
园艺学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 49 ›› Issue (11): 2336-2346.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2021-0804
莫翠萍1, 吴自林2, 郭泳仪1, 张曙光1, 李鹏飞1, 李华平1,*( )
)
收稿日期:2022-04-22
修回日期:2022-07-15
出版日期:2022-11-25
发布日期:2022-11-25
通讯作者:
李华平
E-mail:huaping@scau.edu.cn
基金资助:
MO Cuiping1, WU Zilin2, GUO Yongyi1, ZHANG Shuguang1, LI Pengfei1, LI Huaping1,*( )
)
Received:2022-04-22
Revised:2022-07-15
Online:2022-11-25
Published:2022-11-25
Contact:
LI Huaping
E-mail:huaping@scau.edu.cn
摘要:
商业化的抗番木瓜环斑病毒(papaya ringspot virus,PRSV)的转基因番木瓜品种‘华农1号’的应用成功控制了华南地区该毁灭性病毒。然而近年来在广东和海南的一些转基因或非转基因植株上发现了另一种具有严重危害的病毒——番木瓜畸形花叶病毒(papaya leaf distortion mosaic virus,PLDMV)。为了明确这两种病毒在番木瓜上的相互关系,通过人工接种分析二者在转基因和非转基因番木瓜上的侵染率、症状、细胞病理变化以及病毒积累量等特征。结果表明,‘华农1号’对PRSV有很强的抗性,但对PLDMV却高度感病,且PLDMV并不能协助PRSV克服转基因番木瓜对其的抗性;两种病毒单独侵染和复合侵染非转基因番木瓜均能引致严重的症状,二者症状无明显差异。细胞病理学分析表明,病毒侵染后叶片叶绿体萎缩且排列不紧凑,复合侵染并未对叶肉细胞造成更为严重的损害。接种PRSV的转基因番木瓜15 d后PRSV积累量逐渐减少,直至检测不到;而接种PLDMV后其积累量逐渐升高并保持在一个较高的水平。在转基因和非转基因番木瓜上,PRSV的积累量始终低于PLDMV,在非转基因番木瓜上,两种病毒长期共存,并各自维持相应的病毒含量。这些结果表明,抗PRSV的转基因番木瓜‘华农1号’不抗PLDMV;PRSV和PLDMV复合侵染没有在番木瓜植株中发生协生关系,表现为中性互作。
中图分类号:
莫翠萍, 吴自林, 郭泳仪, 张曙光, 李鹏飞, 李华平. 番木瓜PRSV和PLDMV复合侵染中呈中性互作[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(11): 2336-2346.
MO Cuiping, WU Zilin, GUO Yongyi, ZHANG Shuguang, LI Pengfei, LI Huaping. The Neutral Interaction of Co-infection Papaya Between Papaya Ringspot Virus and Papaya Leaf Distortion Mosaic Virus[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(11): 2336-2346.
