
园艺学报 ›› 2021, Vol. 48 ›› Issue (9): 1768-1784.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2019-0986
收稿日期:2021-04-09
修回日期:2021-05-26
出版日期:2021-09-25
发布日期:2021-09-30
通讯作者:
傅小鹏
E-mail:fuxiaopeng@mail.hzau.edu.cn
基金资助:
LIN Shengnan, LIU Jiewei, ZHANG Xiaoni, BAO Manzhu, FU Xiaopeng*( )
)
Received:2021-04-09
Revised:2021-05-26
Online:2021-09-25
Published:2021-09-30
Contact:
FU Xiaopeng
E-mail:fuxiaopeng@mail.hzau.edu.cn
摘要:
以拟南芥WRKY蛋白序列及保守结构域种子文件(PF03106)检索香石竹(Dianthus caryophyllus L.)基因组数据库,共鉴定出香石竹WRKY家族基因DcaWRKY 53个,分别编码161 ~ 747个氨基酸,蛋白质平均分子量在18.27 ~ 82.58 kD之间,等电点在5.07 ~ 10.25之间,内含子数1 ~ 5。系统发育分析显示,DcaWRKY可分为3组,其中groupⅡ又可进一步分为5个亚组。DcaWRKY结构域具有高度保守性,皆为WRKYGQK七肽结构域,偶有变型。DcaWRKY20的N端WRKYGQK七肽结构域出现缺失,形成了WRK的缺失变型;DcaWRKY39的C端WRKYGQK七肽结构域中的K突变成了N,形成了WRNYGQK七肽结构域;DcaWRKY48为WRKYGKK七肽结构域。DcaWRKY蛋白序列中至少存在10个保守基序,同源关系较近的成员具有相似的保守基序。启动子区的顺式作用元件分析显示DcaWRKY启动子区含有大量与光信号、植物激素、胁迫和分生组织等相关的功能域。转录组数据分析结果显示,有20个DcaWRKY在不定根形成过程中表现出不同程度地上调或下调,推测其可能在香石竹插穗不定根形成过程中发挥重要作用。定量分析结果表明DcaWRKY11、DcaWRKY13、DcaWRKY15、DcaWRKY22、DcaWRKY23、DcaWRKY31及DcaWRKY39的表达模式与转录组结果基本一致,且在香石竹不定根生长过程中表现出多样性。此外,DcaWRKY在生长素处理组和对照组中的表达水平无显著差异性,说明DcaWRKY对生长素不敏感。
中图分类号:
林胜男, 刘杰玮, 张晓妮, 包满珠, 傅小鹏. 香石竹WRKY家族全基因组鉴定及其表达分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2021, 48(9): 1768-1784.
LIN Shengnan, LIU Jiewei, ZHANG Xiaoni, BAO Manzhu, FU Xiaopeng. Genome-wide Identification and Expression Analysis of WRKY Gene Family in Dianthus caryophyllus[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2021, 48(9): 1768-1784.
