
园艺学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 49 ›› Issue (3): 493-508.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2021-1080
王宏1,2,*( ), 杨王莉1,2, 蔺经1,*(
), 杨王莉1,2, 蔺经1,*( ), 杨青松1, 李晓刚1, 盛宝龙1, 常有宏1
), 杨青松1, 李晓刚1, 盛宝龙1, 常有宏1
收稿日期:2021-10-28
修回日期:2021-12-28
出版日期:2022-03-25
发布日期:2022-03-25
通讯作者:
王宏,蔺经
E-mail:wanghong2015@jaas.ac.cn;lj84390224@126.com
基金资助:
WANG Hong1,2,*( ), YANG Wangli1,2, LIN Jing1,*(
), YANG Wangli1,2, LIN Jing1,*( ), YANG Qingsong1, LI Xiaogang1, SHENG Baolong1, CHANG Youhong1
), YANG Qingsong1, LI Xiaogang1, SHENG Baolong1, CHANG Youhong1
Received:2021-10-28
Revised:2021-12-28
Online:2022-03-25
Published:2022-03-25
Contact:
WANG Hong,LIN Jing
E-mail:wanghong2015@jaas.ac.cn;lj84390224@126.com
摘要:
‘苏翠1号’梨因其极早熟、汁多味甜、肉质细脆而深受广大消费者喜欢。为了解‘苏翠1号’成熟果实主要代谢产物及代谢通路相关基因表达情况,探究其果实优异性状形成的物质和分子基础,对‘苏翠1号’及其亲本‘翠冠’和‘华酥’成熟果实样本进行代谢组和转录组测序分析。代谢组分析发现,3个品种间,前25个差异代谢产物主要包括有机酸、碳水化合物、氨基酸、甘油磷酸脂、脂肪酸和绿原酸。HPLC测定表明,蔗糖含量在‘苏翠1号’中最高,葡萄糖含量在‘翠冠’中最高,果糖含量在‘苏翠1号’和‘翠冠’中相似,略高于‘华酥’,山梨醇含量在‘苏翠1号’和‘华酥’中均显著低于‘翠冠’;苹果酸含量在‘苏翠1号’中最高,柠檬酸含量在‘华酥’中最高,‘苏翠1号’和‘华酥’总酸含量相近,均高于‘翠冠’。氨基酸含量分析表明,‘苏翠1号’的氨基酸总含量及天冬氨酸、苯丙氨酸、甲硫氨酸含量显著高于‘翠冠’和‘华酥’。转录组GO和KEGG分析表明,相较于‘翠冠’和‘华酥’,‘苏翠1号’有机底物分解过程、脂质代谢、有机酸生物合成、羧酸生物合成、多糖代谢等生物学过程及代谢途径显著富集。进一步挖掘差异基因发现,糖代谢中的SPS、山梨醇代谢中的S6PDH、SDH,TCA循环中的FUM1、ICDH、PDH、OGDHL,氨基酸代谢途径中的GAT、GLSN、LASPO、SAMS,以及脂肪酸代谢中的DGK1、ACCA、KASC2、ADH、PLDA等基因在‘苏翠1号’中显著高表达。这些基因可能与‘苏翠1号’更活跃的蔗糖、山梨醇、氨基酸、甘油磷酯代谢及TCA循环有关。
中图分类号:
王宏, 杨王莉, 蔺经, 杨青松, 李晓刚, 盛宝龙, 常有宏. 早熟砂梨‘苏翠1号’与其亲本‘翠冠’‘华酥’成熟果实差异代谢产物及差异基因比较分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(3): 493-508.
WANG Hong, YANG Wangli, LIN Jing, YANG Qingsong, LI Xiaogang, SHENG Baolong, CHANG Youhong. Comparative Metabolic and Transcriptomic Analysis of Ripening Fruit in Pear Cultivars of‘Sucui 1’‘Cuiguan’and‘Huasu’[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(3): 493-508.
| 基因名称 Gene name | 基因号 Gene ID | 上游引物(5′-3′) Forward primer | 下游引物(5′-3′) Reverse Primer |
|---|---|---|---|
| GAPDH | Chr13.g23532 | TGGTGTGAACGAGAAGGAAT | CCCTCAACAATCCCAAACC |
| bZIP53 | Chr17.g20327 | ACAGGGAGCGGAGCTACAA | AAGAACATGCCGGAGGAGG |
| ProDH | Chr17.g25295 | CTGGTTTACGCTCTCGAGTATG | GAAGAAGGTGGCAGGGATTT |
| GAT | Chr10.g14827 | GACACAGCCATCGACAAAGA | GCCTCTGCATATTCCCAAGTAG |
| bZIP11 | Chr10.g16677 | CTCCTGACAAGGGATAACAACC | ACCCATCACCTCCACCAATA |
| SDH SPS | Chr7.g31955 Chr10.g17334 | GTCCGTTCCACTGTATGGTT ACCGGATGGAGATGGGGAT | GCAAAGGAGTGGAGGAGTC CATAATCAATGTAAGGTTAGCAAGCTC |
表1 实时荧光定量 PCR 引物
Table 1 Oligo nucleotide sequences for qRT-PCR primers
| 基因名称 Gene name | 基因号 Gene ID | 上游引物(5′-3′) Forward primer | 下游引物(5′-3′) Reverse Primer |
|---|---|---|---|
| GAPDH | Chr13.g23532 | TGGTGTGAACGAGAAGGAAT | CCCTCAACAATCCCAAACC |
| bZIP53 | Chr17.g20327 | ACAGGGAGCGGAGCTACAA | AAGAACATGCCGGAGGAGG |
| ProDH | Chr17.g25295 | CTGGTTTACGCTCTCGAGTATG | GAAGAAGGTGGCAGGGATTT |
| GAT | Chr10.g14827 | GACACAGCCATCGACAAAGA | GCCTCTGCATATTCCCAAGTAG |
| bZIP11 | Chr10.g16677 | CTCCTGACAAGGGATAACAACC | ACCCATCACCTCCACCAATA |
| SDH SPS | Chr7.g31955 Chr10.g17334 | GTCCGTTCCACTGTATGGTT ACCGGATGGAGATGGGGAT | GCAAAGGAGTGGAGGAGTC CATAATCAATGTAAGGTTAGCAAGCTC |
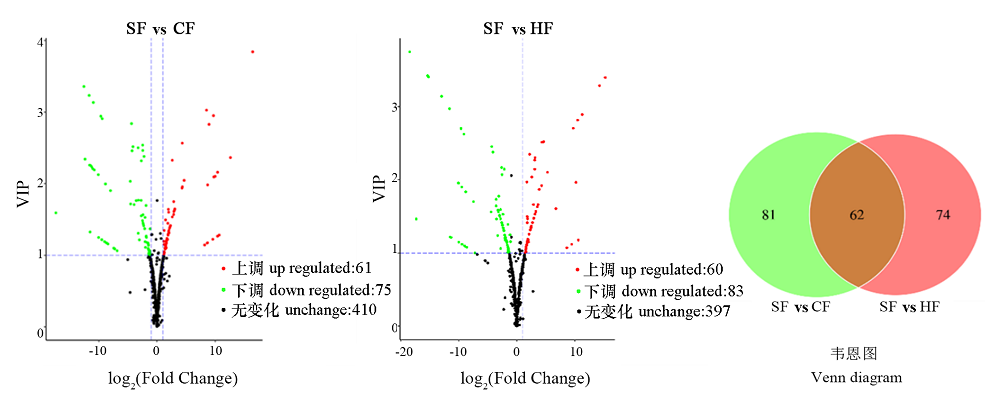
图1 SF vs CF和SF vs HF差异代谢产物散点图及韦恩图 SF:苏翠1号;CF:翠冠;HF:华酥。下同。
Fig. 1 Scatter plots and Venn diagram of differentially expressed metabolism of SF vs CF and SF vs HF SF:Sucui 1;CF:Cuiguan;HF:Huasu. The same below.
