
园艺学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 49 ›› Issue (8): 1795-1804.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2021-0379
聂鑫淼1, 栾恒1, 冯改利1, 王超1,2, 李岩1,2,3, 魏珉1,2,3,*( )
)
收稿日期:2022-02-21
修回日期:2022-04-06
出版日期:2022-08-25
发布日期:2022-09-05
通讯作者:
魏珉
E-mail:minwei@sdau.edu.cn
基金资助:
NIE Xinmiao1, LUAN Heng1, FENG Gaili1, WANG Chao1,2, LI Yan1,2,3, WEI Min1,2,3,*( )
)
Received:2022-02-21
Revised:2022-04-06
Online:2022-08-25
Published:2022-09-05
Contact:
WEI Min
E-mail:minwei@sdau.edu.cn
摘要:
以‘新泰密刺’黄瓜(Cucumis sativus L.)自根幼苗、砧木品种‘黄诚根2号’(Cucurbita moschata Duch)和砧木品种‘云南黑籽南瓜’(Cucurbita ficifolia Bouché)嫁接幼苗为试材,通过水培试验研究了硅营养和砧木类型对黄瓜幼苗耐冷性的影响。结果表明:低温胁迫下,加硅处理的自根黄瓜幼苗冷害指数显著低于不加硅处理;无论是否加硅,嫁接黄瓜的冷害指数均低于自根黄瓜,以‘云南黑籽南瓜’嫁接黄瓜的耐冷性最强;硅营养和嫁接砧木均降低了黄瓜叶片的电解质渗漏率和丙二醛(MDA)含量,增加了脯氨酸(Pro)含量,提高了SOD、POD和CAT活性,嫁接砧木的作用大于硅营养,‘云南黑籽南瓜’的作用大于‘黄诚根2号’。综上,硅营养和嫁接砧木均影响黄瓜幼苗的耐冷性,但以砧木的作用更明显,砧木‘云南黑籽南瓜’作用大于砧木‘黄诚根2号’。
中图分类号:
聂鑫淼, 栾恒, 冯改利, 王超, 李岩, 魏珉. 硅营养和嫁接砧木对黄瓜幼苗耐冷性的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(8): 1795-1804.
NIE Xinmiao, LUAN Heng, FENG Gaili, WANG Chao, LI Yan, WEI Min. Effects of Silicon Nutrition and Grafting Rootstocks on Chilling Tolerance of Cucumber Seedlings[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(8): 1795-1804.
| 硅浓度/(mmol · L-1) Silicon concentration | 冷害指数 Chilling injury index | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 d | 3 d | 5 d | 7 d | |
| 0 | 0.37 ± 0.01 a | 0.63 ± 0.05 b | 0.77 ± 0.03 b | 0.93 ± 0.03 b |
| 0.5 | 0.33 ± 0.03 c | 0.52 ± 0.05 d | 0.64 ± 0.04 d | 0.80 ± 0.02 d |
| 1.0 | 0.33 ± 0.02 bc | 0.59 ± 0.06 c | 0.69 ± 0.03 c | 0.86 ± 0.02 c |
| 1.5 | 0.34 ± 0.02 abc | 0.60 ± 0.05 bc | 0.71 ± 0.03 c | 0.87 ± 0.01 c |
| 2.0 | 0.37 ± 0.02 ab | 0.68 ± 0.05 a | 0.81 ± 0.03 a | 0.96 ± 0.02 a |
表1 营养液硅浓度对低温胁迫下黄瓜自根幼苗冷害指数的影响
Table 1 Effects of silicon concentrations in nutrient solution on chilling injury index of non-grafted cucumber seedlings under low temperature stress
| 硅浓度/(mmol · L-1) Silicon concentration | 冷害指数 Chilling injury index | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 d | 3 d | 5 d | 7 d | |
| 0 | 0.37 ± 0.01 a | 0.63 ± 0.05 b | 0.77 ± 0.03 b | 0.93 ± 0.03 b |
| 0.5 | 0.33 ± 0.03 c | 0.52 ± 0.05 d | 0.64 ± 0.04 d | 0.80 ± 0.02 d |
| 1.0 | 0.33 ± 0.02 bc | 0.59 ± 0.06 c | 0.69 ± 0.03 c | 0.86 ± 0.02 c |
| 1.5 | 0.34 ± 0.02 abc | 0.60 ± 0.05 bc | 0.71 ± 0.03 c | 0.87 ± 0.01 c |
| 2.0 | 0.37 ± 0.02 ab | 0.68 ± 0.05 a | 0.81 ± 0.03 a | 0.96 ± 0.02 a |

图1 不同硅浓度下黄瓜自根幼苗低温胁迫7 d后的冷害症状
Fig. 1 Chilling injury symptoms of non-grafted cucumber seedlings from different silicon concentrations at 7 d after low temperature stress
