
Acta Horticulturae Sinica ›› 2021, Vol. 48 ›› Issue (2): 276-288.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2020-0282
• Research Papers • Previous Articles Next Articles
ZHANG Qingwen, QI Jingjing, XIE Yu, XIE Zhu, PENG Yun, LI Qiang, PENG Aihong, ZOU Xiuping, HE Yongrui, CHEN Shanchun*( ), YAO Lixiao*(
), YAO Lixiao*( )
)
Received:2020-06-24
Revised:2020-09-07
Online:2021-02-25
Published:2021-03-09
Contact:
CHEN Shanchun,YAO Lixiao
E-mail:chenshanchun@cric.cn;yaolixiao@cric.cn
CLC Number:
ZHANG Qingwen, QI Jingjing, XIE Yu, XIE Zhu, PENG Yun, LI Qiang, PENG Aihong, ZOU Xiuping, HE Yongrui, CHEN Shanchun, YAO Lixiao. Preliminary Analysis of CsCalS5 and Callose Deposition in Citrus sinensis Infected with Candidatus Liberibacter asiaticus[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2021, 48(2): 276-288.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.ahs.ac.cn/EN/10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2020-0282
| 引物名称 Primer name | 引物序列(5′-3′) Primer sequence |
|---|---|
| CsCalS5-1 | F:ATAGAGGCAAAAGATGTCACAGAGA;R:TTTTGCCGATCCATCTGTCAC |
| CsCalS5-2 | F:CGTGCTGACGCTGATTTCT;R:AATAACCTCTTTCTCTCGTTCTCC |
| CsCalS5-3 | F:GCTAGCAAGATACCCATAGCATT;R:CTTAAGGAATTCTTGAAGCAAATTC |
| CsCalS5-4 | F:GGAAACCTGAAAATCAAAACCA;R:TCACTCCTTACTTTTGGAAGACCT |
| CsCalS5P | F:CTCATGCTTTATGCCTTT;R:CTTTTGCCTCTATAAATATGAT |
| Actin | F:CATCCCTCAGCACCTTCC;R:CCAACCTTAGCACTTCTCC |
| qCsCalS5 | F:AACGTTCTGGTGATGCTCGT;R:AGCCTTCGCAAGAGCTGAAT |
| OI1/OI2C | F:GCGCGTATGCAATACGAGCGGCA;R:GCCTCGCGACTTCGCAACCCAT |
Table 1 The sequences of primers in this study
| 引物名称 Primer name | 引物序列(5′-3′) Primer sequence |
|---|---|
| CsCalS5-1 | F:ATAGAGGCAAAAGATGTCACAGAGA;R:TTTTGCCGATCCATCTGTCAC |
| CsCalS5-2 | F:CGTGCTGACGCTGATTTCT;R:AATAACCTCTTTCTCTCGTTCTCC |
| CsCalS5-3 | F:GCTAGCAAGATACCCATAGCATT;R:CTTAAGGAATTCTTGAAGCAAATTC |
| CsCalS5-4 | F:GGAAACCTGAAAATCAAAACCA;R:TCACTCCTTACTTTTGGAAGACCT |
| CsCalS5P | F:CTCATGCTTTATGCCTTT;R:CTTTTGCCTCTATAAATATGAT |
| Actin | F:CATCCCTCAGCACCTTCC;R:CCAACCTTAGCACTTCTCC |
| qCsCalS5 | F:AACGTTCTGGTGATGCTCGT;R:AGCCTTCGCAAGAGCTGAAT |
| OI1/OI2C | F:GCGCGTATGCAATACGAGCGGCA;R:GCCTCGCGACTTCGCAACCCAT |
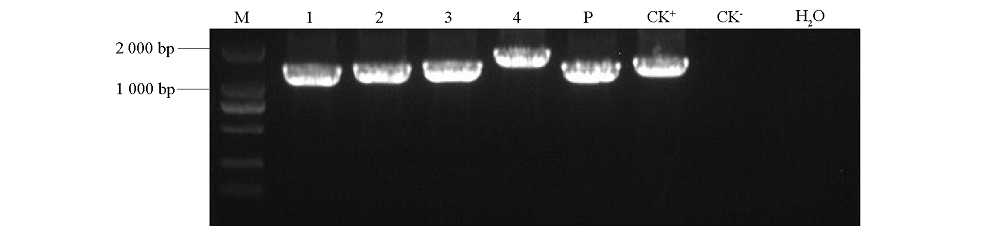
Fig. 1 PCR amplifications of four fragments and promoter of CsCalS5 M:Marker;1-4:PCR product of CsCalS5-1,2,3,4;5P:Promoter sequence;CK+:Positive control;CK-:Negative control.