| 病毒 Virus | 引物 Name | 引物序列 Primer sequence | 大小/bp Size |
|---|---|---|---|
| PRSV | PRSV | F:CTTCAACAGGGCTTTCTTGC;R:GAATTACCAAGAACAATGTG | 927 |
| PRSV-q1 | F:GACATATCTGGTGTCTGGGTAATGATG;R:GCGGCATGTACCTCTCAGTT | 128 | |
| PLDMV | PLDMV | F:TCCGCTCTTGATGCTGGCAAATCC;R:CGGTGAGGTTCCGTTGAATAC | 652 |
| PLDMV-q1 | F:GGAAAACGCAAAGCCCACTT;R:CGGTGAGGTTCCGTTGAATAC | 169 | |
| chy | chy | F:ATCTACAATCTTGCTAACCCTA;R:AGTCATCTTGAGAATAACCCAC | 281 |
| Chy-q | F:CGGATCCTCCCATTTCCCTT; R:CCCACGGTGTAAAAATCAGCAG | 151 |
表1 番木瓜病毒检测引物
Table 1 Primer for RT-PCR and RT-qPCR of papaya virus
| 病毒 Virus | 引物 Name | 引物序列 Primer sequence | 大小/bp Size |
|---|---|---|---|
| PRSV | PRSV | F:CTTCAACAGGGCTTTCTTGC;R:GAATTACCAAGAACAATGTG | 927 |
| PRSV-q1 | F:GACATATCTGGTGTCTGGGTAATGATG;R:GCGGCATGTACCTCTCAGTT | 128 | |
| PLDMV | PLDMV | F:TCCGCTCTTGATGCTGGCAAATCC;R:CGGTGAGGTTCCGTTGAATAC | 652 |
| PLDMV-q1 | F:GGAAAACGCAAAGCCCACTT;R:CGGTGAGGTTCCGTTGAATAC | 169 | |
| chy | chy | F:ATCTACAATCTTGCTAACCCTA;R:AGTCATCTTGAGAATAACCCAC | 281 |
| Chy-q | F:CGGATCCTCCCATTTCCCTT; R:CCCACGGTGTAAAAATCAGCAG | 151 |
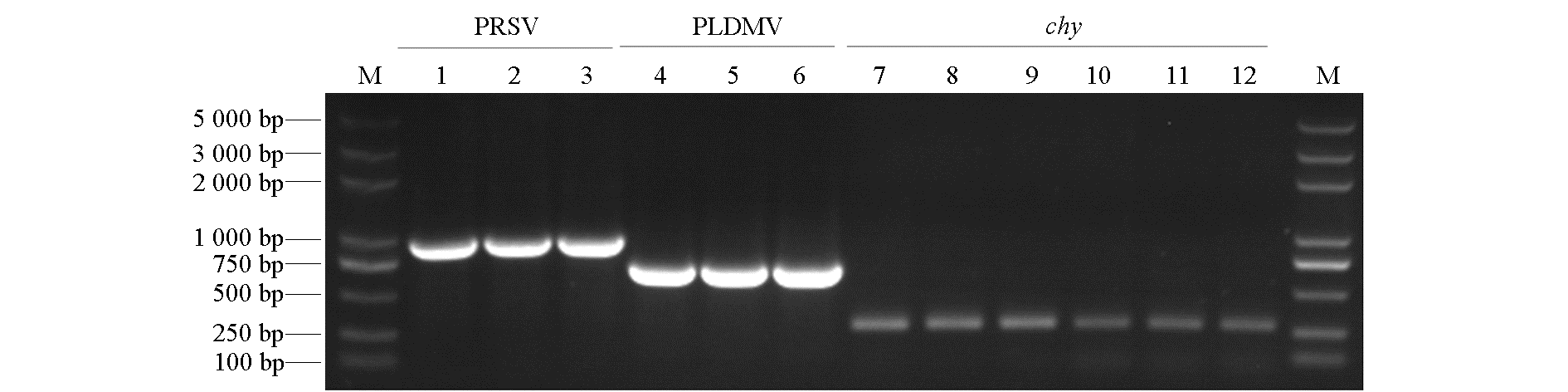
图1 PRSV和PLDMV侵染番木瓜植株的部分样品RT-PCR的检测结果 M:DL2000 plus;chy:番木瓜内参基因。
Fig. 1 RT-PCR detection of PRSV and PLDMV from some infected samples of papaya plants M:DL2000 plus marker;chy:Internal reference gene of papaya.
