
园艺学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 49 ›› Issue (9): 1841-1852.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2021-0566
• 研究论文 • 下一篇
蒋亚君1,2, 陈佳佳1, 谭彬1,3, 郑先波1,3, 王伟1,3, 张郎郎1,3, 程钧1,3,*( ), 冯建灿1,3,*(
), 冯建灿1,3,*( )
)
收稿日期:2022-03-03
修回日期:2022-05-13
出版日期:2022-09-25
发布日期:2022-10-08
通讯作者:
程钧,冯建灿
E-mail:jcheng2007@163.com;jcfeng@henau.edu.cn
基金资助:
JIANG Yajun1,2, CHEN Jiajia1, TAN Bin1,3, ZHENG Xianbo1,3, WANG Wei1,3, ZHANG Langlang1,3, CHENG Jun1,3,*( ), FENG Jiancan1,3,*(
), FENG Jiancan1,3,*( )
)
Received:2022-03-03
Revised:2022-05-13
Online:2022-09-25
Published:2022-10-08
Contact:
CHENG Jun,FENG Jiancan
E-mail:jcheng2007@163.com;jcfeng@henau.edu.cn
摘要:
从‘秋蜜红’桃中克隆到1个IDD转录因子基因PpIDD11。结果显示:PpIDD11编码区全长1 575 bp,编码524个氨基酸,具有保守的ID域。烟草亚细胞定位显示PpIDD11蛋白定位于细胞核,酵母转化试验表明其具有酵母转录自激活活性。荧光定量PCR分析显示PpIDD11主要在花器官中表达,特别在雌蕊中转录水平最高。过表达PpIDD11拟南芥株系出现了柱头高于野生型、荚果变短且结实率下降的表型,同时也出现了莲座叶叶片卷曲、植株变矮的现象。转录组测序分析显示,PpIDD11转基因拟南芥株系共有上调基因3 378个,下调基因3 156个,其中包含LOX4、LOX3、GLC、E6L1等花器官发育调控基因。
中图分类号:
蒋亚君, 陈佳佳, 谭彬, 郑先波, 王伟, 张郎郎, 程钧, 冯建灿. 桃PpIDD11调控花发育的功能研究[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(9): 1841-1852.
JIANG Yajun, CHEN Jiajia, TAN Bin, ZHENG Xianbo, WANG Wei, ZHANG Langlang, CHENG Jun, FENG Jiancan. Function Exploration of PpIDD11 in Regulating Peach Flower Development[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(9): 1841-1852.
| 用途 Use | 引物名称 Primer name | 序列(5′-3′) Sequence |
|---|---|---|
| 克隆 Clone | PpIDD11-F | TGGGGAAAGAAAACAAAGGAGA |
| PpIDD11-R | TCAATTAAACCTTTGCATTCTTAGG | |