| 元件名称 Element name | 序列 Sequence | 数量 Number | 功能 Function | 位置 Location |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GT1 box | GAAAAA | 2 | 病原菌和盐响应 Pathogen or salt-induced responsiveness | -264(+)/-976(-) |
| dof box | AAAG | 23 | 病原菌响应Pathogen responsiveness | -1281/-1178/-1097/-974/-927/ -838/-260/-161/-148/-81/-7(+)-1486/-1340/-1264/-1060/-869/-707/-656/-610/-545/-479/-207/-85(-) |
| W box | TGACT | 2 | 病原菌和损伤响应 Pathogen and wound responsiveness | -474(+)/-582(+) |
| GARE-motif | TCTGTTG | 2 | 赤霉素响应元件Gibberellin-responsive element | -281(+) |
| CCTTTT | -1490(+) | |||
| TCA-element | CCATCTTTTT | 1 | 水杨酸响应元件Salicylic acid responsiveness | -1067(+) |
| ABRE | ACGTG | 1 | 脱落酸响应元件Abscisic acid responsiveness | -814(+) |
| WUN-motif | AAATTACTA | 1 | 损伤响应元件Wound responsiveness | -1369(-) |
| MYC | CATTTG | 2 | 干旱和冻害响应元件 Drought and freeze responsiveness | -1473(+)/-1400(-) |
| MBS | CAACTG | 1 | 参与干旱诱导Involved in drought-inducibility | -1259(-) |
| ARE | AAACCA | 2 | 厌氧诱导所需Essential for the anaerobic induction | -1255(+)/-456(-) |
| MBSI | TTTTTACGGTTA | 1 | 参与类黄酮合成基因的调控 Involved in flavonoid biosynthetic genes regulation | -131(+) |
| RY-element | CATGCATG | 1 | 参与种子特异性调控 Involved in seed-specific regulation | -696(-) |
| GATA-motif | AAGATAAGATT | 1 | 光响应元件Light responsiveness | -1400(-) |
| GT1-motif | GGTTAA | 1 | 光响应元件Light responsiveness | -1336(-) |
| chs-CMA2a | TCACTTGA | 1 | 光响应元件Light responsiveness | -1268(-) |
| Box 4 | ATTAAT | 1 | 光响应元件Light responsiveness | -1293(+) |
| LAMP-element | CTTTATCA | 1 | 光响应元件Light responsiveness | -1123(+) |
| G-box | TACGTG | 2 | 光响应元件Light responsiveness | -810(+) |
| GGTTAAT | -194(+) |
Table 2 cis-Acting elements of CsCalS5 promoter
| 元件名称 Element name | 序列 Sequence | 数量 Number | 功能 Function | 位置 Location |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GT1 box | GAAAAA | 2 | 病原菌和盐响应 Pathogen or salt-induced responsiveness | -264(+)/-976(-) |
| dof box | AAAG | 23 | 病原菌响应Pathogen responsiveness | -1281/-1178/-1097/-974/-927/ -838/-260/-161/-148/-81/-7(+)-1486/-1340/-1264/-1060/-869/-707/-656/-610/-545/-479/-207/-85(-) |
| W box | TGACT | 2 | 病原菌和损伤响应 Pathogen and wound responsiveness | -474(+)/-582(+) |
| GARE-motif | TCTGTTG | 2 | 赤霉素响应元件Gibberellin-responsive element | -281(+) |
| CCTTTT | -1490(+) | |||
| TCA-element | CCATCTTTTT | 1 | 水杨酸响应元件Salicylic acid responsiveness | -1067(+) |
