
Acta Horticulturae Sinica ›› 2021, Vol. 48 ›› Issue (6): 1079-1093.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2020-0902
• Research Papers • Previous Articles Next Articles
MA Junjie1, SONG Lina1, LI Le1, MA Xiaochun1, JIN Lei1, XU Weirong2,3,4,*( )
)
Received:2021-03-16
Revised:2021-05-11
Online:2021-06-25
Published:2021-07-07
Contact:
XU Weirong
E-mail:xuwr@nxu.edu.cn
CLC Number:
MA Junjie, SONG Lina, LI Le, MA Xiaochun, JIN Lei, XU Weirong. VaCBL6 from Vitis amurensis Involved in Abiotic Stress Response and ABA-mediated Pathway[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2021, 48(6): 1079-1093.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.ahs.ac.cn/EN/10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2020-0902
| 引物 Primer | 引物序列(5′-3′) Primer sequence |
|---|---|
| qPCR-CBL6-F | TGCTGCGACTTCCACAAA |
| qPCR-CBL6-R | CTCATACAGTGCCTCCACTTC |
| RT-VvActin-F | CTATCCTTCGTCTTGACCTTGCTG |
| RT-VvActin-R | AGTGGTGAACATGTAACCCCTCTC |
| Semi-CBL6-F | GGAAGAGCTTCAATTGGCGT |
| Semi-CBL6-R | ACTGTGGTGATGTCCTTCAAAT |
| AtActin2-RT-F | TGAGCAAAGAAATCACAGCACT |
| AtActin2-RT-R | CCTGGACCTGCCTCATCATAC |
| VaCBL6-ORF-F | ATGAGTTCTTGGCAGGGAACGGCG |
| VaCBL6-ORF-R | TCATTCTTCAACCTCAGTATTGAAAACAAAGC |
| 221-VaCBL6-F | GAGAGAACACGGGGGACTCTAGAATGAGTTCTTGGCAGGGAACGGCG |
| 221-VaCBL6-R | TTACCCATGGTACCCCGCTCGAGTTCTTCAACCTCAGTATTGAAAACAAAGC |
| BD-CBL6-F | atggccatggaggccgaattcATGAGTTCTTGGCAGGGAACG |
| BD-CBL6-R | ccgctgcaggtcgacggatccTCATTCTTCAACCTCAGTATTGAAAAC |
