
园艺学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 49 ›› Issue (10): 2174-2188.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2022-0600
收稿日期:2022-06-06
修回日期:2022-08-25
出版日期:2022-10-25
发布日期:2022-10-31
通讯作者:
周艳虹
E-mail:yanhongzhou@zju.edu.cn
基金资助:
TANG Mingjia, XU Jin, LIN Rui, SONG Jianing, YU Jingquan, and ZHOU Yanhong( )
)
Received:2022-06-06
Revised:2022-08-25
Online:2022-10-25
Published:2022-10-31
Contact:
and ZHOU Yanhong
E-mail:yanhongzhou@zju.edu.cn
摘要:
设施栽培冬春生产中的低温逆境严重影响番茄等喜温作物的光合作用,而不适宜的光强、光周期、光质等光环境加剧了作物的低温光抑制,导致产量降低和品质变劣。因此,解析植物响应光温逆境的生理分子机制对冬春季节生产中作物抗逆性调控不可或缺。近年来,植物响应光温逆境的分子机制逐渐清晰,然而光温信号整合因子及其功能还有待进一步挖掘。基于此,对番茄响应光温逆境的生理分子机制进行了综述,重点讨论了光及其信号对植物低温抗性的影响,并分析了此领域研究中存在的问题及今后研究的方向,以期为减轻番茄的逆境危害、提高产量和品质等提供参考,也为深入探索新的光温互作因子及其功能奠定基础。
中图分类号:
唐明佳, 徐进, 林锐, 宋珈凝, 喻景权, 周艳虹. 番茄响应光温逆境的生理分子机制研究进展[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(10): 2174-2188.
TANG Mingjia, XU Jin, LIN Rui, SONG Jianing, YU Jingquan, and ZHOU Yanhong. Advances in Physiological and Molecular Mechanism of Tomato Responses to Light and Temperature Stress[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(10): 2174-2188.
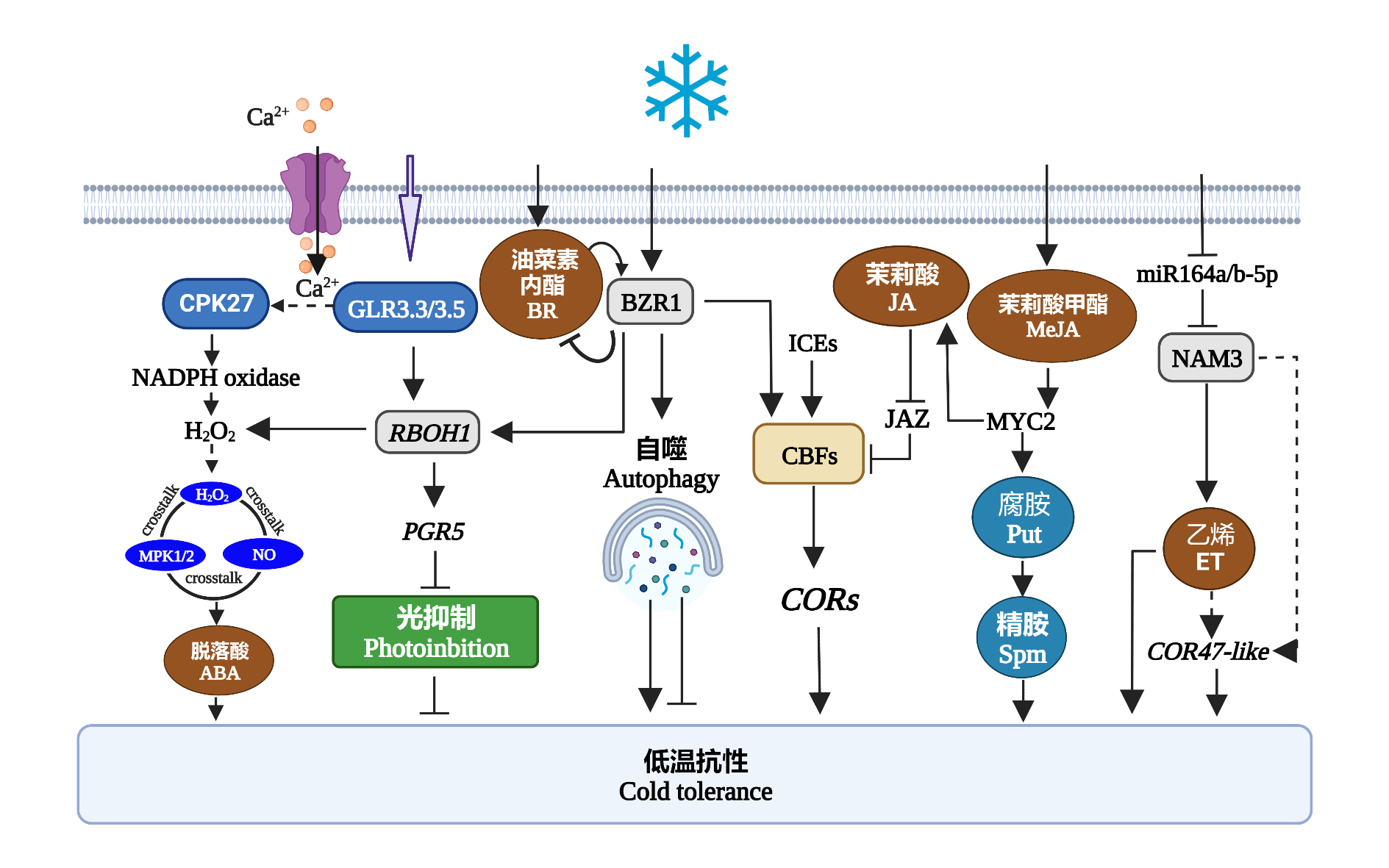
图1 番茄响应低温胁迫的分子调控网络 图片通过biorender.com制作生成。参考文献(Zhou et al.,2014;Wang et al.,2016;Lü et al.,2018;Li et al.,2019;Chi et al.,2020;Min et al.,2021;Dong et al.,2022)。
Fig. 1 Molecular regulatory network of tomato response to cold stress The picture was created by biorender.com. References(Zhou et al.,2014;Wang et al.,2016;Lü et al.,2018;Li et al.,2019;Chi et al.,2020;Min et al.,2021;Dong et al.,2022).