| ABRE | ACGTG | 1 | 脱落酸响应元件Abscisic acid responsiveness | -814(+) |
| WUN-motif | AAATTACTA | 1 | 损伤响应元件Wound responsiveness | -1369(-) |
| MYC | CATTTG | 2 | 干旱和冻害响应元件 Drought and freeze responsiveness | -1473(+)/-1400(-) |
| MBS | CAACTG | 1 | 参与干旱诱导Involved in drought-inducibility | -1259(-) |
| ARE | AAACCA | 2 | 厌氧诱导所需Essential for the anaerobic induction | -1255(+)/-456(-) |
| MBSI | TTTTTACGGTTA | 1 | 参与类黄酮合成基因的调控 Involved in flavonoid biosynthetic genes regulation | -131(+) |
| RY-element | CATGCATG | 1 | 参与种子特异性调控 Involved in seed-specific regulation | -696(-) |
| GATA-motif | AAGATAAGATT | 1 | 光响应元件Light responsiveness | -1400(-) |
| GT1-motif | GGTTAA | 1 | 光响应元件Light responsiveness | -1336(-) |
| chs-CMA2a | TCACTTGA | 1 | 光响应元件Light responsiveness | -1268(-) |
| Box 4 | ATTAAT | 1 | 光响应元件Light responsiveness | -1293(+) |
| LAMP-element | CTTTATCA | 1 | 光响应元件Light responsiveness | -1123(+) |
| G-box | TACGTG | 2 | 光响应元件Light responsiveness | -810(+) |
| GGTTAAT | -194(+) |

Fig. 6 Vein of healthy(A,C)and CLas-infected(B,D)C. sinensis Yellow arrows point to the collapse of the phloem,red arrows point to the callose with blue fluorescence. Co:Cortex;P:Phloem;Fi:Fiber;Pi:Pith;X:Xylem.
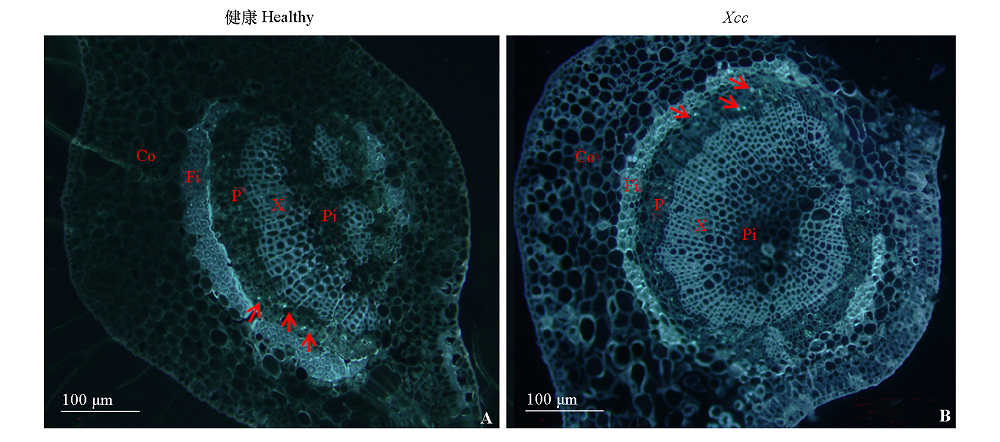
Fig. 8 Vein of healthy(A)and Xcc-infected(B)C. sinensis Red arrows point to the callose with blue fluorescence. Co:Cortex;P:Phloem;Fi:Fiber;Pi:Pith;X:Xylem.
| [1] |
Albrecht U, Bowman K D. 2008. Gene expression in Citrus sinensis(L.)Osbeck following infection with the bacterial pathogen Candidatus Liberibacter asiaticus causing Huanglongbing in Florida. Plant Science, 175:291-306.
doi: 10.1016/j.plantsci.2008.05.001 URL |
| [2] |
Boava L P, Cristofani-Yaly M, Machado M A. 2017. Physiologic,anatomic and gene expression changes in Citrus sunki,Poncirus trifoliata and their hybrids after‘Candidatus Liberibacter asiaticus’infection. Phytopathology, 107:590-599.
doi: 10.1094/PHYTO-02-16-0077-R URL |
| [3] | Chen X Y, Kim J Y. 2009. Callose synthesis in higher plants. Plant Signaling & Behavior, 4:489-492. |
| [4] |
Chen Y, Yu P, Luo J, Jiang Y. 2003. Secreted protein prediction system combining CJ-SPHMM,TMHMM,and PSORT. Mammalian Genome, 14:859-865.
doi: 10.1007/s00335-003-2296-6 URL |
| [5] |
Cui W, Lee J Y. 2016. Arabidopsis callose synthases CalS1/8 regulate plasmodesmal permeability during stress. Nature Plants, 2:16034.