| 处理 Treatment | 华农1号Huanong 1 | 巴西Baxi | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PRSV | PLDMV | PRSV | PLDMV | |
| Mock(健康对照Healthy control) | 0 b | 0 b | 0 b | 0 b |
| PRSV | 8.70 ±1.30 a | 0 b | 94.07 ± 3.23 a | 0 b |
| PLDMV | 0 b | 94.07 ± 3.23 a | 0 b | 100 ± 0 a |
| PRSV + PLDMV | 3.61 ± 1.95 b | 96.28 ± 3.72 a | 97.22 ± 2..78 a | 98.61 ± 1.39 a |
| PRSV→PLDMV | 0 b | 96.76 ± 1.67 a | 90.74 ± 9.26 a | 100 ± 0 a |
| PLDMV→PRSV | 1.85 ± 1.85 b | 100 ± 0 a | 100 ± 0 a | 100 ± 0 a |
表2 番木瓜‘华农1号’和‘巴西’接种PRSV和PLDMV后的侵染率
Table 2 Statistical table of incidence of PRSV and PLDMV on‘Huanong 1’and‘Baxi’papaya %
| 处理 Treatment | 华农1号Huanong 1 | 巴西Baxi | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PRSV | PLDMV | PRSV | PLDMV | |
| Mock(健康对照Healthy control) | 0 b | 0 b | 0 b | 0 b |
| PRSV | 8.70 ±1.30 a | 0 b | 94.07 ± 3.23 a | 0 b |
| PLDMV | 0 b | 94.07 ± 3.23 a | 0 b | 100 ± 0 a |
| PRSV + PLDMV | 3.61 ± 1.95 b | 96.28 ± 3.72 a | 97.22 ± 2..78 a | 98.61 ± 1.39 a |
| PRSV→PLDMV | 0 b | 96.76 ± 1.67 a | 90.74 ± 9.26 a | 100 ± 0 a |
| PLDMV→PRSV | 1.85 ± 1.85 b | 100 ± 0 a | 100 ± 0 a | 100 ± 0 a |
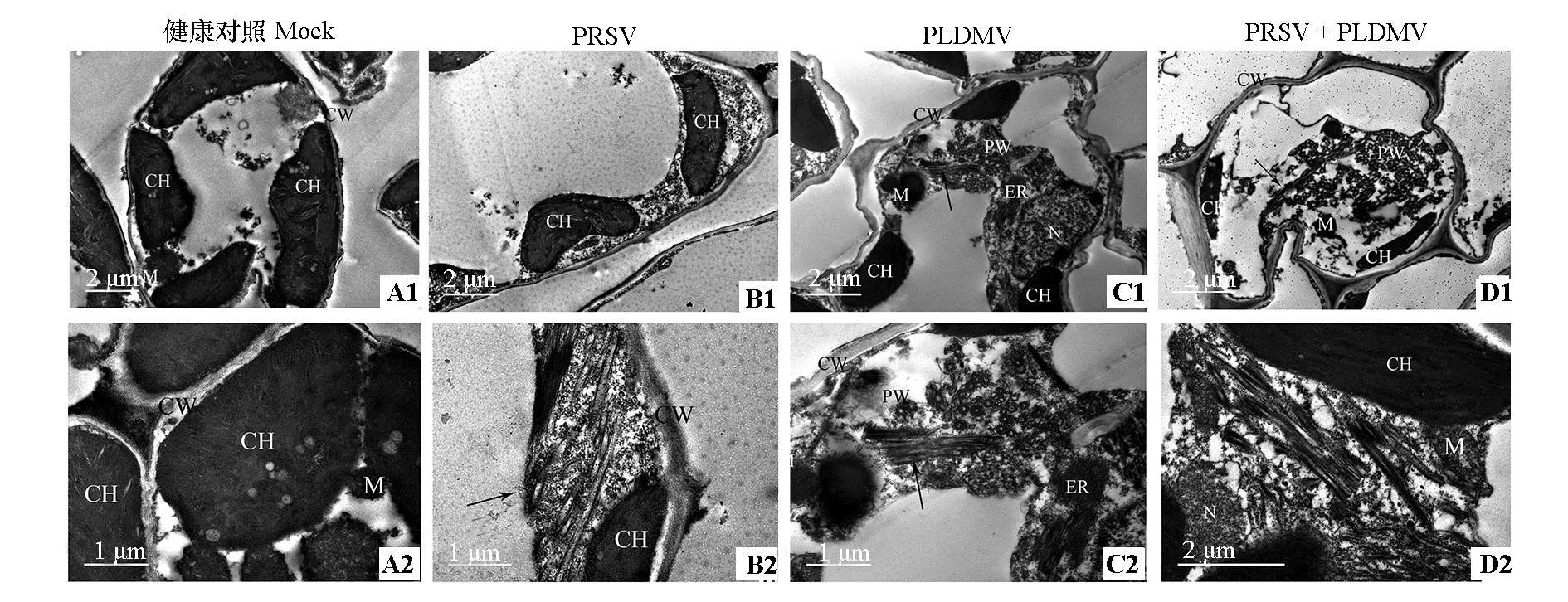
图4 番木瓜PRSV和PLDMV单独及复合侵染60 d叶肉细胞的透射电镜图 A1、A2:相同生育期健康番木瓜叶肉细胞(对照);B1、B2:PRSV单独侵染,叶绿体排列不紧凑;C1、C2:PLDMV单独侵染,叶肉细胞形状不规则,叶绿体萎缩且不紧凑,可见到典型的风轮状内含体和线状病毒粒子;D1、D2:复合侵染,叶绿体萎缩不紧凑,细胞被挤压形状不规则,有大量的风轮状内含体。M:线粒体;N:细胞核;CH:叶绿体;CW:细胞壁;ER:内质网;PW:风轮状体;箭头:线状病毒粒子。
Fig. 4 The cytopathology of mesophyll cell from papaya plants infected with PRSV or PLDMV and co-infected with both viruses at 60 dpi A:Mesophyll cells from healthy papaya at the same growth duration;B:Mesophyll cells from papaya infected with PRSV,chloroplast is arranged separately;C:Mesophyll cells from papaya infected with PLDMV,the shape of mesophyll cells is irregular,and they fill with the typical pinwheels and filamentous virus particles;D:Mesophyll cells from papaya co-infected with both viruses,chloroplast atrophy is not compact,the shape of cells are extruded irregular with a lot of pinwheels-like inclusions. M:Mitochondria;N:Nucleus;CH:Chloroplast;CW:Cell wall;ER:Endoplasmic reticulum;PW:Pinwheel;arrow:Filamentous virus particles.
