
Acta Horticulturae Sinica ›› 2021, Vol. 48 ›› Issue (3): 566-576.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2020-0483
• Research Papers • Previous Articles Next Articles
LI Zheng, LIU Bing, ZHOU Hong, WANG Xiuyun( ), XIA Yiping(
), XIA Yiping( )
)
Received:2020-09-04
Online:2021-03-25
Published:2021-04-02
Contact:
WANG Xiuyun,XIA Yiping
E-mail:wxy.550@163.com;ypxia@zju.edu.cn
CLC Number:
LI Zheng, LIU Bing, ZHOU Hong, WANG Xiuyun, XIA Yiping. Isolation and Function Analysis of the Promoter of a Thermal Inducible Gene RCA1 in Rhododendron hainanense[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2021, 48(3): 566-576.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.ahs.ac.cn/EN/10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2020-0483
| 名称 Name | 序列 Sequence(5′-3′) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| prRCA1-F prRCA1-R | ACTCGGCACAGCTACTACC CAAAGGTGGAAACGGCAG | ||||
| RCA1-F RCA1-R 18S-F 18S-R | TGCTGGTTCAAGAGCAGGAG GTTGAGCTGCTTTGCCATAGA CGCATTCCCCACTGTATTAGAC CGTAACAAGGTTTCCGTAGGTG | ||||
| prRCA1-F-Hind Ⅲ prRCA1-R-Nco I prRCA1-LUC-F prRCA1-LUC-R | ACCTGCAGGCATGCAAGCTTCTACTACCAAGCACCTCCGC TTACCCTCAGATCTACCATGGAGAAATCAAGGGTCTGTTTGGGA GCTTGATATCGAATTCCTGCAGCTACTACCAAGCACCTCCGC GGATCCCCCGGGCTGCAGAGAAATCAAGGGTCTGTTTGGGA | ||||
| P3301-F-Hind Ⅲ P3301-R-Nco Ⅰ pGreen-LUC-F pGreen-LUC-R | ACCTGCAGGCATGCAAGCTT TTACCCTCAGATCTACCATGG GGCGATTAAGTTGGGTAACGC GGTTCCATCTTCCAGCGGATA | ||||
| P3301-F-Hind Ⅲ GUS-R | ACCTGCAGGCATGCAAGCTT CACGGGTTGGGGTTTCTACA |
Table 1 Primers used in this study
| 名称 Name | 序列 Sequence(5′-3′) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| prRCA1-F prRCA1-R | ACTCGGCACAGCTACTACC CAAAGGTGGAAACGGCAG | ||||
| RCA1-F RCA1-R 18S-F 18S-R | TGCTGGTTCAAGAGCAGGAG GTTGAGCTGCTTTGCCATAGA CGCATTCCCCACTGTATTAGAC CGTAACAAGGTTTCCGTAGGTG | ||||
| prRCA1-F-Hind Ⅲ prRCA1-R-Nco I prRCA1-LUC-F prRCA1-LUC-R | ACCTGCAGGCATGCAAGCTTCTACTACCAAGCACCTCCGC TTACCCTCAGATCTACCATGGAGAAATCAAGGGTCTGTTTGGGA GCTTGATATCGAATTCCTGCAGCTACTACCAAGCACCTCCGC GGATCCCCCGGGCTGCAGAGAAATCAAGGGTCTGTTTGGGA | ||||
| P3301-F-Hind Ⅲ P3301-R-Nco Ⅰ pGreen-LUC-F pGreen-LUC-R | ACCTGCAGGCATGCAAGCTT TTACCCTCAGATCTACCATGG GGCGATTAAGTTGGGTAACGC GGTTCCATCTTCCAGCGGATA | ||||
| P3301-F-Hind Ⅲ GUS-R | ACCTGCAGGCATGCAAGCTT CACGGGTTGGGGTTTCTACA |
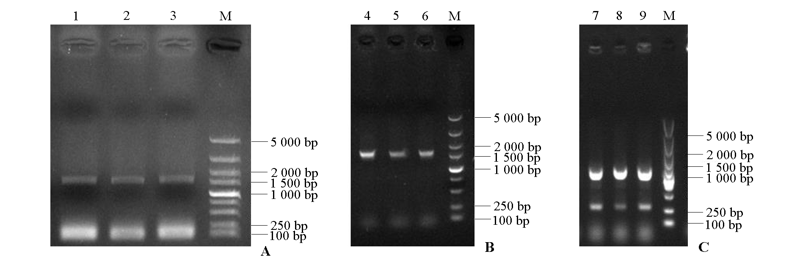
Fig. 4 PCR amplification of RhRCA1 promotor(A)and PCR detection of recombinant plasmids(B,C) 1 -3:fragments of promoter of RhRCA1;4-6:prRCA1::GUS;7-9:prRCA1::LUC;M:DL5000 marker.