doi: 10.1038/nplants.2016.34 URL |
| [6] | Dong Cui-cui, Ma Yan-yan, Xie Rang-jin, Deng Lie, Yi Shi-lai, Lü Qiang, Zheng Yong-qiang, He Shao-lan. 2016. Expression of two Citrus AP2/ERF genes under different hormone and stress treatments. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 43(2):41-50. (in Chinese) |
| 董翠翠, 马岩岩, 谢让金, 邓烈, 易时来, 吕强, 郑永强, 何绍兰. 2016. 柑橘CitEFR9和CitAP2-7在不同逆境和外源激素处理下的表达. 园艺学报, 43(2):41-50. | |
| [7] |
Dong X, Hong Z, Chatterjee J, Kim S, Verma D P S. 2008. Expression of callose synthase genes and its connection with Npr1 signaling pathway during pathogen infection. Planta, 229:87-98.
doi: 10.1007/s00425-008-0812-3 URL |
| [8] |
Enrique R, Siciliano F, Favaro M A, Gerhardt N, Roeschlin R, Rigano L, Sendin L, Castagnaro A, Vojnov A, Marano M R. 2011. Novel demonstration of RNAi in citrus reveals importance of citrus callose synthase in defence against Xanthomonas citri subsp. citri. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 9:394-407.
doi: 10.1111/j.1467-7652.2010.00555.x pmid: 20809929 |
| [9] |
Ellinger D, Naumann M, Falter C, Zwikowics C, Jamrow T, Manisseri C, Somerville S C, Voigt C A. 2013. Elevated early callose deposition results in complete penetration resistance to powdery mildew in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiology, 161:1433-1444.
doi: 10.1104/pp.112.211011 URL |
| [10] | Estrella L, Victoria P, Jérôme R, Flors V, Mauch-Mani B, Ton J. 2011. Callose deposition:a multifaceted plant defense response. Molecular Plant-microbe Interaction, 24:183-193. |
| [11] |
Fan J, Chen C, Yu Q, Khalaf A, Achor D S, Brlansky R H, Moore G A, Li Z G, Gmitter F G. 2012. Comparative transcriptional and anatomical analyses of tolerant rough lemon and susceptible sweet orange in response to‘Candidatus Liberibacter asiaticus’infection. Mol Plant Microbe Interact, 25:1396-407.
doi: 10.1094/MPMI-06-12-0150-R URL |
| [12] |
Finn R D, Tate J, Mistry J, Tate J, Coggill P, Heger A, Pollington J E, Gavin O L, Gunasekaran P, Ceric G, Forslund K, Holm L, Sonnhammer E, Eddy S R, Bateman A. 2008. The pfam protein families database. Nucleic Acids Research, 32:D138-41.
doi: 10.1093/nar/gkh121 URL |
| [13] |
Fromm J R, Hajirezaei M R, Becker V K, Lautner S. 2013. Electrical signaling along the phloem and its physiological responses in the maize leaf. Frontiers in Plant Science, 4:239.
doi: 10.3389/fpls.2013.00239 pmid: 23847642 |
| [14] |
Fu M, Xu M, Zhou T, Wang D, Tian S, Han L, Dong H, Zhang C. 2014. Transgenic expression of a functional fragment of harpin protein Hpa1 in wheat induces the phloem-based defence against English grain aphid. Journal of Experimental Botany, 65:1439-1453.
doi: 10.1093/jxb/ert488 URL |
| [15] |
Gamir J, Pastor V, Sánchez-Bel P, Agut B, Mateu D, García-Andrade J, Flors V. 2018. Starch degradation,abscisic acid and vesicular trafficking are important elements in callose priming by indole-3-carboxylic acid in response to Plectosphaerella cucumerina infection. The Plant Journal, 96:518-531.
doi: 10.1111/tpj.14045 URL |
| [16] | Geourjon C, Deléage G. 1996. SOPMA:Significant improvements in protein secondary structure prediction by consensus prediction from multiple alignments. Computer Applications in the Biosciences Cabios, 11:681-684. |
| [17] |
Granato L M, Galdeano D M, D’Alessandre N D R, Breton M C, Machado M A. 2019. Callose synthase family genes plays an important role in the Citrus defense response to Candidatus Liberibacter asiaticus. European Journal of Plant Pathology, 155:25-38
doi: 10.1007/s10658-019-01747-6 URL |
| [18] |
Gurr S J, Rushton P J. 2005. Engineering plants with increased disease resistance:How are we going to express it? Trends in Biotechnology, 23:283-290.