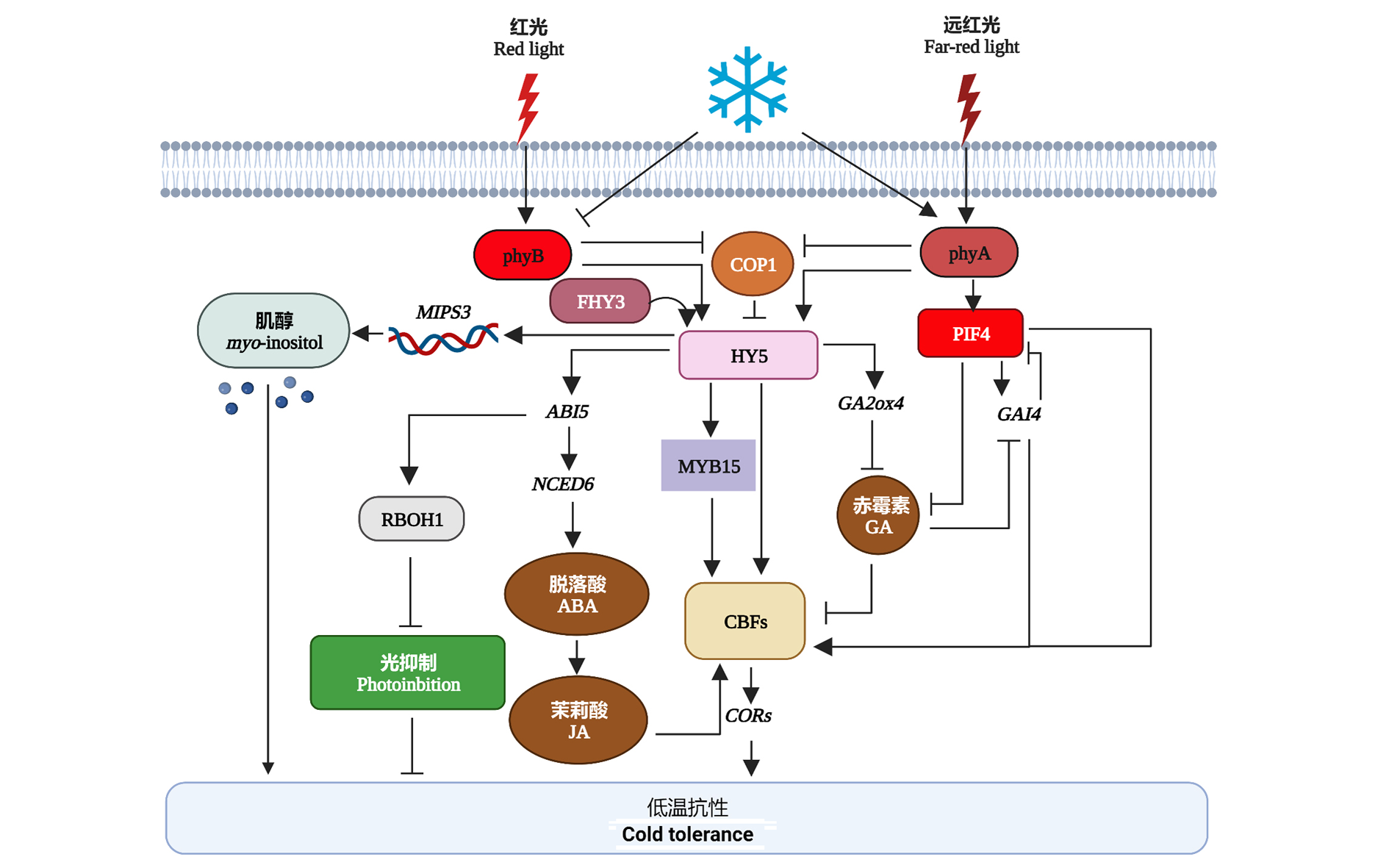
图2 光信号调控番茄低温抗性 图片通过biorender.com制作生成。参考文献(Wang et al.,2018,2019,2020a,2022;Zhang et al.,2020)。
Fig. 2 Regulation of cold tolerance by light signaling in tomato The picture was created by biorender.com. References(Wang et al.,2018,2019,2020a,2022;Zhang et al.,2020)
| [1] |
Aghdam M S, Moradi M, Razavi F, Rabiei V. 2019. Exogenous phenylalanine application promotes chilling tolerance in tomato fruits during cold storage by ensuring supply of NADPH for activation of ROS scavenging systems. Sci Hortic, 246:818-825.
doi: 10.1016/j.scienta.2018.11.074 URL |
| [2] |
Alba R, Kelmenson P M, Cordonnier-Pratt M M, Pratt L H. 2000. The phytochrome gene family in tomato and the rapid differential evolution of this family in angiosperms. Mol Biol Evol, 17 (3):362-373.
pmid: 10723737 |
| [3] |
Allen D J, Ort D R. 2001. Impacts of chilling temperatures on photosynthesis in warm-climate plants. Trends Plant Sci, 6:36-42.
pmid: 11164376 |
| [4] |
Bisbis M B, Gruda N, Blanke M. 2018. Potential impacts of climate change on vegetable production and product quality-a review. J Clean Prod, 170:1602-1620.
doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.09.224 URL |
| [5] |
Bu X, Wang X, Yan J, Zhang Y, Zhou S, Sun X, Yang Y, Ahammed G J, Liu Y, Qi M, Wang F, Li T L. 2021. Genome-wide characterization of B-box gene family and its roles in responses to light quality and cold stress in tomato. Front Plant Sci, 12:698525.