| 类型 Type | 调控元件 Regulated element | 基序 Motif sequence | 数量 Amount | 生物学功能 Biological function |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 非生物胁迫响应元件 Abiotic stress responsive element | ARE | AAACCA | 1 | 厌氧诱导必需的调控元件 cis-acting regulatory element essential for the anaerobic induction |
| TC-rich repeats | GTTTTCTTAC | 1 | 防御和胁迫响应元件cis-acting element involved in defense and stress responsiveness | |
| ABRE | ACGTG | 5 | 脱落酸响应元件cis-acting element involved in the abscisic acid responsiveness | |
| RGAANNTTC | GGGAGTTTC | 1 | HSF1的结合位点 HSF1 binding site | |
| CCAAT-box | CCAAT | 2 | 热激蛋白基因表达元件cis-element for heat shock protein gene expression | |
| 组织特异性相关元件 Tissue-specific element | CACTFTPPCA1 | CACT | 20 | 叶肉特异性表达元件cis-regulatory element for mesophyll-specific gene expression |
| TGACGTVMAMY | TGACGT | 2 | 子叶特异性表达元件cis-element for Expression in cotyledons of germinated seeds | |
| RBCSCONSENSUS | AATCAA | 1 | 光调节和叶特异性表达元件cis-element for light-regulated and leaf-specific expression | |
| 光响应元件 Light responsive element | Box 4 | ATTAAT | 4 | 参与部分光响应保守DNA组件 Part of a conserved DNA module involved in light responsiveness |
| G-box | CACGTC/ACACGTGGC/ TGACACGTGGCTCT | 5 | 参与光反应的元件 cis-acting regulatory element involved in light responsiveness | |
| AE-box | AGAAACTT | 1 | 部分光响应组件 Part of a module for light response | |
| 基础元件 Basal element | CAAT-box | CAAT/TGCCAAC | 28 | 启动子和增强子调控元件 Common cis-acting element in promoter and enhancer regions |
| TATA-box | TATA/TACAAAA | 11 | 转录起始位点 Transcription initiation site | |
| 其他 Others | TGACG-motif | TGACG | 5 | 参与茉莉酸甲酯诱导表达cis-acting regulatory element involved in the MeJA-responsiveness |
Table 2 Part of cis-acting elements in promoter of RhRCA1
| 类型 Type | 调控元件 Regulated element | 基序 Motif sequence | 数量 Amount | 生物学功能 Biological function |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 非生物胁迫响应元件 Abiotic stress responsive element | ARE | AAACCA | 1 | 厌氧诱导必需的调控元件 cis-acting regulatory element essential for the anaerobic induction |
| TC-rich repeats | GTTTTCTTAC | 1 | 防御和胁迫响应元件cis-acting element involved in defense and stress responsiveness | |
| ABRE | ACGTG | 5 | 脱落酸响应元件cis-acting element involved in the abscisic acid responsiveness | |
| RGAANNTTC | GGGAGTTTC | 1 | HSF1的结合位点 HSF1 binding site | |
| CCAAT-box | CCAAT | 2 | 热激蛋白基因表达元件cis-element for heat shock protein gene expression | |
| 组织特异性相关元件 Tissue-specific element | CACTFTPPCA1 | CACT | 20 | 叶肉特异性表达元件cis-regulatory element for mesophyll-specific gene expression |
| TGACGTVMAMY | TGACGT | 2 | 子叶特异性表达元件cis-element for Expression in cotyledons of germinated seeds | |
| RBCSCONSENSUS | AATCAA | 1 | 光调节和叶特异性表达元件cis-element for light-regulated and leaf-specific expression | |
| 光响应元件 Light responsive element | Box 4 | ATTAAT | 4 | 参与部分光响应保守DNA组件 Part of a conserved DNA module involved in light responsiveness |
| G-box | CACGTC/ACACGTGGC/ TGACACGTGGCTCT | 5 | 参与光反应的元件 cis-acting regulatory element involved in light responsiveness | |
