
园艺学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 49 ›› Issue (4): 907-923.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2021-0063
收稿日期:2021-08-06
修回日期:2021-12-27
出版日期:2022-04-25
发布日期:2022-04-25
通讯作者:
王晓卓
E-mail:catreewp@outlook.com
基金资助:
CHEN Tongqiang1, ZHANG Tianzhu2, WANG Xiaozhuo3,*( )
)
Received:2021-08-06
Revised:2021-12-27
Online:2022-04-25
Published:2022-04-25
Contact:
WANG Xiaozhuo
E-mail:catreewp@outlook.com
摘要:
概述了光照对番茄红素生物合成调控的研究进展,探究光照在基因转录、转录后、光胁迫、光合产物等层面对番茄红素生物合成的辅助调控机制。结论表明:红光/远红光对PSY基因转录调控是主要方式之一,红光/远红光、蓝光及紫外光信号转导中存在交叉联系,HY5、PIF及COP1等光响应因子同时参与多种不同光质的信号转导过程。红光/远红光对PSY酶活性和番茄红素生物合成底物葡萄糖的调控,番茄红素对光胁迫下的抗胁迫响应,是番茄红素生物合成的辅助调控方式。
中图分类号:
陈同强, 张天柱, 王晓卓. 光照对番茄果实中番茄红素生物合成的调控研究进展[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(4): 907-923.
CHEN Tongqiang, ZHANG Tianzhu, WANG Xiaozhuo. Research Progress of The Regulation of Light on Lycopene Biosynthesis in Tomato Fruit[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(4): 907-923.
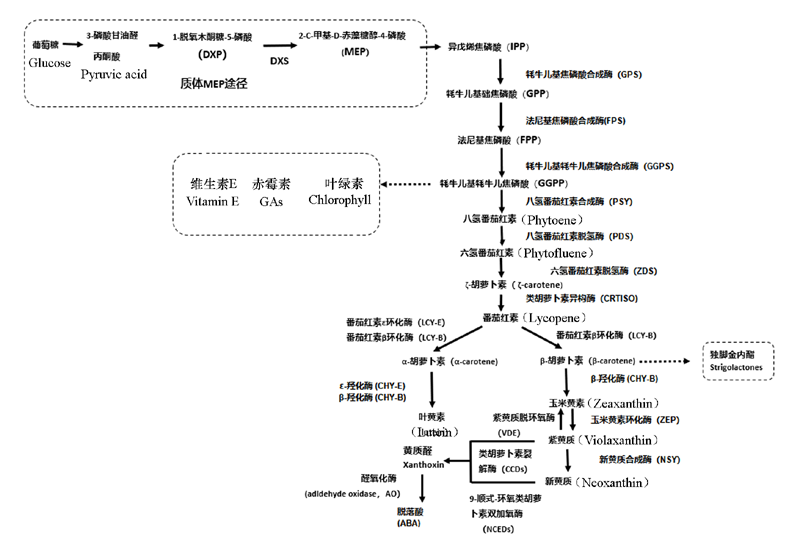
图1 高等植物类胡萝卜素代谢途径
Fig. 1 Biosynthetic pathway of carotenoids in tomato Fraser et al.,2007;Kang et al.,2010;王楠,2016;Wurtzel,2019;Hermanns et al.,2020;刘昕 等,2020.
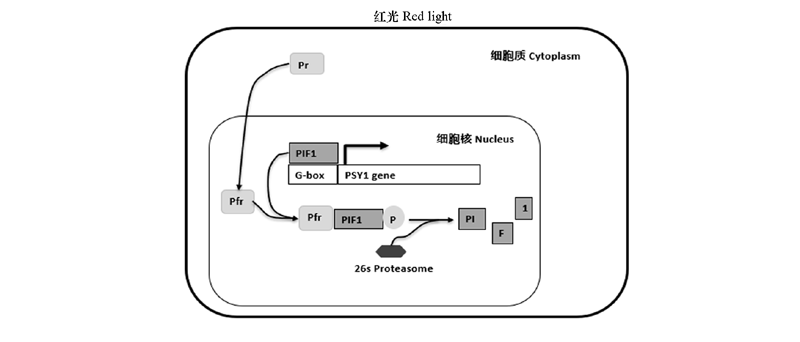
图3 红光下光敏色素PHY对PSY基因转录的调控机制
Fig. 3 The schematic regulation mechanism of phytochromes on PSY gene transcription under red light Llorente et al.,2016;Pham et al.,2018.
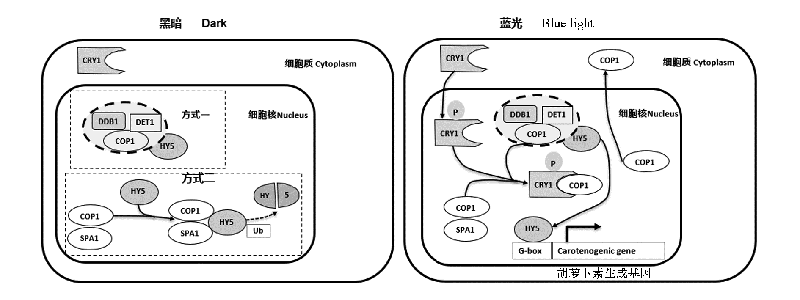
图4 蓝光照射下,隐花色素对PSY基因的调控机制
Fig. 4 The schematic regulation mechanism of Cryptochrome on carotenoid-related genes under blue light treatment Jiao et al.,2007;Pizarro & Stange,2009;Pham et al.,2018.
