
Acta Horticulturae Sinica ›› 2021, Vol. 48 ›› Issue (1): 1-14.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2020-0276
• Research Papers • Next Articles
LI Xinxin1, HOU Hongmin1, XU Jihua2, SUN Xiaohong2, ZHANG Yugang1,**( )
)
Received:2020-05-23
Revised:2020-07-02
Online:2021-01-25
Published:2021-01-29
Contact:
ZHANG Yugang
E-mail:ygzhang@qau.edu.cn
CLC Number:
LI Xinxin, HOU Hongmin, XU Jihua, SUN Xiaohong, ZHANG Yugang. Genome-wide Identification and Abiotic Stress Response Analysis of MLP Family Genes in Apple[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2021, 48(1): 1-14.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.ahs.ac.cn/EN/10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2020-0276
| 基因名称 Gene name | 正向引物序列(5′-3′) Forward primer sequence | 反向引物序列(5′-3′) Revers primer sequences |
|---|---|---|
| MdMLP1 | TAGCGATTGTGGTAAGCTGG | GGAGATGTGGTGTGGTTTGT |
| MdMLP2 | ACGAGAAGTGGGAGGGTAAA | GGAGATGTGGTGTGGTTTGT |
| MdMLP3 | TAGCGATTGTGGTAAGCTGG | GGAGATGTGGTGTGGTTTGT |
| MdMLP4 | GCACGGGAACACAAATGATG | AGACCTCAACTGCAAACTGG |
| MdMLP5/13 | GGCGGTTGCTTATAAGGTGA | AACCTGTTCGTGTGCTTTCT |
| MdMLP6 | CCTTCAGGTCATCCAAGGTG | TTTGGTGTGACTTGAACCGT |
| MdMLP7 | CGAAGGTGATTGGGAGACTG | CGCTTCAACCGTCTCCTTTA |
| MdMLP810 | TTCTAGCAAGGTGGAGACGA | CCACAAGAAGACACAACCCA |
| MdMLP9 | GGAAACACACGGCTCTGTTA | CCGACATGATCCCGATTGTT |
| MdMLP11 | CAAGGCTGCAACTCTGAAAG | TATTCGATCCACAGGTTGGC |
| MdMLP12 | CCCACCTCATCCCAAACATT | GCAATGCAGGTGCTTTCATC |
| MdActin | ATTCAAGTATGCCTGGGTGC | CAGTCAGCCTGTGATGTTCC |
Table 1 Primers for qRT-PCR
| 基因名称 Gene name | 正向引物序列(5′-3′) Forward primer sequence | 反向引物序列(5′-3′) Revers primer sequences |
|---|---|---|
| MdMLP1 | TAGCGATTGTGGTAAGCTGG | GGAGATGTGGTGTGGTTTGT |
| MdMLP2 | ACGAGAAGTGGGAGGGTAAA | GGAGATGTGGTGTGGTTTGT |
| MdMLP3 | TAGCGATTGTGGTAAGCTGG | GGAGATGTGGTGTGGTTTGT |
| MdMLP4 | GCACGGGAACACAAATGATG | AGACCTCAACTGCAAACTGG |
| MdMLP5/13 | GGCGGTTGCTTATAAGGTGA | AACCTGTTCGTGTGCTTTCT |
| MdMLP6 | CCTTCAGGTCATCCAAGGTG | TTTGGTGTGACTTGAACCGT |
| MdMLP7 | CGAAGGTGATTGGGAGACTG | CGCTTCAACCGTCTCCTTTA |