| 亚细胞定位 Subcellular localization | PpIDD11-GFP-EcoRⅠ-F | GTGGATCCAAAGAATTCTCCTTTTTATCTGTATCTTCCTCCA |
| PpIDD11-GFP-EcoRⅠ-R | CTCCTTTACCCATGAATTCATTAAACCTTTGCATTCTTAGG | |
| 自激活鉴定 Self-activation | PpIDD11-BD-EcoRⅠ-F | CCGGAATTCTTTCCTTTTTATCTGTATCTTCCTCCA |
| PpIDD11-BD-PstⅠ-R | GCACTGCAGTCAATTAAACCTTTGCATTCTTAGG | |
| 过表达 Primers for overexpression sites | PpIDD11-SAK-EcoRⅠ-F | CCGGAATTCTGGGGAAAGAAAACAAAGGAGA |
| PpIDD11-SAK-XhoⅠ-R | CCGCTCGAGTCAATTAAACCTTTGCATTCTTAGG | |
| 定量 qRT-PCR | PpIDD11-qPCR-F | ATGTATGGCGGGCTTTTATTC |
| PpIDD11-qPCR-R | TGCTGATGCTGGTCATGTTG | |
| 定量桃内参 Primers for peach internal control | PpTEF2-qPCR-F | GGTGTGACGATGAAGAGTGATG |
| PpTEF2-qPCR-R | TGAAGGAGAGGGAAGGTGAAAG | |
| 定量拟南芥内参 Primers for Arabidopsis internal control | AtUBC-qPCR-F | CTGCGACTCAGGGAATCTTCTAA |
| AtUBC-qPCR-R | TTGTGCCATTGAATTGAACCC |
表1 本研究中所用的引物序列
Table 1 Primer sequences used in this study
| 用途 Use | 引物名称 Primer name | 序列(5′-3′) Sequence |
|---|---|---|
| 克隆 Clone | PpIDD11-F | TGGGGAAAGAAAACAAAGGAGA |
| PpIDD11-R | TCAATTAAACCTTTGCATTCTTAGG | |
| 亚细胞定位 Subcellular localization | PpIDD11-GFP-EcoRⅠ-F | GTGGATCCAAAGAATTCTCCTTTTTATCTGTATCTTCCTCCA |
| PpIDD11-GFP-EcoRⅠ-R | CTCCTTTACCCATGAATTCATTAAACCTTTGCATTCTTAGG | |
| 自激活鉴定 Self-activation | PpIDD11-BD-EcoRⅠ-F | CCGGAATTCTTTCCTTTTTATCTGTATCTTCCTCCA |
| PpIDD11-BD-PstⅠ-R | GCACTGCAGTCAATTAAACCTTTGCATTCTTAGG | |
| 过表达 Primers for overexpression sites | PpIDD11-SAK-EcoRⅠ-F | CCGGAATTCTGGGGAAAGAAAACAAAGGAGA |
| PpIDD11-SAK-XhoⅠ-R | CCGCTCGAGTCAATTAAACCTTTGCATTCTTAGG | |
| 定量 qRT-PCR | PpIDD11-qPCR-F | ATGTATGGCGGGCTTTTATTC |
