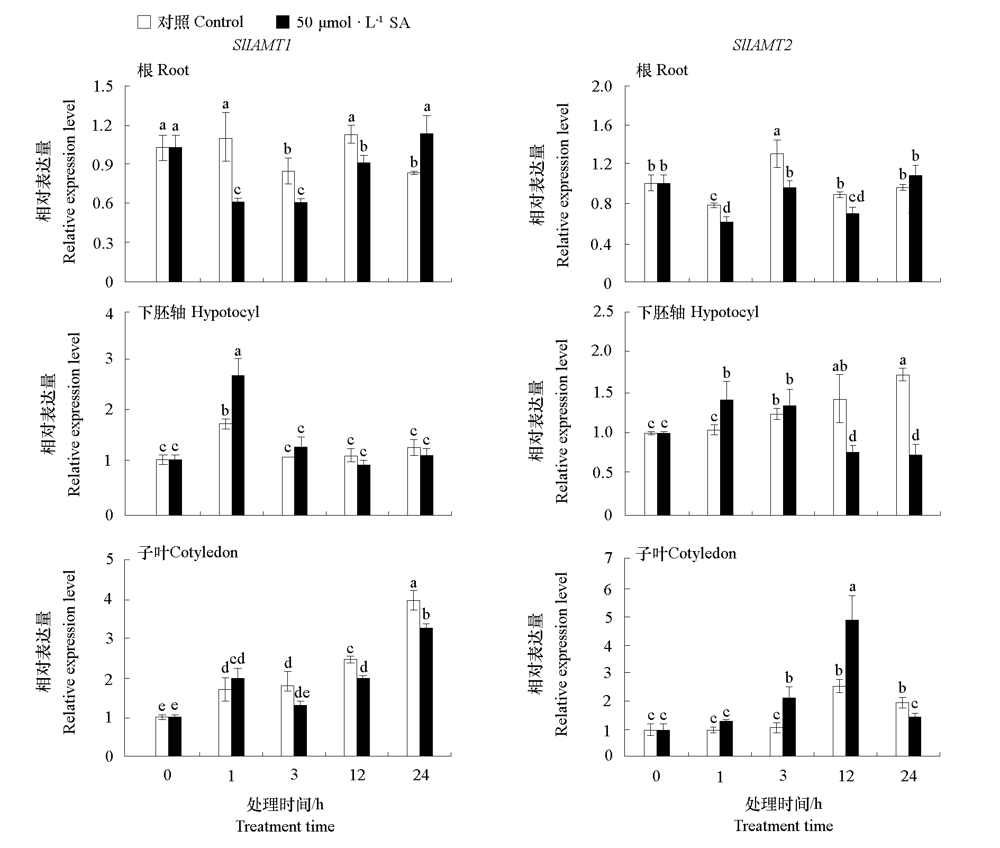
Fig. 9 Expression levels of SlIAMT1 and SlIAMT2 in root,hypocotyl,and cotyledon of tomato seedlings in response to SA Different lowercases indicate significant differences between groups(P < 0.05).
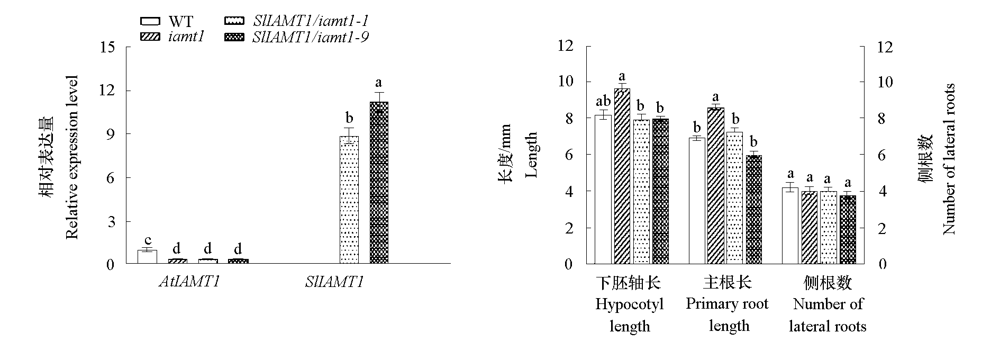
Fig. 10 Effects of SlIAMT1 overexpression on hypocotyl and root growth in Arabidopsis iamt1 mutant Different lowercases indicate significant differences between groups(P < 0.05).