doi: 10.1016/j.tibtech.2005.04.009 URL |
| [19] |
Higo K, Ugawa Y, Iwamoto M, Korenaga T. 1999. Plant cis-acting regulatory DNA elements(PLACE)database:1999. Nucleic acids Research, 27:297-300.
doi: 10.1093/nar/27.1.297 URL |
| [20] | Hocquellet A, Toorawa P, Bové J M, Garnier M. 1999. Detection and identification of the two Candidatus Liberobacter species associated with citrus Huanglongbing by PCR amplification of ribosomal protein genes of the beta operon. Molecular & Cellular probes, 13(5):373-379. |
| [21] |
Hong Z, Delauney A J, Verma D P. 2001. A cell plate-specific callose synthase and its interaction with phragmoplastin. Plant Cell, 13:755-768.
pmid: 11283334 |
| [22] |
Kumar S, Stecher G, Tamura K. 2016. MEGA7:molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 33:1870-1874.
doi: 10.1093/molbev/msw054 URL |
| [23] | Jia Rui-rui. 2018. Gene cloning and expression analysis of canker-related transcription factor CsBZIP40 in citrus[M. D. Dissertation]. Chongqing:Southwest University. (in Chinese). |
| 贾瑞瑞. 2018. 柑橘溃疡病相关转录因子CsBZIP40的功能研究[硕士论文]. 重庆:西南大学. | |
| [24] |
Lescot M. 2002. PlantCARE,a database of plant cis-acting regulatory elements and a portal to tools for in silico analysis of promoter sequences. Nucleic Acids Research, 30:325-327.
doi: 10.1093/nar/30.1.325 URL |
| [25] |
Liu J, Du H, Ding X, Zhou Y, Xie P, Wu J. 2017. Mechanisms of callose deposition in rice regulated by exogenous abscisic acid and its involvement in rice resistance to Nilaparvata lugens Stal(Hemiptera︰Delphacidae). Pest Management Science, 73:2559-2568.
doi: 10.1002/ps.2017.73.issue-12 URL |
| [26] | Long Q, Xie Y, He Y, Li Q, Zou X, Chen S. 2019. Abscisic acid promotes jasmonic acid accumulation and plays a key role in citrus canker development. Frontiers in Plant Science. 10:1634. |
| [27] |
Lü B, Sun W, Zhang S, Zhang C, Qian J, Wang X, Gao R, Dong H. 2011. HrpNEa-induced deterrent effect on phloem feeding of the green peach aphid Myzus persicae requires AtGSL5 and AtMYB44 genes in Arabidopsis thaliana. Journal of Biosciences, 36:123-137.
doi: 10.1007/s12038-011-9016-2 URL |
| [28] |
Nishimura M T, Stein M, Hou B H, Vogel J P, Edwards H, Somerville S C. 2003. Loss of a callose synthase results in salicylic acid-dependent disease resistance. Science, 301:969-972.
doi: 10.1126/science.1086716 URL |
| [29] |
Mauch-Mani B, Baccelli I, Luna E, Flors V. 2017. Defense Priming:An Adaptive Part of Induced Resistance. Annual Review of Plant Biology, 68:485-512.
doi: 10.1146/annurev-arplant-042916-041132 pmid: 28226238 |
| [30] |
Nedukha O M. 2015. Callose:Localization,functions,and synthesis in plant cells. Cytology and Genetics, 49:49-57.
doi: 10.3103/S0095452715010090 URL |
| [31] |
O'Lexy R, Kasai K, Clark N, Fujiwara T, Sozzani R, Gallagher K L. 2018. Exposure to heavy metal stress triggers changes in plasmodesmatal permeability via deposition and breakdown of callose. Journal of Experimental Botany, 69:3715-3728.
doi: 10.1093/jxb/ery171 URL |
| [32] |
Oide S, Bejai S, Staal J, Guan N, Kaliff M, Dixelius C. 2013. A novel role of PR2 in abscisic acid(ABA)mediated,pathogen-induced callose deposition in Arabidopsis thaliana. New Phytologist, 200:1187-1199.