| 基因 Gene | 组 Group | 上游引物(5′-3′) Forward primer | 下游引物(5′-3′) Reverse primer |
|---|---|---|---|
| DcaWRKY11 | Ⅱ-d | CCCGACCCTATACAGCAAGTC | CCATCTCCCTCTTCATCCCC |
| DcaWRKY13 | Ⅱ-e | CGTTGTCGTTGTCGCAGTTT | TGATTCAACAGGTTTGAGGGGA |
| DcaWRKY15 | Ⅱ-a | AGATTACTCGTGTCGCTGTTCG | TCTGTGTTCTCTACTCCGATCAA |
| DcaWRKY22 | Ⅲ | CAAGGGACCCAAGGACACAT | AGAATGGGCAAAATGGGAATGA |
| DcaWRKY23 | Ⅱ-b | ACCCGGCCTTTGCTGATACC | GCCGCCGTGAAATTAGGGTC |
| DcaWRKY31 | Ⅱ-c | TACAAAGACAAGGGCGCGAA | TGCAAAAGACCGTCATCCCT |
| DcaWRKY39 | Ⅰ | CCTAGACCGTTTGTGTCGCT | ACCCGCTTCAGTGATGTCTT |
| DcaGAPDH | — | CGGAAAGTTGACTGGTATGGC | CATCCTCGGTGTAGCCCAAAAT |
表1 本研究中所使用的引物
Table 1 The primers used in this study
| 基因 Gene | 组 Group | 上游引物(5′-3′) Forward primer | 下游引物(5′-3′) Reverse primer |
|---|---|---|---|
| DcaWRKY11 | Ⅱ-d | CCCGACCCTATACAGCAAGTC | CCATCTCCCTCTTCATCCCC |
| DcaWRKY13 | Ⅱ-e | CGTTGTCGTTGTCGCAGTTT | TGATTCAACAGGTTTGAGGGGA |
| DcaWRKY15 | Ⅱ-a | AGATTACTCGTGTCGCTGTTCG | TCTGTGTTCTCTACTCCGATCAA |
| DcaWRKY22 | Ⅲ | CAAGGGACCCAAGGACACAT | AGAATGGGCAAAATGGGAATGA |
| DcaWRKY23 | Ⅱ-b | ACCCGGCCTTTGCTGATACC | GCCGCCGTGAAATTAGGGTC |
| DcaWRKY31 | Ⅱ-c | TACAAAGACAAGGGCGCGAA | TGCAAAAGACCGTCATCCCT |
| DcaWRKY39 | Ⅰ | CCTAGACCGTTTGTGTCGCT | ACCCGCTTCAGTGATGTCTT |
| DcaGAPDH | — | CGGAAAGTTGACTGGTATGGC | CATCCTCGGTGTAGCCCAAAAT |
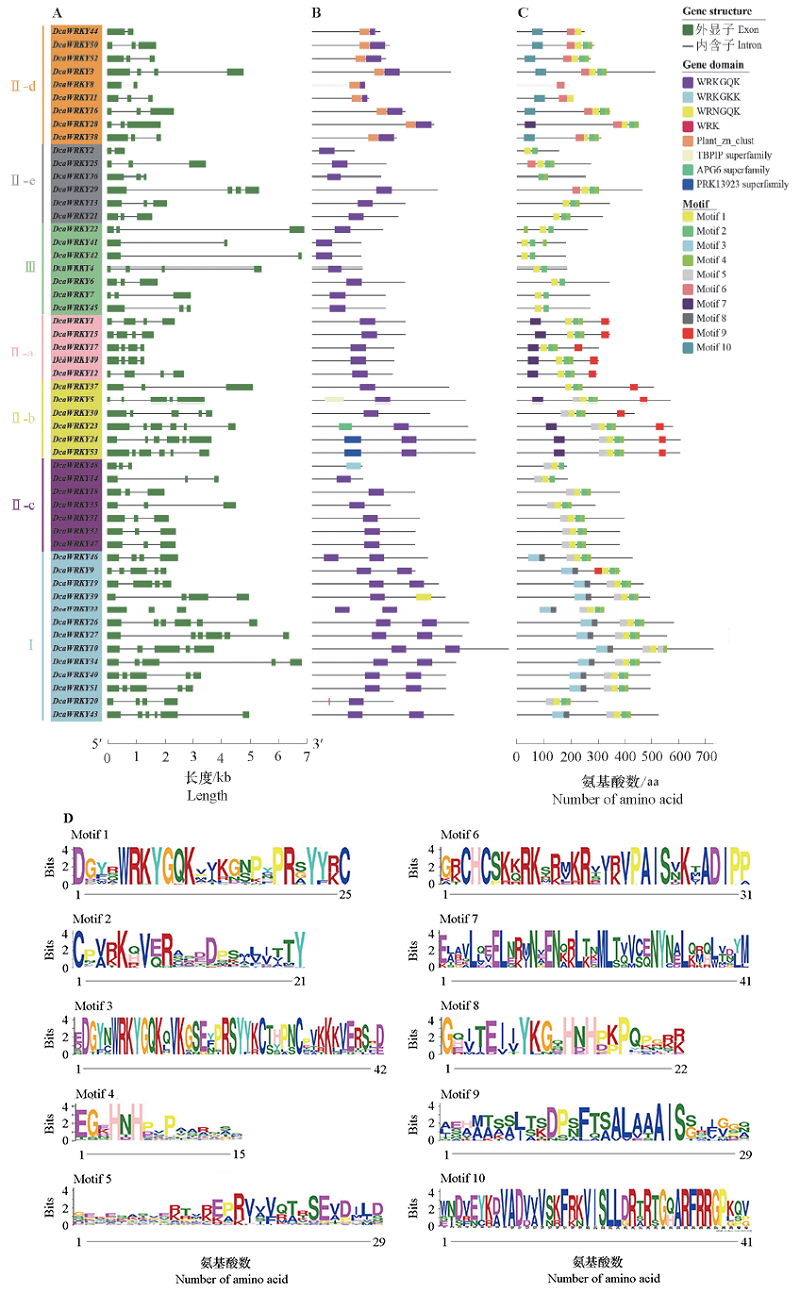
图2 香石竹WRKY蛋白进化分析 A. 基因结构;B. 保守结构域分布;C. 保守基序分布;D. 保守基序序列。
Fig. 2 Analysis of DcaWRKY protein evolution A. Gene structure;B. Conserved domain;C:Protein conserved motif;D:The sequences of protein conserved motif.