| Entry-VaCBL6-F | AAAAAAgCAggCTTTgACTTTATgAgTTCTTggCAgggAACg |
| Entry-VaCBL6-R | AAAgCTgggTCTAgAgACTTTCCTTCTTCAACCTCAgTATTgA |
Table 1 Primers of vector generation and the expression of VaCBL6
| 引物 Primer | 引物序列(5′-3′) Primer sequence |
|---|---|
| qPCR-CBL6-F | TGCTGCGACTTCCACAAA |
| qPCR-CBL6-R | CTCATACAGTGCCTCCACTTC |
| RT-VvActin-F | CTATCCTTCGTCTTGACCTTGCTG |
| RT-VvActin-R | AGTGGTGAACATGTAACCCCTCTC |
| Semi-CBL6-F | GGAAGAGCTTCAATTGGCGT |
| Semi-CBL6-R | ACTGTGGTGATGTCCTTCAAAT |
| AtActin2-RT-F | TGAGCAAAGAAATCACAGCACT |
| AtActin2-RT-R | CCTGGACCTGCCTCATCATAC |
| VaCBL6-ORF-F | ATGAGTTCTTGGCAGGGAACGGCG |
| VaCBL6-ORF-R | TCATTCTTCAACCTCAGTATTGAAAACAAAGC |
| 221-VaCBL6-F | GAGAGAACACGGGGGACTCTAGAATGAGTTCTTGGCAGGGAACGGCG |
| 221-VaCBL6-R | TTACCCATGGTACCCCGCTCGAGTTCTTCAACCTCAGTATTGAAAACAAAGC |
| BD-CBL6-F | atggccatggaggccgaattcATGAGTTCTTGGCAGGGAACG |
| BD-CBL6-R | ccgctgcaggtcgacggatccTCATTCTTCAACCTCAGTATTGAAAAC |
| Entry-VaCBL6-F | AAAAAAgCAggCTTTgACTTTATgAgTTCTTggCAgggAACg |
| Entry-VaCBL6-R | AAAgCTgggTCTAgAgACTTTCCTTCTTCAACCTCAgTATTgA |
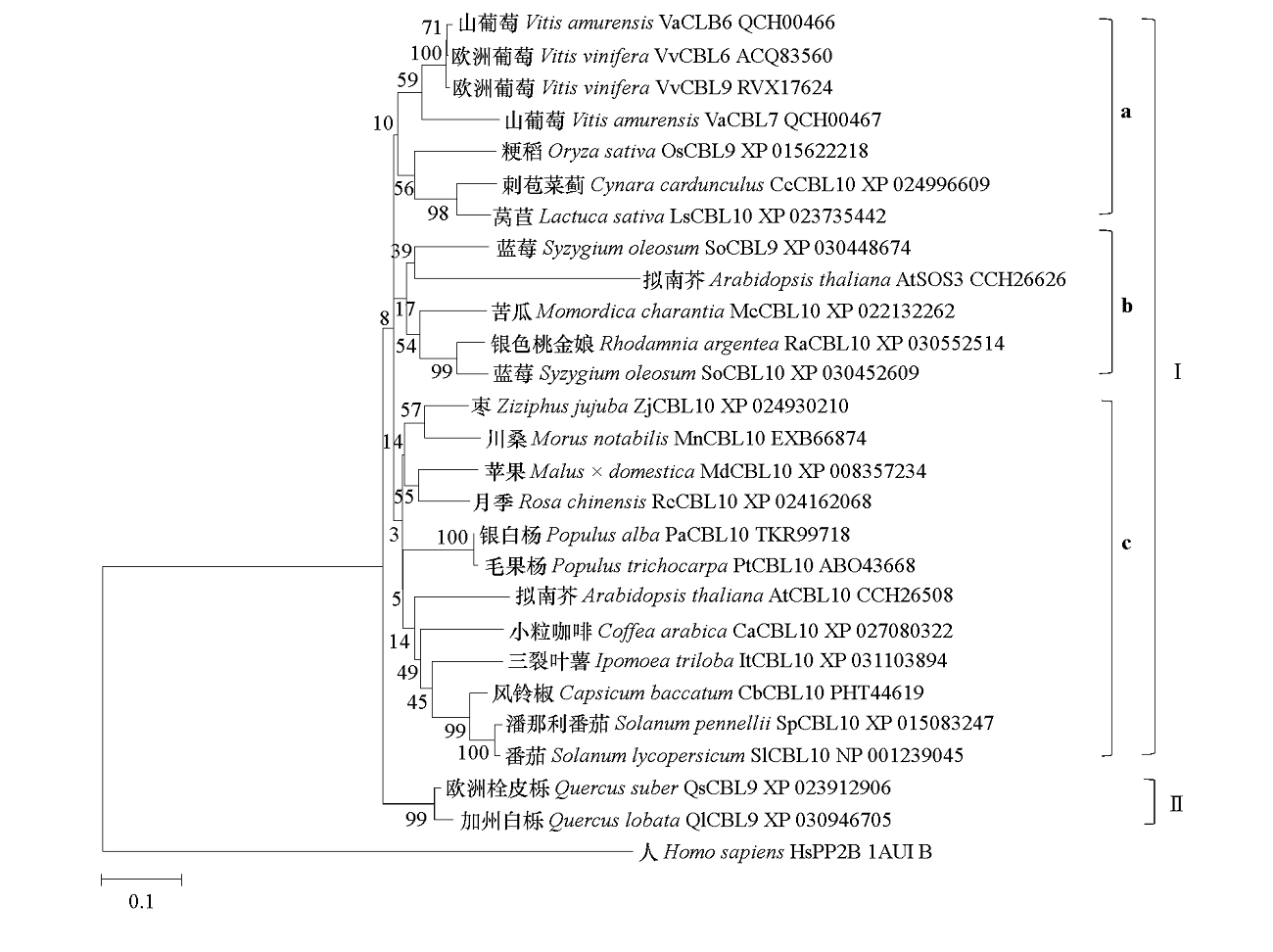
Fig. 2 Phylogenetic relationships of Vitis amurensis VaCBL6 with CBLs from other plant species Protein sequences were aligned to construct a phylogenetic tree using the Neighbor-Joining(NJ)method by MEGA 7.0 software. The percentage of trees with related clusters were displayed next to the branches,and the phylogenetic tree was drawn proportionally with branch lengths measured in the number of substitutions per site. Bootstrap value was 1 000.