doi: 10.1111/nph.2013.200.issue-4 URL |
| [33] | Panu A, Manohar J, Konstantin A, Delphine B, Gabor C, Edouard C, Séverine D, Volker F, Arnaud F, Elisabeth G. 2012. ExPASy:SIB bioinformatics resource portal. Nucleic Acids 40 (Web Server issue):W597-603 |
| [34] | Peng Yun, Fan Hai-fang, Lei Tian-gang, He Yong-rui, Chen Shan-chun, Yao Li-xiao. 2019. Expression analysis of callose synthase gene family in citrus. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 46(2):330-336. (in Chinese) |
| 彭蕴, 范海芳, 雷天刚, 何永睿, 陈善春, 姚利晓. 2019. 柑橘胼胝质合成酶基因家族的表达分析. 园艺学报, 46(2):330-336. | |
| [35] |
Pramod S, Thomas V, Rao K S, Krishnakumar R. 2011. Definitive callose deposition in tapping panel dryness affected bark of Hevea brasiliensis. Journal of Sustainable Forestry, 30:329-342.
doi: 10.1080/10549811.2011.532032 URL |
| [36] |
Park H C, Kim M L, Kang Y H, Jeon J M, Yoo J H, Kim M C, Park C Y, Jeong J C, Moon B C, Lee J H, Yoon H W, Lee S H, Chung W S, Lim C O, Lee S Y, Hong J C, Cho M J. 2004. Pathogen- and NaCl-induced expression of the SCaM-4 promoter Is mediated in part by a GT-1 Box that interacts with a GT-1-Like transcription factor1. Plant Physiology, 135:2150-2161.
doi: 10.1104/pp.104.041442 URL |
| [37] |
Saatian B, Austin R S, Tian G, Chen C, Vi N, Kohalmi S E, Geelen D, Cui Y. 2018. Analysis of a novel mutant allele of GSL8 reveals its key roles in cytokinesis and symplastic trafficking in Arabidopsis. BMC Plant Biology, 18:295.
doi: 10.1186/s12870-018-1515-y pmid: 30466394 |
| [38] |
Shimwela M M, Narouei-Khandan H A, Halbert S E, Keremane M L, Minsavage G V, Timilsina S, Massawe D P, Jones J B, van Bruggen A H C. 2016. First occurrence of Diaphorina citriin East Africa,characterization of the Ca. Liberibacter species causing Huanglongbing(HLB)in Tanzania,and potential further spread of D. citriand HLB in Africa and Europe. European Journal of Plant Pathology, 146:349-368.
doi: 10.1007/s10658-016-0921-y URL |
| [39] | Valente A, Diann A, Frederick G G, Gene A, Nian W. 2013. Transcriptional and microscopic analyses of citrus stem and root responses to Candidatus Liberibacter asiaticus Infection. PlLS NE, 8:e73742. |
| [40] |
Wang X, Xu Y, Zhang S Q, Cao L, Huang Y, Cheng J F, Wu G Z, Tian S L, Chen C L, Liu Y, Yu H W, Yang X M, Lan H, Wang N, Wang L, Xu J D, Jiang X L, Xie Z Z, Tan M L, Larkin R M, Chen L L, Ma B G, Ruan Y J, Deng X X, Xu Q. 2017. Genomic analyses of primitive,wild and cultivated citrus provide insights into asexual reproduction. Nature Genetic, 49:765-772.
doi: 10.1038/ng.3839 URL |
| [41] |
Wang Z, Li X, Wang X, Liu N, Xu B, Peng Q, Guo Z, Fan B, Zhu C, Chen Z. 2019. Arabidopsis endoplasmic reticulum-localized UBAC2 proteins interact with PAMP-INDUCED COILED-COIL to regulate pathogen-induced callose deposition and plant immunity. Plant Cell, 31:153-171.
doi: 10.1105/tpc.18.00334 |
| [42] |
Wawrzynska A, Rodibaugh N L, Innes R W. 2010. Synergistic activation of defense responses in Arabidopsis by simultaneous loss of the GSL5 callose synthase and the EDR1 protein kinase. Mol Plant Microbe Interact, 23:578-584.