| 元件名称 Element name | 保守序列 Consensus sequence | 生物学功能 Biological function | 基因名称 Gene name | 来源 Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A-box | CCGTCC | 顺式作用调节元件 cis-acting regulatory element | DcaWRKY16,33,35,39,41,42,48 | 香芹 Petroselinum crispum |
| CAAT-box | CCAAT | 启动子和增强子区常见的顺式作用元件 Common cis-acting element in promoter and enhancer regions | DcaWRKY1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40,41,43,44,45,46,47,48,49,50,51,53 | 拟南芥 Arabidopsis thaliana |
| G-box | TACGTG | 参与光响应的顺式调控元件 cis-acting regulatory element involved in light responsiveness | DcaWRKY1,3,10,12,13,15,17,18,20,21,26,30,32,33,41,42,43,44,49,50 | 拟南芥 Arabidopsis thaliana |
| ABRE | ACGTG | 参与脱落酸反应的顺式作用元件 cis-acting element involved in the abscisic acid responsiveness | DcWRKY1,2,3,8,9,10,12,13,15,17,18,20,21,22,24,26,27,29,30,32,34,36,43,44,46,49,50,53 | 拟南芥 Arabidopsis thaliana |
| LTR | CCGAAA | 参与低温反应的顺式作用元件 cis-acting element involved in low-temperature responsiveness | DcaWRKY1,3,5,8,9,10,11,12,14,15,16,17,19, 22,25,27,32,36,39,40,43,44,47,49,51 | 大麦 Hordeum vulgare |
| ARE | AAACCA | 厌氧诱导所必需的顺式作用调节元件 cis-acting regulatory element essential for the anaerobic induction | DcaWRKY1,2,3,5,6,7,8,9,10,12,13,14,17,18,19,21,23,25,27,31,32,35,36,37,38,42,43,44,45,46,47,48,49,50 | 玉米 Zea mays |
| TC-rich repeats | GTTTTCTTAC | 参与防御和应激反应的顺式作用元件 cis-acting element involved in defense and stress responsiveness | DcaWRKY1,7,15,17,19,22,23,29,32,33,40,45,49 | 烟草 Nicotiana tabacum |
| GCN4_ motif | TGAGTCA | 参与胚乳表达的顺式调控元件 cis-regulatory element involved in endosperm expression | DcaWRKY4,6,11,15,17,21,30,36,38,48,49 | 水稻 Oryza sativa |
| CGTCA- motif | CGTCA | 参与MeJA反应的顺式调控元件 cis-acting regulatory element involved in the MeJA-responsiveness | DcaWRKY3,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,22,24,26,27,29,30,34,35,38,39,40,41,45,46,48,49,51,53 | 大麦 Hordeum vulgare |