| 硅浓度/(mmol · L-1) Silicon concentration | 株高抑制率/% Inhibition rate of plant height | 茎粗抑制率/% Inhibition rate of stem diameter | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 d | 3 d | 5 d | 7 d | 1 d | 3 d | 5 d | 7 d | |
| 0 | 3.18 ± 0.09 a | 9.71 ± 0.50 a | 15.05 ± 0.24 a | 19.33 ± 0.19 a | 2.36 ± 0.34 b | 11.13 ± 0.31 a | 19.18 ± 1.41 a | 25.02 ± 0.77 b |
| 0.5 | 2.48 ± 0.33 c | 7.12 ± 0.18 c | 11.64 ± 0.29 d | 16.23 ± 0.41 e | 1.71 ± 0.05 c | 6.69 ± 0.32 d | 10.27 ± 0.61 d | 18.84 ± 0.59 d |
| 1.0 | 2.79 ± 0.07 b | 7.70 ± 0.11 b | 11.99 ± 0.35 cd | 17.20 ± 0.30 d | 1.79 ± 0.02 c | 8.30 ± 0.22 c | 14.98 ± 0.78 c | 21.39 ± 0.37 c |
| 1.5 | 2.80 ± 0.04 b | 7.99 ± 0.07 b | 12.26 ± 0.46 c | 17.59 ± 0.02 c | 1.82 ± 0.03 c | 9.40 ± 0.13 b | 16.90 ± 0.93 b | 21.65 ± 0.40 c |
| 2.0 | 3.06 ± 0.07 ab | 9.92 ± 0.15 a | 14.00 ± 0.21 b | 18.55 ± 0.41 b | 2.73 ± 0.20 a | 11.25 ± 0.31 a | 19.00 ± 0.70 a | 27.08 ± 0.22 a |
表2 营养液硅浓度对低温胁迫下黄瓜自根幼苗株高和茎粗的影响
Table 2 Effects of silicon concentrations in nutrient solution on plant height and stem diameter of non-grafted cucumber seedlings under low temperature stress
| 硅浓度/(mmol · L-1) Silicon concentration | 株高抑制率/% Inhibition rate of plant height | 茎粗抑制率/% Inhibition rate of stem diameter | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 d | 3 d | 5 d | 7 d | 1 d | 3 d | 5 d | 7 d | |
| 0 | 3.18 ± 0.09 a | 9.71 ± 0.50 a | 15.05 ± 0.24 a | 19.33 ± 0.19 a | 2.36 ± 0.34 b | 11.13 ± 0.31 a | 19.18 ± 1.41 a | 25.02 ± 0.77 b |
| 0.5 | 2.48 ± 0.33 c | 7.12 ± 0.18 c | 11.64 ± 0.29 d | 16.23 ± 0.41 e | 1.71 ± 0.05 c | 6.69 ± 0.32 d | 10.27 ± 0.61 d | 18.84 ± 0.59 d |
| 1.0 | 2.79 ± 0.07 b | 7.70 ± 0.11 b | 11.99 ± 0.35 cd | 17.20 ± 0.30 d | 1.79 ± 0.02 c | 8.30 ± 0.22 c | 14.98 ± 0.78 c | 21.39 ± 0.37 c |
| 1.5 | 2.80 ± 0.04 b | 7.99 ± 0.07 b | 12.26 ± 0.46 c | 17.59 ± 0.02 c | 1.82 ± 0.03 c | 9.40 ± 0.13 b | 16.90 ± 0.93 b | 21.65 ± 0.40 c |
| 2.0 | 3.06 ± 0.07 ab | 9.92 ± 0.15 a | 14.00 ± 0.21 b | 18.55 ± 0.41 b | 2.73 ± 0.20 a | 11.25 ± 0.31 a | 19.00 ± 0.70 a | 27.08 ± 0.22 a |
| 硅浓度/(mmol · L-1) Silicon concentration | 干物质抑制率/% Inhibition rate of dry matter | 电解质渗漏率/% Electrolyte leakage rate | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 d | 3 d | 5 d | 7 d | 1 d | 3 d | 5 d | 7 d | |
| 0 | 10.99 ± 0.84 a | 24.66 ± 1.12 ab | 33.66 ± 1.03 a | 44.05 ± 0.39 ab | 37.34 ± 1.28 a | 47.25 ± 0.87 a | 50.50 ± 0.54 a | 57.36 ± 1.52 ab |
| 0.5 | 8.94 ± 0.03 c | 21.53 ± 0.57 c | 31.64 ± 0.32 b | 42.64 ± 0.47 b | 34.28 ± 1.79 b | 40.51 ± 0.27 d | 45.32 ± 0.61 c | 51.09 ± 0.60 d |
| 1.0 | 9.43 ± 0.24 b | 22.62 ± 0.09 bc | 32.84 ± 0.35 ab | 43.58 ± 0.35 ab | 36.01 ± 0.59 ab | 43.03 ± 0.28 c | 47.54 ± 0.45 b | 54.53 ± 1.36 c |