| [1] |
Bau H J, Kung Y J, Raja J A J, Chan S J, Chen K C, Chen Y K, Wu H W, Yeh S D. 2008. Potential threat of a new pathotype of papaya leaf distortion mosaic virus infecting transgenic papaya resistant to papaya ringspot virus. Phytopathology, 98 (7):848-856.
doi: 10.1094/PHYTO-98-7-0848 pmid: 18943262 |
| [2] | Cai Jian-he, Fan Huai-zhong. 1994. Investigation and identification of papaya virus disease and papaya ringspot virus strain in south China. Journal of South China Agricultural University, 5 (4):13-17. (in Chinese) |
| 蔡建和, 范怀忠. 1994. 华南番木瓜病毒病及环斑病毒株系的调查鉴定. 华南农业大学学报, 15 (4):13-17. | |
| [3] |
Chávez-Calvillo G, Contreras-Paredes C A, Mora-Macias J, Noa-Carrazana J C, Serrano-Rubio A A, Dinkova T D, Carrillo-Tripp M, Silva-Rosales L. 2016. Antagonism or synergism between papaya ringspot virus and papaya mosaic virus in Carica papaya is determined by their order of infection. Virology, 489:179-191.
doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2015.11.026 pmid: 26765969 |
| [4] |
Cuellar W J, Galvez M, Fuentes S, Tugume J, Kreuze J. 2014. Synergistic interactions of begomoviruses with sweet potato chlorotic stunt virus (genus Crinivirus)in sweet potato(Ipomoea batatas L.). Molecular Plant Pathology, 16 (5):1.
doi: 10.1111/mpp.12155 URL |
| [5] |
Damirdagh I S, Ross A F. 1967. A marked synergistic interaction of PVX and PVY in inoculated leaves of tobacco. Virology, 31 (2):296-307.
pmid: 6021096 |
| [6] |
Dietrich C, Maiss E. 2003. Fluorescent labelling reveals spatial separation of potyvirus populations in mixed infected Nicotiana benthamiana plants. Journal of General Virology, 84 (10):2871-2876.
