
园艺学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 49 ›› Issue (2): 237-251.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2021-0077
• 研究论文 • 下一篇
张瑞, 张夏燚, 赵婷, 王双成, 张仲兴, 刘博, 张德, 王延秀( )
)
收稿日期:2021-05-11
修回日期:2021-07-19
出版日期:2022-02-25
发布日期:2022-02-28
通讯作者:
王延秀
E-mail:wangxy@gsau.edu.cn
基金资助:
ZHANG Rui, ZHANG Xiayi, ZHAO Ting, WANG Shuangcheng, ZHANG Zhongxing, LIU Bo, ZHANG De, WANG Yanxiu( )
)
Received:2021-05-11
Revised:2021-07-19
Online:2022-02-25
Published:2022-02-28
Contact:
WANG Yanxiu
E-mail:wangxy@gsau.edu.cn
摘要:
以干旱盐碱生境苹果属垂丝海棠(Malus halliana Koehen)为试验材料,通过RNA-Seq测序筛选响应盐碱复合胁迫的差异表达基因,为苹果砧木耐盐碱性机制提供理论依据。以正常供水(Hoagland营养液)为对照,进行混合盐碱胁迫(Hoagland营养液 + 100 mmol · L-1 NaCl + NaHCO3)处理,RNA-Seq测序筛选差异表达基因(differentially expression gene,DEG),并对 DEG进行GO(gene ontology)和 KEGG (Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes)功能富集分析。应用实时荧光定量qRT-PCR对主要通路的DEG表达模式进行验证。共鉴定出16 246个DEG,其中上调7 268个,下调8 978个。GO分析表明,在遭受盐碱胁迫时生物过程、细胞组分和分子功能3个方面均存在较大差异。KEGG 聚类分析显示,参与信号传导、碳代谢、氨基酸合成及次生代谢等相关的DEG在响应胁迫中具有关键作用,且主要集中在钙信号通路、植物激素信号传导、苯丙氨酸代谢、类胡萝卜素的合成等过程。对上述主要通路的20个DEG 表达模式的qRT-PCR检测结果与RNA-seq 结果类似。其中天门冬氨酸氨基转移酶(aspartate aminotransferase,GOT1)、抗坏血酸还原酶(NADH)、查尔酮异构酶(chalcone isomerase,CHI)、β-胡萝卜素羟化酶(CrtZ)基因在盐碱胁迫过程中表达量显著升高。垂丝海棠叶片对盐碱胁迫的耐受能力主要与基因对胁迫的响应程度相关,调控基因表达涉及钙信号通路、植物激素信号传导、氨基酸生物合成、类胡萝卜素生物合成等次生代谢物途径。
中图分类号:
张瑞, 张夏燚, 赵婷, 王双成, 张仲兴, 刘博, 张德, 王延秀. 基于转录组分析垂丝海棠响应盐碱胁迫的分子机制[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(2): 237-251.
ZHANG Rui, ZHANG Xiayi, ZHAO Ting, WANG Shuangcheng, ZHANG Zhongxing, LIU Bo, ZHANG De, WANG Yanxiu. Transcriptome Analysis of the Molecular Mechanism of Saline-alkali Stress Response in Malus halliana Leaves[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2022, 49(2): 237-251.