| 分类 Category | 代谢产物Compounds | 相对含量(Area)/106 Relative content | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 苏翠1号 Sucui 1 | 翠冠 Cuiguan | 华酥 Huasu | ||
| 有机酸 Organic acids | 甲基丙二酸Methylmalonic acid | 2.85 ± 0.66 c | 11.73 ± 1.18 a | 6.95 ± 0.27 b |
| 琥珀酸Succinic acid | 2.78 ± 0.61 c | 11.13 ± 1.10 a | 7.11 ± 0.53 b | |
| 柠檬酸Citric acid | 3.09 ± 0.09 b | 3.00 ± 0.46 b | 8.81 ± 0.65 a | |
| 苹果酸L(-)-Malic acid | 5.10 ± 0.57 a | 2.28 ± 0.02 b | 2.62 ± 0.04 b | |
| 丙酸5-Aminolevulinate | 3.04 ± 0.21 b | 2.04 ± 0.33 c | 4.14 ± 0.63 a | |
| 木糖酸D-Xylonic acid | 1.86 ± 0.22 b | 2.35 ± 0.34 a | 1.57 ± 0.28 b | |
| 莽草酸Shikimic acid | 1.64 ± 0.08 a | 1.47 ± 0.15 a | 1.04 ± 0.08 b | |
| 延胡索酸Fumaric acid | 0.97 ± 0.07 a | 1.04 ± 0.12 a | 0.64 ± 0.04 b | |
| 碳水化合物 | 蔗糖D-(+)-Sucrose | 2.45 ± 0.25 a | 1.77 ± 0.56 c | 1.90 ± 0.1 b |
| Carbohydrates | 葡萄糖D-(+)-Glucose | 0.50 ± 0.07 b | 1.83 ± 0.17 a | 0.50 ± 0.13 b |
| 6-磷酸葡萄糖D-Glucose 6-phosphate | 0.68 ± 0.01 c | 1.02 ± 0.06 a | 0.84 ± 0.05 b | |
| 氨基酸Amino acids | 天冬氨酸L-Aspartic acid | 3.51 ± 0.37 a | 3.13 ± 0.26 b | 2.02 ± 0.23 c |
| DL-正缬氨酸Dl-Norvaline | 4.62 ± 0.29 a | 3.11 ± 0.28 b | 2.76 ± 0.18 c | |
| 苯丙氨酸L-Phenylalanine | 2.47 ± 0.29 a | 2.21 ± 0.21 a | 1.52 ± 0.53 b | |
| 甲硫氨酸L-Methionine | 2.07 ± 0.41 a | 0.89 ± 0.20 c | 1.18 ± 0.23 b | |
| 甘油磷脂 | 溶血磷脂酰乙醇胺16:0 LysoPE 16:0 | 12.40 ± 0.89 a | 9.45 ± 0.56 b | 6.08 ± 0.23 c |
| Glycerophospholipids | 溶血磷脂酰胆碱16:0 LysoPC 16:0 | 10.48 ± 1.32 a | 8.87 ± 1.55 b | 8.04 ± 0.46 b |
| 溶血磷脂酰乙醇胺18:2(2n异构)LysoPE 18:2 (2n isomer) | 2.24 ± 0.34 a | 1.58 ± 0.08 b | 1.32 ± 0.09 c | |
| 溶血磷脂酰胆碱18:3(2n异构)LysoPC 18:3 (2n isomer) | 2.31 ± 1.07 a | 1.16 ± 0.29 b | 1.11 ± 0.13 b | |
| 溶血磷脂酰胆碱18:3 LysoPC 18:3 | 1.53 ± 0.20 a | 1.24 ± 0.23 a | 1.12 ± 0.04 a | |
| 溶血磷脂酰胆碱18:2 LysoPC 18:2 | 1.73 ± 0.21 a | 1.09 ± 0.13 b | 1.25 ± 0.03 b | |
| 溶血磷脂酰胆碱18:1 LysoPC 18:1 (2n isomer) | 1.37 ± 0.09 a | 1.06 ± 0.40 b | 0.78 ± 0.24 c | |
| 溶血磷脂酰胆碱18:2 (2n异构)LysoPC 18:2 (2n isomer) | 2.61 ± 0.36 a | 0.80 ± 0.15 b | 0.82 ± 0.19 b | |
| 脂肪酸Fatty acids | 棕榈醛Palmitaldehyde | 1.07 ± 0.11 a | 0.80 ± 0.13 b | 0.67 ± 0.13 c |
| 奎宁酸及衍生物Quinate and its derivatives | 绿原酸Chlorogenic acid (3-O-Caffeoylquinic acid) | 10.21 ± 1.14 b | 31.77 ± 3.21 a | 34.47 ± 0.57 a |
表2 砂梨‘苏翠1号’‘翠冠’和‘华酥’中前25个差异代谢产物
Table 2 Top 25 differential expressed chemical compositions in ripening fruit of‘Sucui 1’‘Cuiguan’and‘Huasu’pears
| 分类 Category | 代谢产物Compounds | 相对含量(Area)/106 Relative content | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 苏翠1号 Sucui 1 | 翠冠 Cuiguan | 华酥 Huasu | ||
| 有机酸 Organic acids | 甲基丙二酸Methylmalonic acid | 2.85 ± 0.66 c | 11.73 ± 1.18 a | 6.95 ± 0.27 b |