| WUN- motif | AAATTTCCT | 损伤反应元件 Wound-responsive element | DcaWRKY18,28 | 芸薹 Brassica oleracea |
| TCA- element | CCATCTTTTT | 参与水杨酸反应的顺式作用元件 cis-acting element involved in salicylic acid responsiveness | DcaWRKY3,4,12,13,15,16,18,25,28,32,40,41,43,48,51 | 烟草 Nicotiana tabacum |
| RY-element | CATGCATG | 参与种子特异性调控的顺式调控元件 cis-acting regulatory element involved in seed-specific regulation | DcaWRKY43 | 向日葵 Helianthus annuus |
| AuxRR- core | GGTCCAT | 参与生长素反应的顺式调控元件 cis-acting regulatory element involved in auxin responsiveness | DcaWRKY12,13,15,16,23,24,39,40,51,53 | 烟草 Nicotiana tabacum |
| MSA-like | TCCAACGGT | 参与细胞周期调控的顺式作用元件 cis-acting element involved in cell cycle regulation | DcaWRKY6,17,49 | 长春花 Catharanthus roseus |
表3 香石竹WRKY启动子顺式作用元件的生物学功能分析
Table 3 Functional analysis of the cis-acting element on the promoter of DcaWRKY
| 元件名称 Element name | 保守序列 Consensus sequence | 生物学功能 Biological function | 基因名称 Gene name | 来源 Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A-box | CCGTCC | 顺式作用调节元件 cis-acting regulatory element | DcaWRKY16,33,35,39,41,42,48 | 香芹 Petroselinum crispum |
| CAAT-box | CCAAT | 启动子和增强子区常见的顺式作用元件 Common cis-acting element in promoter and enhancer regions | DcaWRKY1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40,41,43,44,45,46,47,48,49,50,51,53 | 拟南芥 Arabidopsis thaliana |
| G-box | TACGTG | 参与光响应的顺式调控元件 cis-acting regulatory element involved in light responsiveness | DcaWRKY1,3,10,12,13,15,17,18,20,21,26,30,32,33,41,42,43,44,49,50 | 拟南芥 Arabidopsis thaliana |
| ABRE | ACGTG | 参与脱落酸反应的顺式作用元件 cis-acting element involved in the abscisic acid responsiveness | DcWRKY1,2,3,8,9,10,12,13,15,17,18,20,21,22,24,26,27,29,30,32,34,36,43,44,46,49,50,53 | 拟南芥 Arabidopsis thaliana |
| LTR | CCGAAA | 参与低温反应的顺式作用元件 cis-acting element involved in low-temperature responsiveness | DcaWRKY1,3,5,8,9,10,11,12,14,15,16,17,19, 22,25,27,32,36,39,40,43,44,47,49,51 | 大麦 Hordeum vulgare |