doi: 10.3389/fpls.2021.698525 URL |
| [6] |
Carvalho R F, Campos M L, Azevedo R A. 2011. The role of phytochrome in stress tolerance. J Integ Plant Biol, 53:920-929.
doi: 10.1111/j.1744-7909.2011.01081.x URL |
| [7] |
Castillon A, Shen H, Huq E. 2007. Phytochrome interacting factors:central players in phytochrome-mediated light signaling networks. Trends Plant Sci, 12 (11):514-521.
doi: 10.1016/j.tplants.2007.10.001 pmid: 17933576 |
| [8] |
Catalá R, Medina J Q, Salinas J. 2011. Integration of low temperature and light signaling during cold acclimation response in Arabidopsis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 108:16475-16480.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.1107161108 URL |
| [9] |
Chi C, Li X M, Fang P P, Xia X J, Shi K, Zhou Y H, Zhou J, Yu J Q. 2020. Brassinosteroids act as a positive regulator of NBR1-dependent selective autophagy in response to chilling stress in tomato. J Exp Bot, 71 (3):1092-1106.
doi: 10.1093/jxb/erz466 pmid: 31639824 |
| [10] |
Chi C, Xu X C, Wang M Q, Zhang H, Fang P P, Zhou J, Xia X J, Shi K, Zhou Y H, Yu J Q. 2021. Strigolactones positively regulate abscisic acid-dependent heat and cold tolerance in tomato. Hortic Res, 8:237.
doi: 10.1038/s41438-021-00668-y URL |
| [11] |
Chory J. 2010. Light signal transduction:an infinite spectrum of possibilities. Plant J, 61:982-991.
doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2009.04105.x URL |
| [12] |
Danquah A, de Zelicourt A, Colcombet J, Hirt H. 2014. The role of ABA and MAPK signaling pathways in plant abiotic stress responses. Biotechnol Adv, 32 (1):40-52.
doi: 10.1016/j.biotechadv.2013.09.006 pmid: 24091291 |
| [13] |
Ding F, Ren L, Xie F, Wang M, Zhang S. 2022. Jasmonate and melatonin act synergistically to potentiate cold tolerance in tomato plants. Front Plant Sci, 12:763284.
doi: 10.3389/fpls.2021.763284 URL |
| [14] |
Ding Y, Shi Y, Yang S. 2019. Advances and challenges in uncovering cold tolerance regulatory mechanisms in plants. New Phytol, 222 (4):1690-1704.
doi: 10.1111/nph.15696 pmid: 30664232 |
| [15] |
Dong H, Hu C Y, Liu C C, Wang J C, Zhou Y H, Yu J Q. 2021. ELONGATED HYPOCOTYL 5 mediates blue light-induced starch degradation in tomato. J Exp Bot, 72:2627-2641.
doi: 10.1093/jxb/eraa604 pmid: 33377142 |
| [16] |
Dong Y F, Tang M J, Huang Z L, Song J N, Xu J, Ahammed G J, Yu J Q, Zhou Y H. 2022. The miR164a-NAM3 module confers cold tolerance by inducing ethylene production in tomato. Plant J, 111:440-456.
doi: 10.1111/tpj.15807 URL |
| [17] |
Fan X X, Xu Z G, Liu X Y, Tang C M, Wang L W, Han X L. 2013. Effects of light intensity on the growth and leaf development of young tomato plants grown under a combination of red and blue light. Sci Hort, 153:50-55.
doi: 10.1016/j.scienta.2013.01.017 URL |
| [18] |
Fang P P, Wang Y, Wang M, Wang F, Chi C, Zhou Y H, Zhou J, Shi K, Xia X J, Foyer C H, Yu J Q. 2021. Crosstalk between brassinosteroid and redox signaling contributes to the activation of cbf expression during cold responses in tomato. Antioxidants, 10 (4):509.
doi: 10.3390/antiox10040509 URL |
| [19] |
Guo J, Wang M H. 2010. Ultraviolet a-specific induction of anthocyanin biosynthesis and PAL expression in tomato(Solanum lycopersicum L.). Plant Growth Regul, 62 (1):1-8.
doi: 10.1007/s10725-010-9472-y URL |
| [20] |
Guo X, Li J, Zhang L, Zhang Z, He P, Wang W, Wang M, Wang A, Zhu J. 2020. Heterotrimeric G-protein α subunit(LeGPA1)confers cold stress tolerance to processing tomato plants(Lycopersicon esculentum Mill). BMC Plant Biol, 20 (1):1-16.
doi: 10.1186/s12870-019-2170-7 URL |
| [21] | Guo Z X, Wang F, Xiang X, Ahammed G J, Wang M M, Onac E, Zhou J, Xia X J, Shi K, Yin X R, Chen K S, Yu J Q, Foyer C H, Zhou Y H. 2016. Systemic induction of photosynthesis via illumination of the shoot apex is mediated sequentially by phytochrome B,auxin and hydrogen peroxide in tomato. Plant Physiol, 172 (2):1259-1272. |
| [22] |
Han N, Fan S, Zhang T, Sun H, Zhu Y, Gong H, Guo J. 2020. SlHY 5 is a necessary regulator of the cold acclimation response in tomato. Plant Growth Regul, 91 (1):1-12.
doi: 10.1007/s10725-020-00583-7 URL |
| [23] |
Hardtke C S, Gohda K, Osterlund M T, Oyama T, Okada K, Deng X W. 2000. HY 5 stability and activity in Arabidopsis is regulated by phosphorylation in its COP1 binding domain. EMBO J, 19 (18):4997-5006.
