
Acta Horticulturae Sinica ›› 2021, Vol. 48 ›› Issue (1): 173-182.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2020-0236
• Research Notes • Previous Articles Next Articles
TAO Hang, ZAYINA Mahabat, ZHANG Ye, SUN Litong, HUANG Shenxin, ZHANG Zihui, LIU Wang, SHI Ningxue, CHEN Xiaoren**( )
)
Received:2020-09-22
Revised:2020-12-04
Online:2021-01-25
Published:2021-01-29
Contact:
CHEN Xiaoren
E-mail:xrchen@yzu.edu.cn
CLC Number:
TAO Hang, ZAYINA Mahabat, ZHANG Ye, SUN Litong, HUANG Shenxin, ZHANG Zihui, LIU Wang, SHI Ningxue, CHEN Xiaoren. Identification,Growth Conditions and Fungicide Sensitivity of the Pathogen Causing Black Spot Disease on Peony Leaves[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2021, 48(1): 173-182.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.ahs.ac.cn/EN/10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2020-0236
| 种名 Species | 菌株 Isolate | NCBI基因数据库登录号 GenBank accession | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rDNA-ITS | endoPG | OPA2-1 | Alt a 1 | ||
| 链格孢菌Alternaria alternata | EGS 34-016 | AF347031 | AY295024 | AY295065 | KP275691 |
| EGS 34-039 | ― | AY295025 | AY295064 | ― | |
| 39-190 | ― | AY629218 | AY295060 | ― | |
| S2 | MT269274 | MT505726 | MT505728 | MT505725 | |
| 橘树链格孢Alternaria citriarbusti | SH-MIL-15s | ― | AY295026 | AY295057 | ― |
| 橘斑链格孢Alternaria citrimacularis | BC2-RLR-32s | JX397903 | JX397906 | AY295069 | ― |
| 草莓链格孢Alternaria fragaria | 0-187 | ― | AY629222 | AY631462 | ― |
| 梨黑斑链格孢Alternaria gaisen | EGS 90-0512 | ― | AY295033 | AY631460 | KP275694 |
| 粗柠檬链格孢Alternaria limoniasperae | PR325 | ― | AY629233 | AY295062 | ― |
| 蜜柚链格孢Alternaria tangelonis | EV-MIL-2s | ― | AY295031 | AY295066 | JQ646392 |
| 细极链格孢Alternaria tenuissima | EGS 34-015 | AF347032 | JQ811977 | AY631463 | ― |
| 土耳其链格孢Alternaria turkisafria | EGS 44-159 | ― | AY295022 | AY295054 | JQ646404 |
Table 1 The gene sequences used in phylogenetic analysis
| 种名 Species | 菌株 Isolate | NCBI基因数据库登录号 GenBank accession | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rDNA-ITS | endoPG | OPA2-1 | Alt a 1 | ||
| 链格孢菌Alternaria alternata | EGS 34-016 | AF347031 | AY295024 | AY295065 | KP275691 |
| EGS 34-039 | ― | AY295025 | AY295064 | ― | |
| 39-190 | ― | AY629218 | AY295060 | ― | |
| S2 | MT269274 | MT505726 | MT505728 | MT505725 | |
| 橘树链格孢Alternaria citriarbusti | SH-MIL-15s | ― | AY295026 | AY295057 | ― |
| 橘斑链格孢Alternaria citrimacularis | BC2-RLR-32s | JX397903 | JX397906 | AY295069 | ― |
| 草莓链格孢Alternaria fragaria | 0-187 | ― | AY629222 | AY631462 | ― |
| 梨黑斑链格孢Alternaria gaisen | EGS 90-0512 | ― | AY295033 | AY631460 | KP275694 |
| 粗柠檬链格孢Alternaria limoniasperae | PR325 | ― | AY629233 | AY295062 | ― |
| 蜜柚链格孢Alternaria tangelonis | EV-MIL-2s | ― | AY295031 | AY295066 | JQ646392 |
| 细极链格孢Alternaria tenuissima | EGS 34-015 | AF347032 | JQ811977 | AY631463 | ― |
| 土耳其链格孢Alternaria turkisafria | EGS 44-159 | ― | AY295022 | AY295054 | JQ646404 |

Fig. 1 Symptoms of peony black spot disease A:Natural symptoms;B:Symptoms at 5 days post-inoculation with mycelial plugs of the isolate S2. Ctrl:Control,sterile plug inoculation.