| PpIDD11-qPCR-R | TGCTGATGCTGGTCATGTTG | |
| 定量桃内参 Primers for peach internal control | PpTEF2-qPCR-F | GGTGTGACGATGAAGAGTGATG |
| PpTEF2-qPCR-R | TGAAGGAGAGGGAAGGTGAAAG | |
| 定量拟南芥内参 Primers for Arabidopsis internal control | AtUBC-qPCR-F | CTGCGACTCAGGGAATCTTCTAA |
| AtUBC-qPCR-R | TTGTGCCATTGAATTGAACCC |

图1 序列比对和IDD保守域 At:拟南芥;Os:水稻;Pp:桃;Zm:玉米。下同。
Fig. 1 Sequence alignment and IDD conserved domain At:Arabidopsis;Os:Rice;Pp:Peach;Zm:Maize. The same below.
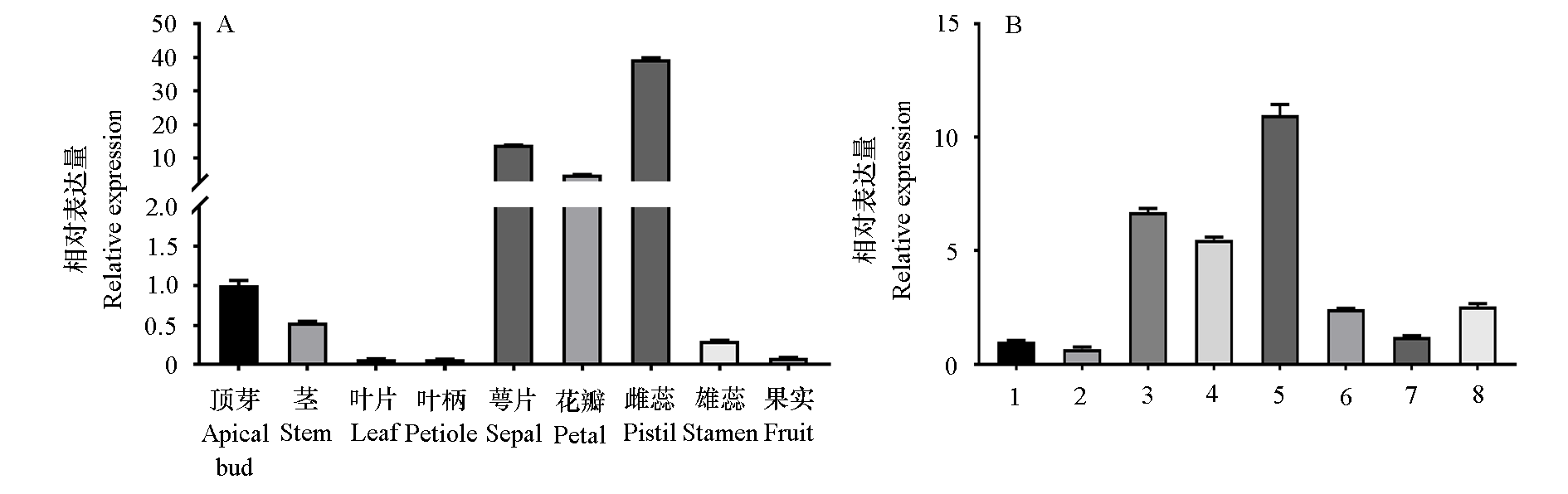
图5 PpIDD11在‘秋蜜红’桃不同组织(A)和不同花发育时期(B)中的相对表达量 1:花芽未分化期;2:花萼分化期;3:花瓣分化期;4:雄蕊分化期;5:雌蕊分化期;6:花蕾;7:花苞;8:盛花。
Fig. 5 The relative expression of PpIDD11 in various tissues(A)and different stages of flower development(B)of‘Qiumihong’peach 1:Undifferentiated flower bud period;2:Calyx differentiation period;3:Petal differentiation period;4:Stamen differentiation period;5:Pistil differentiation period;6:Buds period;7:Budding flower period;8:Full bloom period.
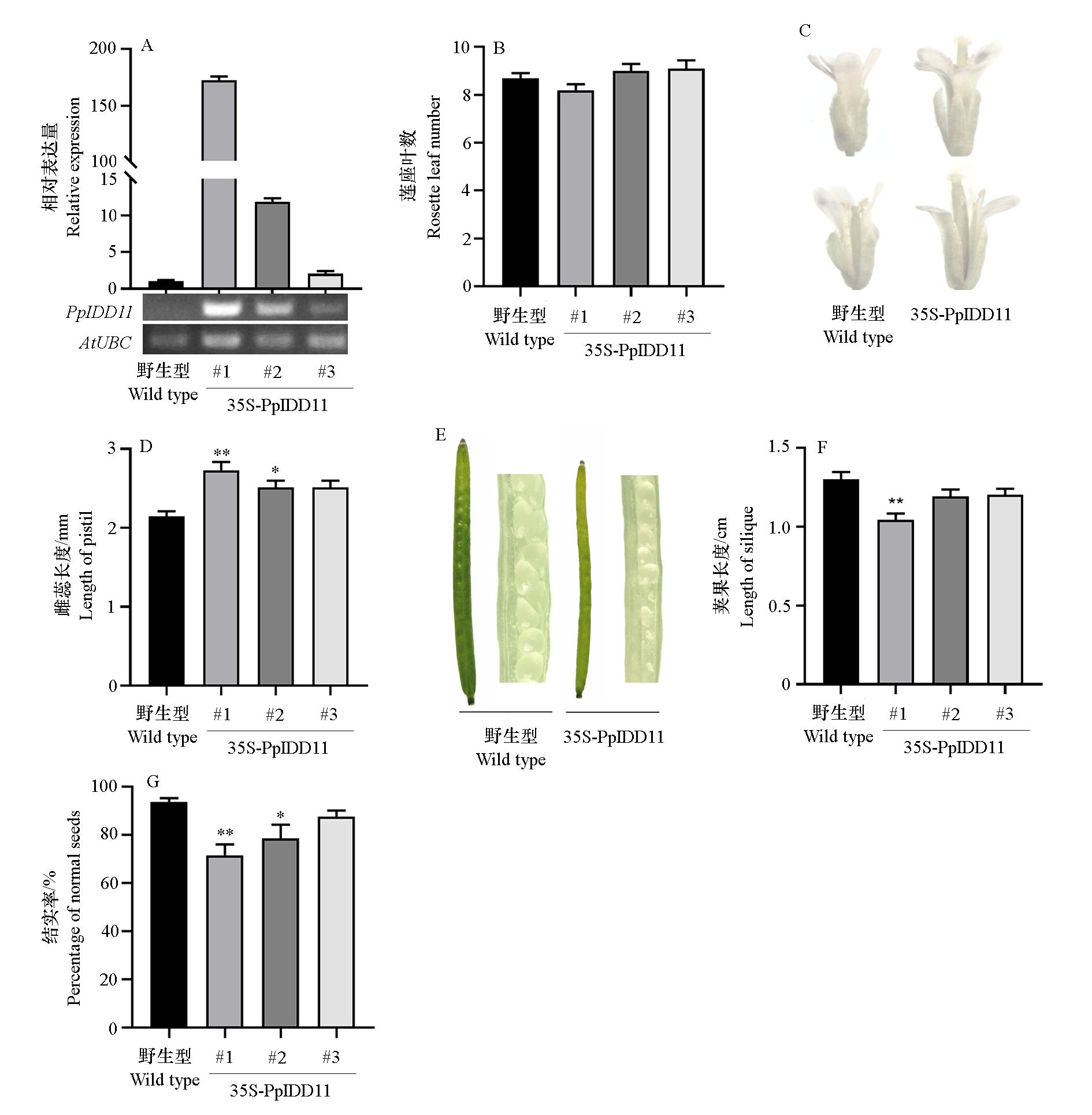
图6 转PpIDD11拟南芥株系的PpIDD11相对表达量(A)及其花和角果特征(B ~ G) * P < 0.05;** P < 0.01.
Fig. 6 Relative expression level(A),flower and silique characteristics(B-G)of PpIDD11 overexpressed Arabidopsis lines
| 基因ID Gene ID | 表达差异 log2(IDD11/WT) | 名称 Name | 功能 Function | 参考文献 Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AT1G21910 | 2.77242 | DREB26 | 植物生长发育 Plant growth and development | Krishnaswamy et al., |
| AT3G18010 | 2.40747 | WOX1 | 分生组织发育 Meristematic tissue development | Zhang et al., |