doi: 10.1093/emboj/19.18.4997 pmid: 10990463 |
| [24] | He Wei, Chen Dan-yan, Hu Xiao-ting, Wang Xiao-xu, Chen Le-han, Zhang Hai-chun, Yang Zhen-chao. 2018. Effects of different photoperiod and light quality ratio on tomato plant growth and development. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-oceidentalis Sinica, 27 (4):562-570. (in Chinese) |
| 何蔚, 陈丹艳, 胡晓婷, 王晓旭, 陈乐涵, 张海春, 杨振超. 2018. 不同光周期与光质配比对番茄植株生长发育的影响. 西北农业学报, 27 (4):562-570. | |
| [25] |
Hu T, Wang S, Wang Q, Xu X, Wang Q, Zhan X. 2021. A tomato dynein light chain gene SlLC6D is a negative regulator of chilling stress. Plant Sci, 303:110753.
doi: 10.1016/j.plantsci.2020.110753 URL |
| [26] | Hu Wen-hai, Qi Chao, Hu Xue-hua, Yan Xiao-hong, Li Xiao-hong. 2022. Effects of different light intensities on chlorophyll fluorescence transient in leaves of tomato during recovery period after low night temperature. J Jinggangshan University(Natural Science), 43 (2):41-47. (in Chinese) |
| 胡文海, 齐超, 胡雪华, 闫小红, 李晓红. 2022. 恢复期不同光强对低夜温后番茄叶片快速叶绿素荧光诱导动力学特征的影响. 井冈山大学学报(自然科学版), 43 (2):41-47. | |
| [27] | Hu Wen-hai, Yu Jing-quan. 2001. Effects of low temperature and weak light on photosynthesis and chlorophyll fluorescence parameters of tomato leaves. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 28 (1):41-46. (in Chinese) |
| 胡文海, 喻景权. 2001. 低温弱光对番茄叶片光合作用和叶绿素荧光参数的影响. 园艺学报, 28 (1):41-46. | |
| [28] |
Hu Y, Jiang L, Wang F, Yu D. 2013. Jasmonate regulates the inducer of INDUCER OF CBFEXPRESSION-C-REPEAT BINDING FACTOR/DRE BINDING FACTOR1 cascade and freezing tolerance in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell, 25 (8):2907-2924.
doi: 10.1105/tpc.113.112631 URL |
| [29] |
Huai J L, Zhang X Y, Li J L, Ma T T, Zha P, Jing Y J, Lin R C. 2018. SEUSS and PIF4 Coordinately regulate light and temperature signaling pathways to control plant growth. Mol Plant, 11:928-942.
doi: S1674-2052(18)30134-5 pmid: 29729397 |
| [30] | Huang Chen-jue, Liu Fang, Ma Lin-lin, Li Na, Zheng Shao-wen. 2020. Effect of exogenous melatonin on the quality of cherry tomato fruit. J Shanxi Agr Sci, 48 (4):527-530. (in Chinese) |
| 黄陈珏, 刘芳, 马琳琳, 李娜, 郑少文. 2020. 外源褪黑素对樱桃番茄果实品质的影响. 山西农业科学, 48 (4):527-530. | |
| [31] |
Jia Y, Ding Y, Shi Y, Zhang X, Gong Z, Yang S. 2016. The cbfs triple mutants reveal the essential functions of CBFs in cold acclimation and allow the definition of CBF regulons in Arabidopsis. New Phytol, 212 (2):345-353.
doi: 10.1111/nph.14088 URL |
| [32] |
Jiang Y P, Cheng F, Zhou Y H, Xia X J, Mao W H, Shi K, Chen Z X, Yu J Q. 2012. Cellular glutathione redox homeostasis plays an important role in the brassinosteroid-induced increase in CO2 assimilation in Cucumis sativus. New Phytol, 194 (4):932-943.
doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8137.2012.04111.x pmid: 22432590 |
| [33] | Kang Zhen, Yuan Luqiao, Jia Yuanjie, Zhang Zhengda, Xue Jiankang, Hu Xiaohui. 2022. Exogenous ALA promotes accumulation and distribution of nutrients element in tomato seedlings under sub-low temperature stress. J Northeast Agr University, 53 (4):9-16. (in Chinese) |
| 康珍, 袁路乔, 贾媛婕, 张政达, 薛建康, 胡晓辉. 2022. 外源ALA促进亚低温胁迫下番茄幼苗营养元素积累与分配. 东北农业大学学报, 53 (4):9-16. | |
| [34] |
Kim H J, Lin M Y, Mitchell C A. 2019. Light spectral and thermal properties govern biomass allocation in tomato through morphological and physiological changes. Environ Exp Bot, 157:228-240.
doi: 10.1016/j.envexpbot.2018.10.019 URL |
| [35] |
Lanoue J, Zheng J, Little C, Thibodeau A, Grodzinski B, Hao X. 2019. Alternating red and blue light-emitting diodes allows for injury free tomato production with continuous lighting. Front Plant Sci, 10:1114.
doi: 10.3389/fpls.2019.01114 pmid: 31572419 |
| [36] |
Lau O S, Deng X W. 2012. The photomorphogenic repressors COP1 and DET1:20 years later. Trends Plant Sci, 17:584-593.
doi: 10.1016/j.tplants.2012.05.004 URL |
| [37] |
Lee J, He K, Stolc V, Lee H, Figueroa P, Gao Y, Tongprasit W, Zhao H Y, Lee I, Deng X W. 2007. Analysis of transcription factor HY5 genomic binding sites revealed its hierarchical role in light regulation of development. Plant Cell, 19:731-749.
pmid: 17337630 |
| [38] | Li Hao. 2021. Study on the development status,obstacles and countermeasures of facility agriculture in China. South Forum, 52 (23):34-37. (in Chinese) |
| 李浩. 2021. 我国设施农业发展现状、障碍及对策研究. 南方农机, 52 (23):34-37. | |
| [39] |
Li H Z, Jiang X C, Lv X Z, Ahammed G J, Guo Z X, Qi Z Y, Yu J Q, Zhou Y H. 2019. Tomato GLR3.3 and GLR3.5 mediate cold acclimation-induced chilling tolerance by regulating apoplastic H2O2 production and redox homeostasis. Plant Cell Environ, 42:3326-3339.