| 1.5 | 9.56 ± 0.23 b | 22.69 ± 0.50 bc | 33.07 ± 1.23 ab | 43.81 ± 0.63 ab | 36.72 ± 1.38 a | 44.98 ± 1.40 b | 48.36 ± 1.38 b | 55.60 ± 2.05 bc |
| 2.0 | 10.90 ± 0.49 a | 24.43 ± 1.29 a | 33.64 ± 1.33 a | 44.82 ± 1.02 a | 38.09 ± 0.19 a | 48.64 ± 1.82 a | 50.66 ± 0.60 a | 58.99 ± 1.44 a |
表3 营养液硅浓度对低温胁迫下黄瓜自根幼苗干物质和叶片电解质渗漏率的影响
Table 3 Effects of silicon concentrations in nutrient solution on dry matter and leaf electrolyte leakage rate of non-grafted cucumber seedlings under low temperature stress
| 硅浓度/(mmol · L-1) Silicon concentration | 干物质抑制率/% Inhibition rate of dry matter | 电解质渗漏率/% Electrolyte leakage rate | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 d | 3 d | 5 d | 7 d | 1 d | 3 d | 5 d | 7 d | |
| 0 | 10.99 ± 0.84 a | 24.66 ± 1.12 ab | 33.66 ± 1.03 a | 44.05 ± 0.39 ab | 37.34 ± 1.28 a | 47.25 ± 0.87 a | 50.50 ± 0.54 a | 57.36 ± 1.52 ab |
| 0.5 | 8.94 ± 0.03 c | 21.53 ± 0.57 c | 31.64 ± 0.32 b | 42.64 ± 0.47 b | 34.28 ± 1.79 b | 40.51 ± 0.27 d | 45.32 ± 0.61 c | 51.09 ± 0.60 d |
| 1.0 | 9.43 ± 0.24 b | 22.62 ± 0.09 bc | 32.84 ± 0.35 ab | 43.58 ± 0.35 ab | 36.01 ± 0.59 ab | 43.03 ± 0.28 c | 47.54 ± 0.45 b | 54.53 ± 1.36 c |
| 1.5 | 9.56 ± 0.23 b | 22.69 ± 0.50 bc | 33.07 ± 1.23 ab | 43.81 ± 0.63 ab | 36.72 ± 1.38 a | 44.98 ± 1.40 b | 48.36 ± 1.38 b | 55.60 ± 2.05 bc |
| 2.0 | 10.90 ± 0.49 a | 24.43 ± 1.29 a | 33.64 ± 1.33 a | 44.82 ± 1.02 a | 38.09 ± 0.19 a | 48.64 ± 1.82 a | 50.66 ± 0.60 a | 58.99 ± 1.44 a |
| 处理 Treatment | 冷害指数 Chilling injury index | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 d | 3 d | 5 d | 7 d | |
| 自根苗 Non-grafted seedlings | 0.37 ± 0.01 a | 0.63 ± 0.05 a | 0.77 ± 0.03 a | 0.93 ± 0.03 a |
| ‘黄诚根2号’嫁接苗‘Huangchenggen 2’grafted seedlings | 0.28 ± 0.03 c | 0.45 ± 0.01 c | 0.59 ± 0.04 c | 0.66 ± 0.02 c |
| ‘云南黑籽南瓜’嫁接苗‘Yunnan Figleaf Gourd’grafted seedlings | 0.23 ± 0.01 d | 0.38 ± 0.02 d | 0.51 ± 0.05 d | 0.59 ± 0.01 d |
| 自根苗 + Si Non-grafted seedlings + Si | 0.33 ± 0.03 b | 0.52 ± 0.05 b | 0.64 ± 0.04 b | 0.80 ± 0.02 b |
| ‘黄诚根2号’嫁接苗 + Si ‘Huangchenggen 2’grafted seedlings + Si | 0.25 ± 0.02 cd | 0.32 ± 0.10 de | 0.51 ± 0.03 d | 0.63 ± 0.02 cd |
| ‘云南黑籽南瓜’嫁接苗 + Si ‘Yunnan Figleaf Gourd’grafted seedlings + Si | 0.22 ± 0.02 d | 0.31 ± 0.03 e | 0.42 ± 0.05 e | 0.53 ± 0.01 e |
表4 砧木和硅营养对低温胁迫下黄瓜幼苗冷害指数的影响
Table 4 Effects of rootstock and silicon nutrition on chilling injury index of cucumber seedlings under low temperature stress
| 处理 Treatment | 冷害指数 Chilling injury index | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 d | 3 d | 5 d | 7 d | |