| [1] |
Ahmad M, Jarillo J A, Smirnova O, Cashmore A R. 1998. The CRY1 blue light photoreceptor of Arabidopsis interacts with phytochrome A in vitro. Mol Cell, 1:939-948.
pmid: 9651577 |
| [2] |
Al-Babili S, Lintig J V, Haubruck H, Beyer P. 1996. A novel,soluble form of phytoene desaturase in Narcissus pseudonarcissus chromoplasts is Hsp 70-complexed & competent for-avinylation,membrane association & enzymatic activation. The Plant Journal, 9:601-612.
doi: 10.1046/j.1365-313X.1996.9050601.x URL |
| [3] |
Alba R, Marie-Michèle Cordonnier-Prat, Pratt L H. 2000. Fruit-localized phytochromes regulate lycopene accumulation independently of ethylene production in tomato. Plant Physiol, 123:363-370.
pmid: 10806253 |
| [4] | Ambasht N K, Agrawal M. 1995. Physiological responses of field grozon Zea may L. plants to enhanced UV-B radiation. Biotronics, 24 (2):15-23. |
| [5] |
Benedict C R, Rosenfield C L, Mahan J R, Madhavan S, Yokoyame H. 1985. The chemical regulation of carotenoid biosynthesis in citrus. Plant Science, 41 (3):169-173.
doi: 10.1016/0168-9452(85)90084-6 URL |
| [6] |
Bramley P M. 2002. Regulation of carotenoid formation during tomato fruit ripening and development. Journal of Experimental Botany, 53 (337):2107-2113.
doi: 10.1093/jxb/erf059 URL |
| [7] |
Briggs W, Tseng T S, Cho H T, Swartz T, Sullivan S, Bogomolni R, Kaiserli E, Christie J. 2007. Phototropins and their LOV domains:versatile plant blue-light receptors. J Integr Plant Biol, 49:4-10.
doi: 10.1111/j.1744-7909.2006.00406.x URL |
| [8] |
Brown B A, Cloix C, Jiang G H, Kaiserli E, Herzyk P, Kliebenstein D J, Jenkins G I. 2005. A UV-B-specific signaling component orchestrates plant UV protection. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 102:18225-18230.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.0507187102 URL |
| [9] |
Bu J W, Ni Z D, Aisikaer G, Jiang Z H, Khan Z U, Mou W S, Ying T J. 2014. Postharvest ultraviolet-C irradiation suppressed Psy1 and Lcy-β expression and altered color phenotype in tomato(Solanum lycopersicum)fruit. Postharvest Biology and Technology, 89:1-6.
doi: 10.1016/j.postharvbio.2013.10.005 URL |
| [10] |
Bu J W, Yu Y C, Aisikaer G, Ying T J. 2013. Postharvest UV-C irradiation inhibits the production of ethylene and the activity of cell wall-degrading enzymes during softening of tomato(Lycopersicon esculentum L.)fruit. Postharvest Biology and Technology, 86:337-345.
doi: 10.1016/j.postharvbio.2013.07.026 URL |
| [11] |
Carrari F, Fernie A R. 2006. Metabolic regulation underlying tomato fruit development. J Exp Bot, 57 (9):1883-1897.
doi: 10.1093/jxb/erj020 URL |
| [12] |
Chen M, Chory J, Fankhauser C. 2004. Light signal transduction in higher plants. Annu Rev Genet, 38:87-117.
doi: 10.1146/annurev.genet.38.072902.092259 URL |
| [13] | Chen Qiang. 2009. Effect of different light emitting diode sources on tomato physiological characteristics & fruit quality of tomato during color transformation[Ph. D. Dissertation]. Tai’an:Shandong Agricultural University, (in Chinese) |
| 陈强. 2009. 不同LED光源对番茄果实转色过程中生理特性及果实品质的影响[博士论文]. 泰安:山东农业大学, | |
| [14] | Chen Qiang, Liu Shi-qi, Zhang Zi-kun, Cui Hui-ru, Hao Shu-qin, Liu Zhong-liang. 2009. Effect of different light emitting diode sources on tomato fruit quality during color-changed period. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 29 (5):156-161. (in Chinese) |
| 陈强, 刘世琦, 张自坤, 崔慧茹, 郝树芹, 刘忠良. 2009. 不同LED光源对番茄果实转色期品质的影响. 农业工程学报, 29 (5):156-161. | |
| [15] | Cheng Lin. 2012. The research of the molecular mechanism of Spd affects the tomato carotenoid metabolism under high temperature & function anlysis of SlMAPK3[Ph. D. Dissertation]. Hangzhou:Zhejiang University, (in Chinese) |
| 程琳. 2012. Spd影响高温下番茄果实类胡萝卜素代谢分子机制研究及SlMAPK3的功能分析[博士论文]杭州:浙江大学, | |
| [16] | Cocaliadis M F, Fern&ez-Munoz R, Pons C, Orzaez D, Granell A. 2014. Increasing tomato fruit quality by enhancing fruit chloroplast function. A double-edged sword? Journal of Experimental Botany, (16):4589-4598. |
| [17] |
Cookson P J, Kiano J W, Shipton C A, Fraser P D, Romer S, Schuch W, Bramley P M, Pyke K A. 2003. Increases in cell elongation,plastid compartment size & phytoene synthase activity underlie the phenotype of the high pigment-1 mutant of tomato. Planta, 217:896-903.