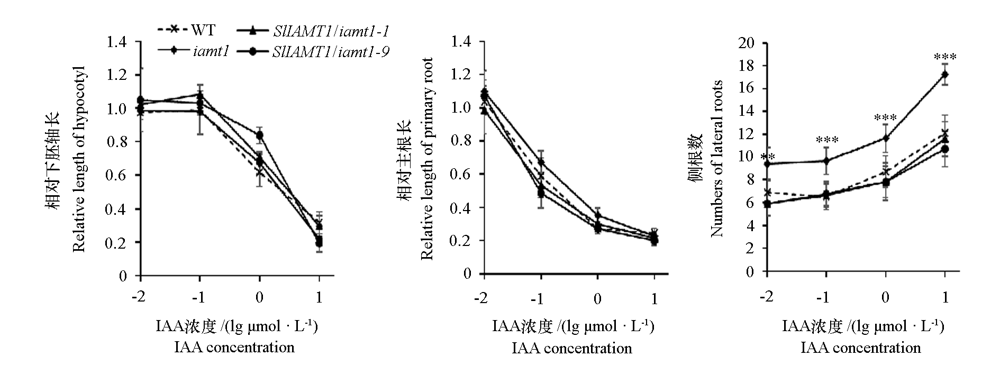
Fig. 11 Effects of overexpression of SlIAMT1 on the response of Arabidopsis iamt1 mutant seedlings to IAA The concentration of IAA is the logarithmic value. **,*** indicate significant differences between groups at 0.01 and 0.001 level,respectively.
| [1] |
Abbas M, Hernández-García J, Blanco-Touriñán N, Aliaga N, Minguet E G, Alabadí D, Blázquez M A. 2018a. Reduction of indole-3-acetic acid methyltransferase activity compensates for high-temperature male sterility in Arabidopsis. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 16 (1):272-279.
doi: 10.1111/pbi.2018.16.issue-1 URL |
| [2] | Abbas M, Hernández-García J, Pollmann S, Samodelov S L, Kolb M, Friml J, Hammes U Z, Zurbriggen M D, Blázquez M A, Alabadí D. 2018b. Auxin methylation is required for differential growth in Arabidopsis. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 115 (26):6864-6869. |
| [3] |
Aloni R. 2013. Role of hormones in controlling vascular differentiation and the mechanism of lateral root initiation. Planta, 238 (5):819-830.
doi: 10.1007/s00425-013-1927-8 pmid: 23835810 |
| [4] |
An J P, Liu X, Song L Q, You C X, Hao Y J. 2017. Functional characterization of the apple RING E 3 ligase MdMIEL1 in transgenic Arabidopsis. Horticultural Plant Journal, 3 (2):53-59.
doi: 10.1016/j.hpj.2017.01.001 URL |
| [5] |
Chhun T, Taketa S, Tsurumi S, Ichii M. 2003. The effects of auxin on lateral root initiation and root gravitropism in a lateral rootless mutant Lrt1 of rice(Oryza sativa L.). Plant Growth Regulation, 39:161-170.
doi: 10.1023/A:1022592511387 URL |
| [6] |
Chung M H, Chen M K, Pan S M. 2000. Floral spray transformation can efficiently generate Arabidopsis transgenic plants. Transgenic Research, 9 (6):471-476.
pmid: 11206976 |
| [7] |
Collett C E, Harberd N P, Leyser O. 2000. Hormonal interactions in the control of Arabidopsis hypocotyl elongation. Plant Physiology, 124 (2):553-561.