| 琥珀酸Succinic acid | 2.78 ± 0.61 c | 11.13 ± 1.10 a | 7.11 ± 0.53 b | |
| 柠檬酸Citric acid | 3.09 ± 0.09 b | 3.00 ± 0.46 b | 8.81 ± 0.65 a | |
| 苹果酸L(-)-Malic acid | 5.10 ± 0.57 a | 2.28 ± 0.02 b | 2.62 ± 0.04 b | |
| 丙酸5-Aminolevulinate | 3.04 ± 0.21 b | 2.04 ± 0.33 c | 4.14 ± 0.63 a | |
| 木糖酸D-Xylonic acid | 1.86 ± 0.22 b | 2.35 ± 0.34 a | 1.57 ± 0.28 b | |
| 莽草酸Shikimic acid | 1.64 ± 0.08 a | 1.47 ± 0.15 a | 1.04 ± 0.08 b | |
| 延胡索酸Fumaric acid | 0.97 ± 0.07 a | 1.04 ± 0.12 a | 0.64 ± 0.04 b | |
| 碳水化合物 | 蔗糖D-(+)-Sucrose | 2.45 ± 0.25 a | 1.77 ± 0.56 c | 1.90 ± 0.1 b |
| Carbohydrates | 葡萄糖D-(+)-Glucose | 0.50 ± 0.07 b | 1.83 ± 0.17 a | 0.50 ± 0.13 b |
| 6-磷酸葡萄糖D-Glucose 6-phosphate | 0.68 ± 0.01 c | 1.02 ± 0.06 a | 0.84 ± 0.05 b | |
| 氨基酸Amino acids | 天冬氨酸L-Aspartic acid | 3.51 ± 0.37 a | 3.13 ± 0.26 b | 2.02 ± 0.23 c |
| DL-正缬氨酸Dl-Norvaline | 4.62 ± 0.29 a | 3.11 ± 0.28 b | 2.76 ± 0.18 c | |
| 苯丙氨酸L-Phenylalanine | 2.47 ± 0.29 a | 2.21 ± 0.21 a | 1.52 ± 0.53 b | |
| 甲硫氨酸L-Methionine | 2.07 ± 0.41 a | 0.89 ± 0.20 c | 1.18 ± 0.23 b | |
| 甘油磷脂 | 溶血磷脂酰乙醇胺16:0 LysoPE 16:0 | 12.40 ± 0.89 a | 9.45 ± 0.56 b | 6.08 ± 0.23 c |
| Glycerophospholipids | 溶血磷脂酰胆碱16:0 LysoPC 16:0 | 10.48 ± 1.32 a | 8.87 ± 1.55 b | 8.04 ± 0.46 b |
| 溶血磷脂酰乙醇胺18:2(2n异构)LysoPE 18:2 (2n isomer) | 2.24 ± 0.34 a | 1.58 ± 0.08 b | 1.32 ± 0.09 c | |
| 溶血磷脂酰胆碱18:3(2n异构)LysoPC 18:3 (2n isomer) | 2.31 ± 1.07 a | 1.16 ± 0.29 b | 1.11 ± 0.13 b | |
| 溶血磷脂酰胆碱18:3 LysoPC 18:3 | 1.53 ± 0.20 a | 1.24 ± 0.23 a | 1.12 ± 0.04 a | |
| 溶血磷脂酰胆碱18:2 LysoPC 18:2 | 1.73 ± 0.21 a | 1.09 ± 0.13 b | 1.25 ± 0.03 b | |
| 溶血磷脂酰胆碱18:1 LysoPC 18:1 (2n isomer) | 1.37 ± 0.09 a | 1.06 ± 0.40 b | 0.78 ± 0.24 c | |
| 溶血磷脂酰胆碱18:2 (2n异构)LysoPC 18:2 (2n isomer) | 2.61 ± 0.36 a | 0.80 ± 0.15 b | 0.82 ± 0.19 b | |
| 脂肪酸Fatty acids | 棕榈醛Palmitaldehyde | 1.07 ± 0.11 a | 0.80 ± 0.13 b | 0.67 ± 0.13 c |
| 奎宁酸及衍生物Quinate and its derivatives | 绿原酸Chlorogenic acid (3-O-Caffeoylquinic acid) | 10.21 ± 1.14 b | 31.77 ± 3.21 a | 34.47 ± 0.57 a |
| 氨基酸Amino acids | 苏翠1号Sucui 1 | 翠冠Cuiguan | 华酥Huasu |
|---|---|---|---|
| L-天冬氨酸 Asp | 351.00 ± 37.02 a | 313.00 ± 26.38 b | 202.00 ± 23.02 c |
| L-苯丙氨酸 Phe | 247.00 ± 28.92 a | 221.00 ± 21.22 b | 152.00 ± 53.21 c |
| L-甲硫氨酸 Met | 207.00 ± 40.93 a | 100.70 ± 19.96 b | 118.00 ± 21.82 b |
| L-(+)-赖氨酸 Lys | 102.00 ± 15.51 a | 46.90 ± 12.10 b | 111.00 ± 10.05 a |
| L-谷氨酸 Glu | 58.80 ± 9.20 a | 51.40 ± 23.28 a | 44.5 ± 12.37 b |
| L-(-)-苏氨酸 Thr | 41.80 ± 6.19 a | 38.70 ± 3.64 b | 26.00 ± 2.29 c |
| L-丙氨酸 Ala | 41.40 ± 5.83 a | 28.50 ± 2.29 b | 24.50 ± 3.67 b |
| L-(+)-精氨酸 Arg | 23.20 ± 4.68 b | 31.40 ± 4.06 a | 18.30 ± 8.30 c |