pmid: 12844264 |
| [18] | Crispin A H, Barry J P. 2006. Carotenoid accumulation & function in seeds & non-green tissues. Plant Cell & Environment, 29:435-445. |
| [19] | Cronje P J R, Barry G H, Huysamer M. 2013. Canopy position affects pigment expression & accumulation of flavedo carbohydrates of“Nules Clementine”madarin fruit,thereby affecting rind condition. J Amer Soc Hortic Sci, 138:217-224. |
| [20] |
Dall’Osto L, Piques M, Ronzani M, Molesini B, Alboresi A, Cazzaniga S, Bassi R. 2013. The Arabidopsis nox mutant lacking carotene hydroxylase activity reveals a critical role for xanthophylls in photosystem I biogenesis. Plant Cell, 25:591-608.
doi: 10.1105/tpc.112.108621 URL |
| [21] |
Davuluri G R, Van Tuinen A, Fraser P D, Manfredonia A, Newman R, Burgess D, Brummell D A, King S R, Palys J, Uhlig J, Bramley P M, Pennings H M J, Bowler C. 2005. Fruit-specific RNAi-mediated suppression of DET1 enhances carotenoid & flavonoid content in tomatoes. Nature Biotechnology, 23 (7):890-895.
pmid: 15951803 |
| [22] |
Eisenreich W, Bacher A, Arigoni D, Arigoni, Rohdich F. 2004. Biosynthesis of isoprenoids via the non-mevalonate pathway. Cell Mol Life Sci, 61:1401-1426.
pmid: 15197467 |
| [23] | Feng Mei, Song Chang-bing. 2005. Fruit pigment & sugar content in Lycium barbarum fruit during fruit development. Northern Horticulture,(6):68-69. (in Chinese) |
| 冯美, 宋长冰. 2005. 枸杞果实发育过程中果实色素、糖含量的变化. 北方园艺,(6):68-69. | |
| [24] | Ford N A, Erdman J W. 2012. Are lycopene metabolites metabolically active. Acta Biochimica Polonica, 59 (1):1-4. |
| [25] |
Fraser P D, Enfissi E M, Halket J M, Truesdale M R, Yu D M, Gerrish C, Bramley P M. 2007. Manipulation of phytoene levels in tomato fruit:effects on is oprenoids,plastids,& intermediary metabolism. Plant Cell, 19 (10):3194-3211.
doi: 10.1105/tpc.106.049817 pmid: 17933904 |
| [26] |
Fraser P D, Truesdale M R, Bird C R, Schuch W, Bramley P M. 1994. Carotenoid biosynthesis during tomato fruit development(Evidence for tissue-specific gene expression). Plant Physiology, 105 (1):405-413.
pmid: 12232210 |
| [27] |
Fray R G, Wallace A, Fraser P D, Valero D, Hedden P, Bramley P M, Grierson D. 1995. Constitutive expression of a fruit phytoene synthase gene in transgenic tomatoes causes dwarfism by redirecting metabolites from the gibberellin pathway. The Plant Journal, 8 (5):693-701.
doi: 10.1046/j.1365-313X.1995.08050693.x URL |
| [28] |
Fuentes P, Pizarro L, Moreno J C, Handford M, Rodriguez-Concepcion M, Stange C. 2012. Light-dependent changes in plastid differentiation influence carotenoid gene expression & accumulation in carrot roots. Plant Molecular Biology, 79:47-59.
doi: 10.1007/s11103-012-9893-2 URL |
| [29] |
Galpaz N, Wang Q, Menda M, Zamir D, Hirschber J. 2008. Abscisic acid deficiency in the tomato mutant high-pigment 3 leading to increased plastid number & higher fruit lycopene content. The Plant Journal, 53:717-730.
pmid: 17988221 |
| [30] | Gao Hui-jun, Ming Jia-qi, Zhang Ya-juan, Xu Juan. 2015. Regulation of carotenoids biosynthesis in horticultural crops. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 42 (9):1633-1648. (in Chinese) |
| 高慧君, 明家琪, 张雅娟, 徐娟. 2015. 园艺植物中类胡萝卜素合成与调控的研究进展. 园艺学报, 42 (9):1633-1648. | |
| [31] |
Giliberto L, Perrotta G, Pallara P, Weller J L, Fraser P D, Bramley P M, Fiore A, Tavazza M, Giuliano G. 2005. Manipulation of the blue light photoreceptor cryptochrome 2 in tomato affects vegetative development,flowering time,& fruit antioxidant content. Plant Physiol, 137:199-208.
pmid: 15618424 |
| [32] |
Hermanns A S, Zhou X S, Xu Q, Tadmor Y. 2020. Carotenoid pigment accumulation in horticultural plants. Horticultural Plant Journal, 6 (6):343-360.
doi: 10.1016/j.hpj.2020.10.002 URL |
| [33] |
Hirschberg J. 2001. Carotenoid biosynthesis in flowering plants. Curr Opin Plant Biol, 4:210-218.
pmid: 11312131 |
| [34] |
Jiao Y L, Lau O S, Deng X W. 2007. Light-regulated transcriptional networks in higher plants. Nature Review Genetic, 8 (3):217-230.
doi: 10.1038/nrg2049 URL |
| [35] |
Jung I C, Yang J Y, Seo H S, Chua N H. 2005. HFRA is targeted by COP1 E3 ligase for post-transcriptional proteolysis during phytochrome A signaling. Genes Develop, 19:593-602.
doi: 10.1101/gad.1247205 URL |
| [36] | Kaiser E, Ouzounis T, Giday H, Schipper R, Heuvelink E, Marcelis L F M. 2019. Adding blue to red supplemental light increases biomass & yield of greenhouse-grown tomatoes,but only to an optimum. Frontiers in Plant Science,(9):1-11. |
| [37] |
Kang B S, Zhao W E, Hou Y B, Tian P. 2010. Expression of carotenogenic genes during the development & ripening of watermelon fruit. Scientia Horticulturae, 124 (3):368-375.