| AT1G65450 | -3.77981 | GLC | 参与植物受精过程 Involved in the process of plant fertilisation | Leshem et al., |
| AT3G12500 | -3.07184 | ATHCHIB | 叶片形态发育Leaf blade morphology development | Robles et al., |
| AT2G33850 | -2.78991 | E6L1 | 参与植物早期授粉过程 Involved in the early pollination process of plants | Doucet et al., |
| AT1G72520 | -2.61478 | LOX4 | 花器官发育 Floral organ development | Caldelari et al., |
| AT1G17420 | -2.54068 | LOX3 | 花器官发育 Floral organ development | Caldelari et al., |
表2 与转基因表型相关的差异基因及其功能
Table 2 Differential genes related to transgenic phenotypes and their functions
| 基因ID Gene ID | 表达差异 log2(IDD11/WT) | 名称 Name | 功能 Function | 参考文献 Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AT1G21910 | 2.77242 | DREB26 | 植物生长发育 Plant growth and development | Krishnaswamy et al., |
| AT3G18010 | 2.40747 | WOX1 | 分生组织发育 Meristematic tissue development | Zhang et al., |
| AT1G65450 | -3.77981 | GLC | 参与植物受精过程 Involved in the process of plant fertilisation | Leshem et al., |
| AT3G12500 | -3.07184 | ATHCHIB | 叶片形态发育Leaf blade morphology development | Robles et al., |
| AT2G33850 | -2.78991 | E6L1 | 参与植物早期授粉过程 Involved in the early pollination process of plants | Doucet et al., |
| AT1G72520 | -2.61478 | LOX4 | 花器官发育 Floral organ development | Caldelari et al., |
| AT1G17420 | -2.54068 | LOX3 | 花器官发育 Floral organ development | Caldelari et al., |
| [1] |
Abdallah D, Baraket G, Perez V, Salhi Hannachi A, Hormaza J I. 2020. Self-compatibility in peach[Prunus persica(L.)Batsch]:patterns of diversity surrounding the S-locus and analysis of SFB alleles. Horticulture Research, 7:170.