| L-(-)-酪氨酸 Tyr | 20.70 ± 2.95 a | 22.40 ± 3.12 a | 6.16 ± 0.27 b |
| L-半胱氨酸 Cys | 9.12 ± 1.47 b | 14.20 ± 0.87 a | 5.14 ± 0.92 c |
| L-异亮氨酸 Ile | 4.19 ± 0.17 a | 3.04 ± 0.45 b | 4.91 ± 0.79 a |
| L-组氨酸 His | 3.61 ± 0.78 a | 0.75 ± 0.17 c | 2.92 ± 0.12 b |
| L-亮氨酸 Leu | 3.55 ± 0.40 b | 2.46 ± 0.31 c | 4.08 ± 0.12 a |
| L-缬氨酸 Val | 52.10 ± 0.02 a | 54.50 ± 0.01 a | 40.42 ± 0.01 b |
| L-脯氨酸 Pro | 8.69 ± 0.02 c | 15.12 ± 0.65 a | 13.20 ± 0.68 b |
| 总量 Total content | 1 114.47 | 966.35 | 772.73 |
表3 砂梨‘苏翠1号’‘翠冠’和‘华酥’成熟果实氨基酸含量
Table 3 Amino acid contents in ripening fruit of‘Sucui 1’‘Cuiguan’and‘Huasu’pears mg · kg-1
| 氨基酸Amino acids | 苏翠1号Sucui 1 | 翠冠Cuiguan | 华酥Huasu |
|---|---|---|---|
| L-天冬氨酸 Asp | 351.00 ± 37.02 a | 313.00 ± 26.38 b | 202.00 ± 23.02 c |
| L-苯丙氨酸 Phe | 247.00 ± 28.92 a | 221.00 ± 21.22 b | 152.00 ± 53.21 c |
| L-甲硫氨酸 Met | 207.00 ± 40.93 a | 100.70 ± 19.96 b | 118.00 ± 21.82 b |
| L-(+)-赖氨酸 Lys | 102.00 ± 15.51 a | 46.90 ± 12.10 b | 111.00 ± 10.05 a |
| L-谷氨酸 Glu | 58.80 ± 9.20 a | 51.40 ± 23.28 a | 44.5 ± 12.37 b |
| L-(-)-苏氨酸 Thr | 41.80 ± 6.19 a | 38.70 ± 3.64 b | 26.00 ± 2.29 c |
| L-丙氨酸 Ala | 41.40 ± 5.83 a | 28.50 ± 2.29 b | 24.50 ± 3.67 b |
| L-(+)-精氨酸 Arg | 23.20 ± 4.68 b | 31.40 ± 4.06 a | 18.30 ± 8.30 c |
| L-(-)-酪氨酸 Tyr | 20.70 ± 2.95 a | 22.40 ± 3.12 a | 6.16 ± 0.27 b |
| L-半胱氨酸 Cys | 9.12 ± 1.47 b | 14.20 ± 0.87 a | 5.14 ± 0.92 c |
| L-异亮氨酸 Ile | 4.19 ± 0.17 a | 3.04 ± 0.45 b | 4.91 ± 0.79 a |
| L-组氨酸 His | 3.61 ± 0.78 a | 0.75 ± 0.17 c | 2.92 ± 0.12 b |
| L-亮氨酸 Leu | 3.55 ± 0.40 b | 2.46 ± 0.31 c | 4.08 ± 0.12 a |
| L-缬氨酸 Val | 52.10 ± 0.02 a | 54.50 ± 0.01 a | 40.42 ± 0.01 b |
| L-脯氨酸 Pro | 8.69 ± 0.02 c | 15.12 ± 0.65 a | 13.20 ± 0.68 b |
| 总量 Total content | 1 114.47 | 966.35 | 772.73 |
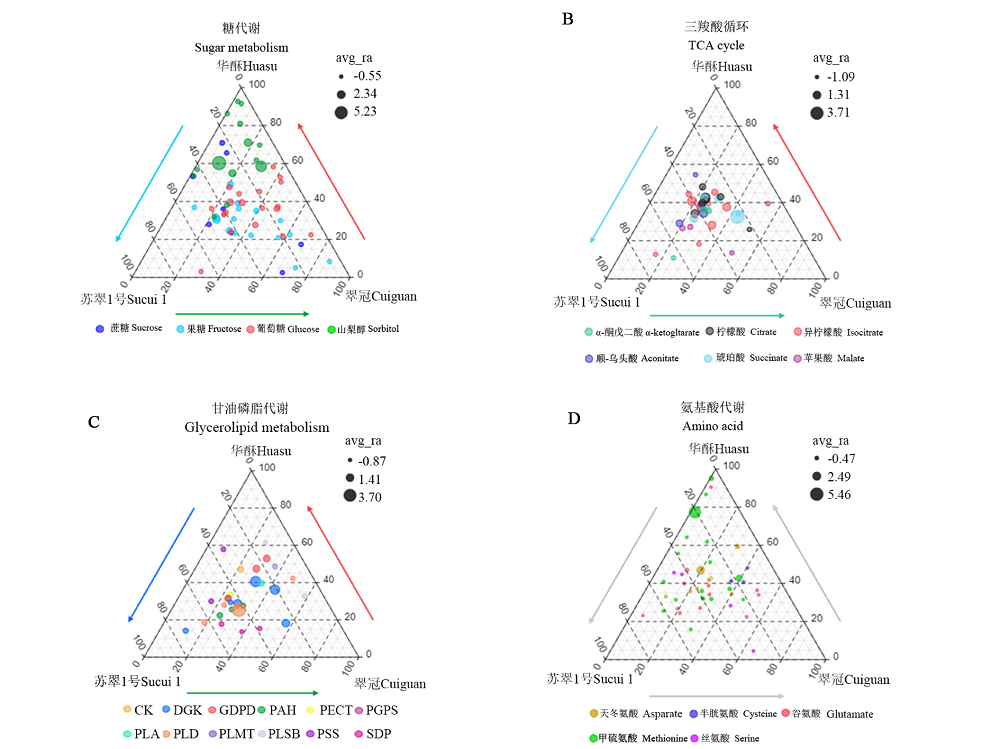
图5 砂梨‘苏翠1号’‘翠冠’及‘华酥’成熟果实中与可溶性糖(A)、三羧酸循环(B)、甘油磷脂代谢(C)及氨基酸(D)代谢途径相关的差异基因分布图
Fig. 5 Ternary plots of DEGs related to soluble sugar(A),TCA cycle(B),glycerolipid metabolism(C)and amino acid(D)metabolism pathways in ripening fruit of‘Sucui 1’‘Cuiguan’and‘Huasu’pears
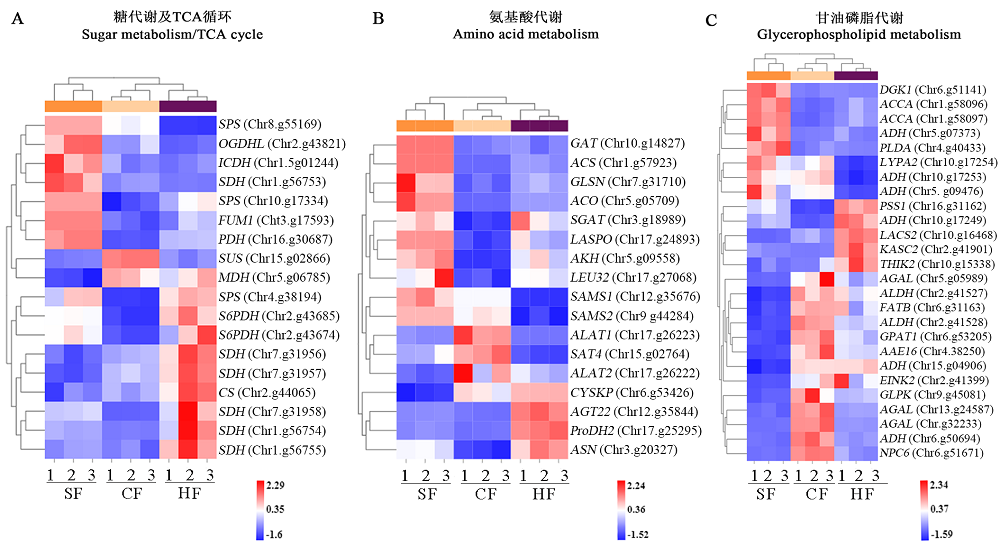
图6 ‘苏翠1号’与‘翠冠’和‘华酥’成熟果实主要代谢途径的差异基因表达分析
Fig. 6 DEGs related to differentially expressed metabolites in ripening fruit of‘Sucui 1’‘Cuiguan’and‘Huasu’pears
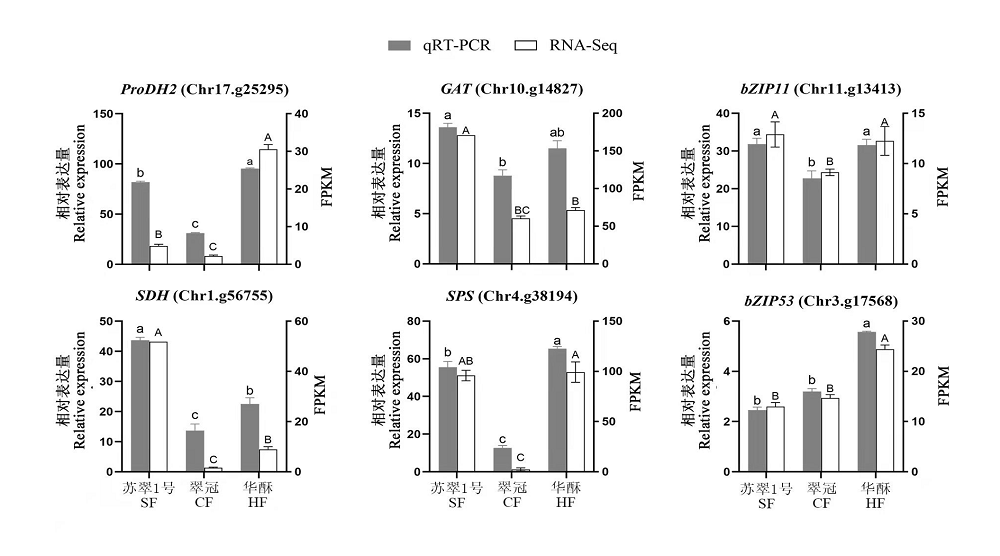
图7 ‘苏翠1号’‘翠冠’和‘华酥’成熟果实中基因相对表达量 不同小写字母表示基因相对表达量差异显著;不同大写字母表示基因FPKM值差异显著(P < 0.05)。
Fig. 7 Relative expression level of genes in ripening fruit of‘Sucui 1’‘Cuiguan’and‘Huasu’pears Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences of relative expression of genes;different capital letters indicate significant differences of FPKM value of genes(P < 0.05).