doi: 10.1111/pce.13623 URL |
| [40] | Li Jun-ming, Xiang Chao-yang, Wang Xiao-xuan, Guo Yan-mei, Huang Ze-jun, Liu Lei, Li Xin, Du Yong-chen. 2021. Current situation of tomato industry in China during'The Thirteenth Five-year Plan'period and future prospect. China Vegetables,(2):13-20. (in Chinese) |
| 李君明, 项朝阳, 王孝宣, 国艳梅, 黄泽军, 刘磊, 李鑫, 杜永臣. 2021. “十三五”我国番茄产业现状及展望. 中国蔬菜,(2):13-20. | |
| [41] |
Li Y, Shi Y, Li M, Fu D, Wu S, Li J, Gong Z, Liu H, Yang S. 2021. The CRY2-COP1-HY5-BBX7/ 8 module regulates blue light-dependent cold acclimation in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell, 33 (11):3555-3573.
doi: 10.1093/plcell/koab215 URL |
| [42] |
Li Y, Xin G, Wei M, Shi Q, Yang F, Wang X. 2017. Carbohydrate accumulation and sucrose metabolism responses in tomato seedling leaves when subjected to different light qualities. Sci Hortic, 225:490-497.
doi: 10.1016/j.scienta.2017.07.053 URL |
| [43] |
Liu C C, Chi C, Jin L J, Zhu J, Yu J Q, Zhou Y H. 2018a. The bZip transcription factor HY5 mediates CRY1a-induced anthocyanin biosynthesis in tomato. Plant Cell Environ, 41:1762-1775.
doi: 10.1111/pce.13171 URL |
| [44] |
Liu J, Shi Y, Yang S. 2018b. Insights into the regulation of C-repeat binding factors in plant cold signaling. J Integr Plant Biol, 60 (9):780-795.
doi: 10.1111/jipb.12657 URL |
| [45] |
Liu T, Jiao X, Yang S, Zhang Z, Ye X, Li J, Qi H, Hu X. 2020a. Crosstalk between GABA and ALA to improve antioxidation and cell expansion of tomato seedling under cold stress. Environ Exp Bot, 180:104228.
doi: 10.1016/j.envexpbot.2020.104228 URL |
| [46] | Liu Xue-jing, Wang Yan, Liu Tong-guang, Zhang Qi-an, Fang Ling, Duan Bao-hui. 2015. Effect of chilling temperature on key enzyme in tomato in colour-changed period. China Cucurbits and Vegetables, 28 (1):19-22. (in Chinese) |
| 刘雪静, 王艳, 刘童光, 张其安, 方凌, 段宝慧. 2015. 低温对番茄果实转色关键酶的影响. 中国瓜菜, 28 (1):19-22. | |
| [47] |
Liu Y, Shi Y, Zhu N, Zhong S, Bouzayen M, Li Z G. 2020b. SlGRAS 4 mediates a novel regulatory pathway promoting chilling tolerance in tomato. Plant Biotechnol J, 18 (7):1620-1633.
doi: 10.1111/pbi.13328 URL |
| [48] |
Liu Z, Jia Y, Ding Y, Shi Y, Li Z, Guo Y, Gong Z, Yang S. 2017. Plasma membrane CRPK1-mediated phosphorylation of 14-3-3 proteins induces their nuclear import to fine-tune CBF signaling during cold response. Mol Cell, 66 (1):117-128.
doi: S1097-2765(17)30131-4 pmid: 28344081 |
| [49] |
Lü X Z, Li H Z, Chen X X, Xiang X, Guo Z X, Yu J Q, Zhou Y H. 2018. The role of calcium-dependent protein kinase in hydrogen peroxide,nitric oxide and ABA-dependent cold acclimation. J Exp Bot, 69 (16):4127-4139.
doi: 10.1093/jxb/ery212 URL |
| [50] |
Min D, Zhou J, Li J, Ai W, Li Z, Zhang X, Fu X, Zhao X, Li F, Li X, Guo Y. 2021. SlMYC 2 targeted regulation of polyamines biosynthesis contributes to methyl jasmonate-induced chilling tolerance in tomato fruit. Postharvest Biol Tec, 174:111443.
doi: 10.1016/j.postharvbio.2020.111443 URL |
| [51] |
Mou W S, Li D D, Luo Z S, Li L, Mao L C, Ying T J. 2018. SlAREB 1 transcriptional activation of NOR is involved in abscisic acid-modulated ethylene biosynthesis during tomato fruit ripening. Plant Sci, 276:239-249.
doi: 10.1016/j.plantsci.2018.07.015 URL |
| [52] |
Novak A, Boldizsar A, Adam E, Kozma-Bognar L, Majlath I, Baga M, Toth B, Chibbar R, Galiba G. 2016. Light-quality and temperature-dependent CBF14gene expression modulates freezing tolerance in cereals. J Exp Bot, 67:1285-1295.
doi: 10.1093/jxb/erv526 URL |
| [53] | Ntatsi G, Savvas D, Kläring HP, Schwarz D. 2014. Growth,yield,and metabolic responses of temperature-stressed tomato to grafting onto rootstocks differing in cold tolerance. J Am Soc Hortic Sci, 139 (2):230-243. |
| [54] |
Oh E, Kang H, Yamaguchi S, Park J, Lee D, Kamiya Y, Choi G. 2009. Genome-wide analysis of genes targeted by PHYTOCHROME INTERACTING FACTOR 3-LIKE 5 during seed germination in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell, 21 (2):403-419.
doi: 10.1105/tpc.108.064691 URL |
| [55] |
Osterlund M T, Hardtke C S, Wei N, Deng X W. 2000. Targeted destabilization of HY5 during light-regulated development of Arabidopsis. Nature, 405:462-466.