doi: 10.1038/s41438-020-00392-z pmid: 34593785 |
| [2] |
Caldelari D, Wang G, Farmer E E, Dong X. 2011. Arabidopsis lox3 lox4 double mutants are male sterile and defective in global proliferative arrest. Plant Molecular Biology, 75:25-33.
doi: 10.1007/s11103-010-9701-9 pmid: 21052784 |
| [3] |
Clough S J, Bent A F. 1998. Floral dip:a simplified method for agrobacterium-mediated transformation of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Journal, 16 (6):735-743.
pmid: 10069079 |
| [4] |
Coelho C P, Huang P, Lee D Y, Brutnell T P. 2018. Making roots,shoots,and seeds:IDD gene family diversification in plants. Trends in Plant Science, 23 (1):66-78.
doi: S1360-1385(17)30204-2 pmid: 29056440 |
| [5] |
Colasanti J, Tremblay R, Wong A Y M, Coneva V, Kozaki A, Mable B K. 2006. The maize INDETERMINATE 1 flowering time regulator defines a highly conserved zinc finger protein family in higher plants. Bmc Genomics, 7 (1):1-17.
doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-7-1 URL |
| [6] |
Colasanti J, Yuan Z, Sundaresan V. 1998. The indeterminate gene encodes a zinc finger protein and regulates a leaf-generated signal required for the transition to flowering in maize. Cell, 93:593-603.
pmid: 9604934 |
| [7] | Cong Qian-qian. 2010. Genetic transformation of Brachypodium distachyon L. and isolation of INDETERMINATE1gene[M. D. Dissertation]. Tai’an: Shandong Agricultural University. (in Chinese) |
| 丛倩倩. 2010. 二穗短柄草的遗传转化及INDETERMINATE1基因的克隆[硕士论文]. 泰安: 山东农业大学. | |
| [8] | Cui D, Zhao J, Jing Y, Fan M, Liu J, Wang Z, Xin W, Hu Y. 2013. The Arabidopsis IDD14,IDD15,and IDD 16 cooperatively regulate lateral organ morphogenesis and gravitropism by promoting auxin biosynthesis and transport. PLoS Genetics, 9 (9):e1003759. |
| [9] | Deng L, Li L, Zhang S, Shen J, Li S, Hu S, Peng Q, Xiao J, Wu C. 2017. Suppressor of rid1(SID1)shares common targets with RID1 on florigen genes to initiate floral transition in rice. PLoS Genetics, 13 (2):e1006642. |
| [10] | Dong Yi, Feng Yufei, Xu Zhongmin, Wang Shimin, Tang Honglü, Huang Wei. 2021. Analysis of the relationship between genetic distance and heterosis by ssr markers in cabbage(Brassica oleracea var. capitata). Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 48 (5):934-946. (in Chinese) |
| 董艺, 冯羽飞, 许忠民, 王世民, 唐鸿吕, 黄炜. 2021. SSR标记遗传距离与结球甘蓝杂种优势的关系分析. 园艺学报, 48 (5):934-946. | |
| [11] |
Doucet J, Truong C, Frank-Webb E, Lee H K, Daneva A, Gao Z, Nowack M K, Goring D R. 2019. Identification of a role for an E6-like 1 gene in early pollen-stigma interactions in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Reproduction, 32 (3):307-322.
doi: 10.1007/s00497-019-00372-x URL |
| [12] |
Fukazawa J, Ohashi Y, Takahashi R, Nakai K, Takahashi Y. 2021. DELLA degradation by gibberellin promotes flowering via GAF1-TPR-dependent repression of floral repressors in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell, 33 (7):2258-2272.
doi: 10.1093/plcell/koab102 URL |
| [13] |
Fukazawa J, Teramura H, Murakoshi S, Nasuno K, Nishida N, Ito T, Yoshida M, Kamiya Y, Yamaguchi S, Takahashi Y. 2014. DELLAs function as coactivators of GAI-ASSOCIATED FACTOR1 in regulation of gibberellin homeostasis and signaling in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell, 26 (7):2920-2938.