| MdMLP810 | TTCTAGCAAGGTGGAGACGA | CCACAAGAAGACACAACCCA |
| MdMLP9 | GGAAACACACGGCTCTGTTA | CCGACATGATCCCGATTGTT |
| MdMLP11 | CAAGGCTGCAACTCTGAAAG | TATTCGATCCACAGGTTGGC |
| MdMLP12 | CCCACCTCATCCCAAACATT | GCAATGCAGGTGCTTTCATC |
| MdActin | ATTCAAGTATGCCTGGGTGC | CAGTCAGCCTGTGATGTTCC |
| 基因名称 Gene name | 基因组登录号 Gene accession No.(GDR) | 编码 区/bp CDS | 染色体位置 Chromosome location | 蛋白质 Protein | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 信号肽 Signal peptide (Sec/SPI) | 长度/ aa Length | 分子量/ kD Molecular weight | pI | 不稳定 指数 Instability index | 亲水性 Hydropa- thicity | ||||
| MdMLP1 | MD00G1063600 | 468 | Chr00:11768127..11768939(+) | 0.0011 | 155 | 17.62 | 5.32 | 27.52 | -0.576 |
| MdMLP2 | MD13G1022700 | 498 | Chr13:1627661..1629214(-) | 0.0021 | 165 | 18.68 | 5.52 | 22.52 | -0.444 |
| MdMLP3 | MD13G1022900 | 468 | Chr13:1645481..1646431(-) | 0.0011 | 155 | 17.62 | 5.32 | 27.52 | -0.576 |
| MdMLP4 | MD13G1023000 | 468 | Chr13:1657247..1658331(-) | 0.0016 | 155 | 17.45 | 5.32 | 26.36 | -0.497 |
| MdMLP5 | MD13G1088200 | 462 | Chr13:6177671..6178671(+) | 0.0006 | 153 | 16.83 | 5.26 | 22.52 | -0.137 |
| MdMLP6 | MD16G1024000 | 474 | Chr16:1729158..1730220(-) | 0.0012 | 157 | 17.58 | 8.43 | 37.24 | -0.258 |
| MdMLP7 | MD16G1024100 | 462 | Chr16:1731391..1732218(-) | 0.0011 | 153 | 17.27 | 4.88 | 30.74 | -0.381 |
| MdMLP8 | MD16G1024300 | 468 | Chr16:1742688..1743368(-) | 0.0007 | 155 | 17.57 | 4.88 | 30.00 | -0.338 |
| MdMLP9 | MD16G1024900 | 558 | Chr16:1792284..1793136(-) | 0.0022 | 185 | 21.01 | 6.71 | 28.99 | -0.334 |
| MdMLP10 | MD16G1025000 | 420 | Chr16:1802244..1802758(-) | 0.0007 | 139 | 15.78 | 5.33 | 27.31 | -0.394 |
| MdMLP11 | MD16G1025800 | 453 | Chr16:1839602..1840796(-) | 0.0017 | 150 | 17.05 | 5.47 | 11.39 | -0.386 |
| MdMLP12 | MD16G1026200 | 387 | Chr16:1862558..1863354(-) | 0.0022 | 128 | 14.68 | 6.14 | 20.19 | -0.303 |
| MdMLP13 | MD16G1088600 | 462 | Chr16:6094690..6095895(+) | 0.0006 | 153 | 16.92 | 4.97 | 23.39 | -0.145 |
Table 2 The MdMLP gene family in Malus × domestica and their basic characteristics