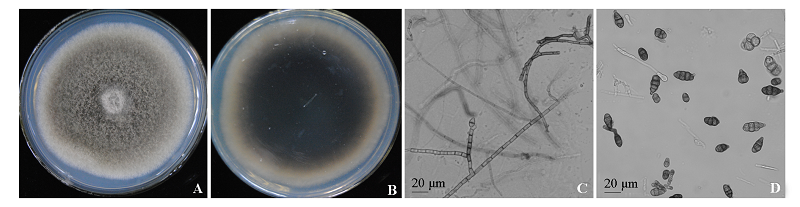
Fig. 2 Morphological characteristics of the pathogen causing black spot disease on peony A:Frontal view of the colony;B:Reverse view of the colony;C:Conidiophores;D:Conidia.
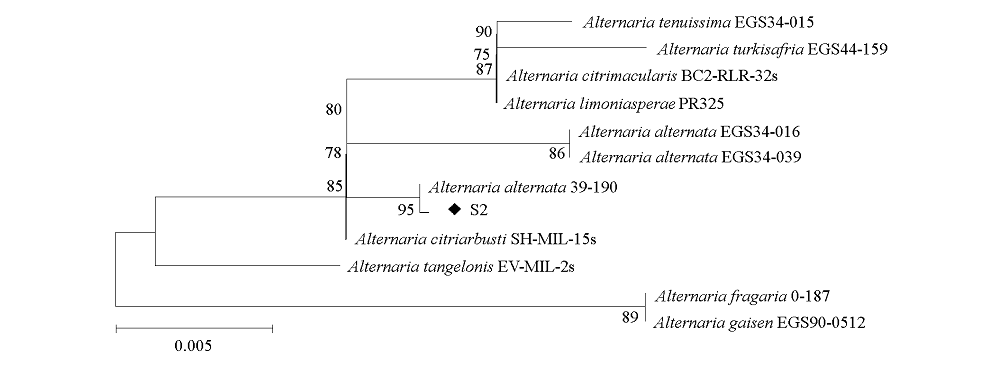
Fig. 3 Phylogenetic tree based on the combination analysis of multiple gene sequences The values on the branches indicate Bayesian posterior probability. The scale bar showed expected change per site.
| 碳源 Carbon source | 菌落直径/mm Colony diameter | 氮源 Nitrogen source | 菌落直径/mm Colony diameter |
|---|---|---|---|
| 蔗糖Sucrose(对照Control) | 45.1 ± 3.9 cde | 硝酸钾KNO3(对照Control) | 44.8 ± 0.8 a |
| 葡萄糖Dextrose | 43.4 ± 2.5 e | 硝酸铵NH4NO3 | 34.5 ± 1.1 b |
| 麦芽糖 Maltose | 63.8 ± 4.1 a | 硝酸钙Ca(NO3)2 | 42.0 ± 2.0 a |
| 乳糖Lactose | 59.7 ± 1.8 ab | 氯化铵NH4Cl | 35.2 ± 2.7 ab |
| 可溶性淀粉Soluble starch | 67.1 ± 5.3 a | 尿素Urea | 26.2 ± 1.4 c |
| 木糖Xylose | 55.6 ± 1.7 abc | 谷氨酸Glutamic acid | 27.9 ± 2.2 c |
| 半乳糖Galactose | 49.4 ± 1.9 bcd |
Table 2 Effect of different carbon and nitrogen sources on mycelial growth of the isolate S2 of A. alternata
| 碳源 Carbon source | 菌落直径/mm Colony diameter | 氮源 Nitrogen source | 菌落直径/mm Colony diameter |
|---|---|---|---|
| 蔗糖Sucrose(对照Control) | 45.1 ± 3.9 cde | 硝酸钾KNO3(对照Control) | 44.8 ± 0.8 a |
| 葡萄糖Dextrose | 43.4 ± 2.5 e | 硝酸铵NH4NO3 | 34.5 ± 1.1 b |
| 麦芽糖 Maltose | 63.8 ± 4.1 a | 硝酸钙Ca(NO3)2 | 42.0 ± 2.0 a |
| 乳糖Lactose | 59.7 ± 1.8 ab | 氯化铵NH4Cl | 35.2 ± 2.7 ab |
| 可溶性淀粉Soluble starch | 67.1 ± 5.3 a | 尿素Urea | 26.2 ± 1.4 c |
| 木糖Xylose | 55.6 ± 1.7 abc | 谷氨酸Glutamic acid | 27.9 ± 2.2 c |
| 半乳糖Galactose | 49.4 ± 1.9 bcd |
| 药剂名称 Fungicide name | 浓度/(mg · L-1) Concentration | 毒力回归方程 Toxicity regression equation | R2 | EC50/(mg · L-1) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.5 | 0.1 | 0.05 | 0.01 | 0 | ||||
| 嘧菌酯Azoxystrobin | 39.6 ab | 34.0 b | 30.9 ab | 20.2 b | 6.2 b | 0 | y = 0.1595x + 0.4086 | 0.9301 | 3.7415 b |
| 吡唑醚菌酯 Pyraclostrobin | 45.1 a | 40.7 a | 33.4 a | 31.8 a | 20.6 a | 0 | y = 0.1165x + 0.4503 | 0.9843 | 2.6706 a |
| 戊唑醇Tebuconazole | 24.0 c | 17.8 c | 17.4 c | 14.4 c | 10.4 bc | 0 | y = 0.0592x + 0.2224 | 0.8870 | 4.8876 × 104 c |