doi: 10.1038/35013076 URL |
| [56] |
Patel D, Basu M, Hayes S, Majlath I, Hetherington F M, Tschaplinski T J, Franklin K A. 2013. Temperature-dependent shade avoidance involves the receptor-like kinase ERECTA. Plant J, 73:980-992.
doi: 10.1111/tpj.12088 URL |
| [57] |
Prerostova S, Černý M, Dobrev P I, Motyka V, Hluskova L, Zupkova B, Gaudinova A, Knirsch V, Janda T, Brzobohaty B, Vankova R. 2021. Light regulates the cytokinin-dependent cold stress responses in Arabidopsis. Front Plant Sci, 11:608711.
doi: 10.3389/fpls.2020.608711 URL |
| [58] | Qi Juan-xia, Wei Feng, Dong Yan, Zhang Ya-hong. 2016. Effects of different light supplement time on the growth and development of greenhouse tomato. Jiangsu Agr Sci, 44 (8):245-248. (in Chinese) |
| 祁娟霞, 韦峰, 董艳, 张亚红. 2016. 不同补光时间对温室番茄生长发育的影响. 江苏农业科学, 44 (8):245-248. | |
| [59] |
Rosado D, Trench B, Bianchetti R, Zuccarelli R, Alves F R R, Purgatto E, Floh E I S, Nogueira F T S, Freschi L, Rossi M. 2019. Downregulation of PHYTOCHROME-INTERACTING FACTOR 4 influences plant development and fruit production. Plant Physiol, 181 (3):1360-1370.
doi: 10.1104/pp.19.00833 pmid: 31519788 |
| [60] |
Shahzad R, Ahmed F, Wang Z, Harlina P W, Nishawy E, Ayaad M, Manan A, Maher M, Ewas M. 2020. Comparative analysis of two phytochrome mutants of tomato(Micro-Tom cv.)reveals specific physiological,biochemical,and molecular responses under chilling stress. J Genet Eng Biotechnol, 18 (1):1-15.
doi: 10.1186/s43141-019-0015-2 URL |
| [61] | Sun Na, Li Yan, Wei Min, Wang Xiu-feng, Shi Qing-hua, Yang Feng-juan, Mi Qing-hua. 2014. Effect of supplementary lighting on growth,quality and yield of tomato overwintering stand in greenhouse. Tianjin Agr Sci, 20 (3):91-93,96. (in Chinese) |
| 孙娜, 李岩, 魏珉, 王秀峰, 史庆华, 杨凤娟, 米庆华. 2014. 补光对日光温室越冬番茄生长及产量品质的影响. 天津农业科学, 20 (3):91-93,96. | |
| [62] |
Sun Q Q, Zhang N, Wang J F, Zhang H J, Li D B, Shi J, Li R, Weeda S, Zhao B, Ren S X, Guo Y D. 2015. Melatonin promotes ripening and improves quality of tomato fruit during postharvest life. J Exp Bot, 66 (3):657-668.
doi: 10.1093/jxb/eru332 pmid: 25147270 |
| [63] | Tang M, Xu C, Cao H, Shi Y, Chen J, Chai Y, Li Z. 2021. Tomato calmodulin-like protein SlCML 37 is a calcium(Ca2+)sensor that interacts with proteasome maturation factor SlUMP1 and plays a role in tomato fruit chilling stress tolerance. J Plant Physiol, 258:153373. |
| [64] |
Trevaskis B, Hemming M N, Dennis E S, Peacock W J. 2007. The molecularbasis of vernalization-induced flowering in cereals. Trends Plant Sci, 12:352-357.
pmid: 17629542 |
| [65] |
Velez-Ramirez A I, Carreño-Quintero N, Vreugdenhil D, Millenaar F F, van Ieperen W. 2017. Sucrose and starch content negatively correlates with PSII maximum quantum efficiency in tomato(Solanum lycopersicum)exposed to abnormal light/dark cycles and continuous light. Plant Cell Physiol, 58:1339-1349.
doi: 10.1093/pcp/pcx068 pmid: 28961989 |
| [66] |
Velitchkova M, Popova A V, Faik A, Gerganova M, Ivanov A G. 2020. Low temperature and high light dependent dynamic photoprotective strategies in Arabidopsis thaliana. Physiol Plantarum, 170 (1):93-108.
doi: 10.1111/ppl.13111 URL |
| [67] |
Venema J H, Dijk B E, Bax J M, Hasselt P R, Elzenga J T M. 2008. Grafting tomato(Solanum lycopersicum)onto the rootstock of a high-altitude accession of Solanum habrochaites improves suboptimal-temperature tolerance. Environ Exp Bot, 63 (1-3):359-367.
doi: 10.1016/j.envexpbot.2007.12.015 URL |
| [68] |
Venema J H, Eekhof M, van Hasselt P R. 2000. Analysis of low-temperature tolerance of a tomato(Lycopersicon esculentum)cybird with chloroplasts from a more chilling-tolerance L. hirsutum accession. Ann Bot, 85 (6):799-807.
doi: 10.1006/anbo.2000.1142 URL |
| [69] | Verma V, Ravindran P, Kumar P. 2016. Plant hormone-mediated regulation of stress responses. BMC Plant Bio, 16:86. |
| [70] |
Wang F, Chen X X, Dong S J, Jiang X C, Wang L Y, Yu J, Zhou Y H. 2020a. Crosstalk of PIF4 and DELLA modulates CBF transcript and hormone homeostasis in cold response in tomato. Plant Biotechnol J, 18 (4):1041-1055.
doi: 10.1111/pbi.13272 URL |
| [71] |
Wang F, Guo Z X, Li H Z, Wang M M, Onac E, Zhou J, Xia X J, Shi K, Yu J Q, Zhou Y H. 2016. Phytochrome A and B function antagonistically to regulate cold tolerance via abscisic acid-dependent jasmonate signaling. Plant Physiol, 170:459-471.