doi: 10.1094/MPMI-23-5-0578 URL |
| [43] | Wen Qingli, Xie Zhu, Wu Liu, He Yongrui, Chen Shanchun, Zou Xiuping. 2018. Clone and expression analysis of the Citrus Phloem Protein 2 gene CsPP2B15 responding to Huanglongbing infection in citrus. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 45(12):2347-2357. (in Chinese) |
| 文庆利, 谢竹, 吴柳, 何永睿, 陈善春, 邹修平. 2018. 柑橘响应黄龙病侵染的韧皮部蛋白2基因CsPP2B15的克隆与表达分析. 园艺学报, 2018,45(12):2347-2357. | |
| [44] | Xie B, Wang X, Zhu M, Zhang Z, Hong Z. 2011. CalS7 encodes a callose synthase responsible for callose deposition in the phloem. Plant Journal for Cell & Molecular Biology, 65:1-14. |
| [45] | Xie Zhu, Zhao Ke, Zheng Lin, Long Junhong, Du Meixia, He Yongrui, Chen Shanchun, Zou Xiuping. 2020. Cloning and expression analysis of alcohol dehydrogenase CsADH1 gene responding to Huanglongbing infection in Citrus. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 47(3):445-454. (in Chinese) |
| 谢竹, 赵珂, 郑林, 龙俊宏, 杜美霞, 何永睿, 陈善春, 邹修平. 2020. 响应黄龙病侵染的柑橘乙醇脱氢酶基因CsADH1的克隆与表达分析. 园艺学报, 47(3):445-454. | |
| [46] |
Xu Q, Chen L L, Ruan X, Chen D, Zhu A, Chen C, Bertrand D, Jiao W B, Hao B H, Lyon M P, Chen J, Gao S, Xing F, Lan H, Chang J W, Ge X, Lei Y, Hu Q, Miao Y, Wang L, Xiao S, Biswas M K, Zeng W, Guo F, Cao H, Yang X, Xu X W, Cheng Y J, Xu J, Liu J H, Luo O J, Tang Z, Guo W W, Kuang H, Zhang H Y, Roose M L, Nagarajan N, Deng X X, Ruan Y. 2013. The draft genome of sweet orange(Citrus sinensis). Nature Genetics, 45:59-66.
doi: 10.1038/ng.2472 URL |
| [47] |
Yu J, Zhang Y, Di C, Zhang Q, Zhang K, Wang C, You Q, Yan H, Dai S Y, Yuan J S. 2015. JAZ7 negatively regulates dark-induced leaf senescence in Arabidopsis. Journal of Experimental Botany, 67:751-762.
doi: 10.1093/jxb/erv487 URL |
| [48] | Zhang H, Shi W L, You J F, Bian M D, Qin X M, Hui Y U, Liu Q, Ryan P R, Yang Z M. 2015. Transgenic Arabidopsis thaliana plants expressing a β-1,3-glucanase from sweet sorghum(Sorghum bicolorβL.)show reduced callose deposition and increased tolerance to aluminium toxicity. Plant Cell & Environment, 38:1178-1188. |
| [49] |
Zhu C Q, Zheng X J, Huang Y, Ye J L, Chen P, Zhang C L, Zhao F, Xie Z Z, Zhang S Q, Wang N, Li H, Wang L, Tang X M, Chai L J, Xu Q, Deng X X. 2019. Genome sequencing and CRISPR/Cas9 gene editing of an early flowering mini citrus(Fortunella hindsii). Plant Biotechnology Journal, 17:2199-2210.