doi: 10.1105/tpc.114.125690 URL |
| [14] |
Galinat W C, Naylor A W. 1951. Relation of photoperiod to inflorescence proliferation in Zea mays L. American Journal of Botany, 38:38-47.
doi: 10.1002/j.1537-2197.1951.tb14245.x URL |
| [15] |
Horiguchi G, Ferjani A, Fujikura U, Tsukaya H. 2006. Coordination of cell proliferation and cell expansion in the control of leaf size in Arabidopsis thaliana. Journal of Plant Research, 119 (1):37-42.
pmid: 16284709 |
| [16] |
Jeong E Y, Seo P J, Woo J C, Park C M. 2015. AKIN10 delays flowering by inactivating IDD 8 transcription factor through protein phosphorylation in Arabidopsis. Bmc Plant Biology, 15:110.
doi: 10.1186/s12870-015-0503-8 URL |
| [17] |
Koornneef M, Hanhart C J, van der Veen J H. 1991. A genetic and physiological analysis of late flowering mutants in Arabidopsis thaliana. Molecular and General Genetics, 229 (1):57-66.
pmid: 1896021 |
| [18] |
Krishnaswamy S, Verma S, Rahman M H, Kav N N. 2011. Functional characterization of four APETALA2-family genes(RAP2.6,RAP2.6L,DREB19and DREB26)in Arabidopsis. Plant Molecular Biology, 75:107-127.
doi: 10.1007/s11103-010-9711-7 pmid: 21069430 |
| [19] |
Kumar M, Le D T, Hwang S, Seo P J, Kim H U. 2019. Role of the INDETERMINATE DOMAIN genes in plants. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20 (9):2286.
doi: 10.3390/ijms20092286 URL |
| [20] |
Leshem Y, Johnson C, Wuest S E, Song X, Ngo Q A, Grossniklaus U, Sundaresan V. 2012. Molecular characterization of the glauce mutant:a central cell-specific function is required for double fertilization in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell, 24 (8):3264-3277.
doi: 10.1105/tpc.112.096420 URL |
| [21] | Li Shengjuan, Xu Zhongmin, Guo Jia, Zhang Enhui, Jiang Jiao, Shi Wenwen. 2019. Comparative heterosis analysis of cabbage based on transcriptome data of cabbage heads leaves. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 46 (6):1079-1092. (in Chinese) |
| 李升娟, 许忠民, 郭佳, 张恩慧, 姜娇, 石汶汶. 2019. 基于叶球转录组数据比较的甘蓝杂种优势分析. 46 (6):1079-1092. | |
| [22] | Lin Jian-li, Zhu Zheng-ge, Gao Jian-wei. 2009. Heterosis in plant research. Acta Agriculture Boreali Sinica, 24 (S2):46-56. (in Chinese) |
|
林建丽, 朱正歌, 高建伟. 2009. 植物杂种优势研究进展. 华北农学报, 24 (S2):46-56.
doi: 10.7668/hbnxb.2009.S2.011 |
|
| [23] |
Love M I, Huber W, Anders S. 2014. Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol, 15 (12):550.
doi: 10.1186/s13059-014-0550-8 URL |
| [24] |
Matsubara K, Yamanouchi U, Wang Z X, Minobe Y, Izawa T, Yano M. 2008. Ehd2,a rice ortholog of the maize INDETERMINATE1gene,promotes flowering by up-regulating Ehd1. Plant Physiology, 148 (3):1425-1435.
doi: 10.1104/pp.108.125542 pmid: 18790997 |
| [25] |
Mutasa-Göttgens E, Hedden P. 2009. Gibberellin as a factor in floral regulatory networks. Journal of Experimental Botany, 60:1979-1989.
doi: 10.1093/jxb/erp040 pmid: 19264752 |
| [26] | Qi Si-yan, Xing Li-bo, Zhang Dong, Du Li-sha, Li You-mei, Fan Sheng, Ma Juan-juan, Zhao Cai-ping, Han Ming-yu. 2017. Molecular cloning and expression analysis of the flowering regulation transcription factor gene MdIDD7 in Malus × domestica. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 44 (5):828-838. (in Chinese) |
| 齐思言, 邢利博, 张东, 杜利莎, 李有梅, 樊胜, 马娟娟, 赵彩平, 韩明玉. 2017. 苹果‘长富2号’开花调控转录因子基因MdIDD7的克隆及表达分析. 园艺学报, 44 (5):828-838. | |
| [27] |
Robles P, Micol J L. 2001. Genome-wide linkage analysis of Arabidopsis genes required for leaf development. Molecular Genetics And Genomics, 266 (1):12-19.