| 基因名称 Gene name | 基因组登录号 Gene accession No.(GDR) | 编码 区/bp CDS | 染色体位置 Chromosome location | 蛋白质 Protein | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 信号肽 Signal peptide (Sec/SPI) | 长度/ aa Length | 分子量/ kD Molecular weight | pI | 不稳定 指数 Instability index | 亲水性 Hydropa- thicity | ||||
| MdMLP1 | MD00G1063600 | 468 | Chr00:11768127..11768939(+) | 0.0011 | 155 | 17.62 | 5.32 | 27.52 | -0.576 |
| MdMLP2 | MD13G1022700 | 498 | Chr13:1627661..1629214(-) | 0.0021 | 165 | 18.68 | 5.52 | 22.52 | -0.444 |
| MdMLP3 | MD13G1022900 | 468 | Chr13:1645481..1646431(-) | 0.0011 | 155 | 17.62 | 5.32 | 27.52 | -0.576 |
| MdMLP4 | MD13G1023000 | 468 | Chr13:1657247..1658331(-) | 0.0016 | 155 | 17.45 | 5.32 | 26.36 | -0.497 |
| MdMLP5 | MD13G1088200 | 462 | Chr13:6177671..6178671(+) | 0.0006 | 153 | 16.83 | 5.26 | 22.52 | -0.137 |
| MdMLP6 | MD16G1024000 | 474 | Chr16:1729158..1730220(-) | 0.0012 | 157 | 17.58 | 8.43 | 37.24 | -0.258 |
| MdMLP7 | MD16G1024100 | 462 | Chr16:1731391..1732218(-) | 0.0011 | 153 | 17.27 | 4.88 | 30.74 | -0.381 |
| MdMLP8 | MD16G1024300 | 468 | Chr16:1742688..1743368(-) | 0.0007 | 155 | 17.57 | 4.88 | 30.00 | -0.338 |
| MdMLP9 | MD16G1024900 | 558 | Chr16:1792284..1793136(-) | 0.0022 | 185 | 21.01 | 6.71 | 28.99 | -0.334 |
| MdMLP10 | MD16G1025000 | 420 | Chr16:1802244..1802758(-) | 0.0007 | 139 | 15.78 | 5.33 | 27.31 | -0.394 |
| MdMLP11 | MD16G1025800 | 453 | Chr16:1839602..1840796(-) | 0.0017 | 150 | 17.05 | 5.47 | 11.39 | -0.386 |
| MdMLP12 | MD16G1026200 | 387 | Chr16:1862558..1863354(-) | 0.0022 | 128 | 14.68 | 6.14 | 20.19 | -0.303 |
| MdMLP13 | MD16G1088600 | 462 | Chr16:6094690..6095895(+) | 0.0006 | 153 | 16.92 | 4.97 | 23.39 | -0.145 |
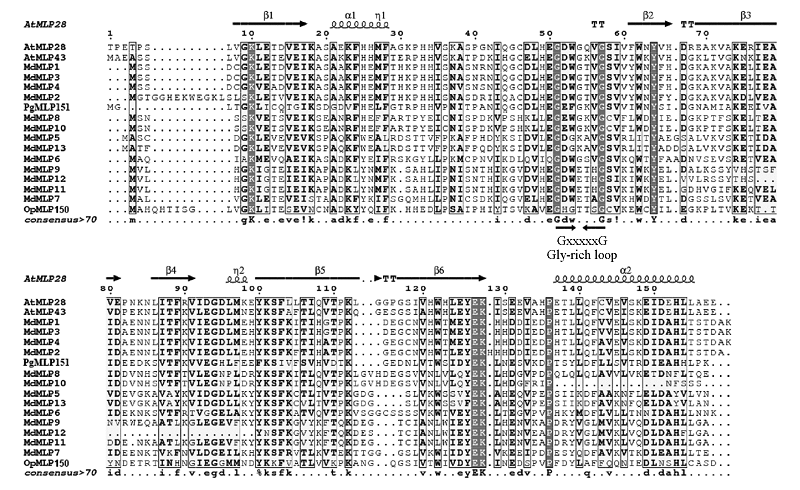
Fig. 1 Multiple sequence alignment of MLP protein from different species Md:Malus × domestica;At:Arabidopsis thaliana;Pg:Panax ginseng;Op:Papaver somniferum.
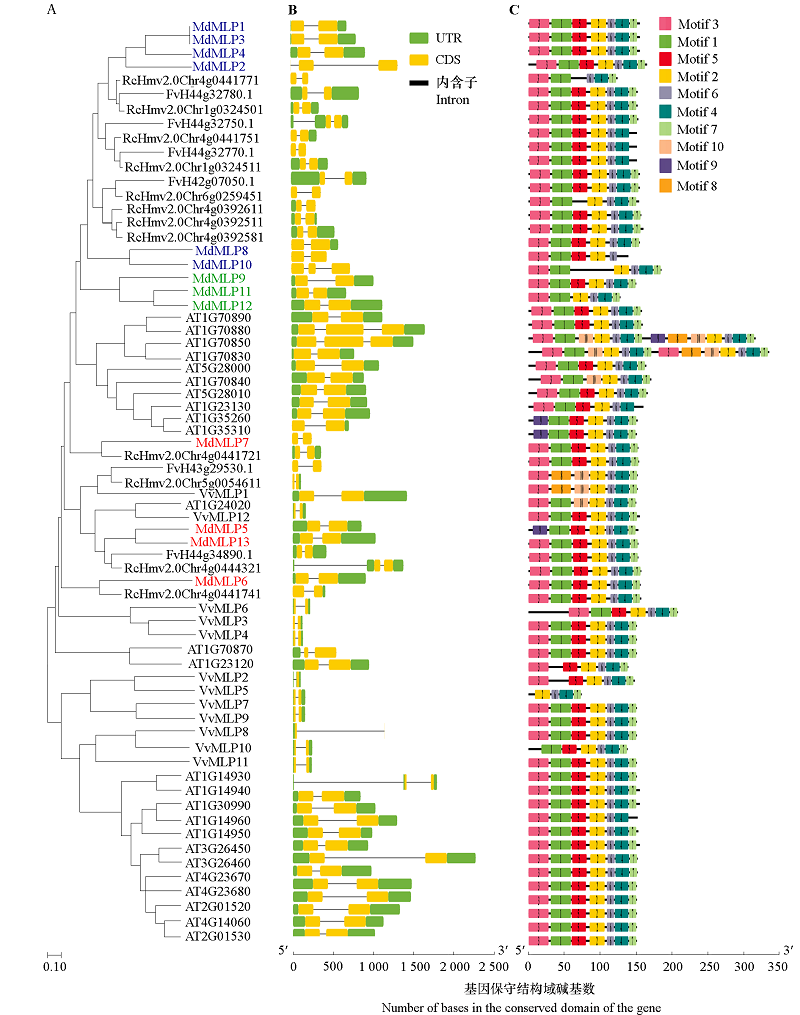
Fig. 3 Phylogenetic relationships,gene structure,architecture of conserved protein motifs in MLP genes from 5 species Md:Malus × domestica;At:Arabidopsis thaliana;Fv:Fragaria vesca;Vv:Vitis vinifera;RcH:Rosa.