doi: 10.1099/vir.0.19245-0 URL |
| [7] |
Elena S F, Bernet G P, Carrasco J L. 2014. The games plant viruses play. Current Opinion in Virology, 8 (1):62-67.
doi: 10.1016/j.coviro.2014.07.003 URL |
| [8] |
García-Viera M A, Sánchez-Segura L, Chavez-Calvillo G, Jarquín-Rosales D, Silva-Rosales L. 2017. Changes in leaf tissue of Carica papaya during single and mixed infections with papaya ringspot virus and papaya mosaic virus. Biologia plantarum, 62 (1):173-180.
doi: 10.1007/s10535-017-0741-8 URL |
| [9] |
Gonsalves D. 1998. Control of papaya ringspot virus in papaya:a case study. Annual Review of Phytopathology, 36 (1):415-437.
doi: 10.1146/annurev.phyto.36.1.415 URL |
| [10] |
Goodman R M, Ross A F. 1974. Enhancement by PVY of PVX synthesis in doubly infected tobacco depends on the timing of invasion by the viruses. Virology, 58 (1):263-271.
pmid: 4821699 |
| [11] | Green M R, Sambrook J. 2017. Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual. 4th ed. He F C trans trans. Beijing:Science Press: 509-545. |
| Green M R, Sambrook J. 2017. 分子克隆实验指南. 第4版. 贺福初译. 北京:科学出版社: 509-545. | |
| [12] |
Guo J, Yang L, Liu X, Guan X, Jiang L, Zhang D. 2009. Characterization of the exogenous insert and development of event-specific PCR detection methods for genetically modified‘Huanong No. 1’papaya. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 57 (16):7205-7212.
doi: 10.1021/jf901198x URL |
| [13] |
Hammond J, Lecoq H, Raccah B. 1999. Epidemiological risks from mixed virus infections and transgenic plants expressing viral genes. Advances in Virus Research, 54:189-314.
pmid: 10547677 |
| [14] | Kawano S, Yonaha T. 1992. The occurrence of papaya leaf-distortion mosaic virus in Okinawa. Tech Bull of FFTC, 132:13-23. |
| [15] | Ke Chong, Chen Hui, Chen Yuan-zhong, Zhang Lian-jun. 1979. Electron microscopic observations of papaya ringspot mosaic disease in fruit. Acta Phytopathologica Sinica, 9 (1):33-36. (in Chinese) |
| 柯冲, 陈辉, 陈元忠, 章连均. 1979. 番木瓜环斑花叶病的电镜观察. 植物病理学报, 9 (1):33-36. | |
| [16] |
Kokkinos C D, Clark C A. 2007. Interactions among sweet potato chlorotic stunt virus and different potyviruses and potyvirus strains infecting sweet potato in the United States. Plant Disease, 90 (10):1347-1352.
doi: 10.1094/PD-90-1347 URL |
| [17] | Li He-ping. 2009. Plant micro technology. 2nd ed. Beijing:Science Press:258. |
| 李和平. 2009. 植物显微技术. 第2版. 北京:科学出版社:258. | |
| [18] | Li Hua-ping, Zhang Shu-guang, Rao Xue-qin, Ruan Xiao-lei, Zhou Guo-hui, Fan Huai-zhong. 2007. Safety evaluation of transgenic papaya ‘Huanong No.1’resistant to PRSV//Proceedings of The Annual Meeting of The Chinese Society For Plant Pathology:209-212. (in Chinese) |
| 李华平, 张曙光, 饶雪琴, 阮小蕾, 周国辉, 范怀忠. 2007. 抗病毒转基因番木瓜华农1号的安全性评价//中国植物病理学会2007年学术年会:209-212. | |
| [19] |
Li S, Zhang T, Zhu Y, Zhou G. 2017. Co-infection of two reoviruses increases both viruses accumulation in rice by up-regulating of viroplasm components and movement proteins bilaterally and RNA silencing suppressor unilaterally. Virology Journal, 14 (1):150.