| [1] |
Adams D O, Yang S F. 1977. Methionine metabolism in apple tissue. Plant Physiol, 60:892-896.
doi: 10.1104/pp.60.6.892 pmid: 16660208 |
| [2] |
Adams D O, Yang S F. 1979. Ethylene biosynthesis:Identification of 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylic acid as an intermediate in the conversion of methionine to ethylene. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 76:170-174.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.1.170 URL |
| [3] |
Batista-Silva W, Nascimento V L, Medeiros D B, Nunes-Nesi A, Ribeiro D M, Zsögön A, Araújo W L. 2018. Modifications in organic acid profiles during fruit development and ripening:correlation or causation? Front Plant Sci, 9:1689.
doi: 10.3389/fpls.2018.01689 pmid: 30524461 |
| [4] |
Castrillo M, Kruger N J, Whatley F R. 1992. Sucrose metabolism in mango fruit during ripening. Plant Sci, 84:45-51.
doi: 10.1016/0168-9452(92)90206-2 URL |
| [5] |
Chen T, Zhang Z Q, Li B Q, Qin G Z, Tian S P. 2021. Molecular basis for optimizing sugar metabolism and transport during fruit development. aBIOTECH, 2:330-340.
doi: 10.1007/s42994-021-00061-2 URL |
| [6] |
Chen W, Gong L, Guo Z L, Wang W S, Zhang H Y, Liu X Q, Yu S B, Xiong L Z, Luo J. 2013. A novel integrated method for large-scale detection,identification,and quantification of widely targeted metabolites:application in the study of rice metabolomics. Molecular Plant, 6(6):1769-1780.
doi: 10.1093/mp/sst080 pmid: 23702596 |
| [7] | Chen Xue-sen, Wang Nan, Zhang Zong-ying, Feng Shou-qian, Chen Xiao-liu, Mao Zhi-quan. 2019. Progress on the resource and breeding of kernel fruits Ⅰ:progress on the germplasm resources,quality development and genetics and breeding of pear in China. Journal of Plant Genetic Resources, 20(4):791-800. (in Chinese) |
| 陈学森, 王楠, 张宗营, 冯守千, 陈晓流, 毛志泉. 2019. 仁果类果树资源育种研究进展I:我国梨种质资源、品质发育及遗传育种研究进展. 植物遗传资源学报, 20(4):791-800. | |
| [8] |
Dai M, Shi Z, Xu C. 2015. Genome-wide analysis of sorbitol dehydrogenase(SDH)genes and their differential expression in two sand pear(Pyrus pyrifolia)fruits. Int J Mol Sci, 16(6):13065-13083.
doi: 10.3390/ijms160613065 URL |
| [9] |
Dave R K, Ramana Rao T V, Nandane A S. 2017. Improvement of post-harvest quality of pear fruit with optimized composite edible coating formulations. J Food Sci Technol, 54(12):3917-3927.
doi: 10.1007/s13197-017-2850-y URL |
| [10] |
Deguchi M, Bennett A B, Yamaki S, Yamada K, Kanahama K, Kanayama Y. 2006. An engineered sorbitol cycle alters sugar composition,not growth,in transformed tobacco. Plant Cell Environ, 29(10):1980-1988.
doi: 10.1111/pce.2006.29.issue-10 URL |
| [11] |
Dobin A, Davis C A, Schlesinger F, Drenkow J, Zaleski C, Jha S, Batut P, Chaisson M, Gingeras T R. 2013. STAR:ultrafast universal RNA-seq aligner. Bioinformatics, 29(1):15-21.
doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bts635 URL |
| [12] |
Dong X G, Wang Z, Tian L M, Zhang Y, Qi D, Huo H L, Xu J Y, Li Z, Liao R, Shi M, Wahocho S A, Liu C, Zhang S M, Tian Z X, Cao Y F. 2020. De novo assembly of a wild pear(Pyrus betuleafolia)genome. Plant Biotechnol J, 18(2):581-595.
doi: 10.1111/pbi.v18.2 URL |
| [13] | Doty T. 1976. Fructose sweetness:a new dimension. Cereal Foods World, 21:62-63. |
| [14] | Duan Min-jie, Yi Hong-wei, Yang Li, Wu Zheng, Wang Jin. 2020. Sugar and acid compositions and their contents in different Pyrus pyrifolia varieties. Journal of Southern Agriculture, 51(9):2236-2244. |
| 段敏杰, 伊洪伟, 杨丽, 武峥, 王进. 2020. 不同砂梨品种果实糖酸组分及含量分析. 南方农业学报, 51(9):2236-2244. | |
| [15] |
Duan Y X, Dong X Y, Liu B H, Li P H. 2013. Relationship of changes in the fatty acid compositions and fruit softening in peach (Prunus persica L. Batsch). Acta Physiol Plant, 35:707-713.
doi: 10.1007/s11738-012-1111-y URL |
| [16] | Fan Jin-bu, Zhang Su-ling, Ma Min, Liu Zhi-qiang, Ren Ya-qian, Wu Chang-qi, Wang Li-bin, Zhang Shao-ling. 2020. Effects of bagging on free amino acid and hydrolyzed amino acid contents in fruit of Pyrus bretschneideri‘Yali’. Journal of Fruit Science, 37(2):204-214. (in Chinese) |
| 樊进补, 张苏玲, 马敏, 刘志强, 任雅倩, 吴昌琦, 王利斌, 张绍铃. 2020. 套袋对‘鸭梨’果实中游离氨基酸和水解氨基酸含量的影响. 果树学报, 37(2):204-214. | |
| [17] |
Fraga C G, Clowers B H, Moore R J, Zink E M. 2010. Signature-discovery approach for sample matching of a nerve-agent precursor using liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry,XCMS,and chemometrics. Anal Chem, 82(10):4165-4173.
doi: 10.1021/ac1003568 URL |
| [18] |
Gong X, Xie Z H, Qi K J, Zhao L Y, Yuan Y Z, Xu J H, Rui W K, Shiratake K, Bao J P, Khanizadeh S, Zhang S L, Tao S T. 2020. PbMC1a/1b regulates lignification during stone cell development in pear(Pyrus bretschneideri)fruit. Hortic Res, 7:59.