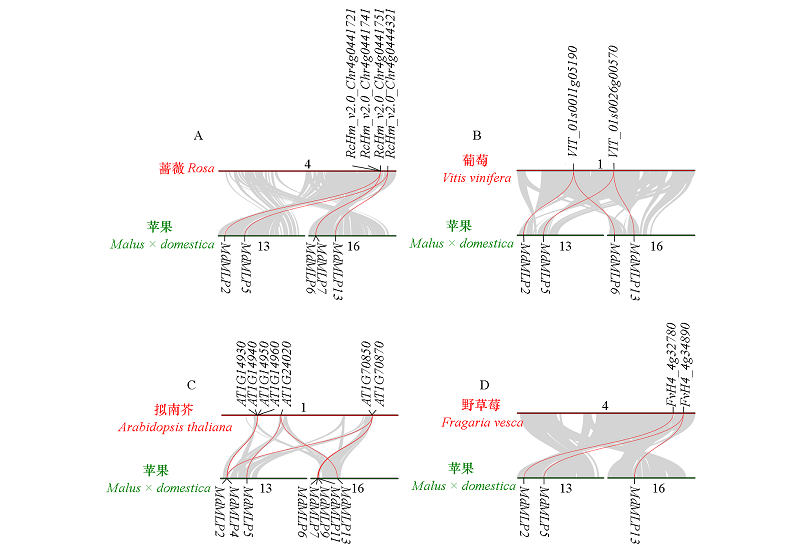
Fig. 4 Synteny analysis of MLP genes between apple and rose,grape,Arabidopsis and strawberry Gray lines in the background indicate the collinear blocks within genomes,while the red lines highlight the syntenic MLP gene pairs.

Fig. 5 Prediction of functional network of interacting proteins of MdMLP Based on Arabidopsis thaliana homologous proteins,String protein database was used to analyze the functional relationship network diagram of MdMLP1-MdMLP13 proteins,including AtMLP28(AT1G70830),AtMLP31(AT1G70840),AtMLP34(AT1G70850),AtMLP43(AT1G70890),AtMLP328(AT2G01520)and AtMLP423(AT1G24020).
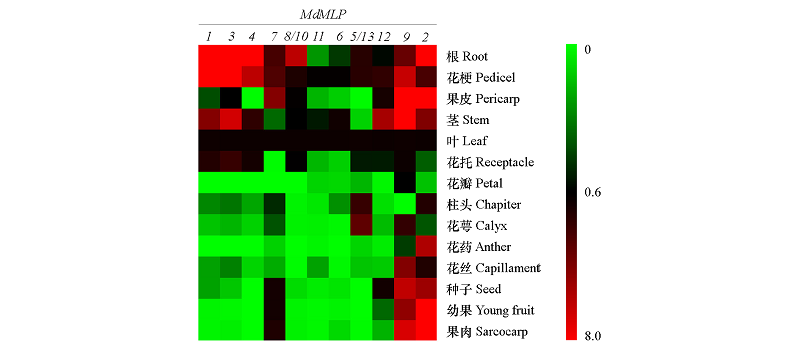
Fig. 6 Expression levels in different organs of‘Xinjiang 1’of MdMLP in apple The expression of MdMLP in leaves was 1,and the data was calculated based on the 2-??Ct method,and three replicates were set.