doi: 10.1186/s12985-017-0819-0 pmid: 28789694 |
| [20] | Liu Fang, Tuo De-cai, Shen Wen-tao, Yan Pu, Li Xiao-ying, Zhou Peng. 2016. Full genomic cDNA cloning and real-time fluorescence quantitative analysis of mixed infection between papaya ringspot virus and papaya leaf distortion mosaic virus. Chinese Journal of Tropical Crops, 37 (4):742-751.. (in Chinese) |
| 刘芳, 庹德财, 沈文涛, 言普, 黎小瑛, 周鹏. 2016. 混合感染番木瓜PRSV/PLDMV株系基因组全长cDNA的克隆和实时荧光定量PCR分析. 热带作物学报, 37 (4):742-751. | |
| [21] |
Maoka T, Kashiwazaki S, Tsuda S, Usugi T, Hibino H. 1996. Nucleotide sequence of the capsid protein gene of papaya leaf distortion mosaic potyvirus. Archives of Virology, 141 (1):197-204.
pmid: 8629948 |
| [22] |
Mascia T, Gallitelli D. 2016. Synergies and antagonisms in virus interactions. Plant Science, 252 (1):176-192.
doi: 10.1016/j.plantsci.2016.07.015 URL |
| [23] |
Mo C, Wu Z, Xie H, Zhang S, Li H. 2020. Genetic diversity analysis of papaya leaf distortion mosaic virus isolates infecting transgenic papaya “Huanong No. 1”in South China. Ecology and Evolution, 10 (20):11671-11683.
doi: 10.1002/ece3.6800 URL |
| [24] | Nguyen T T, Shaw P N, Parat M O, Hewavitharana A K. 2013. Anticancer activity of Carica papaya:a review. Molecular Nutrition & Food Research, 57 (1):153-164. |
| [25] | Power A G, Irwin M E. 1992. Patterns of virulence and benevolence in insect‐borne pathogens of plants. Critical Reviews in Plant Sciences, 4 (11):22. |
| [26] |
Rao X, Li Y, Ruan X, Yan C, Zhang S, Li H. 2012. Variation of neomycin phosphotransferase II marker gene in transgenic papaya plants under the field cultivation. Food Biotechnology, 26 (4):293-306.
doi: 10.1080/08905436.2012.723605 URL |
| [27] | Ren Pei-yu, Fan Huai-zhong. 1964. A preliminary study on papaya mosaic disease. Journal of Plant Protection, 3 (4):423. (in Chinese) |
| 任佩瑜, 范怀忠. 1964. 番木瓜环斑花叶病初步调查研究. 植物保护学报, 3 (4):423. | |
| [28] | Ruan Xiao-lei, Hou Yan, Li Hua-ping. 2010. Preliminary evaluation of food safety of transgenic papaya with the replicase gene of PRSV. Journal of Huazhong Agricultural University, 29 (3):381-386. (in Chinese) |
| 阮小蕾, 侯燕, 李华平. 2010. 转PRSV复制酶基因番木瓜食品安全性的初步评价. 华中农业大学学报, 29 (3):381-386. | |
| [29] |
Saeed F, Arshad M U, Pashab I, Naz R, Batool R, Khan A A, Nasirb M A, Shafique B. 2014. Nutritional and phyto-therapeutic potential of papaya (Carica papaya Linn.):an overview. International Journal of Food Properties, 17 (7):1637-1653.
doi: 10.1080/10942912.2012.709210 URL |
| [30] |
Tatineni S, Alexander J, Gupta Adarsh K, French R. 2018. Asymmetry in Synergistic Interaction between wheat streak mosaic virus and Triticum mosaic virus in wheat. Molecular Plant-Microbe Interactions, 32 (3):336-350.
doi: 10.1094/MPMI-07-18-0189-R URL |
| [31] |
Untiveros M, Fuentes S, Salazar L F. 2007. Synergistic Interaction of Sweet potato chlorotic stunt virus(Crinivirus)with Carla-,Cucumo-,Ipomo-,and Potyviruses infecting sweet potato. Plant Disease, 91 (6):669-676.