| AE-box | AGAAACTT | 1 | 部分光响应组件 Part of a module for light response | |
| 基础元件 Basal element | CAAT-box | CAAT/TGCCAAC | 28 | 启动子和增强子调控元件 Common cis-acting element in promoter and enhancer regions |
| TATA-box | TATA/TACAAAA | 11 | 转录起始位点 Transcription initiation site | |
| 其他 Others | TGACG-motif | TGACG | 5 | 参与茉莉酸甲酯诱导表达cis-acting regulatory element involved in the MeJA-responsiveness |
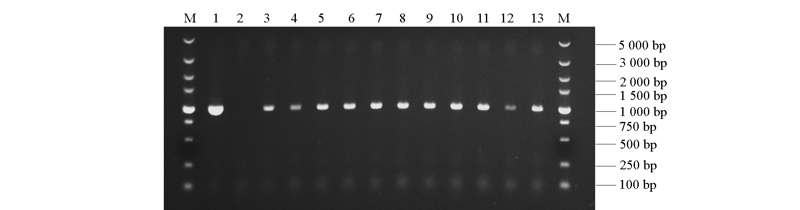
Fig. 6 PCR detection of transgenic Arabidopsis 1:prRCA1::GUS(positive control)plasmid;2:Non-transgenic plant(negative control);3-13:Transgenic plant;M:DL5000 marker.
| [1] |
Attaran E, Major I, Cruz J, Rosa B, Koo A, Chen J, Kramer D, He S, Howe G. 2014. Temporal dynamics of growth and photosynthesis suppression in response to jasmonate signaling. Plant Physiology, 165 (3):1302-1314.
pmid: 24820026 |
| [2] |
Berry J, Bjönkman O. 1980. Photosynthetic response and adaptation to temperature in higher plants. Annual Review of Plant Physiology, 31 (1):491-543.
doi: 10.1146/annurev.pp.31.060180.002423 URL |
| [3] |
Bota J, Medrano H, Flexas J. 2004. Is photosynthesis limited by decreased Rubisco activity and RuBP content under progressive water stress? New Phytologist, 162 (3):671-681.
doi: 10.1111/nph.2004.162.issue-3 URL |
| [4] |
Bracher A, Spencer M, Hartl F, Hayer-Hartl M. 2017. Biogenesis and metabolic maintenance of Rubisco. Annual Review of Plant Biology, 68 (1):29-60.
doi: 10.1146/annurev-arplant-043015-111633 URL |
| [5] |
Chao M N, Yin Z T, Hao D R, Zhang J Y, Song H N, Ning A L, Xu X M, Yu D Y. 2014. Variation in Rubisco activase(RCAβ)gene promoters and expression in soybean[Glycine max(L.)Merr.]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 65 (1):47-59.
doi: 10.1093/jxb/ert346 URL |
| [6] |
Chen C X, Hussain N, Wang Y R, Li M T, Liu T, Qin M Z, Ma N, Gao J P, Sun X M. 2020. An ethylene-inhibited NF-YC transcription factor RhNF-YC 9 regulates petal expansion in rose. Horticultural Plant Journal, 6 (6):419-427.
doi: 10.1016/j.hpj.2020.11.007 URL |
| [7] | Crafts-Brandner S J, Salvucci M E. 2000. Rubisco activase constrains the photosynthetic potential of leaves at high temperature and CO 2. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 97 (24):13430-13435. |
| [8] |
Demirevska-Kepova K, Holzer R, Simova-Stoilova L, Feller U. 2005. Heat stress effects on Ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase,Rubisco binding protein and Rubisco activase in wheat leaves. Biologia Plantarum, 49 (4):521-525.
doi: 10.1007/s10535-005-0045-2 URL |
| [9] | Fukayama H, Abe R, Uchida N. 2010. SDS-dependent proteases induced by ABA and its relation to Rubisco and Rubisco activase contents in rice leaves. Plant Physiology & Biochemistry, 48 (10):808-812. |
| [10] |
Haralampidis K, Milioni D, Rigas S, Hatzopoulos P. 2002. Combinatorial interaction of cis elements specifies the expression of the Arabidopsis AtHsp90-1 gene. Plant Physiology, 129 (3):1138-1149.