| 异菌脲Iprodione | 5.5 d | 5.2 d | 4.9 d | 4.2 d | 2.4 d | 0 | y = 0.0147x + 0.0577 | 0.8798 | 1.2260 × 1030 d |
Table 3 The inhibition rates of 4 fungicides at 6 different concentrations against the mycelial growth of A. alternata S2
| 药剂名称 Fungicide name | 浓度/(mg · L-1) Concentration | 毒力回归方程 Toxicity regression equation | R2 | EC50/(mg · L-1) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.5 | 0.1 | 0.05 | 0.01 | 0 | ||||
| 嘧菌酯Azoxystrobin | 39.6 ab | 34.0 b | 30.9 ab | 20.2 b | 6.2 b | 0 | y = 0.1595x + 0.4086 | 0.9301 | 3.7415 b |
| 吡唑醚菌酯 Pyraclostrobin | 45.1 a | 40.7 a | 33.4 a | 31.8 a | 20.6 a | 0 | y = 0.1165x + 0.4503 | 0.9843 | 2.6706 a |
| 戊唑醇Tebuconazole | 24.0 c | 17.8 c | 17.4 c | 14.4 c | 10.4 bc | 0 | y = 0.0592x + 0.2224 | 0.8870 | 4.8876 × 104 c |
| 异菌脲Iprodione | 5.5 d | 5.2 d | 4.9 d | 4.2 d | 2.4 d | 0 | y = 0.0147x + 0.0577 | 0.8798 | 1.2260 × 1030 d |
| [1] | Chen Xiao-hong, Ye Hua-zhi, Yan Ji-ming, Qin Yun, Wu Guang-qing. 2006. Investigation on the diseases of medicinal plants in Sichuan Province and pathogen identification I. A list of diseases of main cultivated medicinal plants. Southwest China Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 19(1):58-62. (in Chinese) |
| 陈小红, 叶华智, 严吉明, 秦芸, 伍光庆. 2006. 四川药用植物病害调查与病原鉴定Ⅰ. 主要栽培药用植物病害. 西南农业学报, 19(1):58-62. | |
| [2] |
Chen X R, Liu B B, Xing Y P, Cheng B P, Liu M L, Tong Y H, Xu J Y. 2016. Identification and characterization of Phytopythium helicoides causing stem rot of Shatangju mandarin seedlings in China. European Journal of Plant Pathology, 146:715-727.
doi: 10.1007/s10658-016-0952-4 URL |
| [3] | Fang Zhong-da. 1998. Methods used in plant pathology. 3rd ed. Beijing: China Agriculture Press. (in Chinese) |
| 方中达. 1998. 植病研究法. 3版. 北京: 中国农业出版社. | |
| [4] | Huang Zhang-xin. 2001. Experiment guidance for plant chemical protection. Beijing: China Agriculture Press. (in Chinese) |
| 黄彰欣. 2001. 植物化学保护实验指导. 北京: 中国农业出版社. | |
| [5] |
Hong S G, Cramer R A, Lawrence C B, Pryor B M. 2005. Alt a 1 allergen homologs from Alternaria and related taxa:analysis of phylogenetic content and secondary structure. Fungal Genetics and Biology, 42(2):119-129.