| 基因 Gene | 名称 Description | 上游引物(5′-3′) Forward primer | 下游引物(5′-3′) Reverse primer |
|---|---|---|---|
| ANT | 溶质载体家族25 Solute carrier family 25 | CCAACTTCCACCGTGATCTGATG | TCCTTCCACCGCCGAGAATG |
| ATP2A | 钙转运体 Calcium transporter | GGTACAGTAGTCGTGGCTGGTAG | TTCAATGGCGTCACTTCATCTTCC |
| PLCD | 磷脂酰肌醇磷脂酶C Phosphatidylinositol phospholipase C,delta | GGTGTTCGCCAAGTACGCTCAG | GGGTCGTGAACTGGAGGAGGATAG |
| SPHK | 鞘氨醇激酶Sphingosine kinase | CTCATAAGCGGCGTCGTCACAC | CGAACCCCAGGACCTCCTTCTC |
| VDAC1 | 赖性阴离子通道蛋白1 Voltage-dependent anion channel protein 1 | TGCCGAACTGACCCACAGATTTTC | GGTCTCCATTCACGCTGCCATAG |
| ABF | ABA响应元件结合因子 ABA responsive element binding factor | TGACAATGTTGAGTTCCGTGAGC | TCGACGACTGCCTCGCTAAC |
| PR1 | 病程相关蛋白1 Pathogenesis-related protein 1 | ATGGGGTTGTGCAATATTTC | CTAGTAAGGCTTCTCCCCAAC |
| PYL | 脱落酸受体PYR/PYL家族 Abscisic acid receptor PYR/PYL family | ATGTCTTCACCAATCCAGTTTC | AGTACTCCCAAAGAACCACAAA |
| COI-1 | 冠菌素不敏感蛋白1 Coronatine-insensitive protein 1 | CGAGGGCGGCGATGTTCAATC | ACTTCAAGCGGTGGAACGAGTTG |
| GOT1 | 细胞质天冬氨酸转氨酶 Aspartate aminotransferase,cytoplasmic | ACAACGCCTCCAAGCTCCTC | TCTGAGTTCGCCGAGTCCTTC |
| CHI | 查耳酮异构酶Chalcone isomerase | ATGGCTGACGGTGACCAAC | TTATCTAGTGATATGAGCAATAAA |
| ANS | 花青素合成酶Anthocyanidin synthase | ATGGTGAGCTCTGATTCAG | TCACTTGGGGAGCAAAGC |
| ANR | 花青素还原酶Anthocyanidin reductase | ATGGCCACCCAACAACCC | CTAGTTCTGCAGCAGCCC |
| NADH | 单脱水抗坏血酸还原酶 Monodehydroascorbate reductase(NADH) | ATGGGAAGGGCATTTGTG | TCACCACCTCCGGCGCTT |
| CrtY | 番茄红素Lycopene beta-cyclase | ATGGATACATTGCTTAAAACGC | GATTAGAGATAGGACATAGTTCAAC |
| CrtZ | β-胡萝卜素β-carotene 3-hydroxylase | GCAAGGTGGGCTCATAGAACTCTG | AAGAAGGGCAATAGCAGGAACAGC |
| HPD | 羟苯丙酮酸加双氧酶 Hydroxyphenylpyruvate dioxygenase | TGTACCACAGAGACCTGAAGCC | CAGCAGCAGAGCCATCATAACC |
| pckA | 膜伯胺氧化酶 Primary-amine oxidase | CGACGCCTTCCTGTTGCTTCC | CGGTGACGCCAGTCCAATCTTG |
| VPS35 | 液泡蛋白分选相关蛋白35 Vacuolar protein sorting-associated protein 35 | TGAAGATTGGCTGCACTTGACTGG | CCGACAACTGCCCATTGAGGAAG |
| VTA1 | 液泡蛋白分选相关蛋白 Vacuolar protein sorting-associated protein | GGGCTCTGATCCTTCCTACTCTCC | AGTCCCATTTCTGTTGCTCGTCTG |
表1 实时荧光定量引物
Table 1 qRT-PCR primers
| 基因 Gene | 名称 Description | 上游引物(5′-3′) Forward primer | 下游引物(5′-3′) Reverse primer |
|---|---|---|---|
| ANT | 溶质载体家族25 Solute carrier family 25 | CCAACTTCCACCGTGATCTGATG | TCCTTCCACCGCCGAGAATG |
| ATP2A | 钙转运体 Calcium transporter | GGTACAGTAGTCGTGGCTGGTAG | TTCAATGGCGTCACTTCATCTTCC |
| PLCD | 磷脂酰肌醇磷脂酶C Phosphatidylinositol phospholipase C,delta | GGTGTTCGCCAAGTACGCTCAG | GGGTCGTGAACTGGAGGAGGATAG |