doi: 10.1016/j.scienta.2010.01.027 URL |
| [38] | Kang Bao-shan. 2014. Molecular analysis of yellow flesh formation in tomato accession PI114490[Ph. D. Dissertation]. Beijing:China Agricultural University. (in Chinese) |
| 康保珊. 2014. 番茄材料PI114490黄色果肉形成的分子分析[博士论文]. 北京: 中国农业大学. | |
| [39] |
Klee H J, Giovannoni J J. 2011. Genetics & control of tomato ruit ripening & quality attributes. Annu Rev Genet, 45:41-59.
doi: 10.1146/annurev-genet-110410-132507 URL |
| [40] |
Lado J, Alos E, Manzi M, Cronje P J R, Zacarias L. 2019. Light regulation of carotenoid biosynthesis in the peel of madarin sweet orange fruits. Frontiers in Plant Science, 10:1288.
doi: 10.3389/fpls.2019.01288 URL |
| [41] |
Lau O S, Deng X W. 2012. The photomorpho genic repressors COP1 and DET1:20 years later. Trends Plant Sci, 17 (10):584-593.
doi: 10.1016/j.tplants.2012.05.004 URL |
| [42] | Lee G H, Bunn J M, Han Y J, Decoteau D R. 1996. Initiating or delaying ripening of tomatoes with light. Hortic Abstr, 66:6037. |
| [43] | Leivar P, Monte E. 2014. PIFs:systems integrators in plant development. Plant Cell, 176:1025-1038. |
| [44] | Leonelli L, Brooksa M D, Niyogi K K. 2017. Engineering the lutein epoxide cycle into Arabidopsis thaliana. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 114:E7002-E7008. |
| [45] | Li Ji-suo. 2003. The primary studies of the influence factors & heredity on the lycopene content of tomato(Lycopersicum esculentum Mill)[M. D. Dissertation]. Beijing: China Agricultural University. (in Chinese) |
| 李纪锁. 2003. 番茄中番茄红素含量影响因素及遗传的初步研究[硕士论文]. 北京: 中国农业大学. | |
| [46] | Li Yan, Wang Li-wei, Wen Lian-lian, Wei Min, Shi Qing-hua, Yang Feng-juan, Wang Xiu-feng. 2017. Effects of red and blue light qualities on main fruit quality of tomato during color-turning period. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 44 (12):2372-2382. (in Chinese) |
| 李岩, 王丽伟, 文莲莲, 魏珉, 史庆华, 杨凤娟, 王秀峰. 2017. 红蓝光质对转色期间番茄果实主要品质的影响. 园艺学报, 44 (12):2372-2382. | |
| [47] |
Lin C, Shalitin D. 2003. Cryptochrome structure and signal transduction. Annu Rev Plant Biol, 54:469-496.
doi: 10.1146/annurev.arplant.54.110901.160901 URL |
| [48] |
Lintig J V, Welsch R, Bonk M, Giuliano G, Batschauer A, Kleinig H. 1997. Light-dependent regulation of carotenoid biosynthesis occurs at the level of phytoene synthase expression and is mediated by phytochrome in Sinapis alba and Arabidopsis thaliana seedlings. The Plant Journal, 12 (3):625-634.
doi: 10.1046/j.1365-313X.1997.d01-16.x URL |
| [49] |
Liu C H, Cai L Y, Han X X, Ying T J. 2012a. Temporary effect of postharvest UV-C irradiation on gene expression profile in tomato fruit. Gene, 486 (1-2):56-64.
doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2011.07.001 URL |
| [50] | Liu Chang-hong. 2012. Study on the effects and mechanism of UV-C or UV-B treatment on quality and secondary metabolism in postharvest tomato fruit[Ph. D. Dissertation]. Hangzhou:Zhejiang University. (in Chinese) |
| 刘长虹. 2012. 中短波紫外线调节采后番茄品质及相关次生代谢的效应与机理[博士论文]. 杭州: 浙江大学. | |
| [51] | Liu Di, Hu Zhi-bi. 1998. Regulation of biosynthetic pathway of isoprenoids in plants. Plant Physiology Journal, 34 (1):1-9. (in Chinese) |
| 刘涤, 胡之壁. 1998. 植物类异戊二烯生物合成途径的调节. 植物生理学通讯, 34 (1):1-9. | |
| [52] |
Liu L, Jia C, Zhang M, Chen D, Chen S, Guo R, Guo D, Wang Q. 2014. Ectopic expression of a BZR1-1D transcription factor in brassinosteroid signalling enhances carotenoid accumulation and fruit quality attributes in tomato. Plant Biotechnol J, 12:105-115.
doi: 10.1111/pbi.12121 URL |
| [53] |
Liu L, Wei J, Zhang M, Zhang L, Li C, Wang Q. 2012b. Ethylene independent induction of lycopene biosynthesis in tomato fruits by jasmonates. J Exp Bot, 63:5751-5761.
doi: 10.1093/jxb/ers224 URL |
| [54] |
Liu L H, Shao Z Y, Zhang M, Wang Q M. 2015. Regulation of carotenoid metabolism in tomato. Molecular Plant, 8:28-39.
doi: 10.1016/j.molp.2014.11.006 URL |
| [55] |
Liu L H, Zabaras D, Bennett L E, Aguas P, Woonton B W. 2009. Effects of UV-C,red light and sun light on the carotenoid content and physical qualities of tomatoes during post-harvest storage. Food Chem, 115:495-500.
doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2008.12.042 URL |
| [56] | Liu Li-hong. 2016. Regulation of carotenoids accumulation in tomato fruit by jasmonic acid and brassinosteroid[Ph. D. Dissertation]. Hangzhou:Zhejiang University. (in Chinese) |
| 刘丽红. 2016. 茉莉酸和油菜素甾醇调控番茄果实类胡萝卜素积累的机理研究[博士论文]. 杭州: 浙江大学. | |
| [57] | Liu Xiao-ying, Chang Tao-tao, Guo Shi-rong, Xu Zhi-gang, Chen Wen-hao. 2010. Effect of irradiation with blue and red LED on fruit quality of cherry tomato during growth period. China Vegetables,(22):21-27. (in Chinese) |
| 刘晓英, 常涛涛, 郭世荣, 徐志刚, 陈文昊. 2010. 红蓝LED光全生育期照射对樱桃番茄果实品种的影响. 中国蔬菜,(22):21-27. | |
| [58] | Liu Xin, Chen Yunzhu, Kim Pyol, Kim MinJun, Song Hyondok, Li Yuhua, Wang Yu. 2020. Progress on molecular mechanism and regulation of tomato fruit color formation. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 47 (9);1689-1704. (in Chinese) |
| 刘昕, 陈韵竹, Kim Pyol, Kim Min-Jun, Song Hyondok, 李玉花, 王宇. 2020. 番茄果实颜色形成的分子机制及调控研究进展. 园艺学报, 47 (9):1689-1704. | |
| [59] |
Liu Y, Roof S, Ye Z, Barry C, Van T, Vrebalov J, Bowler C, Giovannoni J. 2004. Manipulation of light signal transduction as a means of modifying fruit nutritional quality in tomato. Proc Natl Acad Sci, 101:9897-9902.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.0400935101 URL |
| [60] | Liu Yun-fei, Wan Hong-jian, Yuan Wei, Yu Ke, Yang Yue-jian. 2012. The carotenoid and its changes during the tomato fruit growth and development. Journal of Zhejiang Agricultural Sciences,(11):1506-1512. (in Chinese) |
| 刘云飞, 万红建, 袁伟, 俞锞, 杨悦俭. 2012. 类胡萝卜素及其在番茄果实生长发育中的变化. 浙江农业科学,(11):1506-1512. | |
| [61] |
Llorente B, D'Andrea L, Ruiz-Sola M A, Botterweg E, Pulido P, Andilla J, Loza-Alvarez P, Rodriguez-Concepcion M. 2016. Toamto fruit carotenoid biosynthesis is adjusted to actual ripening progression by a light-dependent mechanism. The Plant Journal, 85 (1):107-119.
doi: 10.1111/tpj.13094 pmid: 26648446 |
| [62] |
Llorente B, Martinez-Garcia J F, Stange C, Rodriguez-Concepcion M. 2017. Illuminating colors regulation of carotenoid biosynthesis and accumulation by light. Current Opinion in Plant Biology, 37:49-55.
doi: S1369-5266(16)30213-8 pmid: 28411584 |
| [63] | Lü Xin, Hou Li-xia, Zhang Xiao-ming, He Qi-wei. 2009. Changes of tomato lycopene contents in its growing process. China Vegetables, (6):21-24. (in Chinese) |
| 吕鑫, 侯丽霞, 张晓明, 李莉, 何启伟. 2009. 番茄果实成熟过程中番茄红素含量的变化. 中国蔬菜,(6):21-24. | |
| [64] |
Luo Jin-feng, Ren Mei-yan, Chen Jing-xin, Ding Xiao-wen. 2011. Research progress in physiological functions and stability of lycopene. Food Science, 32 (19):279-283. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2621.1967.tb01312.x URL |
| 罗金凤, 任美燕, 陈敬鑫, 丁晓雯. 2011. 番茄红素的生理功能及保持其稳定性方法的研究进展. 食品科学, 32 (19):279-283. | |
| [65] | Meng Fan-juan, Wang Fu. 2001. Effectors that influence the lycopene biosynthesis in tomato fruits. Northern Horticulture,(5):15-17. (in Chinese) |
| 孟凡娟, 王富. 2001. 番茄果实内番茄红素的合成及影响因素. 北方园艺,(5):15-17. | |
| [66] |
Mustilli A, Fenzi F, Ciliento R, Alfano F, Bowler C. 1999. Phenotype of tomato high pigment-2 mutants is caused for a mutation in the tomato homolog of Deetiolated1. Plant Cell, 11:145-157.
pmid: 9927635 |
| [67] |
Nisar N, Li L, Lu S, Khin C, Pogson B J. 2015. Carotenoid metabolism in plants. Molecular Plant, 8:68-82.
doi: 10.1016/j.molp.2014.12.007 URL |
| [68] |
Oravecz A, Baumann A, Máté Z, Brzezinska A, Molinier J, Oakeley E J, Ádám É, Schäfer E, Nagy F, Ulm R. 2006. CONSTITUTIVELY PHOTOMORPHOGENIC1 Is required for the UV-B response in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell, 18:1975-1990.
pmid: 16829591 |
| [69] |
Pecker I, Gabbay R, Francis X, Cunningham Jr, Hirschberg J. 1996. Cloning and characterization of the cDNA for lycopene β-fl-cyclase from tomato reveals decrease in its expression during fruit ripening. Plant Molecular Biology, 30:807-819.
pmid: 8624411 |
| [70] |
Pham V N, Kathare P K, Huq E. 2018. Phytochromes and phytochrome interacting factors. Plant Physiology, 176:1025-1038.