doi: 10.1111/pbi.v17.11 URL |
| [50] | Zhang Y Y, Liu X L, Huang H H. 2012. Molecular cloning of Crustin-like gene in the white shrimp(Litopenaeus vannamei)and its mRNA expression with Vibrio parahaemolyticus challenge. Journal of Northwest A & F University, 40:119-132. |
| [51] | Zhong Xi. 2018. Transcriptomic and proteomic analysis of Citrus hystrix responses to‘Candidatus Liberibacter asiaticus’in early and late stage of infection[M. D. Dissertation]. Chongqing:Southwest University. (in Chinese) |
| 钟晰. 2018. 马蜂柑响应黄龙病菌侵染前期与后期的转录组和蛋白组学研究[硕士论文]. 重庆:西南大学. |
| [1] | ZHAO Xueyan, WANG Qi, WANG Li, WANG Fangyuan, WANG Qing, LI Yan. Comparative Transcriptome Analysis of Differential Expression in Different Tissues of Corydalis yanhusuo [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(1): 177-187. |
| [2] | LI Zhenxi, PAN Ruixuan, XU Meirong, ZHENG Zheng, DENG Xiaoling. Development of Duplex Real-time PCR Assay of‘Candidatus Liberibacter asiatics’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(1): 188-196. |
| [3] | GAO Yanlong, WU Yuxia, ZHANG Zhongxing, WANG Shuangcheng, ZHANG Rui, ZHANG De, WANG Yanxiu. Bioinformatics Analysis of Apple ELO Gene Family and Its Expression Analysis Under Low Temperature Stress [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(8): 1621-1636. |
| [4] | QIU Ziwen, LIU Linmin, LIN Yongsheng, LIN Xiaojie, LI Yongyu, WU Shaohua, YANG Chao. Cloning and Functional Analysis of the MbEGS Gene from Melaleuca bracteata [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(8): 1747-1760. |
| [5] | ZHENG Lin, WANG Shuai, LIU Yunuo, DU Meixia, PENG Aihong, HE Yongrui, CHEN Shanchun, ZOU Xiuping. Gene Cloning and Expression Analysis of NAC Gene in Citrus in Response to Huanglongbing [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(7): 1441-1457. |
| [6] | MA Weifeng, LI Yanmei, MA Zonghuan, CHEN Baihong, MAO Juan. Identification of Apple POD Gene Family and Functional Analysis of MdPOD15 Gene [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(6): 1181-1199. |
| [7] | ZHANG Kai, MA Mingying, WANG Ping, LI Yi, JIN Yan, SHENG Ling, DENG Ziniu, MA Xianfeng. Identification of HSP20 Family Genes in Citrus and Their Expression in Pathogen Infection Responses Citrus Canker [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(6): 1213-1232. |
| [8] | LIANG Chen, SUN Ruyi, XIANG Rui, SUN Yimeng, SHI Xiaoxin, DU Guoqiang, WANG Li. Genome-wide Identification of Grape GRF Family and Expression Analysis [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(5): 995-1007. |
| [9] | XIAO Xuechen, LIU Mengyu, JIANG Mengqi, CHEN Yan, XUE Xiaodong, ZHOU Chengzhe, WU Xingjian, WU Junnan, GUO Yinsheng, YEH Kaiwen, LAI Zhongxiong, LIN Yuling. Whole-genome Identification and Expression Analysis of SNAT,ASMT and COMT Families of Melatonin Synthesis Pathway in Dimocarpus longan [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(5): 1031-1046. |
| [10] | GAO Weilin, ZHANG Liman, XUE Chaoling, ZHANG Yao, LIU Mengjun, ZHAO Jin. Expression of E-type MADS-box Genes in Flower and Fruits and Protein Interaction Analysis in Chinese Jujube [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(4): 739-748. |
| [11] | LIU Mengyu, JIANG Mengqi, CHEN Yan, ZHANG Shuting, XUE Xiaodong, XIAO Xuechen, LAI Zhongxiong, LIN Yuling. Genome-wide Identification and Expression Analysis of GDSL Esterase/Lipase Genes in Dimocarpus longan [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(3): 597-612. |
| [12] | JIANG Cuicui, FANG Zhizhen, ZHOU Danrong, LIN Yanjuan, YE Xinfu. Identification and Expression Analysis of Sugar Transporter Family Genes in‘Furongli’(Prunus salicina) [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(2): 252-264. |
| [13] | WANG Zhiyu, CHANG Beibei, LIU Qi, CHENG Xiaofan, DU Xiaoyun, YU Xiaoli, SONG Laiqing, ZHAO Lingling. Study on Expression and Anthocyanin Accumulation of Solute Carrier Gene MdSLC35F2-like in Apple [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(11): 2293-2303. |
| [14] | HUANG Renwei, REN Yinghong, QI Weiliang, ZENG Rui, LIU Xinyu, DENG Binyan. Cloning of Mulberry MaERF105-Like Gene and Its Expression Under Drought Stress [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(11): 2439-2448. |
| [15] | BIAN Shicun, LU Yani, XU Wujun, CHEN Boqing, WANG Guanglong, XIONG Aisheng. Garlic Circadian Clock Genes AsRVE1 and AsRVE2 and Their Expression Analysis Under Osmotic Stress [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2021, 48(9): 1706-1716. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2012 Acta Horticulturae Sinica 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
Tel: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
Support by: Beijing Magtech Co.Ltd