pmid: 11027706 |
| [8] | Dias M C, Oliveira H, Costa A, Santos C. 2014. Improving elms performance under drought stress:the pretreatment with abscisic acid. Environmental & Experimental Botany, 100:64-73. |
| [9] | Ding Mao-yu, Hou Xian-hui, Liu Sai-nan, Li Lin-chuan, Chen Zhang-liang, Kang Ding-ming, Qu Li-jia. 2013. Study on expression pattern of Arabidopsis MeIAA esterase genes. Journal of China Agricultural University, 18 (2):1-8. (in Chinese) |
| 丁茂予, 侯仙慧, 刘赛男, 李林川, 陈章良, 康定明, 瞿礼嘉. 2013. 拟南芥MeIAA酯解酶基因表达模式的初步研究. 中国农业大学学报, 18 (2):1-8. | |
| [10] |
Du M, Spalding E P, Gray W M. 2020. Rapid auxin-mediated cell expansion. Annual Review of Plant Biology, 71 (1):1-24.
doi: 10.1146/annurev-arplant-081519-035831 URL |
| [11] |
Feng Han-qian, Li Chao. 2018. Research advances of auxin signal transduction. Biotechnology Bulletin, 34 (7):24-30. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.13560/j.cnki.biotech.bull.1985.2018-0488 |
|
冯寒骞, 李超. 2018. 生长素信号转导研究进展. 生物技术通报, 34 (7):24-30.
doi: 10.13560/j.cnki.biotech.bull.1985.2018-0488 |
|
| [12] |
Gallei M, Luschnig C, Friml J. 2020. Auxin signalling in growth:Schrödinger's cat out of the bag. Current Opinion in Plant Biology, 53:43-49.
doi: 10.1016/j.pbi.2019.10.003 URL |
| [13] |
Han W X, Han D L, He Z P, Hu H, Wu Q, Zhang J J, Jiang J M, Qin G J, Cui Y H, Lai J B, Yang C W. 2018. The SWI/SNF subunit SWI3B regulates IAMT1 expression via chromatin remodeling in Arabidopsis leaf development. Plant Science, 271:127-132.
doi: 10.1016/j.plantsci.2018.03.021 URL |
| [14] | Hou Xian-hui, Ding Mao-yu, Liu Sai-nan, Li Lin-chuan, Qu Li-jia. 2009. Isolation and positional cloning of methyl-indole-3-aceticacid resistant mutants in Arabidopsis. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 44 (1):52-58. (in Chinese) |
| 侯仙慧, 丁茂予, 刘赛男, 李林川, 瞿礼嘉. 2009. 拟南芥MeIAA抗性突变体的筛选和初步图位克隆分析. 植物学报, 44 (1):52-58. | |
| [15] |
Kolosova N, Sherman D, Karlson D, Dudareva N. 2001. Cellular and subcellular localization of S-adenosyl-L-methionine:benzoic acid carboxyl methyltransferase,the enzyme responsible for biosynthesis of the volatile ester methylbenzoate in snapdragon flowers. Plant Physiology, 126:956-964.
pmid: 11457946 |
| [16] |
Lam K C, Ibrahim R K, Behdad B, Dayanandan S. 2007. Structure,function,and evolution of plant O-methyltransferases. Genome, 50:1001-1013.
doi: 10.1139/G07-077 URL |
| [17] |
Li L, Hou X H, Tsuge T, Ding M Y, Aoyama T, Oka A, Gu H Y, Zhao Y D, Qu L J. 2008. The possible action mechanisms of indole-3-acetic acid methyl ester in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Reports, 27 (3):575-584.