doi: 10.1104/pp.17.01384 URL |
| [71] | Pizarro L, Stange C. 2009. Light-dependent regulation of carotenoid biosynthesis in plants. Ciencia e Investigación Agrarian, 36 (2):143-162. |
| [72] | Pu Gao-bin, Liu Shi-qi, Du Hong-tao, Liu Lei. 2005. Effect of light quality on tomato fruit qualities in turning-color period. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 21 (4):176-178. (in Chinese) |
| 蒲高斌, 刘世琦, 杜洪涛, 刘磊. 2005. 光质对番茄果实转色期品质变化的影响. 中国农学通报, 21 (4):176-178. | |
| [73] |
Rao M G, Paliyath G, Ormrod D P. 1995. Difference response of photosyntheic pigment,rubisco activity and rubisco protein of Arabidopsis thaliana exposed to UV-B and ozone. Photochemistry and Photobiology, 62 (4):727-735.
doi: 10.1111/j.1751-1097.1995.tb08722.x URL |
| [74] |
Rodrigo M J, Marcos J F, Zacarias L. 2004. Biochemical and molecular analysis of carotenoid biosynthesis in flavedo of orange(Citrus sinensis L.) during fruit development and maturation. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 52 (22):6724-6731.
doi: 10.1021/jf049607f URL |
| [75] |
Rodriguez-Concepcion M, Ahumada I, Diez-Juez E, Sauret-Gueto S, Lois L M, Gallego F, Carretero-Paulet L, Campos N, Boronat A. 2001. 1-deoxy-D-xylulose 5-phosphate reductoisomerase and plastid isoprenoid biosynthesis during tomato fruit ripening. Plant J, 27:213-222.
doi: 10.1046/j.1365-313x.2001.01089.x URL |
| [76] |
Ronen G, Cohen M, Zamir D, Hirschberg J. 1999. Regulation of carotenoid biosynthesis during tomato fruit development:expression of the gene for lycopene epsilon-cyclase is down-regulated during ripening and is elevated in the mutant delta. Plant J, 17 (4):341-351.
pmid: 10205893 |
| [77] |
Rosati C, Aquilani R, Dharmapuri S, Pallara P, Marusic C, Tavazza R, Bouvier F, Camara B, Giuliano G. 2000. Metabolic engineering of beta-carotene and lycopene content in tomato fruit. The Plant Journal, 24 (3):413-420.
doi: 10.1046/j.1365-313x.2000.00880.x URL |
| [78] | Rui Wen-jing, Wang Xiao-min, Gao Yan-ming, Li Jian-she. 2017. Research progress of effects of environmental factors on fruit quality and flavor of tomatoes. Journal of Anhui Agri Sci, 45 (6):34-36. |
| 芮文婧, 王晓敏, 高艳明, 李建设. 2017. 环境对番茄果实品质和风味影响的研究进展. 安徽农业科学, 45 (6):34-36. | |
| [79] |
Schfer L, Sandmann M, Woitsch S, Sandmann G. 2006. Coordinate up-regulation of carotenoid biosynthesis as a response to light stress in Synechococcus PCC 7942. Plant Cell and Environment, 29 (7):1349-1356.
doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3040.2006.01515.x URL |
| [80] |
Schofield A, Paliyath G. 2005. Modulation of carotenoid biosynthesis during tomato fruit ripening through phytochrome regulation of phytoene synthase activity. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 43 (12):1052-1060.
pmid: 16442806 |
| [81] |
Shalitin D, Yu X, Maymon M, MocklerT, Lin C. 2003. Blue light-dependent in vivo and in vitro phosphorylation of Arabidopsis cryptochrome1. Plant Cell, 15:2421-2429.
pmid: 14523249 |
| [82] | Shewmaker C K, Sheehy J A, Daley M, Colburn S, Ke D. 1999. Seed-specific overexpression of phytoene synthase increase in carotenoids and other metabolic effects,Plant J, 20 (4):401-412. |
| [83] |
Srinivas A, Rajendra K. Behera, Kagawa T, Wada M, Sharma R. 2004. High pigment1 mutation negatively regulates phototropic signal transduction in tomato seedlings. Plant Physiology, 134:790-800.
doi: 10.1104/pp.103.030650 URL |
| [84] |
Sun L, Yuan B, Zhang M, Wang L, Cui M, Wang Q, Leng P. 2012. Fruit-specific RNAi-mediated suppression of SlNCED1 increases both lycopene and beta-carotene contents in tomato fruit. J Exp Bot, 63:3097-3108.
doi: 10.1093/jxb/ers026 URL |
| [85] | Sun Na. 2015. Effects of light quality on growth,physiological metabolism,fruit yield and quality of tomato[M. D. Dissertation]. Tai’an: Shandong Agricultural University. (in Chinese) |
| 孙娜. 2015. 光质对番茄生长,生理代谢及果实产品品质的影响[硕士论文]. 泰安: 山东农业大学. | |
| [86] | Tao Jun, Zhang Shang-long, An Xin-min, Zhao Zhi-zhong. 2003. Effects of light on carotenoid and color formation of citrus fruit peel. Chinese Journal of Appled Ecology, 14 (11):1833-1836. (in Chinese) |
| 陶俊, 张上隆, 安新民, 赵智中. 2003. 光照对柑橘果皮类胡萝卜素和色泽形成的影响. 应用生态学报, 14 (11):1833-1836. | |
| [87] |
Toledo-Ortiz G, Huqb E, Rodriguez-Concepcion M. 2010. Direction regulation of phytoene synthase gene expression and carotenoid biosynthesis by phytochrome-interacting factors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 107:11626-11631.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.0914428107 URL |
| [88] |
Von L J, Welsch R, Bonk M. 1997. Light-dependent regulation of carotenoid biosynthesis occurs at the level of phytoene synthase expression and is mediated by phytochrome in Sinapis alba and Arabidopsis thaliana seedlings. Plant J, 12:625-634.