| SPHK | 鞘氨醇激酶Sphingosine kinase | CTCATAAGCGGCGTCGTCACAC | CGAACCCCAGGACCTCCTTCTC |
| VDAC1 | 赖性阴离子通道蛋白1 Voltage-dependent anion channel protein 1 | TGCCGAACTGACCCACAGATTTTC | GGTCTCCATTCACGCTGCCATAG |
| ABF | ABA响应元件结合因子 ABA responsive element binding factor | TGACAATGTTGAGTTCCGTGAGC | TCGACGACTGCCTCGCTAAC |
| PR1 | 病程相关蛋白1 Pathogenesis-related protein 1 | ATGGGGTTGTGCAATATTTC | CTAGTAAGGCTTCTCCCCAAC |
| PYL | 脱落酸受体PYR/PYL家族 Abscisic acid receptor PYR/PYL family | ATGTCTTCACCAATCCAGTTTC | AGTACTCCCAAAGAACCACAAA |
| COI-1 | 冠菌素不敏感蛋白1 Coronatine-insensitive protein 1 | CGAGGGCGGCGATGTTCAATC | ACTTCAAGCGGTGGAACGAGTTG |
| GOT1 | 细胞质天冬氨酸转氨酶 Aspartate aminotransferase,cytoplasmic | ACAACGCCTCCAAGCTCCTC | TCTGAGTTCGCCGAGTCCTTC |
| CHI | 查耳酮异构酶Chalcone isomerase | ATGGCTGACGGTGACCAAC | TTATCTAGTGATATGAGCAATAAA |
| ANS | 花青素合成酶Anthocyanidin synthase | ATGGTGAGCTCTGATTCAG | TCACTTGGGGAGCAAAGC |
| ANR | 花青素还原酶Anthocyanidin reductase | ATGGCCACCCAACAACCC | CTAGTTCTGCAGCAGCCC |
| NADH | 单脱水抗坏血酸还原酶 Monodehydroascorbate reductase(NADH) | ATGGGAAGGGCATTTGTG | TCACCACCTCCGGCGCTT |
| CrtY | 番茄红素Lycopene beta-cyclase | ATGGATACATTGCTTAAAACGC | GATTAGAGATAGGACATAGTTCAAC |
| CrtZ | β-胡萝卜素β-carotene 3-hydroxylase | GCAAGGTGGGCTCATAGAACTCTG | AAGAAGGGCAATAGCAGGAACAGC |
| HPD | 羟苯丙酮酸加双氧酶 Hydroxyphenylpyruvate dioxygenase | TGTACCACAGAGACCTGAAGCC | CAGCAGCAGAGCCATCATAACC |
| pckA | 膜伯胺氧化酶 Primary-amine oxidase | CGACGCCTTCCTGTTGCTTCC | CGGTGACGCCAGTCCAATCTTG |
| VPS35 | 液泡蛋白分选相关蛋白35 Vacuolar protein sorting-associated protein 35 | TGAAGATTGGCTGCACTTGACTGG | CCGACAACTGCCCATTGAGGAAG |
| VTA1 | 液泡蛋白分选相关蛋白 Vacuolar protein sorting-associated protein | GGGCTCTGATCCTTCCTACTCTCC | AGTCCCATTTCTGTTGCTCGTCTG |

图2 垂丝海棠在盐碱胁迫下0、2、4、6 d 时叶片DAB与台盼蓝染色表型变化
Fig. 2 Phenotypic changes of DAB and Trypa blue staining in the leaves of Malus halliana after 0,2,4,6 d under saline-alkali stress
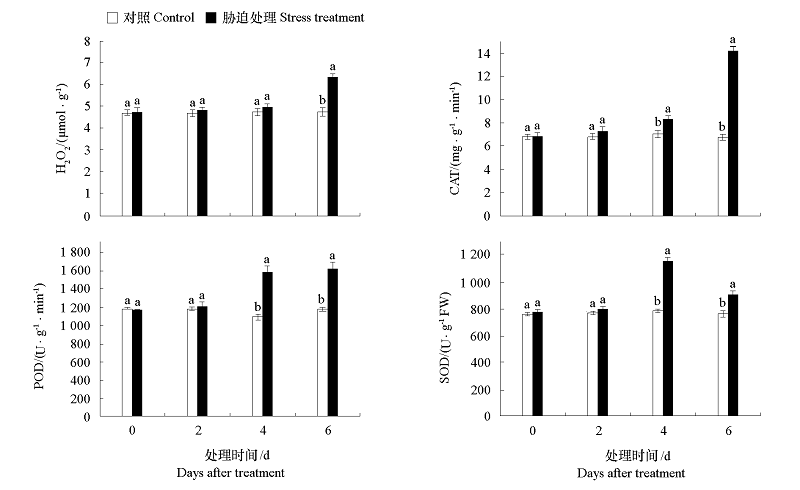
图3 盐碱胁迫0、2、4、6 d垂丝海棠的H2O2含量和CAT、POD、SOD活性的变化 盐碱胁迫0、2、4、6 d垂丝海棠的H2O2含量和CAT、POD、SOD活性变化,平均值 ± 标准差,不同的小写英文字母表示同一指标同一天处理与对照在0.05水平上显著差异(P < 0.05)。
Fig. 3 Changes of H2O2 content and CAT,POD,SOD activity in Malus halliana under saline-alkali stress for 0,2,4,6 d Changes of H2O2 content and CAT,POD,SOD activity in Malus halliana under saline-alkali stress for 0,2,4,6 d,average ± standard,different lowercase English letters indicate a significant difference at 0.05 level between treatment and control for the same index on the same day.