doi: 10.1007/s00299-007-0458-9 URL |
| [18] | Li Lin-chuan, Qu Li-jia. 2006. Regulation of leaf development by auxin in Arabidopsis. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 23 (5):459-465. (in Chinese) |
| 李林川, 瞿礼嘉. 2006. 生长素对拟南芥叶片发育调控的研究进展. 植物学通报, 23 (5):459-465. | |
| [19] | Li Min, Yang Shuang, Ruan Yan-ye, Fan Jin-juan, Zhang Li-jun. 2006. Identification of ATSUC3 with T-DNA insertion by PCR. Plant Physiology Communications, 42 (1):91-94. (in Chinese) |
| 李敏, 杨双, 阮燕晔, 樊金娟, 张立军. 2006. 拟南芥T-DNA插入突变体ATSUC3的PCR鉴定. 植物生理学通讯, 42 (1):91-94. | |
| [20] | Li Shuang. 2012. Preliminary study of regulation of phytohormone methylation in Arabidopsis growth and development[M. D. Dissertation]. Beijing: Peking University. (in Chinese) |
| 李爽. 2012. 植物激素甲基化修饰调控拟南芥生长发育的初步研究[硕士论文]. 北京: 北京大学. | |
| [21] | Li Shu-yu, Li Chuan-you. 2016. Developmental plasticity of plant roots. China Basic Science, 18 (2):14-21. (in Chinese) |
| 李淑钰, 李传友. 2016. 植物根系可塑性发育的研究进展与展望. 中国基础科学, 18 (2):14-21. | |
| [22] | Liu J, Shi M, Wang J, Zhang B, Li Y, Wang J, El-Sappah A H, Liang Y. 2020. Comparative transcriptomic analysis of the development of sepal morphology in tomato(Solanum lycopersicum L.). International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21 (16):E5914. |
| [23] |
Livak K J, Schmittgen T D. 2001. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2-ΔΔCT method. Methods, 25 (4):402-408.
pmid: 11846609 |
| [24] |
Ljung K. 2013. Auxin metabolism and homeostasis during plant development. Development, 140 (5):943-950.
doi: 10.1242/dev.086363 URL |
| [25] |
Park J E, Park J Y, Kim Y S, Staswick P E, Jeon J, Yun J, Kim S Y, Kim J, Lee Y H, Park C M. 2007. GH3-mediated auxin homeostasis links growth regulation with stress adaptation response in Arabidopsis. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 282 (13):10036-10046.
doi: 10.1074/jbc.M610524200 URL |
| [26] |
Qin G J, Gu H Y, Zhao Y D, Ma Z Q, Shi G L, Yang Y, Pichersky E, Chen H D, Liu M H, Chen Z L, Qu L J. 2005. An indole-3-acetic acid carboxyl methyltransferase regulates Arabidopsis leaf development. Plant Cell, 17 (10):2693-2704.
doi: 10.1105/tpc.105.034959 URL |
| [27] |
Qu L J, Li S, Xing S F. 2010. Methylation of phytohormones by the SABATH methyltransferases. Chinese Science Bulletin, 55 (21):2211-2218.
doi: 10.1007/s11434-010-3245-x URL |
| [28] | Rahman A, Bannigan A, Sulaman W, Pechter P, Blancaflor E B. 2007. Auxin,actin and growth of the Arabidopsis thaliana primary root. Plant Journal for Cell & Molecular Biology, 50 (3):514. |
| [29] | Roychoudhury A, Paul S, Basu S. 2013. Cross-talk between abscisic acid-dependent and abscisic acid-independent pathways during abiotic stress. Plant Cell, 32 (7):985-1006. |
| [30] |
Takubo E, Kobayashi M, Hirai S, Aoi Y, Ge C, Dai X, Fukui K, Hayashi K I, Zhao Y, Kasahara H. 2020. Role of Arabidopsis indole-3-acetic acid carboxyl methyltransferase 1 in auxin metabolism. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 527 (4):1033-1038.
doi: S0006-291X(20)30938-4 pmid: 32444138 |
| [31] |
Vanneste S, Friml J. 2009. Auxin:a trigger for change in plant development. Cell, 136 (6):1005-1016.
doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2009.03.001 pmid: 19303845 |
| [32] |
Vilches-Barro A, Maizel A. 2015. Talking through walls:mechanisms of lateral root emergence in Arabidopsis thaliana. Current Opinion in Plant Biology, 23:31-38.