pmid: 11589569 |
| [28] |
Seo P J, Ryu J, Kang S K, Park C M. 2011. Modulation of sugar metabolism by an INDETERMINATE DOMAIN transcription factor contributes to photoperiodic flowering in Arabidopsis. The Plant Journal, 65:418-429.
doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2010.04432.x URL |
| [29] | Simpson G G, Dean C. 2002. Arabidopsis,the rosetta stone of flowering time? Science, 296 (5566):285-289. |
| [30] |
Singleton W R. 1946. Inheritance of indeterminate growth in maize. Journal of Heredity, 37 (2):61-64.
doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jhered.a105582 URL |
| [31] | Wu C Y, You C J, Li C H, Long T, Chen G X, Byrne M E, Zhang Q F. 2008. RID1,encoding a Cys2/His2-type zinc finger transcription factor,acts as a master switch from vegetative to floral development in rice. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 105 (35):12915-12920. |
| [32] |
Wu X, Tang D, Li M, Wang K, Cheng Z. 2013. Loose plant architecture1,an INDETERMINATE DOMAIN protein involved in shoot gravitropism,regulates plant architecture in rice. Plant Physiology, 161 (1):317-329.
doi: 10.1104/pp.112.208496 URL |
| [33] | Xiang Yuan-ping, Wang Yi-dan, He Hong-jun, Xu Qi-jiang. 2020. Plant transposable elements and the effects of insertion mutations on flower development in horticultural plants. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 47 (11):180-199. (in Chinese) |
| 相元萍, 王一丹, 贺洪军, 徐启江. 2020. 植物转座子类型及其插入突变对园艺植物花发育影响的研究进展. 园艺学报, 47 (11):180-199. | |
| [34] | Xu Yong. 2007. Study on MADS genes related to floral organ development in peach[Ph. D. Dissertation]. Beijing:Capital Normal University. (in Chinese) |
| 徐勇. 2007. 桃花发育相关MADS基因研究[博士论文]. 北京: 首都师范大学. | |
| [35] | Zhang Xi-xian. 2014. The role of Arabidopsis zinc finger protein AtIDD4 in the process of filament elongation[M. D. Dissertation]. Kunming: Yunnan University. (in Chinese) |
| 张喜贤. 2014. 拟南芥锌指蛋白AtIDD4在花丝伸长过程中的作用[硕士论文]. 昆明: 云南大学. | |
| [36] | Zhang Xu-jia, Hu Ling-zhi, Chen Zhe-hao, Li Ying, Wang Li-lin. 2014. Research progress in regulation mechanism of floral organ size. Plant Physiology Journal, 50 (6):691-697. (in Chinese) |
| 张栩佳, 胡灵芝, 陈哲皓, 李颖, 王利琳. 2014. 花器官大小调控机制的研究进展. 植物生理学报, 50 (6):691-697. | |
| [37] |
Zhang Y, Wu R, Qin G, Chen Z, Gu H, Qu L J. 2011. Over-expression of WOX1 leads to defects in meristem development and polyamine homeostasis in Arabidopsis. Journal of Integrative Plant Biology, 53 (6):493-506.