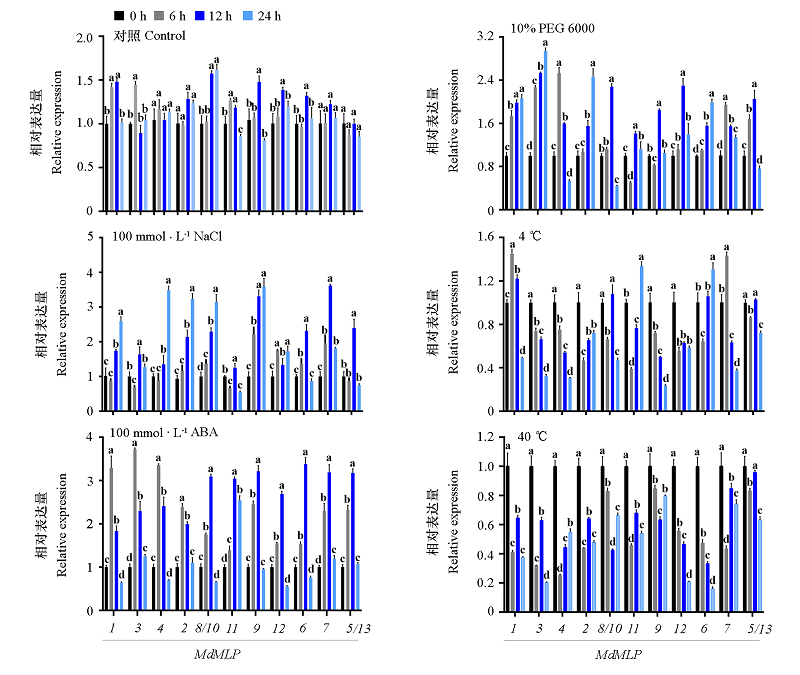
Fig. 7 Expression of MdMLP genes in apple cultured under different abiotic stress The expression level of MdMLPs at 0 hour was set as 1,and the data was calculated based on the 2-??Ct method,and three replicates were set. The difference between the same gene and different treatment time was analyzed with a confidence interval of 5%(P < 0.05).
| [1] |
Benedetto R, Fiorenza Z, Silvana P, Angela R, Serena V, Pietro T, Giovannoni J, Angelo R. 2002. Characterization of a major latex protein(MLP)gene down-regulated by ethylene during peach fruitlet abscission. Plant Science, 163:265-272.
doi: 10.1016/S0168-9452(02)00094-8 URL |
| [2] | Bong K P, Jin H C, Jong S J, Seong H B, Tae R H. 2007. Comparative proteomic analysis of blue light signaling components in the Arabidopsis Cryptochrome 1 mutant. Molecules and Cells, 23:154-160. |
| [3] | Cai J J, Huang H J, Xu X Z, Zhu G H. 2020. An Arabidopsis WD40 repeat-containing protein XIW1 promotes salt inhibition of seed germination. Plant Signaling & Behavior,Doi: 10.1080/15592324.2020.1712542. |
| [4] |
Chen J Y, Dai X F. 2010. Cloning and characterization of the Gossypium hirsutum major latex protein gene and functional analysis in Arabidopsis thaliana. Planta, 231:861-873.
doi: 10.1007/s00425-009-1092-2 URL |
| [5] |
Choi S H, Hong M K, Kim H J, Ryoo N, Rhim H, Nah S Y, Kang L W. 2015. Structure of ginseng major latex-like protein 151 and its proposed lysophosphatidic acid-binding mechanism. Biological Crystallography, 71:1039-1050.
doi: 10.1107/S139900471500259X URL |
| [6] | Craig L N, Wolfgang G W, Lawrence E P. 1990. Isolation and analysis of the major latex protein genes of opium poppy. Plant Molecular Biology Update Plant Molccular Biology, 15:951-953. |
| [7] | D’Avino R, Bernardi M L, Wallner M, Palazzo P, Camardella L, Tuppo L, Alessandri C, Breiteneder H, Ferreira F, Ciardiello M A, Mari A. 2011. Kiwifruit Act d 11 is the first member of the ripening-related protein family identified as an allergen. Allergy,Doi: 10.1111/j.1398-9995.2011.02555.x. |
| [8] |
Griffing L P, Nessler C L. 1989. Immunolocalization of the major latex proteins in developing laticifers of opium poppy(Papaver somniferum L.). Plant Physiol, 134:357-363.
doi: 10.1016/S0176-1617(89)80256-1 URL |
| [9] |
Guo D, Wong W S, Xu W Z, Sun F F, Qing D J, Li N. 2011. cis-Cinnamic acid-enhanced 1 gene plays a role in regulation of Arabidopsis bolting. Plant Mol Biol, 75:481-495.
doi: 10.1007/s11103-011-9746-4 URL |
| [10] |
Inui H, Sawada M, Goto J, Yamazaki K, Kodama N, Tsuruta H, Eun H. 2013. A major latex-like protein is a key factor in crop contamination by persistent organic pollutants. Plant Physiology, 161:2128-2135.