| 样品 Sample | 原始数据 Raw reads | 过滤数据 Clean reads | 有效碱基/% Valid bases | Q30含量/% Q30 content | GC含量/% GC content |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 对照 Control | 49 794 146 | 47 025 046 | 90.15 | 93.52 | 47.70 |
| 胁迫处理 Stress treatment | 49 258 400 | 47 513 110 | 92.50 | 94.63 | 47.90 |
表2 垂丝海棠叶片响应盐碱胁迫的转录组测序数据统计
Table 2 Summary of transcriptome sequencing data from leaves of Malus halliana under saline-alkali stress
| 样品 Sample | 原始数据 Raw reads | 过滤数据 Clean reads | 有效碱基/% Valid bases | Q30含量/% Q30 content | GC含量/% GC content |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 对照 Control | 49 794 146 | 47 025 046 | 90.15 | 93.52 | 47.70 |
| 胁迫处理 Stress treatment | 49 258 400 | 47 513 110 | 92.50 | 94.63 | 47.90 |
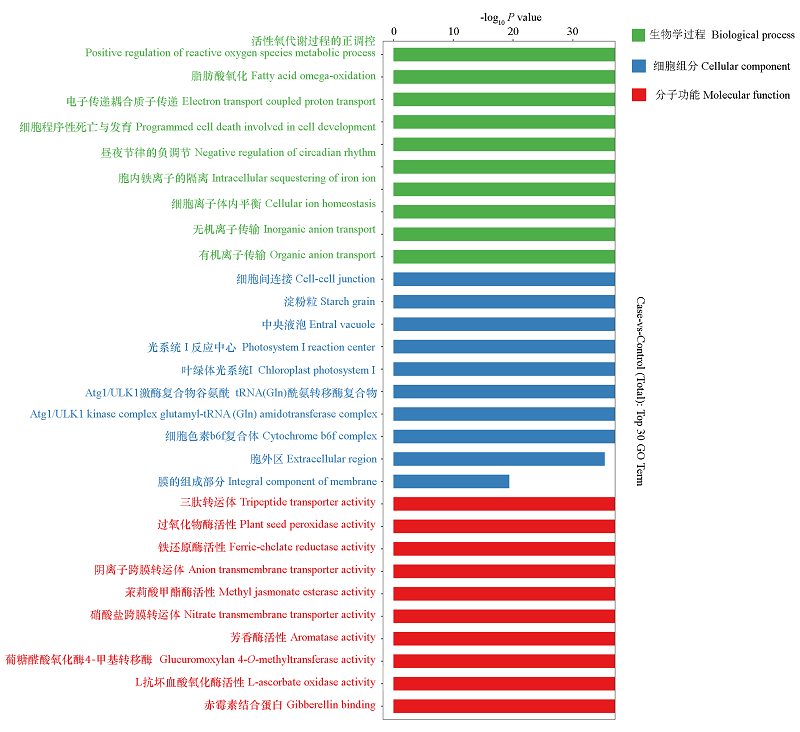
图4 垂丝海棠叶片在盐碱胁迫下功能基因GO富集前30的分类图