| ARE | AAACCA | 厌氧诱导所必需的顺式作用调节元件 cis-acting regulatory element essential for the anaerobic induction | DcaWRKY1,2,3,5,6,7,8,9,10,12,13,14,17,18,19,21,23,25,27,31,32,35,36,37,38,42,43,44,45,46,47,48,49,50 | 玉米 Zea mays |
| TC-rich repeats | GTTTTCTTAC | 参与防御和应激反应的顺式作用元件 cis-acting element involved in defense and stress responsiveness | DcaWRKY1,7,15,17,19,22,23,29,32,33,40,45,49 | 烟草 Nicotiana tabacum |
| GCN4_ motif | TGAGTCA | 参与胚乳表达的顺式调控元件 cis-regulatory element involved in endosperm expression | DcaWRKY4,6,11,15,17,21,30,36,38,48,49 | 水稻 Oryza sativa |
| CGTCA- motif | CGTCA | 参与MeJA反应的顺式调控元件 cis-acting regulatory element involved in the MeJA-responsiveness | DcaWRKY3,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,22,24,26,27,29,30,34,35,38,39,40,41,45,46,48,49,51,53 | 大麦 Hordeum vulgare |
| WUN- motif | AAATTTCCT | 损伤反应元件 Wound-responsive element | DcaWRKY18,28 | 芸薹 Brassica oleracea |
| TCA- element | CCATCTTTTT | 参与水杨酸反应的顺式作用元件 cis-acting element involved in salicylic acid responsiveness | DcaWRKY3,4,12,13,15,16,18,25,28,32,40,41,43,48,51 | 烟草 Nicotiana tabacum |
| RY-element | CATGCATG | 参与种子特异性调控的顺式调控元件 cis-acting regulatory element involved in seed-specific regulation | DcaWRKY43 | 向日葵 Helianthus annuus |
| AuxRR- core | GGTCCAT | 参与生长素反应的顺式调控元件 cis-acting regulatory element involved in auxin responsiveness | DcaWRKY12,13,15,16,23,24,39,40,51,53 | 烟草 Nicotiana tabacum |
| MSA-like | TCCAACGGT | 参与细胞周期调控的顺式作用元件 cis-acting element involved in cell cycle regulation | DcaWRKY6,17,49 | 长春花 Catharanthus roseus |
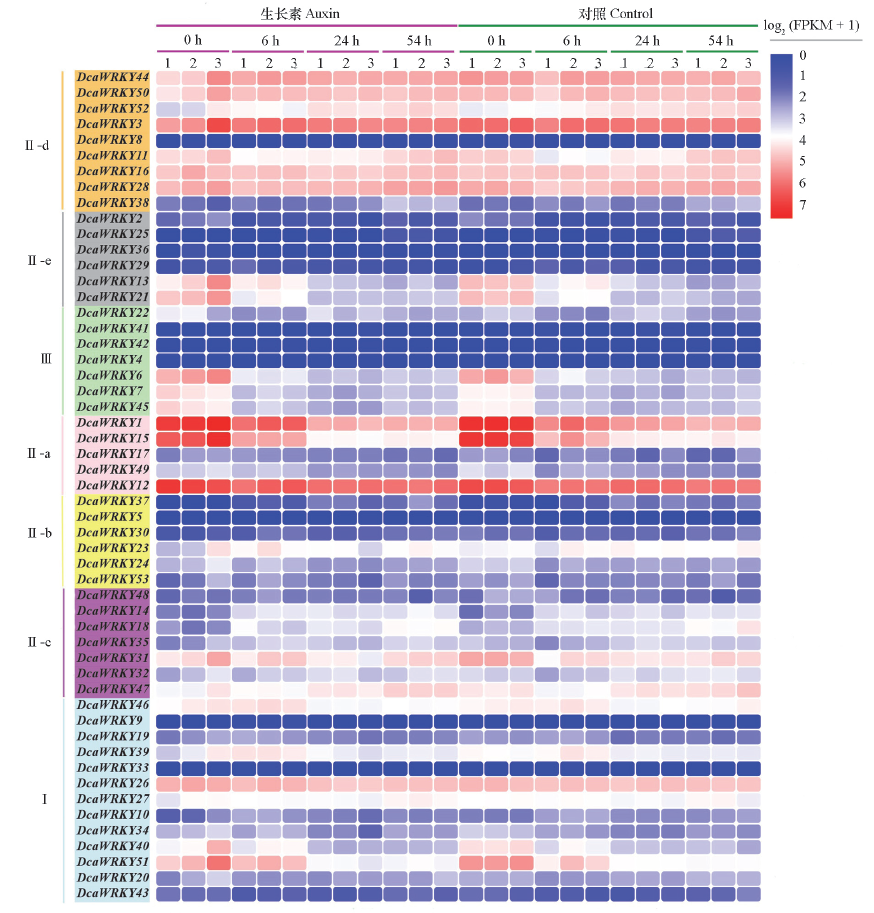
图4 香石竹WRKY基因家族成员在香石竹插穗不定根形成过程中的表达模式分析 图中1、2和3代表3次生物学重复。
Fig. 4 Analysis of expression patterns of the DcaWRKY gene family members during adventitious root formation in carnation stem cuttings 1,2 and 3 represent three biological replicates.