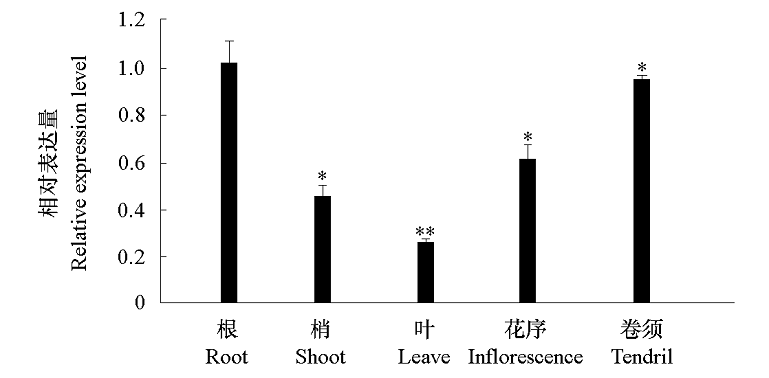
Fig. 4 Expression pattern of VaCBL6 in various tissues of Vitis amurensis *,** indicated significant differences compared with the expression level of root(expression level is 1)(* α = 0.05,** α = 0.01).
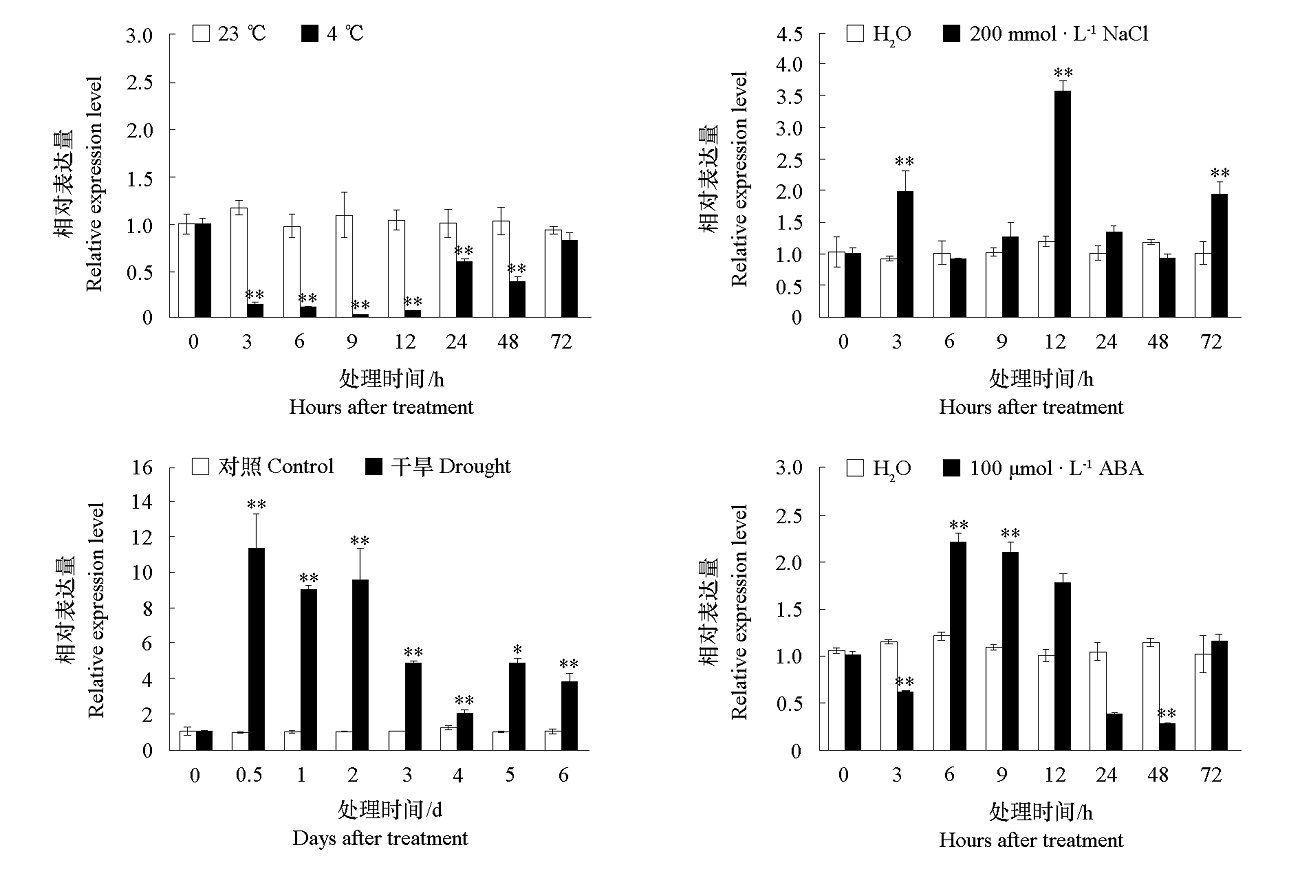
Fig. 5 Expression pattern of VaCBL6 in grape leaves under abiotic stress and ABA treatment * and ** indicated significant differences compared with control groups(* α = 0.05,** α = 0.01).
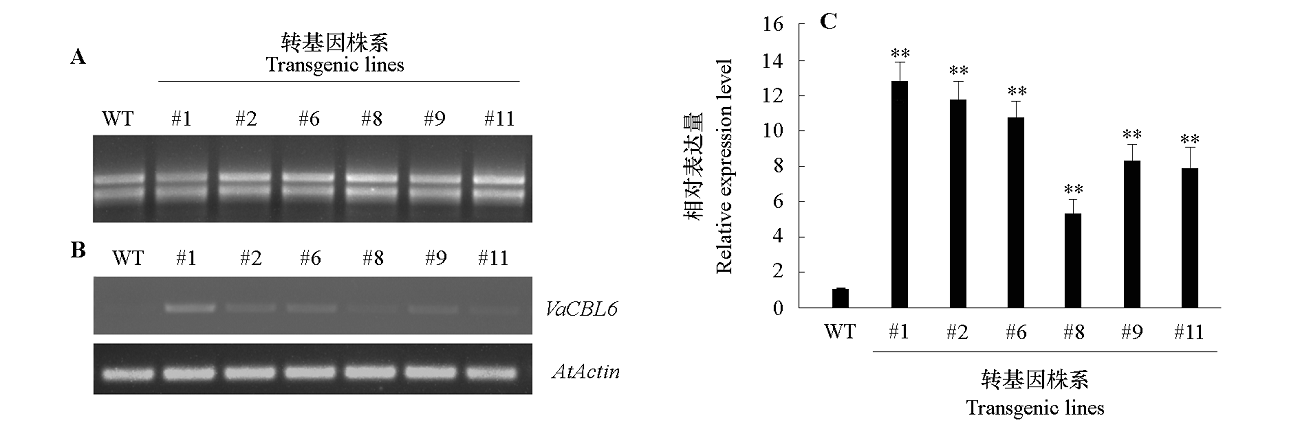
Fig. 8 Identification of VaCBL6-overexpressing lines in Arabidopsis thaliana A:Agarose gel electrophoresis of RNA;B:Expression of VaCBL6 analyzed by semi quantitative RT-PCR;C:Expression level of VaCBL6 analyzed by qRT-PCR. WT:Wild type. ** α = 0.01.

Fig. 9 Phenotypes of Arabidopsis thaliana overexpressing VaCBL6 lines(#1,#2 and #6)on 1/2 MS medium supplemented with different concentrations of NaCl WT:Wild type;#1,#2 and #6:35S::VaCBL6 transgenic lines. The same below.