doi: 10.1016/j.pbi.2014.10.005 pmid: 25449724 |
| [33] |
Weijers D, Wagner D. 2016. Transcriptional responses to the auxin hormone. Annual Review of Plant Biology, 67 (1):539-574.
doi: 10.1146/arplant.2016.67.issue-1 URL |
| [34] |
Woodward A W, Bartel B. 2005. Auxin:regulation,action,and interaction. Annals of Botany, 95 (5):707-735.
pmid: 15749753 |
| [35] |
Yang Y, Xu R, Ma C J, Vlot A C, Klessig D F, Pichersky E. 2008. Inactive methyl indole-3-acetic acid ester can be hydrolyzed and activated by several esterases belonging to the AtMES esterase family of Arabidopsis. Plant Physiology, 147 (3):1034-1045.
doi: 10.1104/pp.108.118224 pmid: 18467465 |
| [36] |
Zhang J, Peer W A. 2017. Auxin homeostasis:the DAO of catabolism. Journal of Experimental Botany, 68 (12):3145-3154.
doi: 10.1093/jxb/erx221 pmid: 28666349 |
| [37] |
Zhang Y L, Li X. 2019. Salicylic acid:biosynthesis,perception,and contributions to plant immunity. Current Opinion in Plant Biology, 50:29-36.
doi: 10.1016/j.pbi.2019.02.004 URL |
| [38] |
Zhang Z L, Ji R H, Li H Y, Zhao T, Liu J, Lin C T, Liu B. 2014. CONSTANS-LIKE 7 (COL7)is involved in phytochrome B (phyB)-mediated light-quality regulation of auxin homeostasis. Molecular Plant, 7 (9):1429-1440.
doi: 10.1093/mp/ssu058 URL |
| [39] |
Zhao N, Ferrer J L, Ross J, Guan J, Yang Y, Pichersky E, Noel J P, Chen F. 2008. Structural,biochemical,and phylogenetic analyses suggest that indole-3-acetic acid methyltransferase is an evolutionarily ancient member of the SABATH family. Plant Physiology, 146 (2):455-467.
pmid: 18162595 |
| [40] |
Zhao N, Guan J, Lin H, Chen F. 2007. Molecular cloning and biochemical characterization of indole-3-acetic acid methyltransferase from poplar. Phytochemistry, 68 (11):1537-1544.
pmid: 17499822 |
| [41] |
Zhao Y D. 2010. Auxin biosynthesis and its role in plant development. Annual Review of Plant Biology, 61:49-64.
doi: 10.1146/arplant.2010.61.issue-1 URL |
| [42] | Zou Li-ping, Pan Cheng, Wang Meng-xin, Cui Lin, Han Bao-yu. 2020. Progress on the mechanism of hormones regulating plant flower formation. Hereditas(Beijing), 42 (8):739-751. |
| 邹礼平, 潘铖, 王梦馨, 崔林, 韩宝瑜. 2020. 激素调控植物成花机理研究进展. 遗传, 42 (8):739-751. | |
| [43] |
Zubieta C, Ross J R, Koscheski P, Yang Y, Pichersky E, Noel J P. 2003. Structural basis for substrate recognition in the salicylic acid carboxyl methyltransferase family. Plant Cell, 15:1704-1716.