doi: 10.1104/pp.004044 URL |
| [11] | He Ya-fei, Li Xia, Xie Yin-feng. 2017. Advances in molecular mechanisms of Rubisco and Rubisco activase. Molecular Plant Breeding, 15 (8):3295-3301. (in Chinese) |
| 何亚飞, 李霞, 谢寅峰. 2017. Rubisco与Rubisco活化酶的分子机理研究进展. 分子植物育种, 15 (8):3295-3301. | |
| [12] |
Jefferson R A, Kavanagh T A, Bevan M W. 1987. GUS fusions:beta-glucuronidase as a sensitive and versaile gene fusion marker in higher plants. The EMBO Journal, 6 (13):3901-3907.
doi: 10.1002/embj.1987.6.issue-13 URL |
| [13] | Jensen R G. 2000. Activation of Rubisco regulates photosynthesis at high temperature and CO2. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 97 (24):12937-12939. |
| [14] |
Jiao Yu-ling, Sun L O, Wang Deng-xing. 2007. Light-regulated transcriptional networks in higher plants. Nature Reviews Genetics, 8 (3):217-230.
doi: 10.1038/nrg2049 URL |
| [15] |
Kurek I, Chang T K, Bertain S M, Madrigal A, Lu Liu, Lassner W M, Zhu Gen-hai. 2007. Enhanced thermostability of Arabidopsis Rubisco activase improves photosynthesis and growth rates under moderate heat stress. The Plant Cell, 19 (10):3230-3241.
doi: 10.1105/tpc.107.054171 URL |
| [16] | Liu Yu, Song Xi-qiang, Shi You-hai. 2018. Physiological responses comparison of Rhododendron hainanense and Rhododendron mucronatum(Blume) G. Don under high temperature stress. Molecular Plant Breeding, 16 (17):5827-5834. (in Chinese) |
| 刘宇, 宋希强, 史佑海. 2018. 高温胁迫下海南杜鹃和白花杜鹃的生理响应比较分析. 分子植物育种, 16 (17):5827-5834. | |
| [17] |
Liu Zong-rang, Taub C C, McClung C R. 1996. Identification of an Arabidopsis thaliana Ribulose-1,5-Bisphosphate Carboxylase Oxygenase Activase(RCA)minimal promoter regulated by light and the circadian clock. Plant Physiology, 112 (1):43-51.
doi: 10.1104/pp.112.1.43 URL |
| [18] | Makino A, Mae T, Ohira K. 1983. Purification and storage of Ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase from rice leaves. Plant and Cell Physiology, 24 (6):1169-1173. |
| [19] | Neuwald A F, Aravind L, Spouge J L, Koonin E. 1999. AAA+:a class of chaperone-like ATPases associated with the assembly,operation,and disassembly of protein complexes. Genome Research, 9 (1):27-43. |
| [20] |
Orozco B M, Orgen W L. 1993. Localization of light-inducible and tissue-specific regions of the spinach ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase oxygenase(Rubisco)activase promoter in transgenic tobacco plants. Plant Molecular Biology, 23 (6):1129-1138.
doi: 10.1007/BF00042347 URL |
| [21] |
Pelham H R. 1982. A regulatory upstream promoter element in the Drosophila hsp 70 heat-shock gene. Cell, 30 (2):517-528.
pmid: 6814763 |
| [22] |
Pernille K, Vollaard N B J, Gustafsson T, Gallagher I J, Sundberg C J, Tuomo R, Britton S L, Claude B, Koch L G, Timmons J A. 2010. A transcriptional map of the impact of endurance exercise training on skeletal muscle phenotype. Journal of Applied Physiology, 110 (1):46-59.
doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00634.2010 URL |
| [23] | Ponjavic J, Lenhard B, Kai C, Kawai J, Carninci P, Hayashizaki Y, Sandelin A. 2006. Transcriptional and structural impact of TATA-initiation site spacing in mammalian core promoters. Genome Biology, 7 (8):5-19. |
| [24] |
Portis A R. 2003. Rubisco activase-Rubisco's catalytic chaperone. Photosynthesis Research, 75 (1):11-27.