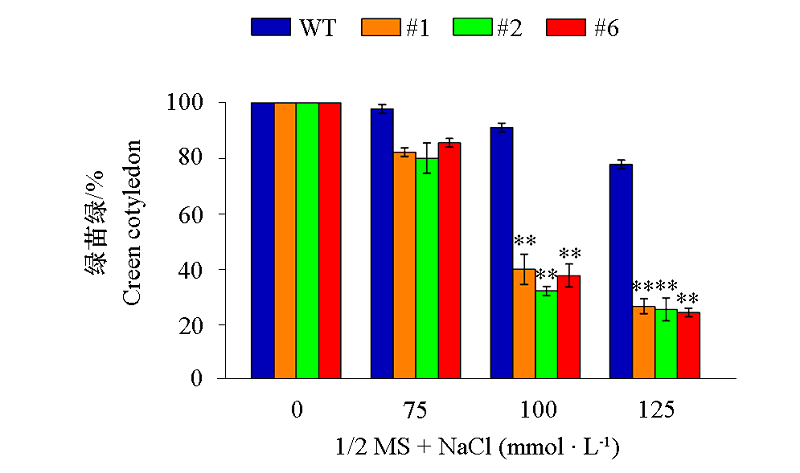
Fig. 11 Germination rates of green cotyledon of seedlings of Arabidopsis thaliana overexpressing VaCBL6 lines (#1,#2 and #6)grown for 10 days under different concentrations of NaCl

Fig. 12 Phenotypes of Arabidopsis thaliana overexpressing VaCBL6 lines(#1,#2 and #6) on 1/2 MS medium supplemented with different concentrations of ABA
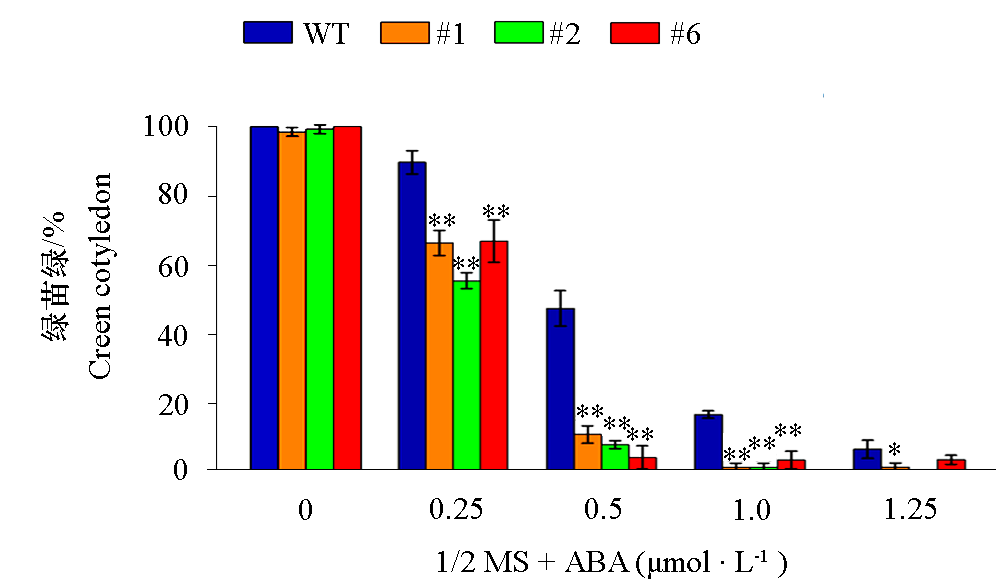
Fig. 14 Germination rates of green cotyledon of seedlings of Arabidopsis thaliana overexpressing VaCBL6 lines (#1,#2 and #6)grown for 10 d under different concentrations of ABA
| [1] |
Albrecht V, Ritz O, Linder S, Harter K, Kudla J. 2001. The NAF domain defines a novel protein-protein interaction module conserved in Ca2+ regulated kinases. The EMBO Journal, 20 (5):1051-1063.
doi: 10.1093/emboj/20.5.1051 URL |
| [2] |
Batistič O, Waadt R, Steinhorst L, Held K, Kudla J. 2010. CBL mediated targeting of CIPKs facilitates the decoding of calcium signals emanating from distinct cellular stores. The Plant Journal, 61 (2):211-222.
doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2009.04045.x URL |
| [3] | Batistič O, Kudla J. 2012. Analysis of calcium signaling pathways in plants. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta(BBA)-General Subjects, 1820 (8):1283-1293. |
| [4] |
Carmona M J, Cubas P, Calonje M, Martinez-Zapater J M. 2007. Flowering transition in grapevine(Vitis vinifera L.). Canadian Journal of Botany, 85 (8):701-711.
doi: 10.1139/B07-059 URL |
| [5] | Chen Sha-sha, Lan Hai-yan. 2011. Signal transduction pathways in response to salt stress in plants. Plant Physiology Journal, 47 (2):119-128. (in Chinese) |
| 陈莎莎, 兰海燕. 2011. 植物对盐胁迫响应的信号转导途径. 植物生理学报, 47 (2):119-128. | |
| [6] |
Chen X, Gu Z, Xin D, Hao L, Liu C, Huang J, Ma B, Zhang H. 2011. Identification and characterization of putative CIPK genes in maize. Journal of Genetics and Genomics, 38 (2):77-87.
doi: 10.1016/j.jcg.2011.01.005 URL |
| [7] |
Clough S J, Bent A F. 1998. Floral dip:a simplified method for Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of Arabidopsis thaliana. The Plant Journal, 16 (6):735-743.
doi: 10.1046/j.1365-313x.1998.00343.x URL |
| [8] | Dong Lian-hong, Shi Su-juan, Nuruzzaman Manik S. 2015. Advances in research of CBL family in plant. Journal of Nuclear Agricultural Sciences, 29 (5):892-898. (in Chinese) |
| 董连红, 史素娟, Nuruzzaman Manik S. 2015. 植物CBL基因家族的研究进展. 核农学报, 29 (5):892-898. | |
| [9] |
Gu Z, Ma B, Jiang Y, Chen Z, Su X, Zhang H. 2008. Expression analysis of the calcineurin B-like gene family in rice(Oryza sativa L.)under environmental stresses. Gene, 415 (1-2):1-12.
doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2008.02.011 URL |
| [10] |
Hepler P K. 2005. Calcium:a central regulator of plant growth and development. The Plant Cell, 17 (8):2142-2155.
doi: 10.1105/tpc.105.032508 URL |
| [11] |
Ishitani M, Liu J, Halfter U, Kim C S, Shi W, Zhu J K. 2000. SOS 3 function in plant salt tolerance requires N-myristoylation and calcium binding. The Plant Cell, 12:1667-1677.
doi: 10.1105/tpc.12.9.1667 URL |
| [12] |
Kolukisaoglu U, Weinl S, Blazevic D, Batistič O, Kudla J. 2004. Calcium sensors and their interacting protein kinases:genomics of the Arabidopsis and rice CBL-CIPK signaling networks. Plant Physiology, 134 (1):43-58.
doi: 10.1104/pp.103.033068 URL |
| [13] | Ling Q, Zeng Q, Wu J, Hu F, Li Q, Qi Y. 2019. Expression analysis of CBL1 and CBL6 genes in sugarcane under abiotic stress. Molecular Plant Breeding, 10 (1):1-10. |
| [14] |
Liu J, Zhu J K. 1998. A calcium sensor homolog required for plant salt tolerance. Science, 280:1943-1945.
doi: 10.1126/science.280.5371.1943 URL |
| [15] |
Liu P, Duan Y, Liu C, Xue Q, Guo J, Qi T, Kang Z, Guo J. 2018. The calcium sensor TaCBL4 and its interacting protein TaCIPK 5 are required for wheat resistance to stripe rust fungus. Journal of Experimental Botany, 69 (21):4443-4457.
doi: 10.1093/jxb/ery227 URL |
| [16] | Mullins M G, Bouquet A, Williams L E. 1992. Biology of the grapevine. UK: Cambridge University Press. |
| [17] | Qiu Q S, Guo Y, Dietrich M A, Schumaker K S, Zhu J K. 2002. Regulation of SOS1,a plasma membrane Na+/H+ exchanger in Arabidopsis thaliana,by SOS2 and SOS3. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 99 (12):8436-8441. |
| [18] |
Quan R, Lin H, Mendoza I, Zhang Y, Cao W, Yang Y, Shang M, Chen S, Pardo J M, Guo Y. 2007. SCABP8/CBL10,a putative calcium sensor,interacts with the protein kinase SOS 2 to protect Arabidopsis shoots from salt stress. The Plant Cell, 19 (4):1415-1431.