Fig. 4 Gene Ontology(GO)classification of unigenes enrichment top 30 item map in Malus halliana leaves under saline-alkali stress
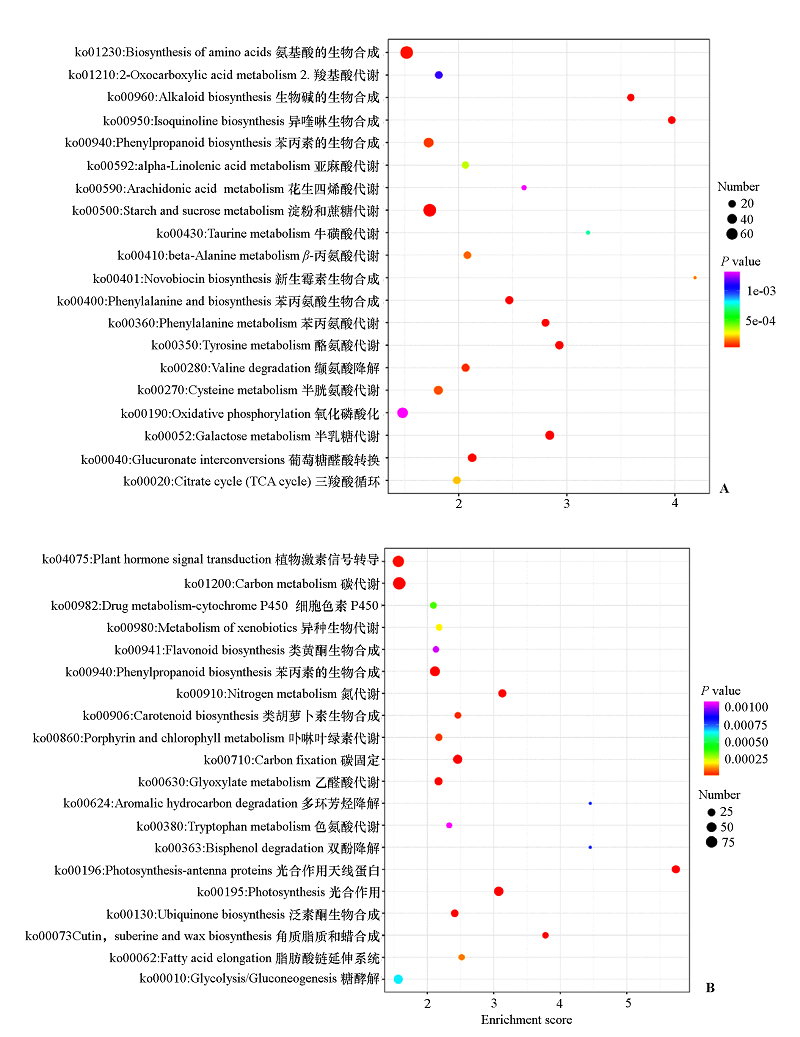
图5 垂丝海棠叶片响应盐碱胁迫的上调(A)和 下调(B)表达的前20差异基因KEGG富集散点图
Fig. 5 Scatterplot of KEGG enrichment of the top 20 differential genes up-regulated(A)and down-regulated(B)in response to saline-alkali stress in leaves of Malus halliana
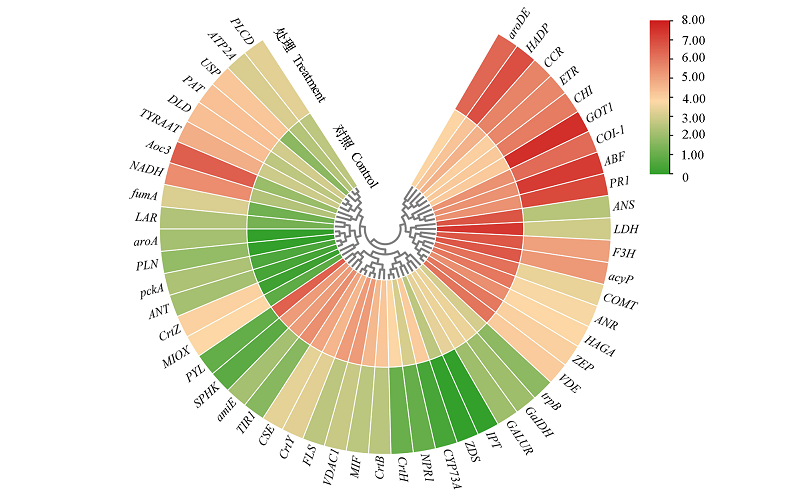
图6 盐碱胁迫下垂丝海棠叶片钙信号、植物激素信号转导和关键代谢物合成途径相关的DEG热图分析
Fig. 6 Heat map analysis of DEG related to calcium signaling,plant hormone signal transduction and key metabolite synthesis pathways in leaves of Malus halliana under saline-alkali stress
| [1] |
Abdallah S B, Auang B, Ayot L, Lalin I, Lachaal M. 2016. Salt stress(NaCl)affects plant growth and branch pathways of carotenoid and flavonoid biosyntheses in Solanum nigrum. Acta Physiologiae Plantarum, 38 (3):1-13.