doi: 10.1104/pp.15.01171 pmid: 26527654 |
| [72] |
Wang F, Wang X, Zhang Y, Yan J, Ahammed G J, Bu X, Sun X, Liu Y, Xu T, Qi H, Qi M, Li T. 2022. SlFHY3 and SlHY 5 act compliantly to enhance cold tolerance through the integration of myo-inositol and light signaling in tomato. New Phytol, 233 (5):2127-2143.
doi: 10.1111/nph.17934 URL |
| [73] |
Wang F, Wu N, Guo Z X, Zhang L Y, Ahammed G J, Chen X X, Xiang X, Zhou J, Xia X J, Shi K, Yu J Q, Foyer C H, Zhou Y H. 2018. Light signaling-dependent regulation of photoinhibition and photoprotection in tomato. Plant Physiol, 176:1311-1326.
doi: 10.1104/pp.17.01143 pmid: 29146776 |
| [74] |
Wang F, Zhang L, Chen X, Wu X, Xiang X, Zhou J, Xia X, Shi K, Yu J, Foyer C H, Zhou Y H. 2019. SlHY 5 integrates temperature,light,and hormone signaling to balance plant growth and cold tolerance. Plant Physiol, 179 (2):749-760.
doi: 10.1104/pp.18.01140 URL |
| [75] | Wang M, Xue S, Wu T, Luo S, Xie D, Zhong Y. 2020b. Effects of illumination and temperature regulation on synthesis of carotenogenesis in tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.). Fruit Mol Plant Breeding, 18:6158-6164. |
| [76] |
Wang M, Zhang S, Ding F. 2020c. Melatonin mitigates chilling-induced oxidative stress and photosynthesis inhibition in tomato plants. Antioxidants, 9 (3):218.
doi: 10.3390/antiox9030218 URL |
| [77] |
Wang W H, Wang P W, Li X J, Wang Y Y, Tian S P, Qin G Z. 2021. The transcription factor SlHY 5 regulates the ripening of tomato fruit at both the transcriptional and translational levels. Hortic Res, 8:83.
doi: 10.1038/s41438-021-00523-0 URL |
| [78] | Wang Yan-wen, Luo Na, Wang Guang-yin. 2021. Effects of combined application of brassinolide and exogenous calcium on growth,fruit setting and yield of over-winter tomato in solar greenhouse. Chin Agr Sci Bull, 37 (4):43-48. (in Chinese) |
| 王岩文, 雒娜, 王广印. 2021. 油菜素内酯及配施外源钙对日光温室越冬茬番茄生长、坐果及产量的影响. 中国农学通报, 37 (4):43-48. | |
| [79] | Weng Qian, Zhou Bao-lia, Yu Yang, Fu Ya-wen. 2007. Effects of exogenous ABA,BR,ETH on changes of lycopene's contents in fruit of tomato. J Shenyang Agr University, 38 (6):784-787. (in Chinese) |
| 翁倩, 周宝利, 于洋, 付亚文. 2007. 外源ABA、BR和ETH对番茄果实番茄红素含量的影响. 沈阳农业大学学报, 38 (6):784-787. | |
| [80] | Wu Q, Bai J W, Tao X Y, Mou W S, Luo Z S, Mao L C, Ban Z J, Ying T J, Li L. 2018. Synergistic effect of abscisic acid and ethylene on color development in tomato(Solanum lycopersicum L.). Fruit Sci Hortic, 235:169-180. |
| [81] |
Xia X J, Fang P P, Guo X, Qian X J, Zhou J, Shi K, Zhou Y H, Yu J Q. 2018. Brassinosteroid-mediated apoplastic H2O2-glutaredoxin 12/ 14 cascade regulates antioxidant capacity in response to chilling in tomato. Plant Cell Environ, 41 (5):1052-1064.
doi: 10.1111/pce.13052 URL |
| [82] | Xu J, Guo Z X, Jiang X C, Ahammed G J, Zhou Y H. 2021. Light regulation of horticultural crop nutrient uptake and utilization. Hortic Plant J, 7 (5):367-379. |
| [83] | Yan Pei-yu, Pan Kai, Liu Shou-wei, Wu Feng-zhi. 2017. Effects of different exogenous hormones on the rate of bear fruit,fruit appearance quality and yield of overwintering tomato. Northern Horticult,(10):11-15. (in Chinese) |
| 颜培玉, 潘凯, 刘守伟, 吴凤芝. 2017. 不同外源激素对越冬番茄坐果率、果实外观品质及产量的影响. 北方园艺,(10):11-15. | |
| [84] | Yang You-xin, Wang Feng, Cai Jia-xing, Yu Jing-quan, Zhou Yan-hong. 2014. Recent advances in the role of light quality and phytochrome in plant defense resistance against environmental stresses. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 41 (9):1861-1872. (in Chinese) |
| 杨有新, 王峰, 蔡加星, 喻景权, 周艳虹. 2014. 光质和光敏色素在植物逆境响应中的作用研究进展. 园艺学报, 41 (9):1861-1872. | |
| [85] | Yang Zhong-wu, Liu Yi, Jin Zhuo-jun, Xu Wei-hong. 2020. Effects of light quality on nutrition and flavor quality in tomato. Chin Agr Sci Bull, 36 (34):134-141. (in Chinese) |
| 杨忠武, 刘翼, 金卓君, 徐卫红. 2020. 光质对番茄营养与风味品质的影响. 中国农学通报, 36 (34):134-141. | |
| [86] | You Jie, Zhang Yu-yang, Pu Min, Xu Zhi-gang. 2020. Effects of supplemental-lighting ways on growth,development of overwintering tomatoes in facilities. China Illuminating Engineering Journal, 31 (5):39-45. (in Chinese) |
| 尤杰, 张宇阳, 浦敏, 徐志刚. 2020. 补光方式对设施越冬番茄生长发育的影响. 照明工程学报, 31 (5):39-45. | |
| [87] |
Zhang L Y, Jiang X C, Liu Q Y, Jalal G J, Lin R, Wang L Y, Shao S J, Yu J Q, Zhou Y H. 2020. The HY5 and MYB15 transcription factors positively regulate cold tolerance in tomato via the CBF pathway. Plant Cell Environ, 43:2712-2726.