| 自根苗 Non-grafted seedlings | 0.37 ± 0.01 a | 0.63 ± 0.05 a | 0.77 ± 0.03 a | 0.93 ± 0.03 a |
| ‘黄诚根2号’嫁接苗‘Huangchenggen 2’grafted seedlings | 0.28 ± 0.03 c | 0.45 ± 0.01 c | 0.59 ± 0.04 c | 0.66 ± 0.02 c |
| ‘云南黑籽南瓜’嫁接苗‘Yunnan Figleaf Gourd’grafted seedlings | 0.23 ± 0.01 d | 0.38 ± 0.02 d | 0.51 ± 0.05 d | 0.59 ± 0.01 d |
| 自根苗 + Si Non-grafted seedlings + Si | 0.33 ± 0.03 b | 0.52 ± 0.05 b | 0.64 ± 0.04 b | 0.80 ± 0.02 b |
| ‘黄诚根2号’嫁接苗 + Si ‘Huangchenggen 2’grafted seedlings + Si | 0.25 ± 0.02 cd | 0.32 ± 0.10 de | 0.51 ± 0.03 d | 0.63 ± 0.02 cd |
| ‘云南黑籽南瓜’嫁接苗 + Si ‘Yunnan Figleaf Gourd’grafted seedlings + Si | 0.22 ± 0.02 d | 0.31 ± 0.03 e | 0.42 ± 0.05 e | 0.53 ± 0.01 e |

图2 不同砧木嫁接和硅营养处理黄瓜幼苗低温胁迫7 d后的冷害症状
Fig. 2 Chilling injury symptoms of cucumber seedlings treated with different rootstocks and silicon nutrition at 7 d after low temperature stress
| 处理 Treatment | 干物质抑制率Inhibition rate of dry matter | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 d | 3 d | 5 d | 7 d | |
| 自根苗 Non-grafted seedlings | 10.99 ± 0.84 a | 24.66 ± 1.12 a | 33.66 ± 1.03 a | 44.05 ± 0.39 a |
| ‘黄诚根2号’嫁接苗‘Huangchenggen 2’grafted seedlings | 8.50 ± 0.88 bc | 21.62 ± 0.43 b | 31.48 ± 0.77 b | 41.59 ± 0.78 bc |
| ‘云南黑籽南瓜’嫁接苗‘Yunnan Figleaf Gourd’grafted seedlings | 8.00 ± 0.37 b | 20.35 ± 0.56 bc | 30.84 ± 1.77 bc | 41.02 ± 1.33 b |
| 自根苗 + Si Non-grafted seedlings +Si | 8.94 ± 0.03 b | 21.53 ± 0.57 bc | 31.64 ± 0.32 b | 42.64 ± 0.47 ab |
| ‘黄诚根2号’嫁接苗 + Si‘Huangchenggen 2’grafted seedlings +Si | 7.91 ± 0.21 bc | 20.48 ± 1.11 bc | 30.39 ± 0.83 bc | 40.71 ± 0.89 bc |
| ‘云南黑籽南瓜’嫁接苗 + Si‘Yunnan Figleaf Gourd’grafted seedlings + Si | 7.24 ± 0.33 c | 19.60 ± 0.65 c | 29.51 ± 0.63 c | 38.72 ± 0.91 c |
| 处理 Treatment | 电解质渗漏率Electrolyte leakage rate | |||
| 1 d | 3 d | 5 d | 7 d | |
| 自根苗 Non-grafted seedlings | 37.34 ± 1.28 a | 47.25 ± 0.87 a | 50.50 ± 0.54 a | 57.36 ± 1.52 ab |
| ‘黄诚根2号’嫁接苗‘Huangchenggen 2’grafted seedlings | 31.93 ± 0.71 c | 35.34 ± 2.68 c | 41.38 ± 0.81 c | 43.21 ± 0.27 c |
| ‘云南黑籽南瓜’嫁接苗 ‘Yunnan Figleaf Gourd’grafted seedlings | 28.95 ± 0.80 d | 33.25 ± 2.60 cd | 39.01 ± 1.03 d | 40.56 ± 0.72 d |
| 自根苗 + Si Non-grafted seedlings + Si | 34.28 ± 1.79 b | 40.51 ± 0.27 b | 45.32 ± 0.61 b | 51.09 ± 0.60 b |
| ‘黄诚根2号’嫁接苗 + Si‘Huangchenggen 2’grafted seedlings + Si | 27.74 ± 0.89 d | 33.95 ± 0.70 c | 37.66 ± 0.90 d | 39.67 ± 2.50 d |
| ‘云南黑籽南瓜’嫁接苗 + Si‘Yunnan Figleaf Gourd’grafted seedlings + Si | 25.81 ± 0.19 e | 30.05 ± 0.95 d | 32.95 ± 1.22 e | 34.93 ± 0.30 e |
表5 嫁接砧木和硅营养对低温胁迫下黄瓜幼苗干物质和电解质渗漏率的影响
Table 5 Effects of rootstock and silicon nutrition on dry matter and electrolyte leakage rate of cucumber seedlings under low temperature stress %