doi: 10.1111/j.1744-7909.2011.01054.x URL |
| [38] | Zhang Yu-xing. 2003. Monographs of fruit cultivation.. Version 3). Beijing: China Agriculture Press. (in Chinese) |
| 张玉星. 2003. 果树栽培学各论. 3版). 北京: 中国农业出版社. | |
| [39] | Zhang Yun, Liu Qing-lin. 2003. Proceedings on molecular mechanism of plant flower development. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 20 (5):589-601. (in Chinese) |
| 张云, 刘青林. 2003. 植物花发育的分子机理研究进展. 植物学通报, 20 (5):589-601. | |
| [40] | Zhao Yujie, Liu Cuiyu, Zhao Xueqing, Wang Yuying, Yan Ming, Yuan Zhaohe. 2021. Cloning and spatiotemporal expression analysis of PgWUS and PgBEL1 in Punica granatum. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 48 (2):355-366. |
| 赵玉洁, 刘翠玉, 招雪晴, 汪钰莹, 闫明, 苑兆和. 2021. 石榴花器官发育相关基因PgWUS和PgBEL1克隆及其时空表达分析. 园艺学报, 48 (2):355-366. |
| [1] | 翟含含, 翟宇杰, 田义, 张叶, 杨丽, 温陟良, 陈海江. 桃SAUR家族基因分析及PpSAUR5功能鉴定[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(1): 1-14. |
| [2] | 袁馨, 徐云鹤, 张雨培, 单楠, 陈楚英, 万春鹏, 开文斌, 翟夏琬, 陈金印, 甘增宇. 猕猴桃后熟过程中ABA响应结合因子AcAREB1调控AcGH3.1的表达[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(1): 53-64. |
| [3] | 邢柱东, 吕福堂, 郭尚敬, 张演义. 新品种‘聊大红金’桃[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(1): 225-226. |
| [4] | 杨兴旺, 王海波, 王莹莹, 王小龙, 王志强, 刘培培, 刘万春, 王孝娣. 中熟抗寒桃新品种‘中农甘爽’[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(S2): 15-16. |
| [5] | 杨兴旺, 王海波, 王莹莹, 张艺灿, 王宝亮, 刘培培, 史祥宾, 刘万春, 王孝娣. 中熟抗寒桃新品种‘中农白干’[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(S2): 17-18. |
| [6] | 杨兴旺, 刘凤之, 王海波, 王莹莹, 王志强, 史祥宾, 冀晓昊, 刘万春, 王孝娣. 中熟抗寒桃新品种‘中农寒水蜜’[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(S2): 19-20. |
| [7] | 杨兴旺, 刘凤之, 王海波, 王莹莹, 张艺灿, 李 鹏, 王小龙, 刘万春, 王孝娣. 晚熟抗寒桃新品种‘中农秋香’[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(S2): 21-22. |
| [8] | 王莹莹, 刘立常, 刘志伍, 杨兴旺, 刘万春, 王孝娣, . 极晚熟桃新品种‘中农冬蜜’[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(S2): 23-24. |
| [9] | 王莹莹, 刘立常, 刘志伍, 杨兴旺, 刘万春, 王孝娣, . 小果油桃新品种‘中农珍珠’[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(S2): 25-26. |
| [10] | 吴延军, 刘庆忠, 陈鸿才, 戚行江, 朱东姿, 郑家祥, 曹学敏, 方丹燕. 甜樱桃新品种‘江南锦’[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(S2): 29-30. |
| [11] | 张晓明, 闫国华, 周 宇, 王 晶, 段续伟, 吴传宝, 张开春. 甜樱桃砧木新品种‘京春2号’[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(S2): 31-32. |
| [12] | 宋 放, 陈 奇, 袁炎良, 陈 沙, 尹海军, 蒋迎春, . 黄肉猕猴桃新品种‘先沃1号’[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(S2): 47-48. |
| [13] | 齐永杰, 高正辉, 马 娜, 王清明, 柯凡君, 陈 钱, 徐义流, . 黄肉抗溃疡病猕猴桃新品种‘皖农金果’[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(S2): 49-50. |
| [14] | 张慧琴, 楼国荣, 陆玲鸿, 古咸彬, 宋根华, 谢 鸣. 黄肉中华猕猴桃新品种‘金义’[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(S2): 51-52. |
| [15] | 季琳琳, 陈素传, 吴志辉, 常 君, 韩文妍, 陶汝鹏. 早花山核桃新品种‘宁国山核桃2号’[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(S2): 53-54. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
版权所有 © 2012 《园艺学报》编辑部 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
编辑部地址: 北京市海淀区中关村南大街12号中国农业科学院蔬菜花卉研究所 邮编: 100081
电话: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
技术支持:北京玛格泰克科技发展有限公司