doi: 10.1105/tpc.106.042291 URL |
| [19] |
Sánchez-Barrena M J, Martínez-Ripoll M, Zhu J K, Albert A. 2005. The structure of the Arabidopsis thaliana SOS3:molecular mechanism of sensing calcium for salt stress response. Journal of Molecular Biology, 345 (5):1253-1264.
doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2004.11.025 URL |
| [20] |
Tang R J, Liu H, Yang Y, Yang L, Gao X S, Garcia V J, Luan S, Zhang H X. 2012. Tonoplast calcium sensors CBL2 and CBL 3 control plant growth and ion homeostasis through regulating V-ATPase activity in Arabidopsis. Cell Research, 22 (12):1650-1665.
doi: 10.1038/cr.2012.161 URL |
| [21] | Tang R J, Yang Y, Yang L, Liu H, Wang C T, Yu M M, Gao X S, Zhang H X. 2014. Poplar calcineurin B-like proteins PtCBL10A and PtCBL10B regulate shoot salt tolerance through interaction with PtSOS 2 in the vacuolar membrane. Plant Cell & Environment, 37 (3):573-588. |
| [22] |
Weinl S, Kudla J. 2009. The CBL-CIPK Ca 2+-decoding signaling network: function and perspectives. New Phytologist, 184 (3):517-528.
doi: 10.1111/nph.2009.184.issue-3 URL |
| [23] |
Wu F H, Shen S C, Lee L-Y, Lee S H, Chan M T, Lin C S. 2009. Tape- Arabidopsis Sandwich-a simpler Arabidopsis protoplast isolation method. Plant Methods, 5:16.
doi: 10.1186/1746-4811-5-16 URL |
| [24] |
Xu W, Shen W, Ma J, Ya R, Zheng Q, Wu N, Yu Q, Yao W, Zhang N, Zhang J. 2020. Role of an Amur grape CBL-interacting protein kinase VaCIPK02 in drought tolerance by modulating ABA signaling and ROS production. Environmental and Experimental Botany, 172:103999.
doi: 10.1016/j.envexpbot.2020.103999 URL |
| [25] |
Yu Y, Xia X, Yin W, Zhang H. 2007. Comparative genomic analysis of CIPK gene family in Arabidopsis and Populus. Plant Growth Regulation, 52 (2):101-110.
doi: 10.1007/s10725-007-9165-3 URL |
| [26] | Yu Yi-he, Li Xiu-zhen, Guo Da-long, Yang Ying-jun, Li Gui-rong, Li Xue-qiang, Zhang Guo-hai. 2016. Isolation and expression analysis of calcineurin B-like protein VvCBL4 in grapevines. Journal of Fruit Science, 33 (4):385-392. (in Chinese) |
| 余义和, 李秀珍, 郭大龙, 杨英军, 李桂荣, 李学强, 张国海. 2016. 葡萄类钙调磷酸酶B亚基蛋白基因 VvCBL4的克隆与表达分析. 果树学报, 33 (4):385-392. | |
| [27] |
Zhang H, Yin W, Xia X. 2008. Calcineurin B-Like family in Populus:comparative genome analysis and expression pattern under cold,drought and salt stress treatment. Plant Growth Regulation, 56 (2):129-140.