doi: 10.1016/j.fgb.2004.10.009 URL |
| [6] | Jiang Yao, Ge Jin-tao, Ning Chuan-long, Tao Jun. 2013. Disease investigation of herbaceous peony and disease susceptibility of cultivars. Jiangsu Agricultural Science, 41(1):125-127. (in Chinese) |
| 姜瑶, 葛金涛, 宁传龙, 陶俊. 2013. 芍药病害种类及其品种感病性调查. 江苏农业科学, 41(1):125-127. | |
| [7] | Lan Ying, Zhao Gui-hua, Zheng Peng-peng. 1984. Studies on Cladosporium red spot of peony. Journal of Nanjing Institute of Forestry,(1):16-29. (in Chinese) |
| 蓝莹, 赵桂华, 郑彭彭. 1984. 芍药红斑病的研究. 南京林业院学报,(1):16-29. | |
| [8] | Li Gui-fan, Wang Qi-yan, Hu Guo-yan. 2001. Common disease and control in herbaceous peony in cold district. Northern Horticulture,(5):56. (in Chinese) |
| 李桂凡, 王启燕, 胡国岩. 2001. 高寒地区芍药露地栽培常见病害及其防冶. 北方园艺,(5):56. | |
| [9] | Li Li, Song Shu-xiang, Liu Hui-xiang, Guo Xian-feng. 2016. Identification of red spot pathogens on peony in Shandong Province. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 43(2):365-372. (in Chinese) |
| 李丽, 宋淑香, 刘会香, 郭先锋. 2016. 山东省芍药红斑病病原菌鉴定. 园艺学报, 43(2):365-372. | |
| [10] | Liu Chu-rong, Dong Yue, Lü Qing-yang, Li Ying-bin, Jiang Na, Luo Lai-xin, Zhu Tian-sheng, Li Jian-qiang. 2019. Screening of fungicides and their cocktail mixture for controlling black spot of jujube. Plant Protection, 45(5):263-268. (in Chinese) |
| 刘础荣, 董玥, 吕青阳, 李迎宾, 蒋娜, 罗来鑫, 朱天生, 李健强. 2019. 防治红枣黑斑病的杀菌剂筛选和复配研究. 植物保护, 45(5):263-268. | |
| [11] | Liu Xia, Yang Ke-qiang, Jiang Xing-yin, An Hai-shan, Wang Can-can. 2013. Sensitivity of walnut-associated Alternaria alternata to four fungicides. Agrochemicals, 52(1):67-70. (in Chinese) |
| 刘霞, 杨克强, 姜兴印, 安海山, 王灿灿. 2013. 危害核桃的链格孢(Alternaria alternata)对4种杀菌剂的敏感性. 农药, 52(1):67-70. | |
| [12] |
Peever T L, Carpenter-Boggs L, Timmer L W, Carris L M, Bhatia A. 2005. Citrus black rot is caused by phylogenetically distinct lineages of Alternaria alternata. Phytopathology, 95:512-518.