doi: 10.1104/pp.112.213645 URL |
| [11] |
Javier P, Romero M K, Guy H, Marie L S, Beatrice M, Rodolphe S. 1995. Characterization of a family of genes encoding a fruit-specific wound-stimulated protein of bell pepper(Capsicum annuum):identification of a new family of transposable elements. Plant Molecular Biology, 28:1011-1025.
doi: 10.1007/BF00032663 URL |
| [12] | Khalid M H B, Raza M A, Yu H Q, Khan I, Sun F A, Feng L Y, Qu J T, Fu F L, Li W C. 2019. Expression,subcellular localization,and interactions of CPK family genes in maize. International Journal of Molecular Sciences,Doi: 10.3390/ijms20246173. |
| [13] |
Kim H S, Yu Y, Snesrud E C, Moy L P, Linford L D, Haas B J, Nierman W C, Quackenbush J. 2010. Transcriptional divergence of the duplicated oxidative stress-responsive genes in the Arabidopsis genome. Plant J, 41:212-220.
doi: 10.1111/tpj.2005.41.issue-2 URL |
| [14] |
Kimbrough J M, Salinasmondragon R, Boss W F, Brown C S, Sederoff H W. 2004. The fast and transient transcriptional network of gravity and mechanical stimulation in the Arabidopsis root apex1. Plant Physiol, 136:2790-2805.
pmid: 15347791 |
| [15] |
Konstantinidis K T, Tiedje J M. 2004. Trends between gene content and genome size in prokaryotic species with larger genomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 101:3160-3165.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.0308653100 URL |
| [16] | Kumar S, Pandey A K. 2013. Chemistry and biological activities of flavonoids:an overview. The Scientific World Journal, 16:27-50. |
| [17] | Li Rong. 2018. Investigation on Major Latex Protein 423(MdMLP423)from apple in response to abiotic stress[M. D. Dissertation]. Tai’an:Shandong Agricultural University. (in Chinese) |
| 李荣. 2018. 苹果乳胶蛋白MdMLP423响应非生物胁迫的研究[硕士论文]. 泰安:山东农业大学. | |
| [18] |
Litholdo C G, Parker B L, Eamens A L, Larsen M R, Cordwell S J, Waterhouse P M. 2016. Proteomic identification of putative microRNA394 target genes in Arabidopsis thaliana Identifies Major Latex Protein family members critical for normal development. Mol Cell Proteomics, 15:2033-2047.
doi: 10.1074/mcp.M115.053124 URL |
| [19] | Lynch M, Conery J S. 2003. The origins of genome complexity. Sci, 302:1401-1404. |
| [20] | Lytle B L, Song J, Cruz N B D L, Peterson F C, Volkman B F. 2010. Structures of two Arabidopsis thaliana Major Latex Proteins represent novel Helix-Grip folds. Proteins Structure Function & Bioinformatics, 76:237-243. |
| [21] | Miao Lili, Liu Xiulin, Zhang Hongji, Mao Xinguo, Jing Ruilian. 2019. Research progress on SnRK2,a multi-functional plant regulator. Journal of Triticeae crop, 39(7):787-793.(in Chinese) |
| 苗丽丽, 刘秀林, 张宏纪, 毛新国, 景蕊莲. 2019. 植物多功能调控因子SnRK2研究进展. 麦类作物学报, 39(7):787-793. | |
| [22] |
Mirza O, Henriksen A, Ipsen H, Larsen J N, Wissenbach M, Spangfort M D, Gajhede M. 2000. Dominant epitopes and allergic cross-reactivity:complex formation between a fab fragment of a monoclonal murine IgG antibody and the major allergen from birch pollen Bet v 1. The Journal of Immunology, 165:331-338.
doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.165.1.331 URL |
| [23] |
Nam Y W, Tichit L, Leperlier M, Cuerq B, Marty I, Lelièvre J M. 1999. Isolation and characterization of mRNAs differentially expressed during ripening of wild strawberry(Fragaria vesca L.)fruits. Plant Mol Biol, 39:629.
pmid: 10092188 |
| [24] |
Nessler C L, Allen R D, Galewsky S. 1985. Identification and characterization of Latex-specific proteins in opium poppy. Plant Physiol, 79:499-504.
pmid: 16664439 |
| [25] |
Niu D K, Jiang L. 2013. Can ENCODE tell us how much junk DNA we carry in our genome? Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 430:1340-1343.
doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2012.12.074 URL |
| [26] |
Osmark P, Boyle B, Brisson N. 1998. Sequential and structural homology between intracellular pathogenesis-related proteins and a group of latex proteins. Plant Mol Biol, 38:1243.