doi: 10.1007/s11738-015-2023-4 URL |
| [2] |
Affenzeller M J. 2009. Salt stress-induced cell death in the unicellular green alga Micrasterias denticulata. Journal of Experimental Botany, 60 (3):939-954.
doi: 10.1093/jxb/ern348 pmid: 19213813 |
| [3] |
Aslam RE, Williams L, Bhatti F, Virk N. 2017. Genome-wide analysis of wheat calcium ATPases and potential role of selected ACAs and ECAs in calcium stress. BMC Plant Biology, 17:174-187.
doi: 10.1186/s12870-017-1112-5 URL |
| [4] |
Bi Y M, Kenton P, Mur L. 1995. Hydrogen peroxide does not function downstream of salicylic acid in the induction of PR protein expression. The Plant Journal, 8 (2):235-245.
doi: 10.1046/j.1365-313X.1995.08020235.x URL |
| [5] |
Boneh U, Biton I, Zheng C. 2012. Characterization of potential ABA receptors in Vitis vinifera. Plant Cell Reports, 31 (2):311-321.
doi: 10.1007/s00299-011-1166-z pmid: 22016084 |
| [6] |
Buchfink B, Xie C, Huson D H. 2015. Fast and sensitive protein alignment using DIAMOND. Nature Methods, 12 (1):59-60.
doi: 10.1038/nmeth.3176 URL |
| [7] |
Dahro, Wang F, Peng T, Liu J H. 2016. PtrA/NINV,an alkaline/neutral invertase gene of Poncirus trifoliata,confers enhanced tolerance to multiple abiotic stresses by modulating ROS levels and maintaining photosynthetic efficiency. BMC Plant Biology, 16:76.
doi: 10.1186/s12870-016-0761-0 URL |
| [8] |
Du C X. 2010. Proteomic analysis of cucumber seedling roots subjected to salt stress. Phytochemistry, 71 (13):1450-1459.
doi: 10.1016/j.phytochem.2010.05.020 URL |
| [9] | Gupta B, Huang B. 2014. Mechanism of salinity tolerance in plants:physiological,biochemical,and molecular characterization. International Journal of Genomics,1-18. |
| [10] |
Jaina M, Rober D F, Sean R E, Alex B, Marco P. 2013. Challenges in homology search:HMMER3 and convergent evolution of coiled-coil regions. Nucleic Acids Research, 41 (12):e121.
doi: 10.1093/nar/gkt263 URL |
| [11] |
Jia X M, Wang H, Svetla S, Zhu Y F, Hu Y, Wang Y X. 2019a. Comparative physiological responses and adaptive strategies of apple Malus halliana to salt,alkali and saline-alkali stress. Scientia Horticulturae, 245:154-162.
doi: 10.1016/j.scienta.2018.10.017 URL |
| [12] |
Jia X M, Zhu Y F, Hu Y, Zhang R, Wang Y X. 2019b. Integrated physiologic,proteomic,and metabolomic analyses of Malus halliana adaptation to saline-alkali stress. Horticulture Research, 6 (1):91.
doi: 10.1038/s41438-019-0172-0 URL |
| [13] | Jia Xu-mei, Zhu Yan-fang, Wang Hai, Wu Yu Xia. 2019. Physiological response of the salt-alkali compound stress of Malus halliana. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 39 (17):6349-6361. (in Chinese) |
| 贾旭梅, 朱燕芳, 王海, 吴玉霞. 2019. 垂丝海棠应对盐碱复合胁迫的生理响应. 生态学报, 39 (17):6349-6361. | |
| [14] | Karuppanapandian T, Moon J, Kim C. 2011. Reactive oxygen species in plants:their generation,signal transduction,and scavenging mechanisms. Australian Journal of Crop Science, 5 (6):709-725. |
| [15] |
Lakshman N P, Yoichi T, Shinjiro T. 2012. Reducing the antigenicity of milk whey protein using acid proteinases from Monascus pilosus. Process Biochemistry, 46 (3):806-810.