doi: 10.1094/PDIS-91-6-0669 pmid: 30780474 |
| [32] |
Vance V B. 1991. Replication of potato virus X RNA is altered in coinfections with potato virus Y. Virology, 182 (2):486-494.
pmid: 2024486 |
| [33] |
Wilhelm J, Pingoud A. 2003. Real-time polymerase chain reaction. Chem Bio Chem, 4 (11):1120-1128.
doi: 10.1002/cbic.200300662 URL |
| [34] |
Wu Z, Mo C, Zhang S, Li H. 2018. Characterization of papaya ringspot virus isolates infecting transgenic papaya‘Huanong No.1’in South China. Scientific Reports, 8 (1):8206-8217.
doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-26596-x URL |
| [35] | Wu Zi-lin, Li Hua-ping. 2016. Discovery and identification of papaya leaf distortion mosaic virus in Guangdong Province//Proceedings of the Annual Meeting of Chinese Society of Plant Pathology. Nanjing:267. (in Chinese) |
| 吴自林, 李华平. 2016. 广东省番木瓜畸形花叶病毒的发现与鉴定//中国植物病理学会2016年学术年会. 南京:267. | |
| [36] |
Xia Z, Zhao Z, Chen L, Li M, Zhou T, Deng C, Zhou Q, Fan Z. 2016. Synergistic infection of two viruses MCMV and SCMV increases the accumulations of both MCMV and MCMV-derived siRNAs in maize. Scientific Reports, 6 (1):20520-20531.
doi: 10.1038/srep20520 URL |
| [37] |
Yeh S D, Jan F J, Chiang C H, Doong T J, Chen M C, Chung P H, Bau H J. 1992. Complete nucleotide sequence and genetic organization of papaya ringspot virus RNA. Journal of General Virology, 73 (10):2531-2541.
doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-73-10-2531 URL |
| [38] | Yonaha T. 1977. Viruses isolated from papaya in Okinawa(Japan)1. Properties of papaya ringspot virus. Ball Coll Agric Univ Ryukyus, 23:115-124. |
| [39] | Zhang Yuliang, Huang Qixing, Guo Anping, Ceng Huicai, Zhao Hui, Kong Hua, Liu Zhixin. 2013. Occurrence and distribution of papaya ring spot virus and papaya leaf-distortion mosaic virus in Hainan Province. Chinese Journal of Tropical Crops, 34 (12):2436-2441. (in Chinese) |
| 张雨良, 黄启星, 郭安平, 曾会才, 赵辉, 孔华, 刘志昕. 2013. 海南番木瓜PRSV和PLDMV病毒发生情况及分子鉴定. 热带作物学报, 34 (12):2436-2441. | |
| [40] | Zhao Qin, Li Hua-Ping,Xie Da-Sen,He Xiao-Ming,Zhang Shu-Guang,Luo Shao-Bo. 2012. Preparation and application of the antiserum specific to the coat protein expressed prokatically of Papaya ring spot virus. Acta Horticulturae Sinice, 39 (8):1457-1464. (in Chinese) |
| 赵芹, 李华平, 谢大森, 何晓明, 张曙光, 罗少波. 2012. 番木瓜环斑病毒外壳蛋白基因原核表达蛋白的抗血清制备及其检测应用. 园艺学报, 39 (8):1457-1464. | |
| [41] |
Zhou C, Zhang X, Liu S, Wang Y, Li D, Yu J, Han C. 2017. Synergistic infection of BrYV and PEMV 2 increases the accumulations of both BrYV and BrYV-derived siRNAs in Nicotiana benthamiana. Scientific Reports, 7 (1):45132-45143.