doi: 10.1007/s10725-008-9293-4 URL |
| [1] | XU Xiaoping, CAO Qingying, CAI Roudi, GUAN Qingxu, ZHANG Zihao, CHEN Yukun, XU HAN, LIN Yuling, LAI Zhongxiong. Gene Cloning and Expression Analysis of miR408 and Its Target DlLAC12 in Globular Embryo Development and Abiotic Stress in Dimocarpus longan [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(9): 1866-1882. |
| [2] | WANG Sha, ZHANG Xinhui, ZHAO Yujie, LI Bianbian, ZHAO Xueqing, SHEN Yu, DONG Jianmei, YUAN Zhaohe. Cloning and Functional Analysis of PgMYB111 Related to Anthocyanin Synthesis in Pomegranate [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(9): 1883-1894. |
| [3] | JIA Xin, ZENG Zhen, CHEN Yue, FENG Hui, LÜ Yingmin, ZHAO Shiwei. Cloning and Expression Analysis of RcDREB2A Gene in Rosa chinensis‘Old Blush’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(9): 1945-1956. |
| [4] | LIN Yuanmi, ZHU Wenjiao, CHEN Min, XUE Chunmei, JIN Fangyu, ZHU Yuping, JIANG Xinyue, YE Lingfeng, NI Shunanling, YANG Qing. Mir396b Negatively Regulates Eggplant Defense Response to Verticillium Wilt [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(8): 1713-1722. |
| [5] | QIU Ziwen, LIU Linmin, LIN Yongsheng, LIN Xiaojie, LI Yongyu, WU Shaohua, YANG Chao. Cloning and Functional Analysis of the MbEGS Gene from Melaleuca bracteata [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(8): 1747-1760. |
| [6] | ZHENG Lin, WANG Shuai, LIU Yunuo, DU Meixia, PENG Aihong, HE Yongrui, CHEN Shanchun, ZOU Xiuping. Gene Cloning and Expression Analysis of NAC Gene in Citrus in Response to Huanglongbing [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(7): 1441-1457. |
| [7] | MA Weifeng, LI Yanmei, MA Zonghuan, CHEN Baihong, MAO Juan. Identification of Apple POD Gene Family and Functional Analysis of MdPOD15 Gene [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(6): 1181-1199. |
| [8] | LIU Yaoyao, WU Yanyan, Shi Yan, MAO Tianyu, BAO Manzhu, ZHANG Junwei, ZHANG Jie. Preliminary Study on the Relationship Between Promoter Sequence Difference of PmTAC1 and Weeping Trait of Prunus mume [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(6): 1327-1338. |
| [9] | ZHOU Zhiming, YANG Jiabao, ZHANG Cheng, ZENG Linglu, MENG Wanqiu, SUN Li. Genome-wide Identification and Expression Analyses of Long-chain Acyl-CoA Synthetases Under Abiotic Stresses in Helianthus annuus [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(2): 352-364. |
| [10] | SONG Mengfei, ZHA Gaohui, CHEN Jinfeng, LOU Qunfeng. Research Progress on Molecular Basis of Plant Architecture Related Traits in Cucumber [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(12): 2683-2702. |
| [11] | XIE Siyi, ZHOU Chengzhe, ZHU Chen, ZHAN Dongmei, CHEN Lan, WU Zuchun, LAI Zhongxiong, GUO Yuqiong. Genome-wide Identification and Expression Analysis of CsTIFY Transcription Factor Family Under Abiotic Stress and Hormone Treatments in Camellia sinensis [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(1): 100-116. |
| [12] | LI Maofu, YANG Yuan, WANG Hua, FAN Youwei, SUN Pei, JIN Wanmei. Identification and Analysis of Self Incompatibility S-RNase in Rose [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(1): 157-165. |
| [13] | LIANG Zhile, WANG Kuanhong, YANG Jing, ZHU Biao, ZHU Zhujun. The Importance of Glucosinolates on Plant Response to Abiotic Stress in Brassicaceae Family [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(1): 200-220. |
| [14] | BIAN Shicun, LU Yani, XU Wujun, CHEN Boqing, WANG Guanglong, XIONG Aisheng. Garlic Circadian Clock Genes AsRVE1 and AsRVE2 and Their Expression Analysis Under Osmotic Stress [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2021, 48(9): 1706-1716. |
| [15] | YANG Tianchen, CHEN Xiaotong, LÜ Ke, ZHANG Di. Expression Pattern and Regulation Mechanism of ApSK3 Dehydrin (Agapanthus praecox)Response to Abiotic Stress and Hormone Signals [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2021, 48(8): 1565-1578. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2012 Acta Horticulturae Sinica 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
Tel: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
Support by: Beijing Magtech Co.Ltd