pmid: 12897246 |
| [1] | ZHENG Qingbo, BAO Zeyang, LAN Qingqing, ZHOU Yuwen, ZHOU Yufei, ZHENG Caixia, and LI Xu, . Advances in Studies on Adventitious Root Formation by Juvenile- and Auxin-determined [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(2): 441-450. |
| [2] | ZHAO Xueyan, WANG Qi, WANG Li, WANG Fangyuan, WANG Qing, LI Yan. Comparative Transcriptome Analysis of Differential Expression in Different Tissues of Corydalis yanhusuo [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(1): 177-187. |
| [3] | ZHANG Xiaoming, YAN Guohua, ZHOU Yu, WANG Jing, DUAN Xuwei, WU Chuanbao, and ZHANG Kaichun. A New Sweet Cherry Rootstock Cultivar‘Jingchun 2’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(S2): 31-32. |
| [4] | YU Yangjun, WANG Weihong, SU Tongbing, ZHANG Fenglan, ZHANG Deshuang, ZHAO Xiuyun, YU Shuancang, LI Peirong, XIN Xiaoyun, and WANG Jiao. A New Chinese Cabbage Cultivar‘Jingchun CR3’with Clubroot Resistance and Bolting Tolerance [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(S2): 87-88. |
| [5] | WANG Lili, WANG Xin, WU Haidong, WEN Qiang, and Yang Xiaofei. A New Chinese Cabbage Cultivar‘Liaobai 28’with Resistance to Clubroot Disease [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(S2): 89-90. |
| [6] | TIAN Hongmei, LIU Juan, ZHANG Changkun, TAO Zhen, ZHANG Jian, and WANG Pengcheng, . A New Pumpkin Cultivar‘Wanzhen 6’for Melon Rootstock [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(S2): 127-128. |
| [7] | GAO Yanlong, WU Yuxia, ZHANG Zhongxing, WANG Shuangcheng, ZHANG Rui, ZHANG De, WANG Yanxiu. Bioinformatics Analysis of Apple ELO Gene Family and Its Expression Analysis Under Low Temperature Stress [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(8): 1621-1636. |
| [8] | LIU Chaoyang, LIAO Zhichan, LU Xinxin, HE Yehua. Identification of CslD Gene Family in Pineapple and Functional Analysis of AcoCslD2a [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(8): 1650-1662. |
| [9] | WANG Yu, ZHANG Xue, ZHANG Xueying, ZHANG Siyu, WEN Tingting, WANG Yingjun, GAN Caixia, PANG Wenxing. The Effect of Camalexin on Chinese Cabbage Resistance to Clubroot [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(8): 1689-1698. |
| [10] | ZHANG Wanqing, ZHANG Hongxiao, LIAN Xiaofang, LI Yuying, GUO Lili, HOU Xiaogai. Analysis of DNA Methylation Related to Callus Differentiation and Rooting Induction of Paeonia ostii‘Fengdan’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(8): 1735-1746. |
| [11] | QIU Ziwen, LIU Linmin, LIN Yongsheng, LIN Xiaojie, LI Yongyu, WU Shaohua, YANG Chao. Cloning and Functional Analysis of the MbEGS Gene from Melaleuca bracteata [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(8): 1747-1760. |
| [12] | NIE Xinmiao, LUAN Heng, FENG Gaili, WANG Chao, LI Yan, WEI Min. Effects of Silicon Nutrition and Grafting Rootstocks on Chilling Tolerance of Cucumber Seedlings [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(8): 1795-1804. |
| [13] | ZHENG Xiaodong, XI Xiangli, LI Yuqi, SUN Zhijuan, MA Changqing, HAN Mingsan, LI Shaoxuan, TIAN Yike, WANG Caihong. Effects and Regulating Mechanism of Exogenous Brassinosteroids on the Growth of Malus hupehensis Under Saline-alkali Stress [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(7): 1401-1414. |
| [14] | ZHENG Lin, WANG Shuai, LIU Yunuo, DU Meixia, PENG Aihong, HE Yongrui, CHEN Shanchun, ZOU Xiuping. Gene Cloning and Expression Analysis of NAC Gene in Citrus in Response to Huanglongbing [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(7): 1441-1457. |
| [15] | CHEN Sijie, ZHANG Tao, JIA Baosen, DU Juan, YAN Siyuan, GU Peiwen. Study on Antibacterial Activity of Dark Septate Endophytes Against Fusarium oxysporum in Chinese Wolfberry [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(7): 1519-1531. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2012 Acta Horticulturae Sinica 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
Tel: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
Support by: Beijing Magtech Co.Ltd