doi: 10.1038/srep45132 URL |
| [1] | 周陈平, 杨敏, 郭金菊, 邝瑞彬, 杨护, 黄炳雄, 魏岳荣. 番木瓜成熟过程中全基因组DNA甲基化和转录组变化分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(3): 519-532. |
| [2] | 林晓敏, 彭梅芳, 范晓丽, 陈克贵. 四川成都地区复合侵染南瓜4种病毒的分子鉴定分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2021, 48(11): 2299-2310. |
| [3] | 郑巧玲, 申 威, 姚文孔, 徐伟荣, . 山葡萄低温诱导酵母双杂三框cDNA文库构建和VaCIPK18互作蛋白筛选鉴定[J]. 园艺学报, 2020, 47(12): 2301-2316. |
| [4] | 陈永萍1,高 峰2,申艳红3,赵湾湾4,陈桂信1,*,王 平4,*. 番木瓜ERF家族与果实成熟相关成员的分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2019, 46(2): 252-264. |
| [5] | 刘 微1,史晓斌2,唐 鑫2,张 宇2,张德咏2,周序国1,*,刘 勇2,*. 云南番茄褪绿病毒和番茄黄化曲叶病毒复合侵染的分子鉴定[J]. 园艺学报, 2018, 45(3): 552-560. |
| [6] | 赵丽玲,钟 静,尹跃艳,丁 铭*,张仲凯*. 两种菜豆金色花叶病毒属病毒复合侵染番茄及重组特征[J]. 园艺学报, 2016, 43(7): 1305-1314. |
| [7] | 潘亚南1,2,*,韩 剑1,2,*,吴海波3,吉艳玲4,王纯利5,刘 芳5,罗 明1,2,**,张祥林6. 新疆哈密瓜病毒的DAS-ELISA检测和分子鉴定[J]. 园艺学报, 2016, 43(6): 1107-1116. |
| [8] | 刘锴栋*,冯少娴,盘耀亮,黎海利,陈 燕,袁长春*. 番木瓜开花相关基因CpFT1及启动子的克隆与表达分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2016, 43(12): 2359-2368. |
| [9] | 吴淑华1,李廷芳1,赵文浩1,程兆榜1,郭青云4,赵统敏2,余文贵2,朱叶芹3,*,季英华1,*. 江苏省番茄黄化曲叶病毒和褪绿病毒复合侵染的分子检测[J]. 园艺学报, 2016, 43(1): 89-99. |
| [10] | 申艳红*,陈晓静,蔡雪玲,叶一江,耿姣姣,杨菲颖. 番木瓜半胱氨酸蛋白酶基因CpCP的分离及表达分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2015, 42(9): 1789-1797. |
| [11] | 熊 艳1,周常勇1,2,*,李 茵1,王春艳1,孙现超1,青 玲1,2,*. PaLCuCNV和TYLCCNV复合侵染引起更严重的番茄黄化曲叶病[J]. 园艺学报, 2014, 41(2): 268-276. |
| [12] | 杨国峰, 沈文涛, 言 普, 黎小瑛, 周 鹏. 原核表达的PRSV HC-Pro 基因同源dsRNA 诱导番木瓜抗性的研究[J]. 园艺学报, 2013, 40(7): 1269-1277. |
| [13] | 赵芹, 李华平, 谢大森, 何晓明, 张曙光, 罗少波. 番木瓜环斑病毒外壳蛋白基因原核表达蛋白的抗血清制备及其检测应用[J]. 园艺学报, 2012, 39(8): 1457-. |
| [14] | 申艳红;陈晓静;卢秉国;何玮毅 . 番木瓜果实成熟相关基因的cDNA-AFLP分析及克隆 [J]. 园艺学报, 2011, 38(6): 1081-1088. |
| [15] | 赵 芹;李华平;谢大森;罗少波;彭庆务 . 侵染节瓜的3种病毒多重PCR检测体系的建立 [J]. 园艺学报, 2011, 38(11): 2215-2222. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
版权所有 © 2012 《园艺学报》编辑部 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
编辑部地址: 北京市海淀区中关村南大街12号中国农业科学院蔬菜花卉研究所 邮编: 100081
电话: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
技术支持:北京玛格泰克科技发展有限公司