doi: 10.1038/s41438-020-0280-x URL |
| [19] | He Zi-shun, Li Fang-fang, Zhang Shao-ling, Bai Ru, Zhang Hu-ping. 2016. Changes in free fatty acid and free amino acid contents in fruit of Pyrus sinkiangensis‘Kuerle Xiangli’by bagging. Journal of Fruit Science, 33(7):804-813. (in Chinese) |
| 何子顺, 李芳芳, 张绍铃, 白茹, 张虎平. 2016. 套袋对‘库尔勒香梨’果实中游离脂肪酸和游离氨基酸含量的影响. 果树学报, 33(7):804-813. | |
| [20] |
Hermanns A S, Zhou X S, Xu Q, Tadmor Y, Li L. 2020. Carotenoid pigment accumulation in horticultural plants. Horticultural Plant Journal, 6(6):343-360.
doi: 10.1016/j.hpj.2020.10.002 URL |
| [21] | Huo Yue-qing. 2007. Study on characteristics of sugars,acids and stone cell in different sand pears from germplasm resources[M. D. Dissertation]. Wuhan: Huazhong Agricultural University. (in Chinese) |
| 霍月青. 2007. 砂梨品种资源糖酸及石细胞含量特点的研究[硕士论文]. 武汉: 华中农业大学. | |
| [22] | Jia Cai-hong, Lin Shui-yu, Zhang Jian-bin, Liu Ju-hua, Jin Zhi-qiang, Xu Bi-yu. 2009. Cloning and characterization of a novel S-Adenosyl-L- Methionine synthase gene in banana. Journal of Fruit Science, 26(3):329-333. (in Chinese) |
| 贾彩红, 林水玉, 张建斌, 刘菊华, 金志强, 徐碧玉. 2009. 香蕉中一个新的S-腺苷甲硫氨酸合成酶基因的克隆及采后表达分析. 果树学报, 26(3):329-333. | |
| [23] | Jiang Shuang, Yue Xiao-yan, Teng Yuan-wen, Wang Xiao-qing, Shi Chun-hui, Xu Fang-jie, Zhang Xue-ying, Bai Song-ling, Luo Jun. 2016. The contents of sugars and acids,and the expression analysis of metabolism-associated genes in fruit of Pyrus pyrifolia. Journal of Fruit Science, 33(S1):65-70. (in Chinese) |
| 蒋爽, 岳晓燕, 滕元文, 王晓庆, 施春晖, 徐芳杰, 张学英, 白松龄, 骆军. 2016. 不同砂梨果实中糖酸含量及代谢相关基因表达分析. 果树学报, 33(S1):65-70. | |
| [24] |
Kim D, Langmead B, Salzberg S L. 2015. HISAT:a fast spliced aligner with low memory requirements. Nat Methods, 12(4):357-360.
doi: 10.1038/NMETH.3317 |
| [25] |
Li J M, Zheng D M, Li L T, Qiao X, Wei S W, Bai B, Zhang S L, Wu J. 2015. Genome-wide function,evolutionary characterization and expression analysis of sugar transporter family genes in pear(Pyrus bretschneideri Rehd). Plant Cell Physiol, 56(9):1721-1737.
doi: 10.1093/pcp/pcv090 URL |
| [26] | Lin Jing, Sheng Bao-long, Li Xiao-gang, Yang Qing-song, Wang Zhong-hua, Li Hui, Wang Hong, Chang You-hong. 2013. A new Pyrus pyrifolia cultivar‘Sucui 1’. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 40(9):1849-1850. (in Chinese) |
| 蔺经, 盛宝龙, 李晓刚, 杨青松, 王中华, 李慧, 王宏, 常有宏. 2013. 早熟砂梨新品种‘苏翠1号’. 园艺学报, 40(9):1849-1850. | |
| [27] | Lin Shui-yu. 2006. Cloning and expression analysis of S-Adenosyl-L-Methionine synthase gene in Musa acuminate[M. D. Dissertation]. Haikou: South China University of Tropical Agriculture. (in Chinese) |
| 林水玉. 2006. 香蕉中S-腺苷-L-蛋氨酸合成酶基因的克隆及表达分析[硕士论文]. 海口: 华南热带农业大学. | |
| [28] |
Liu L, Chen C X, Zhu Y F, Xue L, Liu Q W, Qi K J, Zhang S L, Wu J. 2016. Maternal inheritance has impact on organic acid content in progeny of pear(Pyrus spp.)fruit. Euphytica, 209:305-321.
doi: 10.1007/s10681-015-1627-5 URL |
| [29] | Liu Zheng, An Li-yuan, Lin Shi-hua, Qin Zhong-lin, Wu Tao, Li Xian-ming, Tu Jun-fan, Yang Fu-chen, Zhu Hong-yan, Yang Li. 2018. Research progress of sorbitol metabolism and regulator in pear. South China Fruits, 47(4):165-168. (in Chinese) |
| 刘政, 安莉园, 林世华, 秦仲麒, 伍涛, 李先明, 涂俊凡, 杨夫臣, 朱红艳, 杨立. 2018. 梨树山梨醇代谢及其调控因子研究进展. 中国南方果树, 47(4):165-168. | |
| [30] |
Luo Y, Lin Y, Mo F, Ge C, Jiang L, Zhang Y, Chen Q, Sun B, Wang Y, Wang X, Tang H. 2019. Sucrose promotes strawberry fruit ripening and affects ripening-related processes. Int J Genomics,DOI: 10.1155/2019/9203057.
doi: 10.1155/2019/9203057 URL |
| [31] |
Lü J H, Tao X, Yao G F, Zhang S L, Zhang H P. 2020. Transcriptome analysis of low- and high-sucrose pear cultivars identifies key regulators of sucrose biosynthesis in fruits. Plant Cell Physiol, 61(8):1493-1506.
doi: 10.1093/pcp/pcaa068 URL |
| [32] |
Meng D, He M Y, Bai Y, Xu H X, Dandekar A M, Fei Z J, Cheng L L. 2018. Decreased sorbitol synthesis leads to abnormal stamen development and reduced pollen tube growth via an MYB transcription factor,MdMYB39L,in apple(Malus domestica). New Phytol, 217(2):641-656.
doi: 10.1111/nph.14824 URL |
| [33] |
Nishio S, Hayashi T, Shirasawa K, Saito T, Terakami S, Takada N, Yukie T, Moriya S, Itai A. 2021. Genome-wide association study of individual sugar content in fruit of Japanese pear(Pyrus spp.). BMC Plant Biol, 21(1):378.
doi: 10.1186/s12870-021-03130-2 pmid: 34399685 |
| [34] | Pancoast H M, Junk W R. 1980. Handbook of sugars. 2nd edition. Westport, Connecticut, USA: AVI Publishing Company:387-389. |
| [35] |
Pangborn R. 1963. Relative taste intensities of selected sugars and organic acids. J Food Sci, 28:726-733.
doi: 10.1111/jfds.1963.28.issue-6 URL |
| [36] |
Pattyn J, Vaughan-Hirsch J, van de Poel B. 2021. The regulation of ethylene biosynthesis:a complex multilevel control circuitry. New Phytol, 229:770-782.