doi: 10.1111/pce.13868 URL |
| [88] |
Zhang Y, Liu Z, Liu R, Hao H, Bi Y. 2011. Gibberellins negatively regulate low temperature-induced anthocyanin accumulation in a HY5/HYH-dependent manner. Plant Signal Behav, 6:632-634.
doi: 10.4161/psb.6.5.14343 pmid: 21636970 |
| [89] | Zhang Yi, Liang Yi, Han Jing, Guo Shu-xun, Shi Yu,Hou Lei-ping. 2022. Effect of photoperiod and exogenous iron on photosynthetic characteristics,fruit quality and mineral elements of tomato. J Northwest A & F University(Nat Sci Ed), 50 (1):104-111. (in Chinese) |
| 张毅, 梁祎, 韩静, 郭树勋, 石玉, 侯雷平. 2022. 光周期和外源铁对番茄光合特性、果实品质及矿质元素含量的影响. 西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版), 50 (1):104-111. | |
| [90] |
Zhao C, Zhang Z, Xie S, Si T, Li Y, Zhu J K. 2016. Mutational evidence for the critical role of CBF transcription factors in cold acclimation in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol, 171 (4):2744-2759.
doi: 10.1104/pp.16.00533 URL |
| [91] |
Zhou J, Xia X J, Zhou Y H, Shi K, Chen Z X, Yu J Q. 2014. RBOH1-dependent H2O2 production and subsequent activation of MPK1/ 2 play an important role in acclimation-induced cross-tolerance in tomato. J Exp Bot, 65 (2):595-607.
doi: 10.1093/jxb/ert404 pmid: 24323505 |
| [92] | Zhou Jie, Xia Xiao-jian, Hu Zhang-jian, Fan Peng-xiang, Shi Kai, Zhou Yan-hong, Yu Jing-quan. 2021. Development and prospect of greenhouse vegetable production and technology in China during'The Thirteenth Five-year Plant'period. China Vegetables, 10:20-34. (in Chinese) |
| 周杰, 夏晓剑, 胡璋健, 范鹏祥, 师恺, 周艳虹, 喻景权. 2021. “十三五”我国设施蔬菜生产和科技进展及其展望. 中国蔬菜,(10):20-34. | |
| [93] |
Zhou Y H, Yu J Q, Huang L F, Nogués S. 2004. The relationship between CO2 assimilation,photosynthetic electron transport and water-water cycle in chill-exposed cucumber leaves under low light and subsequent recovery. Plant Cell Environ, 27:1503-1514.
doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3040.2004.01255.x URL |
| [1] | 史洪丽, 李腊, 郭翠梅, 余婷婷, 简伟, 杨星勇. 番茄灰霉病生防菌株TL1的分离、鉴定及其生防能力分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(1): 79-90. |
| [2] | 忽靖宇, 阙开娟, 缪田丽, 吴少政, 王田田, 张磊, 董鲜, 季鹏章, 董家红. 侵染鸢尾的番茄斑萎病毒鉴定[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(1): 170-176. |
| [3] | 郑积荣, 王同林, 胡松申. 高品质番茄新品种‘杭杂603’[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(S2): 103-104. |
| [4] | 郑积荣, 王同林. 番茄新品种‘杭杂601’[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(S2): 105-106. |
| [5] | 郑积荣, 王同林. 樱桃番茄新品种‘杭杂503’[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(S2): 107-108. |
| [6] | 黄婷婷, 刘淑芹, 张永志, 李 平, 张志焕, 宋立波. 樱桃番茄新品种‘樱莎红4号’[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(S2): 109-110. |
| [7] | 张前荣, 李大忠, 裘波音, 林 珲, 马慧斐, 叶新如, 刘建汀, 朱海生, 温庆放. 设施番茄新品种‘闽农科2号’[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(S1): 73-74. |
| [8] | 韩帅, 吴婕, 张河庆, 席亚东. 四川莴笋上番茄斑萎病毒的电镜观察与小RNA测序鉴定[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(9): 2007-2016. |
| [9] | 陈礼浪, 杨天章, 蔡儒平, 林小漫, 邓南康, 车海彦, 林雅婷, 孔祥义. 海南西番莲主要病毒种类的分子检测与鉴定[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(8): 1785-1794. |
| [10] | 路涛, 余宏军, 李强, 蒋卫杰. 叶果量调控对番茄生长发育、果实品质和产量的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(6): 1261-1274. |
| [11] | 孟宪敏, 崔青青, 段韫丹, 庄团结, 濮丹, 董春娟, 杨文才, 尚庆茂. 烯效唑对番茄幼苗嫁接愈合的促进作用及其机理研究[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(6): 1275-1289. |
| [12] | 崔东禹, 李长青, 孙焱鑫, 王激清, 邹国元, 杨俊刚. 温室番茄东西向栽培条件下矮化密植对其生长和产量的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(4): 875-884. |
| [13] | 陈同强, 张天柱, 王晓卓. 光照对番茄果实中番茄红素生物合成的调控研究进展[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(4): 907-923. |
| [14] | 彭轶, 李元慧, 杨瑞, 张子怡, 李亚楠, 韩云昊, 赵文超, 王绍辉. 茉莉酸合成基因LoxD参与调控番茄的抗旱性[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(2): 319-331. |
| [15] | 王晋, 王新宇, 沈渊博, 张清花, 娄茜棋, 张世杰, 赵攀, 梁燕. 番茄果实叶绿体发育调控及其应用的研究进展[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(12): 2669-2682. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
版权所有 © 2012 《园艺学报》编辑部 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
编辑部地址: 北京市海淀区中关村南大街12号中国农业科学院蔬菜花卉研究所 邮编: 100081
电话: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
技术支持:北京玛格泰克科技发展有限公司