| 处理 Treatment | 干物质抑制率Inhibition rate of dry matter | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 d | 3 d | 5 d | 7 d | |
| 自根苗 Non-grafted seedlings | 10.99 ± 0.84 a | 24.66 ± 1.12 a | 33.66 ± 1.03 a | 44.05 ± 0.39 a |
| ‘黄诚根2号’嫁接苗‘Huangchenggen 2’grafted seedlings | 8.50 ± 0.88 bc | 21.62 ± 0.43 b | 31.48 ± 0.77 b | 41.59 ± 0.78 bc |
| ‘云南黑籽南瓜’嫁接苗‘Yunnan Figleaf Gourd’grafted seedlings | 8.00 ± 0.37 b | 20.35 ± 0.56 bc | 30.84 ± 1.77 bc | 41.02 ± 1.33 b |
| 自根苗 + Si Non-grafted seedlings +Si | 8.94 ± 0.03 b | 21.53 ± 0.57 bc | 31.64 ± 0.32 b | 42.64 ± 0.47 ab |
| ‘黄诚根2号’嫁接苗 + Si‘Huangchenggen 2’grafted seedlings +Si | 7.91 ± 0.21 bc | 20.48 ± 1.11 bc | 30.39 ± 0.83 bc | 40.71 ± 0.89 bc |
| ‘云南黑籽南瓜’嫁接苗 + Si‘Yunnan Figleaf Gourd’grafted seedlings + Si | 7.24 ± 0.33 c | 19.60 ± 0.65 c | 29.51 ± 0.63 c | 38.72 ± 0.91 c |
| 处理 Treatment | 电解质渗漏率Electrolyte leakage rate | |||
| 1 d | 3 d | 5 d | 7 d | |
| 自根苗 Non-grafted seedlings | 37.34 ± 1.28 a | 47.25 ± 0.87 a | 50.50 ± 0.54 a | 57.36 ± 1.52 ab |
| ‘黄诚根2号’嫁接苗‘Huangchenggen 2’grafted seedlings | 31.93 ± 0.71 c | 35.34 ± 2.68 c | 41.38 ± 0.81 c | 43.21 ± 0.27 c |
| ‘云南黑籽南瓜’嫁接苗 ‘Yunnan Figleaf Gourd’grafted seedlings | 28.95 ± 0.80 d | 33.25 ± 2.60 cd | 39.01 ± 1.03 d | 40.56 ± 0.72 d |
| 自根苗 + Si Non-grafted seedlings + Si | 34.28 ± 1.79 b | 40.51 ± 0.27 b | 45.32 ± 0.61 b | 51.09 ± 0.60 b |
| ‘黄诚根2号’嫁接苗 + Si‘Huangchenggen 2’grafted seedlings + Si | 27.74 ± 0.89 d | 33.95 ± 0.70 c | 37.66 ± 0.90 d | 39.67 ± 2.50 d |
| ‘云南黑籽南瓜’嫁接苗 + Si‘Yunnan Figleaf Gourd’grafted seedlings + Si | 25.81 ± 0.19 e | 30.05 ± 0.95 d | 32.95 ± 1.22 e | 34.93 ± 0.30 e |
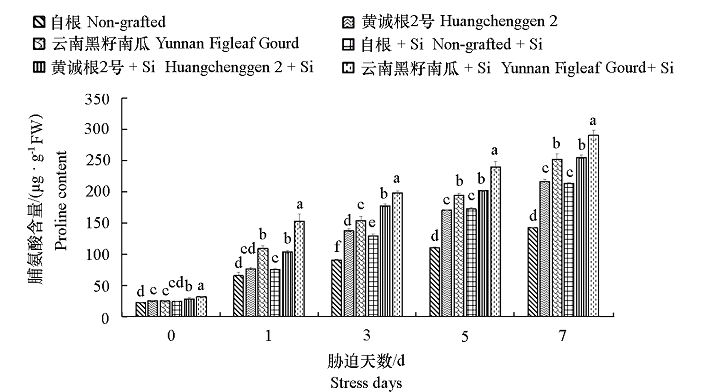
图3 嫁接砧木和硅营养对低温胁迫下黄瓜幼苗脯氨酸含量的影响 图中不同小写字母表示差异显著(P < 0.05)。下同。
Fig. 3 Effects of grafting rootstocks and silicon nutrition on proline content in cucumber seedlings under low temperature stress Different lowercase letters indicate significant difference(P < 0.05). The same below.
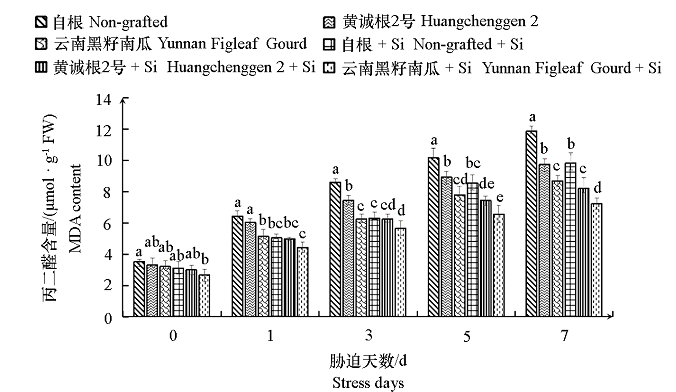
图4 嫁接砧木和硅营养对低温胁迫下黄瓜幼苗丙二醛含量的影响
Fig. 4 Effects of grafting rootstocks and silicon nutrition on malondialdehyde content in cucumber seedlings under low temperature stress
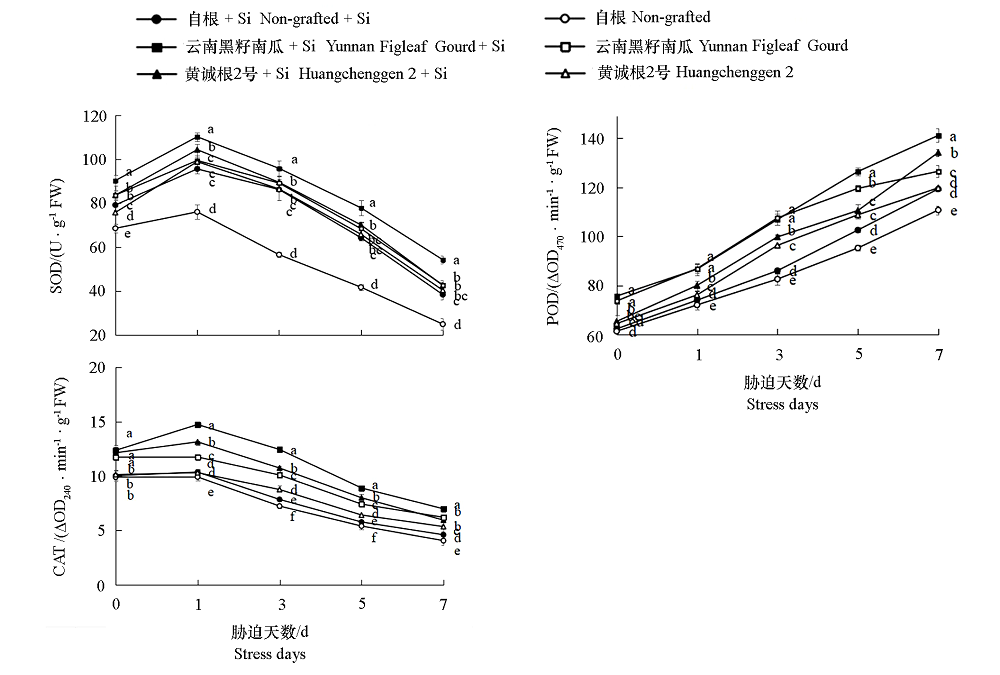
图5 嫁接砧木和硅营养对低温胁迫下黄瓜幼苗CAT、SOD、POD酶活性的影响
Fig. 5 Effects of grafting rootstocks and silicon nutrition on CAT,SOD,POD activity in cucumber seedlings under low temperature stress
| [1] |
Cakmak I, Marschner H. 1992. Magnesium deficiency and high light intensity enhance activities of superoxide dismutase,ascorbate peroxidase,and glutathione reductase in bean leaves. Plant Physiology, 98 (4):1222-1227.