pmid: 9869429 |
| [27] |
Pasternak O, Bujacz G D, Fujimoto Y, Hashimoto Y, Jelen F, Otlewski J, Sikorski M M, Jaskolski M. 2006. Crystal structure of Vigna radiata cytokinin-specific binding protein in complex with zeatin. The Plant Cell, 18:2622-2634.
doi: 10.1105/tpc.105.037119 URL |
| [28] | Seyyed K K, Sahar F, Hamid N Z. 2020. Identification and in silico evaluation of bHLH genes in the Sesamum indicum genome:growth regulation and stress dealing specially through the metal ions homeostasis and flavonoid biosynthesis. Gene Reports,Doi: 10.1016/j.genrep.2020.100639. |
| [29] |
Spangfort M D, Mirza O, Ipsen H, Neerven R J, Gajhede M, Larsen J N. 2003. Dominating Ig E-binding epitope of Bet_v_1,the major allergen of birch pollen,characterized by X-ray crystallography and site-directed mutagenesis. The Journal of Immunology, 171:3084-3090.
doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.171.6.3084 URL |
| [30] | Takuro S K Y, Hitoshi M, Kiyotoshi T, Yamaki S. 1999. Cloning cDNAs for genes preferentially expressed during fruit growth in cucumber. Jamer Sochort Sci, 124:136-139. |
| [31] |
Wang Y, Yang L, Chen X, Ye T, Zhong B, Liu R, Wu Y, Chan Z. 2015. Major latex protein-like protein 43(MLP43)functions as a positive regulator during abscisic acid responses and confers drought tolerance in Arabidopsis thaliana. Journal of Experimental Botany, 67:421-434.
doi: 10.1093/jxb/erv477 URL |
| [32] | Wang Wenjie, Wu Qiong, Wu Fangyun. 2016. Research progress on the activity of phenylalanine ammonia-lyase induced by mechanical injury in plants. Modern Agricultural Science and Technology,(1):157-160. (in Chinese) |
| 王文杰, 吴琼, 吴方云. 2016. 机械损伤诱导植物苯丙氨酸解氨酶活性研究进展. 现代农业科技,(1):157-158,160. | |
| [33] | Xu P, Zhang X Y, Su H, Liu X F, Wang Y F, Hong G J. 2020. Genome-wide analysis of PYL-PP2C-SnRK2s family in Camellia sinensis. Bioengineered,Doi: 10.1080/21655979.2019.1710932. |
| [34] |
Yang C L, Liang S, Wang H Y, Han L B, Wang F X, Cheng H Q, Wu X M, Qu Z L, Wu J H, Xia G X. 2015. Cotton Major Latex Protein 28 functions as a positive regulator of the ethylene responsive factor 6 in defense against Verticillium dahliae. Molecular Plant, 8:399-411.
doi: 10.1016/j.molp.2014.11.023 URL |
| [35] | Yuan G P, He S S, Bian S X, Han X L, Liu K, Cong P H, Zhang C X . 2020. Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of major latex protein(MLP)family genes in the apple(Malus domestica Borkh.)genome. Gene,Doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2019.144275. |
| [36] | Zuo Ran, Xu Meiling, Wen Zewen, Zhang Donguan. 2012. Study on the functions of plastid-specific ribosomal protein 4 gene(Psrp-4)of Arabidopsis in photosyntheticsis. Genomics and Applied Biology, 31(3):257-262. (in Chinese) |
| 左然, 徐美玲, 温泽文, 张东远. 2012. 拟南芥Psrp-4基因参与光合作用机制的研究. 基因组学与应用生物学, 31(3):257-262. | |
| [37] | Zhang N B, Li R M, Shen W, Jiao S Z, Zhang J X, Xu W R. 2018. Genome-wide evolutionary characterization and expression analyses of major latex protein(MLP)family genes in Vitis vinifera. Molecular Genetics & Genomics, 293:1-15. |
| [38] | Zhong R L, Wang Yu X, Gai R N, Xi D D, Mao C J, Ming F . 2020. Rice SnRK protein kinase OsSAPK8 acts as a positive regulator in abiotic stress responses. Plant Science,Doi: 10.1016/j.plantsci.2019.110373. |
| [1] | WANG Zhiyu, CHANG Beibei, LIU Qi, CHENG Xiaofan, DU Xiaoyun, YU Xiaoli, SONG Laiqing, ZHAO Lingling. Study on Expression and Anthocyanin Accumulation of Solute Carrier Gene MdSLC35F2-like in Apple [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(11): 2293-2303. |
| [2] | LI Shifan, SHAO Yuchun, QI Haonan, YANG Lan, LI Xiaowei, XU Bingliang, CHEN Yahan. Detection and Genetic Diversity Analysis of Apple Necrotic Mosaic Virus in Gansu Province [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(11): 2431-2438. |