doi: 10.1016/j.procbio.2010.11.014 URL |
| [16] | Leckie C P, Mcainsh M R, Allen G J. 1998. Abscisic acid-induced stomatal closure mediated by cyclic ADP-ribose. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 95 (26):15837-15842. |
| [17] |
Liu N N. 2019. Effects of IAA and ABA on the immature peach fruit development process. Horticultural Plant Journal, 5 (4):145-154.
doi: 10.1016/j.hpj.2019.01.005 URL |
| [18] | Lofke C, Zwiewka M, Heilmann I. 2013. Asymmetric gibberellin signaling regulates vacuolar trafficking of PIN auxin transporters during root gravitropism. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 110 (9):3627-3632. |
| [19] |
Lopezberges Lopezberges, Rispail N, Pradosrosales R C. 2010. A nitrogen response pathway regulates virulence functions in Fusarium oxysporum via the protein kinase TOR and the bZIP protein MeaB. The Plant Cell, 22 (7):2459-2475.
doi: 10.1105/tpc.110.075937 URL |
| [20] | Manishankar P, Wang N, Ster P. 2018. Calcium signaling during salt stress and in the regulation of ion homeostasis. Journal of Experimental Botany,(17):17. |
| [21] |
Maria K, Aldona W, Agineszka P. 2017. A heterozygous mutation in GOT1 is associated with familial macro-aspartate aminotransferase. Journal of Hepatology, 67 (5):1026-1030.
doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2017.07.003 URL |
| [22] | Meng L S. 2015. Arabidopsis AINTEGUMENTA mediates salt tolerance by trans-repressing SCABP8. Journal of Cell Science, 128 (15):2919-2927. |
| [23] | Nadia V, Cristina S C. 2012. Comparative study of phenolic compounds in different Brazilian rice(Oryza sativa L.)genotypes. Journal of Food Composition & Analysis, 22 (5):405-409. |
| [24] | Pi E, Zhu C, Fan W. 2018. Quantitative phosphoproteomic and metabonomic analyses reveal GmMYB 173 optimizes flavonoid metabolism in soybean under salt stress. Molecular & Cellular Proteomics Mcp, 17 (2):1209-1224. |
| [25] |
Şahin-Çevik M, Çevik B, Coşkan A. 2020. Identification and expression analysis of salinity-induced genes in rangpur lime(Citrus limonia). Horticultural Plant Journal, 6 (5):267-276.
doi: 10.1016/j.hpj.2020.07.005 URL |
| [26] |
Sanchez D H, Pieckenstain F L, Escaray F, Erban A, Kopka J. 2011. Comparative ionomics and metabolomics in extremophile and glycophytic Lotus species under salt stress challenge the metabolic preadaptation hypothesis. Plant Cell Environment, 34:605-617.
doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3040.2010.02266.x URL |
| [27] |
Sandra D, Santos O, Luis R. 2012. Contactin-associated protein 1(Caspr1)regulates the traffic and synaptic content of α-amino-3- hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid (AMPA)-type glutamate receptors. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 287 (9):68-77.
doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.271205 URL |
| [28] | Sanoubar R, Cellini A, Gianfranco G, Spinelli F. 2020. Osmoprotectants and antioxidative enzymes as screening tools for salinity tolerance in radish (Raphanus sativus). Horticultural Plant Journal, 6 (1):11-24. |
| [29] |
Shen Jia-zhi, Zou Z W, Zhu X J. 2018. Metabolic analyses reveal different mechanisms of leaf color change in two purple-leaf tea plant(Camellia sinensis L.)cultivars. Horticulture Research, 5 (1):7.
doi: 10.1038/s41438-017-0010-1 URL |
| [30] |
Vinocur B, Altman A. 2005. Recentadvances inengineering plant tolerance to abiotic stress:achievements and limitations. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 16:123-132.