doi: 10.1104/pp.98.4.1222 pmid: 16668779 |
| [2] | Gao Dan, Chen Jining, Cai Kunzheng, Luo Shiming. 2010. Distribution and absorption of silicon in plant and its role in plant disease resistance under environmental stress. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 30 (10):2745-2755. (in Chinese) |
| 高丹, 陈基宁, 蔡昆争, 骆世明. 2010. 硅在植物体内的分布和吸收及其在病害逆境胁迫中的抗性作用. 生态学报, 30 (10):2745-2755. | |
| [3] | Han Min, Cao Bili, Liu Shusen, Xu Kun. 2018. Effects of rootstock and scion interaction on chilling tolerance of grafted tomato seedlings. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 45 (2):279-288. (in Chinese) |
| 韩敏, 曹逼力, 刘树森, 徐坤. 2018. 番茄嫁接苗根穗互作对其耐冷性的影响. 园艺学报, 45 (2):279-288. | |
| [4] | Han Min, Cao Bili, Liu Shusen, Xu Kun. 2019. Effects of rootstock and scion interactions on ascorbate-glutathione cycle in tomato seedlings under low temperature stress. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 46 (1):65-73. (in Chinese) |
|
韩敏, 曹逼力, 刘树森, 徐坤. 2019. 低温胁迫下番茄幼苗根穗互作对其抗坏血酸—谷胱甘肽循环的影响. 园艺学报, 46 (1):65-73.
doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2018-0110 |
|
| [5] | Jin Ning, Lü Jian, Yu Jihua, Xie Jianming, Jin Li, Zhang Guobin, Feng Zhi. 2020. Effect of exogenous silicon on seed germination and expression of related genes in cucumber under osmotic stress. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 47 (1):41-52. (in Chinese) |
| 金宁, 吕剑, 郁继华, 颉建明, 金莉, 张国斌, 冯致. 2020. 外源硅对PEG 渗透胁迫下黄瓜种子萌发及相关基因表达的影响. 园艺学报, 47 (1):41-52. | |
| [6] | Kleiber T. 2018. The role of silicon in plant tolerance to abiotic stress //Hasanuzzaman M,Fujita M,Oku H,Nahar K,Hawrylak-Nowak B eds.eds. Plant Nutrients and Abiotic Stress Tolerance. Singapore:Springer:253-267. |
| [7] |
Lee J M. 1994. Cultivation of grafted vegetables I:current status,grafting methods,and benefits. HortScience, 29 (4):235-239.
doi: 10.21273/HORTSCI.29.4.235 URL |
| [8] | Lee J M, Bang H J, Ham H S. 1999. Quality of cucumber fruit as affected by rootstock. Acta Horticulturae, 483:117-120. |
| [9] |
Lee S H, Ahn S J, Im Y J, Cho K, Chung G C, Cho B H, Han O. 2005. Differential impact of low temperature on fatty acid unsaturation and lipoxygenase activity in figleaf gourd and cucumber roots. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 330 (4):1194-1198.
doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2005.03.098 URL |
| [10] | Li Fu-de, Fu Xin, Bi Huan-gai, Ai Xi-zhen. 2019. Response to low temperature and weak light of different cucumber rootstocks and its relationship with ABA content. China Vegetables,(5):30-37. (in Chinese) |
| 李福德, 付鑫, 毕焕改, 艾希珍. 2019. 不同黄瓜砧木对低温弱光胁迫的响应及与ABA含量的关系. 中国蔬菜,(5):30-37. | |
| [11] | Li He-sheng. 2004. Plant physiology experimental guidance. Beijing: Higher Education Press. (in Chinese) |
| 李合生. 2004. 植物生理学实验指导. 北京: 高等教育出版社. | |
| [12] | Li Hong-li, Wang Ming-lin, Yu Xian-chang, Wang Huaseng, Gao Jun-jie, Yu Chao. 2006. Effect of different scions/rootstocks on quality of cucumber fruits in greenhouse. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 39 (8):1611-1616. (in Chinese) |
| 李红丽, 王明林, 于贤昌, 王华森, 高俊杰, 于超. 2006. 不同接穗/砧木组合对日光温室黄瓜果实品质的影响. 中国农业科学, 39 (8):1611-1616. | |
| [13] | Li Qing-fang, Ma Cheng-cang. 2002. Effect of available silicon in soil on cucumber seed germination and seedling growth metabolism. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 29 (5):433-437. (in Chinese) |
| 李清芳, 马成仓. 2002. 土壤有效硅对黄瓜种子萌发和幼苗生长代谢的影响. 园艺学报, 29 (5):433-437. | |
| [14] |
Liang Y, Si J, Römheld V. 2005. Silicon uptake and transport is an active process in Cucumis sativus. New Phytologist, 167 (3):797-804.
doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8137.2005.01463.x URL |
| [15] | Liu Qing. 2011. Effects of different rootstocks on fruit quality and silicon distribution characteristics of grafted cucumber[M. D. Dissertation]. Tai’an: Shandong Agricultural University. (in Chinese) |
| 刘青. 2011. 不同砧木对嫁接黄瓜果实品质和硅分配特性的影响[硕士论文]. 泰安: 山东农业大学. | |
| [16] | Liu Qing, Wei Min, Shen Qiong, Wang Xiu-feng, Yang Feng-juan, Shi Qing-hua. 2012. Effects of different rootstocks on bloom formation and absorption and distribution of silicon in grafted cucumber. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 39 (5):897-904. (in Chinese) |
| 刘青, 魏珉, 沈琼, 王秀峰, 杨凤娟, 史庆华. 2012. 不同砧木对嫁接黄瓜蜡粉形成及硅吸收分配的影响. 园艺学报, 39 (5):897-904. | |
| [17] | Marschner H. 1995. Mineral nutrition of higher plants. 2nd Edition. London: Academic Press Limited:313-363. |
| [18] | Tian Xue-mei. 2011. Effects of different rootstocks on tolerance of grafted cucumber to low temperature,weak light and salt stress[M. D. Dissertation]. Tai’an: Shandong Agricultural University. (in Chinese) |
| 田雪梅. 2011. 不同砧木对嫁接黄瓜耐低温弱光和耐盐性的影响研究[硕士论文]. 泰安: 山东农业大学. | |
| [19] | Wang Hai-hong, Zhu Peng-fei, Shu Liang-zuo, Zhou Xiu-jie. 2011. Effects of silicon on growth of cucumber seedlings under low temperature stress. Ecological Science, 30 (1):38-42. (in Chinese) |
| 王海红, 祝鹏飞, 束良佐, 周秀杰. 2011. 硅对低温胁迫下黄瓜幼苗生长的影响. 生态科学, 30 (1):38-42. | |
| [20] | Wu Yan, Gao Qing-hai. 2010. Physiological responses of savoy to exogenous silicon under chilling stress. Plant Physiology Communications, 46 (9):928-932. (in Chinese) |
| 吴燕, 高青海. 2010. 低温胁迫下乌塌菜对外源硅的生理响应. 植物生理学通讯, 46 (9):928-932. | |
| [21] | Xu Y, Guo S, Li H, Sun H, Sun Z, Lu N, Shu S, Sun J. 2017. Resistance of cucumber grafting rootstock pumpkin cultivars to chilling and salinity stresses. Korean Journal of Horticultural Science & Technology, 35 (2):220-231. |
| [22] | Yu Xian-chang, Xing Yu-xian, Ma Hong, Wei Min. 1998. Effect of different rootstocks and scions on chilling tolerance in grafted cucumber seedlings. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 31 (2):36-40. (in Chinese) |
| 于贤昌, 邢禹贤, 马红, 魏珉. 1998. 不同砧木与接穗对黄瓜嫁接苗抗冷性的影响. 中国农业科学, 31 (2):36-40. | |
| [23] | Zeng Yi-an, Zhu Yue-lin, Huang Bao-jian, Yang Li-fei. 2004. Effects of Cucurbita ficifolia as rootstock on growth,fruit setting,disease resistance and leaf nutrient element contents in Cucumis sativus. Journal of Plant Resources and Environment, 13 (4):15-19. (in Chinese) |
| 曾义安, 朱月林, 黄保健, 杨立飞. 2004. 黑籽南瓜砧木对黄瓜生长结实、抗病性及营养元素含量的影响. 植物资源与环境学报, 13 (4):15-19. | |
| [24] | Zhao Peipei, Yu Lihe, Zhao Changjiang. 2015. Effects of silicon on growth and physiological parameters of spring wheat seedlings under low temperature conditions. Jourmal of Heilongjiang Bayi Agricultural University, 27 (1):15-21,36. (in Chinese) |
| 赵培培, 于立河, 赵长江. 2015. 低温下硅对春小麦幼苗生长及生理特性的影响. 黑龙江八一农垦大学学报, 27 (1):15-21,36. | |
| [25] | Zhao Sheng, Li Zhihong, Shen Qiong, Wang Hui, Zhou Xin, Wei Min. 2018. Effects of silicon nutrition and rootstocks on silicon uptake and distribution and expression of silicon transporter genes in grafted cucumbers. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 45 (6):1115-1124. (in Chinese) |
| 赵升, 李治红, 沈琼, 王慧, 周鑫, 魏珉. 2018. 外源硅对不同砧木嫁接黄瓜果面蜡粉和硅吸收及相关基因表达的影响. 园艺学报, 45 (6):1115-1124. | |
| [26] | Zhai Jiang, Gao Yuan, Zhang Xiaowei, Han Lujie, Bi Huangai, Li Qingming, Ai Xizhen. 2019. Effects of silicon and calcium on photosynthesis,yield and quality of cucumber in solar-greenhouse. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 46 (4):701-713. (in Chinese) |
| 翟江, 高原, 张晓伟, 韩鲁杰, 毕焕改, 李清明, 艾希珍. 硅钙对日光温室黄瓜光合作用及产量和品质的影响. 园艺学报, 46 (4):701-713. | |
| [27] |
Zhou Y H, Huang L F, Zhang Y L, Shi K, Yu J Q, Nogués S. 2007. Chilling-induced decrease in capacity of RuBP carboxylation and associated H2O2 accumulation in cucumber leaves are alleviated by grafting onto figleaf gourd. Annals of Botany, 100 (4):839-847.