doi: 10.1046/j.1365-313X.1997.d01-16.x URL |
| [89] |
Wang H Y, Ma L G, Li J M, Zhao H Y, Deng X W. 2001. Direct interaction of Arabidopsis cryptochromes with cop 1 in light control development. Science, 294 (5540):154-158.
pmid: 11509693 |
| [90] | Wang Nan. 2016. Developmental changes in gene expression drive accumulation of lycopene and β-carotene in watermelon[M. D. Dissertation]. Harbin: Northeast Agricultural University. (in Chinese) |
| 王楠. 2016. 西瓜果实番茄红素和β-胡萝卜素积累及其代谢相关酶基因的表达分析[硕士论文]. 哈尔滨: 东北农业大学. | |
| [91] | Wang Xue-ting, Xu Xue-wen, Chen Xue-hao. 2022. Progress on fruit flesh color in horticultural crops. Molecular Plant Breeding, 20 (3):1014-1025. (in Chinese) |
| 王雪婷, 许学文, 陈学好. 2022. 园艺作物果肉颜色研究进展. 分子植物育种, 20 (3):1014-1025. | |
| [92] | Wang Ying-li, Wang Xun-ling, Yue Ming. 2000. Effects of supplementary radiation of UV-B and red light on fruit quality of tomato in winter plastic greenhouse. Acta Bot Boreal-Occidentalia Sinica, 20 (4):590-595. (in Chinese) |
| 王英利, 王勋凌, 岳明. 2000. UV-B及红光对大棚番茄品质的影响. 西北植物学报, 20 (4):590-595. | |
| [93] |
Welsch R, Beyer P, Hugueney P, Lintig K J V. 2000. Regulation and activation of phytoene synthase,a key enzyme in carotenoid biosynthesis,during photomorphogenesis. Planta, 211:846-854.
pmid: 11144270 |
| [94] |
Woitsch S, Römer S. 2003. Expression of xanthophyll biosynthetic genes during light-dependent chloroplast differentiation. Plant Physiology, 132:1508-1517.
pmid: 12857831 |
| [95] | Wu Jiang, Chen Jian-hui, Yang Fu-chen, Xie Ming, Lei Ming. 2007. Relationship between berry coloration and sugar accumulation of Vitis vinifera cv. Red Globe and Centennial seedless grown in greenhouse. Journal of Fruit Science, 24 (4):444-448. (in Chinese) |
| 吴江, 程建徽, 杨夫臣, 谢鸣, 雷鸣. 2007. 红地球和无核白鸡心葡萄设施栽培条件下糖积累与果实着色的关系. 果树学报, 24 (4):444-448. | |
| [96] |
Wurtzel E T. 2019. Changing form and function through carotenoids and synthetic biology. Plant Physiology, 179:830-843.
doi: 10.1104/pp.18.01122 URL |
| [97] |
Xie B X, Wei J J, Zhang Y T, Song S W, Su W, Sun G W, Hao Y W, Liu H C. 2019. Supplemental blue and red light promote lycopene synthesis in tomato fruits. Journal of Integrative Agriculture, 18 (3):590-598.
doi: 10.1016/S2095-3119(18)62062-3 URL |
| [98] |
Yang H Q, Tang R H, Cashmore A R. 2001. The signalling mechanism of Arabidopsis CRY1 involves direct interaction with COP1. Plant Cell, 13:2573-2587.
pmid: 11752373 |
| [99] |
Yang H Q, Wu Y J, Tang R H, Liu D, Liu Y, Cashmore A R. 2000. The C termini of Arabidopsis cryptochromes mediate a constitutive light response. Cell, 103:815-827.
pmid: 11114337 |
| [100] | Yang Shang-long. 2015. Effect of light intensity on yield and quality of tomato[M. D. Dissertation]. Shihezi: Shihezi University. (in Chinese) |
| 杨尚龙. 2015. 光照强度对番茄产量和品质的影响[硕士论文]. 石河子: 石河子大学. | |
| [101] | Yao Jian-gang, Zhang He, Xu Xiang-yang, Li Jing-fu. 2010. Research progress on color change during tomato fruit ripening. China Vegetables,(8):1-6. (in Chinese) |
| 姚建刚, 张贺, 许向阳, 李景富. 2010. 番茄果实成熟过程中色泽变化的研究进展. 中国蔬菜,(8):1-6. | |
| [102] | Yu Yang. 2016. Studies on main pigment formation and physiological mechanism in tomato by exogenous GA3 and ABA[Ph. D. Dissertation]. Shenyang: Shenyang Agricultural University. (in Chinese) |
| 于洋. 2016. 外源GA3和ABA对番茄果实主要色素形成的影响及生理机制研究[博士论文]. 沈阳: 沈阳农业大学. | |
| [103] | Yu Yang, Weng Qian, Zhou Bao-li. 2011. Changes in contents of carotenoids and sugar in peparate tissues and their correlation during ripening of tomato fruit. Journal of Shenyang Agricultural University, 42 (6):683-687. (in Chinese) |
| 于洋, 翁倩, 周宝利. 2011. 番茄果实成熟过程中不同部位类胡萝卜素和糖含量变化及其相关性. 沈阳农业大学学报, 42 (6):683-687. | |
| [104] | Zhang Dian-yong. 2014. Effects of film colors and N,P and K concentration in the nutrient solution on tomato yield and quality of tomato fruit[Ph. D. Dissertation]. Tai’an: Shandong Agricultural University. (in Chinese) |