doi: 10.1111/nph.v229.2 URL |
| [37] |
Pfaffl M W. 2001. A new mathematical model for relative quantification in real-time RT-PCR. Nucleic Acids Res, 29:e45.
doi: 10.1093/nar/29.9.e45 pmid: 11328886 |
| [38] |
Qiu W, Su W, Cai Z, Dong L, Li C, Xin M, Fang W, Liu Y, Wang X, Huang Z, Ren H, Wu Z. 2020. Combined analysis of transcriptome and metabolome reveals the potential mechanism of coloration and fruit quality in yellow and purple Passiflora edulis sims. J Agric Food Chem, 68(43):12096-12106.
doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.0c03619 URL |
| [39] | Sha Shou-feng. 2012. Pear organic acid components,content changes and genetic identification[Ph. D. Dissertation]. Nanjing: Nanjing Agricultural University. (in Chinese) |
| 沙守峰. 2012. 梨有机酸组分及含量变化与遗传鉴定[博士论文]. 南京: 南京农业大学. | |
| [40] |
Sorrequieta A, Ferraro G, Boggio S B, Valle E M. 2010. Free amino acid production during tomato fruit ripening:a focus on L-glutamate. Amino Acids, 38(5):1523-1532.
doi: 10.1007/s00726-009-0373-1 pmid: 19876714 |
| [41] | Souty M, André P. 1975. Composition biochimique et qualité des pêches. Ann Technol Agric, 24:217-236. |
| [42] | Su Jun, Huang Xing-long, Chen Xia, He Ying-yun, Li Zi-sheng, Shu Qun. 2018. Analysis of amino acid composition and content in three new varieties of red sand pear. Journal of Fruit Science, 35(S1):114-117. (in Chinese) |
| 苏俊, 黄兴龙, 陈霞, 何英云, 李自生, 舒群. 2018. 3个红色砂梨新品种的果实氨基酸组分与含量分析. 果树学报, 35(S1):114-117. | |
| [43] | Sun H J, Zhou X, Zhou Q, Zhao Y B, Kong X M, Luo M L, Ji S J. 2020. Disorder of membrane metabolism induced membrane instability plays important role in pericarp browning of refrigerated‘Nanguo’pears. Food Chem, 320:126684. |
| [44] |
Sun Li-qiong, Hao Wen-jing, Tang Xiao-qing, Wang Kang-cai, Zhang Shao-ling. 2020. Analysis of characteristic polyphenols and triterpenic acids in ripe pears of 36 cultivars by UPLC-MS/MS. Food Science, 41(22):206-214. (in Chinese)
doi: 10.1111/jfds.1976.41.issue-1 URL |
| 孙莉琼, 郝雯菁, 唐晓清, 王康才, 张绍铃. 2020. UPLC-MS/MS研究36个梨品种成熟果实中的特征性多酚和三萜酸类物质. 食品科学, 41(22):206-214. | |
| [45] |
Tanase K, Yamaki S. 2000. Sucrose synthase isozymes related to sucrose accumulation during fruit development of Japanese pear(Pyrus pyrifolia Nakai). J Jpn Soc Hortic Sci, 69:671-676.
doi: 10.2503/jjshs.69.671 URL |
| [46] |
Tian H, Ma L, Zhao C, Hao H, Gong B, Yu X, Wang X. 2010. Antisense repression of sucrose phosphate synthase in transgenic muskmelon alters plant growth and fruit development. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 393(3):365-370.
doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2010.01.124 URL |
| [47] |
Trapnell C, Roberts A, Goff L, Pertea G, Kim D, Kelley D R, Pimentel H, Salzberg S L, Rinn J L, Pachter L. 2012. Differential gene and transcript expression analysis of RNA-seq experiments with TopHat and Cufflinks. Nat protoc, 7(3):562-578.
doi: 10.1038/nprot.2012.016 pmid: 22383036 |
| [48] | van de Poel B, Bulens I, Oppermann Y, Hertog M L, Nicolai B M, Sauter M, Geeraerd A H. 2013. S-adenosyl-L-methionine usage during climacteric ripening of tomato in relation to ethylene and polyamine biosynthesis and transmethylation capacity. Physiol Plant, 148(2):176-188. |
| [49] | Wang H, Lin J, Chang Y H, Jiang C Z. 2017. Comparative transcriptomic analysis reveals that ethylene/H2O2-mediated hypersensitive response and programmed cell death determine the compatible interaction of sand pear and Alternaria alternata. Front Plant Sci, 8:195. |
| [50] |
Wang L F, Qi X X, Huang X S, Xu L L, Jin C, Wu J, Zhang S L. 2016. Overexpression of sucrose transporter gene PbSUT2 from Pyrus bretschneideri,enhances sucrose content in Solanum lycopersicum fruit. Plant Physiol Biochem, 105:150-161.
doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2016.04.019 URL |
| [51] |
Wu J, Wang D, Liu Y, Wang L, QiaO X, Zhang S. 2014. Identification of miRNAs involved in pear fruit development and quality. BMC Genomics, 15(1):953.
doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-15-953 URL |
| [52] | Xiao Liang, Chen Rui-bing, Wu Yu, Zhang Lei. 2020. Research progress on effect of AP2/ERF transcription factors in regulating secondary metabolite biosynthesis. China Journal of Chinese Material Medica, 45:110-118. (in Chinese) |
| 肖亮, 陈瑞兵, 吴宇, 张磊. 2020. AP2/ERF转录因子调控次生代谢产物生物合成的研究进展. 中国中药杂志, 45:110-118. | |
| [53] |
Xie C, Mao X Z, Huang J J, Ding Y, Wu J M, Dong S, Kong L, Gao G, Li C Y, Wei L P. 2011. KOBAS 2.0:a web server for annotation and identification of enriched pathways and diseases. Nucleic Acids Res, 39(Web Server issue):W316-322.
doi: 10.1093/nar/gkr483 URL |
| [54] | Xu J Y, Zhang Y, Qi D, Huo H L, Dong X G, Tian L M, Liu C, Cao Y F. 2021. Metabolomic and transcriptomic analyses highlight the influence of lipid changes on the post-harvest softening of Pyrus ussurian Max.‘Zaoshu Shanli’. Genomics, 113(1 Pt 2):919-926. |
| [55] |
Yang J J, Zhu L C, Cui W F, Zhang C, Li D X, Ma B Q, Cheng L L, Ruan Y L, Ma F W, Li M J. 2018. Increased activity of MdFRK2,a high-affinity fructokinase,leads to upregulation of sorbitol metabolism and downregulation of sucrose metabolism in apple leaves. Hortic Res, 5:71.
doi: 10.1038/s41438-018-0099-x URL |
| [56] | Yao Gai-fang, Zhang Shao-ling, Wu Jun, Cao Yu-fen, Liu Jun, Han Kai, Yang Zhi-jun. 2011. Analysis of components and contents of soluble sugars and organic acids in ten cultivars of pear by high performance liquid chromatography. Journal of Nanjing Agricultural University, 34(5):25-31. (in Chinese) |
| 姚改芳, 张绍铃, 吴俊, 曹玉芬, 刘军, 韩凯, 杨志军. 2011. 10个不同系统梨品种的可溶性糖与有机酸组分含量分析. 南京农业大学学报, 34(5):25-31. | |
| [57] |
Young M D, Wakefield M J, Smyth G K, Oshlack A. 2010. Method gene ontology analysis for RNA-seq:accounting for selection bias. Genome Biol, 11:R14.