doi: 10.1093/aob/mcm181 URL |
| [28] |
Zhu Z J, Wei G Q, Li J, Qian Q Q, Yu J Q. 2004. Silicon alleviates salt stress and increases antioxidant enzymes activity in leaves of salt-stressed cucumber(Cucumis sativus L.). Plant Science, 167 (3):527-530.
doi: 10.1016/j.plantsci.2004.04.020 URL |
| [1] | 任 菲, 卢苗苗, 刘吉祥, 陈信立, 刘道凤, 眭顺照, 马 婧. 蜡梅胚胎晚期丰富蛋白基因CpLEA的表达及抗性分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(2): 359-370. |
| [2] | 蔺海娇, 梁雨晨, 李玲, 马军, 张璐, 兰振颖, 苑泽宁. 薰衣草CBF途径相关耐寒基因挖掘与调控网络分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(1): 131-144. |
| [3] | 张晓明, 闫国华, 周 宇, 王 晶, 段续伟, 吴传宝, 张开春. 甜樱桃砧木新品种‘京春2号’[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(S2): 31-32. |
| [4] | 黄树苹, 谈 杰, 陈 霞, 张洪源, 李 烨, 王本启, 陈 浩, 吴雪霞, 张 敏, . 茄子新品种‘鄂茄六号’[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(S2): 101-102. |
| [5] | 罗天宽, 吴海涛, 张圣美, 黄宗安, 孙 继, 水德聚, 陈先知. 黄瓜新品种‘瓯翠1号’[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(S2): 125-126. |
| [6] | 田红梅, 刘 娟, 张长坤, 陶 珍, 张 建, 王朋成, . 甜瓜砧木用南瓜新品种‘皖砧6号’[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(S2): 127-128. |
| [7] | 王鹤冰, 向华丰, 陈新中, 张 生, 张洪成. 华南型黄瓜新品种‘新燕095’[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(S1): 79-80. |
| [8] | 许春梅, 张作标, 柳景兰, 王 昕, 杨 龙, 赵 丹, 刘思宇, 贾云鹤, 孟雪娇, 崔嵩岑. 黄瓜新品种‘绿春2号’[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(S1): 81-82. |
| [9] | 张利东, 黄洪宇, 孔维良, 李加旺, 李愚鹤, . 华北型黄瓜新品种‘津优355’[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(S1): 83-84. |
| [10] | 王惠哲, 杨瑞环, 邓 强, 曹明明, 李淑菊, . 抗黑星病黄瓜新品种‘津冬369’[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(S1): 85-86. |
| [11] | 郑晓东, 袭祥利, 李玉琪, 孙志娟, 马长青, 韩明三, 李少旋, 田义轲, 王彩虹. 油菜素内酯对盐碱胁迫下平邑甜茶幼苗生长的影响及调控机理研究[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(7): 1401-1414. |
| [12] | 李琼, 李丽丽, 侯娟, 罗忍忍, 王瑞丹, 胡建斌, 黄松. 瓜类作物响应低温胁迫机制的研究进展[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(6): 1382-1394. |
| [13] | 刘众杰, 郑婷, 赵方贵, 傅伟红, 诸葛雅贤, 张志昌, 房经贵. 葡萄砧木对渗透胁迫的抗性差异及生理响应机理[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(5): 984-994. |
| [14] | 韩鲁杰, 冯一清, 杨秀华, 张宁, 毕焕改, 艾希珍. 有机肥化肥配施对大棚黄瓜根区土壤与根系特征的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(5): 1047-1059. |
| [15] | 权建华, 段誉, 罗天, 袁强, 齐鑫, 王勤礼. 黄瓜新品种‘裕研9号’[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(3): 703-704. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
版权所有 © 2012 《园艺学报》编辑部 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
编辑部地址: 北京市海淀区中关村南大街12号中国农业科学院蔬菜花卉研究所 邮编: 100081
电话: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
技术支持:北京玛格泰克科技发展有限公司