doi: 10.1016/j.copbio.2005.02.001 pmid: 15831376 |
| [31] | Watanabe M, Balazadeh S, Hoefgen R. 2013. Comprehensive dissection of spatiotemporal metabolic shifts in primary,secondary,and lipid metabolism during developmental senescence in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiolohy, 162:1290-1310. |
| [32] | Xu Ji-hua, Zhao Zheng-yang, Wang Lei-cun, Gao Hua, Liu Zhen-zhong, Fan Hong-ke. 2011. Selection of factors for apple fruit quality evaluation. Agricultural Research in the Arid Areas, 29 (6):269-274. (in Chinese) |
| 徐吉花, 赵政阳, 王雷存, 高华, 刘振中, 樊红科. 2011. 苹果果实品质评价因子的选择研究. 干旱地区农业研究, 29 (6):269-274. | |
| [33] | Xue Hao, Zhang Feng, Zhang Zhi-hong, Fu Jun-fan, Wang Feng, Zhang Bing, Ma Yue. 2015. Differences in salt tolerance between the diploid and autotetraploid‘Hanfu’apple. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 42 (5):826-832. (in Chinese) |
| 薛浩, 张锋, 张志宏, 傅俊范, 王丰, 张兵, 马跃. 2015. ‘寒富’苹果与其同源四倍体耐盐差异研究. 园艺学报, 42 (5):826-832. | |
| [34] | Yoshida T, Mogami J, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K. 2015. Omics approaches toward defining the comprehensive abscisic acid signaling network in plants. Plant & Cell Physiology, 56 (6):1043-1052. |
| [35] | Yoshihisa K, Kazuyoshi T, Masafumi H. 2012. Arabidopsis ABCB 21 is a facultative auxin importer/exporter regulated by cytoplasmic auxin concentration. Plant & Cell Physiology, 53 (12):2090-2100. |
| [36] | Yu Le, Liu Yong-hai, Yuan Wei-chao, Zhou Li-ping, Peng Chang-lian. 2016. Advances in plant ascorbic acid accumulation and its molecular mechanism. Acta Botanica Sinica, 51 (3):396-410. (in Chinese) |
| 俞乐, 刘拥海, 袁伟超, 周丽萍, 彭长连. 2016. 植物抗坏血酸积累及其分子机制的研究进展. 植物学报, 51 (3):396-410. | |
| [37] |
Zhang L S. 2019. Advance of horticultural plant genomes. Horticultural Plant Journal, 5 (6):229-230.
doi: 10.1016/j.hpj.2019.12.002 URL |
| [38] | Zhang Xing-xu. 2011. Effects of salt and drought stress on alkaloid production in endophyte-infected drunken horse grass(Achnatherum inebrians). Biochemical Systematics & Ecology, 39 (4-6):471-476. |
| [39] | Zheng J Y, Yang Y, Guo X, Jin L P, Xiong X Y. 2020. Eukaryotic translation initiation factors shape RNA viruses resistance in plants. Horticultural Plant Journal, 6 (2):99-110. |
| [40] |
Zhu Jian-kang. 2002. Salt and drought stress signal transduction in plants. Annu Rev Plant Biol, 53:247-273.
pmid: 12221975 |
| [41] | Zhu Yan-fang. 2018. Resistance physiology and proteomics analysis of apple rootstocks under mixed saline-alkali stress[M. D. Dissertation]. Lanzhou: Gansu Agricultural University. (in Chinese) |
| 朱燕芳. 2018. 混合盐碱胁迫下苹果砧木的抗性生理和蛋白组学分析[硕士论文]. 兰州: 甘肃农业大学. |
| [1] | 蔺海娇, 梁雨晨, 李玲, 马军, 张璐, 兰振颖, 苑泽宁. 薰衣草CBF途径相关耐寒基因挖掘与调控网络分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(1): 131-144. |
| [2] | 郑晓东, 袭祥利, 李玉琪, 孙志娟, 马长青, 韩明三, 李少旋, 田义轲, 王彩虹. 油菜素内酯对盐碱胁迫下平邑甜茶幼苗生长的影响及调控机理研究[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(7): 1401-1414. |
| [3] | 王春夏,尹 玥,王志平,严 瑞,付麟岚,孙红梅*. 多倍化兰州百合和细叶百合组培苗再生和耐非生物胁迫能力[J]. 园艺学报, 2019, 46(12): 2359-2368. |
| [4] | 楚爱香;杨英军;汤庚国;童丽丽. 河南垂丝海棠品种数量分类研究[J]. 园艺学报, 2009, 36(3): 377-384. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
版权所有 © 2012 《园艺学报》编辑部 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
编辑部地址: 北京市海淀区中关村南大街12号中国农业科学院蔬菜花卉研究所 邮编: 100081
电话: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
技术支持:北京玛格泰克科技发展有限公司