doi: 10.1094/PHYTO-95-0512 pmid: 18943316 |
| [13] | Shi Liang-hong, Li Ling, Shen Hong-wei, Sun Feng-yi, Zhao Lan-yong. 2014. The identification and analysis of ITS sequence on tree peony red spot. Journal of Agriculture, 4(10):32-35. (in Chinese) |
| 石良红, 李玲, 申宏伟, 孙逢毅, 赵兰勇. 2014. 牡丹红斑病病原鉴定与ITS序列分析. 农学学报, 4(10):32-35. | |
| [14] | Shi Yan-tong, Zhang Xiu-xin, Xue Jing-qi, Wu Rui, Shi Feng-rui. 2014. Diseases investigation of herbaceous peony and selection of resistant varieties. Southwest China Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 27(5):1979-1983. (in Chinese) |
| 石颜通, 张秀新, 薛璟祺, 吴蕊, 石丰瑞. 2014. 芍药病害调查及抗性品种筛选. 西南农业学报, 27(5):1979-1983. | |
| [15] | White T J, Bruns T, Lee S, Taylor J. 1990. Amplification and direct sequencing of fungal ribosomal RNA genes for phylogenetics//Innis M A,Gelfand D H,Sninsky J J,White T J. PCR protocols:a guide to methods and applications. PCR protocols: a guide to methods and applications. San Diego:Academic Press. |
| [16] | Wu Yu-zhu, Ji Yan-ping, Liu Yu, Zhao Gui-hua, Niu Ying-fu, Wang Hai-ming, Zhao Hai-jun. 2005. Study on red spot disease of peony tree. Forest Research, 15(6):711-716. (in Chinese) |
| 吴玉柱, 季延平, 刘愚, 赵桂华, 牛迎福, 王海明, 赵海军. 2005. 牡丹红斑病的研究. 林业科学研究, 15(6):711-716. | |
| [17] | Xiao Chun-fang, Tian Heng-lin, Shen Yan-fen, Gao Jian-hua, Zhang Yuan-xue, Chen Jia-ji. 2015. Toxicity and control efficacy of azoxystrobin against potato early blight Alternaria solani. Hunan Agricultural Sciences,(8):46-48. (in Chinese) |
| 肖春芳, 田恒林, 沈艳芬, 高剑华, 张远学, 陈家吉. 2015. 嘧菌酯对马铃薯早疫病菌Alternaria solani的毒力及防效. 湖南农业科学,(8):46-48. | |
| [18] | Yang Rui-xian, Wang Zu-hua, Ye Wen-yu. 2010. Identification of four kinds of fungal diseases on tree peony and herbaceous peony in Luoyang. Subtropical Agriculture Research, 6(2):102-105. (in Chinese) |
| 杨瑞先, 王祖华, 叶文雨. 2010. 洛阳牡丹、芍药4种真菌性病害鉴定. 亚热带农业研究, 6(2):102-105. | |
| [19] | Yang Ting, Yang Kuan, He Chi, Wang Hui-ling, Wang Wen-peng, Jin Xin, Zhu Shu-sheng, Zhu You-yong, He Xia-hong. 2018. Biological characteristics of Alternaria alternata causing dark speckle disease of Panax notoginseng. Journal of Chinese Medicinal Materials, 41(4):763-770. (in Chinese) |
| 杨婷, 杨宽, 何迟, 王慧玲, 王文鹏, 金鑫, 朱书生, 朱有勇, 何霞红. 2018. 三七黑斑病病原菌Alternaria alternata Keissl.生物学特性研究. 中药材, 41(4):763-770. | |
| [20] | Yu Si-jia, Zhang Zhou-shuang, Lei Zeng-pu, Fei Yu-zhen. 1993. The preliminary study of integrated management of major diseases of tree peony and peony in Beijing area. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 15(2):103-108. (in Chinese) |
| 俞思佳, 张佐双, 雷增普, 费玉珍. 1993. 北京地区牡丹和芍药主要病害的综合防治. 北京林业大学学报, 15(2):103-108. | |
| [21] |
Zhang D, Gao F, Li W X, Jakovlić I, Zou H, Zhang J, Wang G T. 2020. PhyloSuite: an integrated and scalable desktop platform for streamlined molecular sequence data management and evolutionary phylogenetics studies. Molecular Ecology Resources, 20:348-355.