doi: 10.1023/A:1022458108678 URL |
| [25] |
Qu D, Song Y, Li W M, Pei X W, Wang Z X, Jia S R, Zhang Y Q. 2011. Isolation and characterization of the organ-specific and light-inducible promoter of the gene encoding Rubisco activase in potato(Solanum tuberosum). Genetics and Molecular Research, 10 (2):621-631.
doi: 10.4238/vol10-2gmr1088 pmid: 21491372 |
| [26] | Rieping M, Schöffl F. 1992. Synergistic effect of upstream sequences,CCAAT box elements,and HSE sequences for enhanced expression of chimaeric heat shock genes in transgenic tobacco. MGG Molecular & General Genetics, 231 (2):226-232. |
| [27] |
Salvucci M E. 2008. Association of Rubisco activase with chaperonin-60β:a possible mechanism for protecting photosynthesis during heat stress. Journal of Experimental Botany, 59 (7):1923-1933.
doi: 10.1093/jxb/erm343 pmid: 18353762 |
| [28] |
Scafaro A P, Haynes P A, Atwell B J. 2009. Physiological and molecular changes in Oryza meridionalis Ng.,a heat-tolerant species of wild rice. Journal of Experimental Botany, 61 (1):191-201.
doi: 10.1093/jxb/erp294 URL |
| [29] |
Shelton A M, Zhao J Z, Roush R T. 2002. Economic,ecological,food safety,and social consequences of the development of Bt transgenic plants. Annual Review of Entomology, 47:845-881.
doi: 10.1146/annurev.ento.47.091201.145309 URL |
| [30] | Shi You-hai, Li Shao-peng, Liang Wei-hong, Song Xi-qiang, Tan Jin-hong. 2010. Germplasm resourses of Rhododendron in Hainan. Chinese Journal of Tropical Crops, 31 (4):551-555. (in Chinese) |
| 史佑海, 李绍鹏, 梁伟红, 宋希强, 谭金红. 2010. 海南野生杜鹃花属植物种质资源调查研究. 热带作物学报, 31 (4):551-555. | |
| [31] |
Wang Xiu-yun, Li Zheng, Liu Bing, Zhou Hong, Elmongy M S, Xia Yi-ping. 2020. Combined proteome and transcriptome analysis of heat-primed azalea reveals new insights into plant heat acclimation memory. Frontiers in Plant Science, 11:1278. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2020.01278.
doi: 10.3389/fpls.2020.01278 URL |
| [32] |
Xu Dong-qing, Li Ji-gang, Gangappa S N, Chamari H, Lin Fang, Mats A X, Jiang Yan, Wang Deng-xing, Magnus H. 2014. Convergence of light and ABA signaling on the ABI5 promoter. PLoS Genetics, 10 (2):e1004197.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1004197 URL |
| [33] |
Yang Zhi-pan, Lu Qing-tao, Wen Xiao-gang, Chen Fan, Lu Cong-ming. 2012. Functional analysis of the rice rubisco activase promoter in transgenic Arabidopsis. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 418 (3):565-570.
doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2012.01.073 URL |
| [34] |
Zhao Ying, Yu Wen-gang, Hu Xiang-yu, Shi You-hai, Liu Yu, Zhong Yun-fang, Wang Peng, Deng Shu-ya, Niu Jun, Yu Xu-dong. 2018. Physiological and transcriptomic analysis revealed the involvement of crucial factors in heat stress response of Rhododendron hainanense. Gene, 660:109-119.