| 张典勇. 2014. 棚膜颜色和氮磷钾浓度对番茄产量和品质的影响[博士论文]. 泰安: 山东农业大学. | |
| [105] | Zhang Jian-cheng, Liu He. 2007. Recent advances in carotenoid biosynthesis,regulation and manipulation. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin,(11):211-218. (in Chinese) |
| 张建成, 刘和. 2007. 植物类胡萝卜素生物合成及其调控与遗传操作. 中国农学通报,(11):211-218. | |
| [106] | Zhang J Y, Zhang Y T, Song S W, Su W, Hai T W, Liu H C. 2020. Supplementary red light results in the earlier ripening of tomato fruit depending on ethylene production. Environmental and Experimental Botany, 175:1-10. |
| [107] | Zhou Zhen-jiang, Niu Xiao-li, Chen Si, Dai Shun-dong, Hu Tian-tian. 2013. Effect of water-fertilizer supply on tomato lycopene content under alternate subarea root-zone irrigation. China Vegetables,(2):46-51. (in Chinese) |
| 周振江, 牛晓丽, 陈思, 代顺冬, 胡田田. 2013. 根系分区交替灌溉条件下水肥供应对番茄中番茄红素含量的影响. 中国蔬菜,(2):46-51. | |
| [108] | Zhu Guang-tao, Guo Yan-mei, Wang Xiao-xuan, Gao Jian-chang, Hu Hong, Du Yong-chen. 2012. Research progress on gene related to lycopene biosynthesis and gene engineering. China Vegetables,(14):1-8. (in Chinese) |
| 祝光涛, 国艳梅, 王孝宣, 高建昌, 胡鸿, 杜永臣. 2012. 番茄红素生物合成相关基因及其基因工程研究进展. 中国蔬菜,(14):1-8. | |
| [109] | Zhuang Xue-ping, Zhang Wen, Zheng Cai-xia, Du Wei-min. 2007. Effect of glucose,sodium glutamate and ethephon on synthetic quantity of lycopene in tomato fruits. Journal of Anhui Agri Sci, 35 (19):5664-5669. (in Chinese) |
| 庄学平, 张雯, 郑彩霞, 杜为民. 2007. 3种物质对番茄果实中番茄红素合成量的影响. 安徽农业科学, 35 (19):5664-5669. |
| [1] | 史洪丽, 李腊, 郭翠梅, 余婷婷, 简伟, 杨星勇. 番茄灰霉病生防菌株TL1的分离、鉴定及其生防能力分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(1): 79-90. |
| [2] | 忽靖宇, 阙开娟, 缪田丽, 吴少政, 王田田, 张磊, 董鲜, 季鹏章, 董家红. 侵染鸢尾的番茄斑萎病毒鉴定[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(1): 170-176. |
| [3] | 郑积荣, 王同林, 胡松申. 高品质番茄新品种‘杭杂603’[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(S2): 103-104. |
| [4] | 郑积荣, 王同林. 番茄新品种‘杭杂601’[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(S2): 105-106. |
| [5] | 郑积荣, 王同林. 樱桃番茄新品种‘杭杂503’[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(S2): 107-108. |
| [6] | 黄婷婷, 刘淑芹, 张永志, 李 平, 张志焕, 宋立波. 樱桃番茄新品种‘樱莎红4号’[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(S2): 109-110. |
| [7] | 张前荣, 李大忠, 裘波音, 林 珲, 马慧斐, 叶新如, 刘建汀, 朱海生, 温庆放. 设施番茄新品种‘闽农科2号’[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(S1): 73-74. |
| [8] | 韩帅, 吴婕, 张河庆, 席亚东. 四川莴笋上番茄斑萎病毒的电镜观察与小RNA测序鉴定[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(9): 2007-2016. |
| [9] | 陈礼浪, 杨天章, 蔡儒平, 林小漫, 邓南康, 车海彦, 林雅婷, 孔祥义. 海南西番莲主要病毒种类的分子检测与鉴定[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(8): 1785-1794. |
| [10] | 路涛, 余宏军, 李强, 蒋卫杰. 叶果量调控对番茄生长发育、果实品质和产量的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(6): 1261-1274. |
| [11] | 孟宪敏, 崔青青, 段韫丹, 庄团结, 濮丹, 董春娟, 杨文才, 尚庆茂. 烯效唑对番茄幼苗嫁接愈合的促进作用及其机理研究[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(6): 1275-1289. |
| [12] | 崔东禹, 李长青, 孙焱鑫, 王激清, 邹国元, 杨俊刚. 温室番茄东西向栽培条件下矮化密植对其生长和产量的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(4): 875-884. |
| [13] | 彭轶, 李元慧, 杨瑞, 张子怡, 李亚楠, 韩云昊, 赵文超, 王绍辉. 茉莉酸合成基因LoxD参与调控番茄的抗旱性[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(2): 319-331. |
| [14] | 王晋, 王新宇, 沈渊博, 张清花, 娄茜棋, 张世杰, 赵攀, 梁燕. 番茄果实叶绿体发育调控及其应用的研究进展[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(12): 2669-2682. |
| [15] | 孟臻, 张伟萍, 王莹, 李龙, 姬小雪, 董贝, 乔康. 番茄枯萎病菌RT-PCR检测技术的建立与应用[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(11): 2479-2488. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
版权所有 © 2012 《园艺学报》编辑部 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
编辑部地址: 北京市海淀区中关村南大街12号中国农业科学院蔬菜花卉研究所 邮编: 100081
电话: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
技术支持:北京玛格泰克科技发展有限公司