doi: 10.1111/1755-0998.13096 pmid: 31599058 |
| [22] | Zhang Jun-hua, Li Yun-peng, Han Yu-tong, Yang Ming-xiu, Song Shuang, Zhong Qing-yan, Fan Lin. 2018. Study on pathogen identification and biological characteristics of rice brown panicle disease in Heilongjiang Province. Journal of Northeast Agricultural University, 49(1):27-38. (in Chinese) |
| 张俊华, 李云鹏, 韩雨桐, 杨明秀, 宋爽, 钟庆艳, 范琳. 2018. 黑龙江省水稻褐变穗病病原鉴定及生物学特性研究. 东北农业大学学报, 49(1):27-38. | |
| [23] | Zhang Tian-yu. 2003. Flora Fungorum sinicorum. Vol 16. Alternaria. Beijing: Science Press. (in Chinese) |
| 张天宇. 2003. 中国真菌志. 16卷. 链格孢属. 北京: 科学出版社. |
| [1] | LI Ruiya, SONG Chengwei, NIU Tongfei, WEI Zhenzhen, GUO Lili, and HOU Xiaogai. The Emitted Pattern Analysis of Flower Volatiles and Cloning of PsGDS Gene in Tree Peony Cultivar‘High Noon’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(2): 331-344. |
| [2] | ZHU Wei, CAO Jinjin, CHEN Xi, ZHANG Wei, SUN Rongze, ZHU Shaocai, ZHAO Jiageng, CUI Yaqi, WANG Yuxuan, and YU Xiaonan. New Herbaceous Peony Cultivars‘Fluttering Pink’‘Fairy’s Cheek’ ‘Blushing Smile’and‘Tiny Lotus’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(2): 457-458. |
| [3] | HE Zhihong, HE Lixia, ZHANG Yandong, YANG Guozhou, LI Rui, XU Jingjing, QU Dan, and LI Jingjing. A New Tree Peony Cultivar‘Yuxia Sanqi’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(S2): 219-220. |
| [4] | ZHAO Haijun, GAI Shupeng, CHAO Zhen, YAN Shanshan, FANG Yifu, and ZHANG Pei. A New Tree Peony Cultivar‘Fu Zhao Fen Lan’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(S2): 221-222. |
| [5] | LIU Peng, LI Qin, ZHANG Weirui, HE Sheqi, ZHANG Suping, MA Xiaoxu, YUAN Wangjun. Identification,Biological Characteristics and Fungicide Sensitivity of the Pathogen Causing Brown Spot Disease on Forsythia [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(8): 1805-1814. |
| [6] | JI Fengjiao, MA Yan, QI Shuai, GUO Xianfeng, CHEN Junqiang. Cloning and Functional Analysis of Peony PlSVP Gene in Regulating Flowering [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(11): 2367-2376. |
| [7] | LIU Rong, CI Huiting, REN Xiuxia, GAO Jie, WANG Shunli, ZHANG Xiuxin. Optimization of Callus Induction from Immature Embryo and Establishment Regeneration System of Paeonia ostii‘Fengdan’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(1): 166-174. |
| [8] | YE Kang, HU Yonghong, and ZHANG Ying. A New Tree Peony Cultivar‘Jinliu Hewu’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2021, 48(S2): 2959-2960. |
| [9] | YE Kang, HU Yonghong, and ZHANG Ying. A New Tree Peony Cultivar‘Yinsu Ziran’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2021, 48(S2): 2961-2962. |
| [10] | WANG Yi, WANG Kaixuan, HU Siyuan, ZHOU Shuang, SHI Guoan. Effects of Ethylene Metabolism and Energy Status on Vase Quality of Cut Itoh Peony‘Bartzella’Flowers [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2021, 48(6): 1135-1149. |
| [11] | LI Rungen, ZENG Huilan, LU Qineng, HUANG Qin, YAN Decong. Identification,Partial Biological Characteristics and Sensitivity to Fungicides of Fusarium commune Causing Bulb Rot on Lily [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2021, 48(1): 162-172. |
| [12] | PIAO Xingmao1,WANG Fu2,LI Qingdao3,MA Jun2,WANG Lianying1,and YUAN Tao1,*. A New Orange Tree Peony‘Yuhou Caihong’ [J]. ACTA HORTICULTURAE SINICA, 2019, 46(S2): 2897-2898. |
| [13] | WU Hong,LIU Chunying,FU Xiangmei,GAI Shupeng,and ZHANG Yuxi*. Screening,Cloning and Expression Patterns Analysis of PsGRASs Associated with Dormancy Release in Tree Peony(Paeonia suffruticosa) [J]. ACTA HORTICULTURAE SINICA, 2019, 46(2): 365-374. |
| [14] | LIU Xin*,ZENG Rong*,XU Lihui,GAO Shigang,and DAI Fuming**. Resistance Mechanism to Boscalid and Molecular Mutation-detection Based on SdhB Gene of Botrytis cinerea from Strawberry [J]. ACTA HORTICULTURAE SINICA, 2019, 46(11): 2155-2163. |
| [15] | YANG Ruowen*,ZHANG Ping*,XUE Yuqian,XUE Jingqi,WANG Shunli**,and ZHANG Xiuxin**. Effects of Ethylene on Opening and Senescence Process of Herbaceous Peony Cut Flowers‘Banker Hill’and‘Yangfei Chuyu’ [J]. ACTA HORTICULTURAE SINICA, 2018, 45(8): 1575-1586. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2012 Acta Horticulturae Sinica 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
Tel: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
Support by: Beijing Magtech Co.Ltd