doi: S0378-1119(18)30320-2 pmid: 29604462 |
| [35] | Zou Cheng, Sun Ke-lian, Mackaluso J D, Seddon A E, Jin Rong, Thomashow M F, Shin-Han S. 2011. Cis-regulatory code of stress-responsive transcription in Arabidopsis thaliana. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 108 (36):14992-14997. |
| [1] | YU Tingting, LI Huan, NING Yuansheng, SONG Jianfei, PENG Lulin, JIA Junqi, ZHANG Weiwei, and YANG Hongqiang. Genome-wide Identification of GRAS Gene Family in Apple and Expression Analysis of Its Response to Auxin [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(2): 397-409. |
| [2] | YUAN Xin, XU Yunhe, ZHANG Yupei, SHAN Nan, CHEN Chuying, WAN Chunpeng, KAI Wenbin, ZHAI Xiawan, CHEN Jinyin, GAN Zengyu. Studies on AcAREB1 Regulating the Expression of AcGH3.1 During Postharvest Ripening of Kiwifruit [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(1): 53-64. |
| [3] | WANG Dan, WANG Mi, LIU Jun, ZHOU Xiaohui, LIU Songyu, YANG Yan, ZHUANG Yong. Cloning of U6 Promoters and Establishment of CRISPR/Cas9 Mediated Gene Editing System in Eggplant [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(4): 791-800. |
| [4] | XIANG Li, ZHAO Lei, WANG Mei, LÜ Yi, WANG Yanfang, SHEN Xiang, CHEN Xuesen, YIN Chengmiao, MAO Zhiquan. Cloning and Functional Analysis of MdWRKY74 in Apple [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(3): 482-492. |
| [5] | SONG Fang, LI Zixuan, WANG Ce, WANG Zhijing, HE Ligang, JIANG Yingchun, WU Liming, BAI Fuxi. Cloning and Function Analysis of Mycorrhizal Signaling Receptor Protein Lysin Motif Receptor-like Kinases 2 Gene(LYK2)in Citrus [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(2): 281-292. |
| [6] | SUN Wei, SUN Shiyu, CHEN Yiran, WANG Yuhan, ZHANG Yan, JU Zhigang, YI Yin. Cloning and Function Analysis of Chalcone Isomerase Gene RdCHI1 in Rhododendron delavayi [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(11): 2407-2418. |
| [7] | HUANG Renwei, REN Yinghong, QI Weiliang, ZENG Rui, LIU Xinyu, DENG Binyan. Cloning of Mulberry MaERF105-Like Gene and Its Expression Under Drought Stress [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(11): 2439-2448. |
| [8] | YANG Tianchen, CHEN Xiaotong, LÜ Ke, ZHANG Di. Expression Pattern and Regulation Mechanism of ApSK3 Dehydrin (Agapanthus praecox)Response to Abiotic Stress and Hormone Signals [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2021, 48(8): 1565-1578. |
| [9] | DENG Zeyi, SONG Xiang, HONG Yan, DAI Silan. Applications of Promoters in the Genetic Engineering of Ornamental Plants:A Review [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2021, 48(6): 1250-1264. |
| [10] | CAI Roudi, LI Xue, CHEN Yan, XU Xiaoping, CHEN Xiaohui, LAI Zhongxiong, LIN Yuling. Genome-wide Identification and Expression Analysis of DRB Gene Family in Dimocarpus longan [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2021, 48(5): 921-933. |
| [11] | XIE Dejin, ZHOU Chengcheng, YANG Ke, REN Ke, YANG Deming, CHEN Lingyan, RONG Jundong, ZHENG Yushan. Cloning and Analysis of MoDXS Gene and Its Promoter in Morinda officinalis [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2021, 48(3): 577-589. |
| [12] | LIU Bing, LI Mengyuan, ZHANG Na, SHANG Boxing, LIU Guotian, XU Yan. Cloning and Functional Analysis of the CDS and Promoter of VpPR4b Gene Response to Downy Mildew in Chinese Wild Grape [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2021, 48(2): 265-275. |
| [13] | WANG Pengjie,CAO Hongli,CHEN Dan,CHEN Di,CHEN Guixin,YNAG Jiangfan,and YE Naixing*. Cloning and Expression Analysis of Fatty Acid Desaturase Family Genes in Camellia sinensis [J]. ACTA HORTICULTURAE SINICA, 2020, 47(6): 1141-1152. |
| [14] | LIU Yong1,*,WANG Zeqiong1,2,*,GONG Linzhong1,**,WANG Furong1,WANG Huiliang1,AI Xiaoyan1,and HE Huaping1,**. Cloning and Functional Analysis of ERF Transcription Factor Gene PpERF1a in Peach [J]. ACTA HORTICULTURAE SINICA, 2020, 47(6): 1165-1171. |
| [15] | FENG Jing1,YANG Can1,LU Juanfang1,and XI Wanpeng1,2,*. Cloning and cis-acting Element Analysis of CCD1 and CCD4 Promoter in Apricot [J]. ACTA HORTICULTURAE SINICA, 2020, 47(5): 939-952. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2012 Acta Horticulturae Sinica 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
Tel: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
Support by: Beijing Magtech Co.Ltd