| [3] | YU Lu, NIU Zimian, LI Quan, LIN Lu, WANG Hongning, LI Zhiqiang, LI Hongyan. A New Apple Dwarf Rootstock Cultivar‘Sc5’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(11): 2519-2520. |
| [4] | YU Jianqiang, GU Kaidi, WANG Chuanzeng, HU Dagang. Functional Characterization of An Apple Pyrophosphate-dependent Phosphofructokinase Gene MdPFPβ in Regulating Soluble Sugar Accumulation [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(10): 2223-2235. |
| [5] | SUN Jiamao, CUI Quanshi, WANG Yuqing, SI Yajing, SHI Yufan, BU Haidong, YUAN Hui, and WANG Aide. Effects of Brassinolides and Methyl Jasmonate Spraying on the Postharvest Quality of Apple Fruit [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(10): 2236-2248. |
| [6] | YANG Bo, WEI Jia, LI Kunfeng, WANG Chengliang, NI Junbei, TENG Yuanwen, and BAI Songling. PpyERF060-PpyABF3-PpyMADS71 Regulates Ethylene Signaling Pathway- Mediated Pear Bud Dormancy Process [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(10): 2249-2262. |
| [7] | DING Zhijie, BAO Jinbo, ROUXIAN Guli, ZHU Tiantian, LI Xueli, MIAO Haoyu, TIAN Xinmin. Comparative Chloroplast Genome Study of Mallus servisii‘Red Delicious’and‘Golden Delicious’ [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(9): 1977-1990. |
| [8] | GAO Yanlong, WU Yuxia, ZHANG Zhongxing, WANG Shuangcheng, ZHANG Rui, ZHANG De, WANG Yanxiu. Bioinformatics Analysis of Apple ELO Gene Family and Its Expression Analysis Under Low Temperature Stress [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(8): 1621-1636. |
| [9] | ZHENG Xiaodong, XI Xiangli, LI Yuqi, SUN Zhijuan, MA Changqing, HAN Mingsan, LI Shaoxuan, TIAN Yike, WANG Caihong. Effects and Regulating Mechanism of Exogenous Brassinosteroids on the Growth of Malus hupehensis Under Saline-alkali Stress [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(7): 1401-1414. |
| [10] | XIA Yan, HUANG Song, WU Xueli, LIU Yiqi, WANG Miaomiao, SONG Chunhui, BAI Tuanhui, SONG Shangwei, PANG Hongguang, JIAO Jian, ZHENG Xianbo. Identification and Analysis of Apple Viruses Diseases Based on Virome Sequencing Technology [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(7): 1415-1428. |
| [11] | LIU Zhaoxia, ZHANG Xin, WANG Lu, MA Yuting, CHEN Qian, ZHU Zhanling, GE Shunfeng, JIANG Yuanmao. Effects of Fertilizer Hole Application Sites on Fine Root Growth,15N Absorption and Utilization,Yield and Quality of Apple Trees [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(7): 1545-1556. |
| [12] | MA Weifeng, LI Yanmei, MA Zonghuan, CHEN Baihong, MAO Juan. Identification of Apple POD Gene Family and Functional Analysis of MdPOD15 Gene [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(6): 1181-1199. |
| [13] | FENG Chen, HUANG Xuewang, LI Xingliang, ZHOU Jia, LI Tianhong. Comparative Study on Drought Resistance of Different Apple Dwarfing Rootstock and Scion Combinations [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(5): 945-957. |
| [14] | ZHANG Xiaoyun, TANG Yuwei, WANG Kai, ZHANG Dong, YANG Weiwei. Simulation Analysis of Effects of Shoot Type Composition on Canopy Light Interception Efficiency and Photosynthetic Productivity in Apple Trees [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(4): 709-722. |
| [15] | YU Bo, QIN Sijun, LÜ Deguo. Continuous Supply of Zinc in Suitable Level Stimulates the Growth and Absorption and Utilization of Nitrogen in Malus hupehensis Seedlings [J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(3): 473-481. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
Copyright © 2012 Acta Horticulturae Sinica 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
Tel: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
Support by: Beijing Magtech Co.Ltd