doi: 10.1186/gb-2010-11-2-r14 URL |
| [58] |
Zhang B B, Guo J Y, Ma R J, Cai Z X, Yan J, Zhang C H. 2015. Relationship between the bagging microenvironment and fruit quality in‘Guibao’peach [Prunus persica(L.)Batsch]. J Hortic Sci Biotech, 90:3,303-310.
doi: 10.1080/14620316.2015.11513187 URL |
| [59] |
Zhang C M, Hao Y J. 2020. Advances in genomic,transcriptomic,and metabolomic analyses of fruit quality in fruit crops. Horticultural Plant Journal, 6(6):361-371.
doi: 10.1016/j.hpj.2020.11.001 URL |
| [60] |
Zhang M Y, Xue C, Hu H j, Li J M, Xue Y S, Wang R Z, Fan J, Zou C, Tao S T, Qin M F, Bai B, Li X L, Gu C, Wu S, Chen X, Yang G Y, Liu Y Y, Sun M Y, Fei Z J, Zhang S L, Wu J. 2021. Genome-wide association studies provide insights into the genetic determination of fruit traits of pear. Nat Commun, 12:1144.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-21378-y URL |
| [61] | Zhang Xiao-shuang, Zheng Ying-chun, Cao Yu-fen, Tian Lu-ming, Dong Xing-guang, Zhang Ying, Qi Dan, Huo Hong-liang. 2017. The composition and content of polyphenols in 16 parts of‘Zaosu’and‘Nanguoli’. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 50(3):545-555. (in Chinese) |
| 张小双, 郑迎春, 曹玉芬, 田路明, 董星光, 张莹, 齐丹, 霍宏亮. 2017. ‘早酥’和‘南果梨’16个部位多酚物质组成及含量分析. 中国农业科学, 50(3):545-555. | |
| [62] | Zhao Xin, Liang Ke-hong, Zhu Hong, Liu Li, Wang Jing. 2020. Comparative research on nutritional quality and flavor compounds of different pear varieties. Journal of Food Safety and Quality, 11(21):7797-7805. (in Chinese) |
| 赵欣, 梁克红, 朱宏, 刘莉, 王靖. 2020. 不同品种梨营养品质及风味物质比较研究. 食品安全质量检测学报, 11(21):7797-7805. | |
| [63] | Zhou Hong-sheng, Hu Hua-li, Luo Shu-fen, Zhang Lei-gang, Li Peng-xia. 2018. The storage characteristics of Sucui 1 pear during storage at different temperatures. Storage and Process, (6):13-19. (in Chinese) |
| 周宏胜, 胡花丽, 罗淑芬, 张雷刚, 李鹏霞. 2018. 苏翠1号梨在不同温度下的贮藏特性研究. 保鲜与加工, (6):13-19. | |
| [64] |
Zhu G, Wang S, Huang Z, Zhang S, Liao Q, Zhang C, Lin T, Qin M, Peng M, Yang C, Cao X, Han X, Wang X, van der Knaap E, Zhang Z, Cui X, Klee H, Fernie A R, Luo J, Huang S. 2018. Rewiring of the fruit metabolome in tomato breeding. Cell, 172(1):249-261.
doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019 URL |
| [1] | 范 净, 陈启亮, 张靖国, 杨晓平, 杜 威, 田 瑞, 周德平, 胡红菊, . 中熟红皮砂梨新品种‘金彤’[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(S2): 11-12. |
| [2] | 路涛, 余宏军, 李强, 蒋卫杰. 叶果量调控对番茄生长发育、果实品质和产量的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(6): 1261-1274. |
| [3] | 李黎, 冯丹丹, 潘慧, 李文艺, 邓蕾, 汪祖鹏, 钟彩虹. 猕猴桃花粉灭菌方法比较及对果实品质的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(4): 769-777. |
| [4] | 刘文欢, 邱芳颖, 王娅, 陈朗, 马岩岩, 吕强, 易时来, 谢让金, 郑永强. 枯草芽孢杆菌液态肥对柑橘养分吸收和果实品质的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(3): 509-518. |
| [5] | 张瑞, 张夏燚, 赵婷, 王双成, 张仲兴, 刘博, 张德, 王延秀. 基于转录组分析垂丝海棠响应盐碱胁迫的分子机制[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(2): 237-251. |
| [6] | 曾译可, 石莹, 陈思怡, 李国敬, 黄先彪, 谢宗周, 李春龙, 郭大勇, 刘继红. 地面覆膜提升椪柑果实品质的效果和可能机制探究[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(11): 2419-2430. |
| [7] | 孙嘉茂, 崔全石, 王语晴, 司雅静, 时瑀繁, 卜海东, 袁晖, 王爱德. 苹果采前喷施EBR与MeJA对采后品质的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(10): 2236-2248. |
| [8] | 周铁, 潘斌, 李菲菲, 马小川, 汤孟婧, 廉雪菲, 常媛媛, 陈岳文, 卢晓鹏. 膨大期干旱对温州蜜柑品质形成的影响及复水后树体水分吸收转运规律[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(1): 11-22. |
| [9] | 徐红霞, 周慧芬, 李晓颖, 姜路花, 陈俊伟. 低温胁迫下枇杷不同发育阶段的花果转录组比较分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2021, 48(9): 1680-1694. |
| [10] | 戚行江, 郑锡良, 李小白, 张淑文, 任海英, 俞浙萍. 不同颜色避雨膜形成的光质环境对杨梅果实成熟和品质的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2021, 48(9): 1794-1804. |
| [11] | 张志强, 卢世雄, 马宗桓, 李彦彪, 高彩霞, 陈佰鸿, 毛娟. 草莓LIM家族候选基因的鉴定及在非生物胁迫下的表达[J]. 园艺学报, 2021, 48(8): 1485-1503. |
| [12] | 朱俊飞, 李鑫, 董康挺, 唐志菲, 边秀举, 王丽宏, 李会彬, 孙鑫博. 转匍匐翦股颖AsHSP26.8a拟南芥株系的光合作用研究[J]. 园艺学报, 2021, 48(8): 1619-1625. |
| [13] | 贾兵, 郭国凌, 王友煜, 叶振风, 刘莉, 刘普, 衡伟, 朱立武. ‘黄金梨’缺铁黄化叶片受GA3诱导复绿的机理研究[J]. 园艺学报, 2021, 48(2): 254-264. |
| [14] | 邹震, 于爱水, 任洪春, 战良, 刘更森, 冷翔鹏, 房经贵. 日光温室‘藤稔’葡萄更新修剪时期对其生长、产量和品质的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2021, 48(12): 2471-2480. |
| [15] | 卢素文, 郑暄昂, 王佳洋, 房经贵. 葡萄类黄酮代谢研究进展[J]. 园艺学报, 2021, 48(12): 2506-2524. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
版权所有 © 2012 《园艺学报》编辑部 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
编辑部地址: 北京市海淀区中关村南大街12号中国农业科学院蔬菜花卉研究所 邮编: 100081
电话: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
技术支持:北京玛格泰克科技发展有限公司