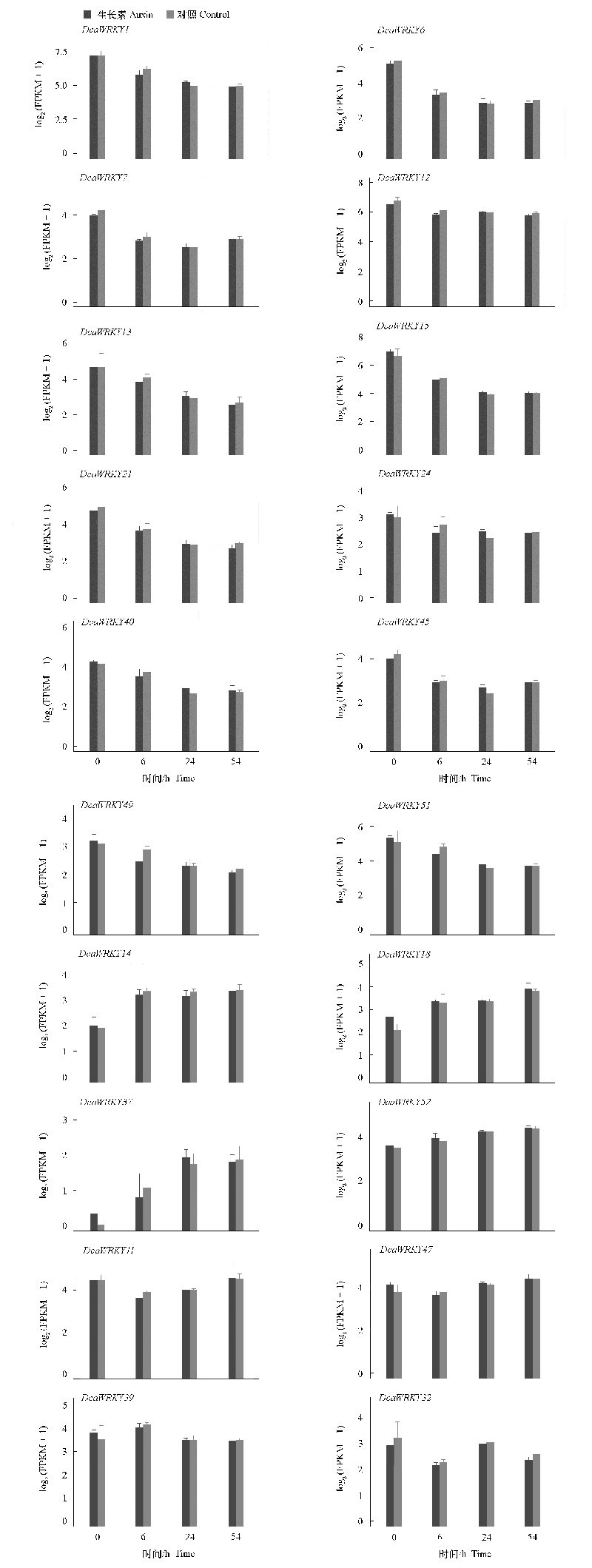
图5 部分香石竹WRKY基因家族成员在香石竹插穗不定根形成过程中的表达模式
Fig. 5 The expression patterns of part DcaWRKY gene family members during adventitious root formation in carnation stem cuttings
| [1] |
Balakrishnan S, Gao S, Lercher M J, Hu S, Chen W H. 2019. Evolview v3:a webserver for visualization,annotation,and management of phylogenetic trees. Nucleic Acids Research, 47(W1):W270-W275.
doi: 10.1093/nar/gkz357 |
| [2] |
Cai C, Niu E, Du H, Zhao L, Feng Y, Guo W. 2014. Genome-wide analysis of the WRKY transcription factor gene family in Gossypium raimondii and the expression of orthologs in cultivated tetraploid cotton. The Crop Journal, 2:87-101.
doi: 10.1016/j.cj.2014.03.001 URL |
| [3] | Chen P, Liu Q. 2019. Genome-wide characterization of the WRKY gene family in cultivated strawberry(Fragaria × ananassa Duch.)and the importance of several group Ⅲ members in continuous cropping. Scientific Reports, 9:1-12. |
| [4] |
Chen X, Chen R, Wang Y, Wu C, Huang J. 2019. Genome-wide identification of WRKY transcription factors in Chinese jujube(Ziziphus jujuba Mill.)and their involvement in fruit developing,ripening,and abiotic stress. Genes, 10:360.
doi: 10.3390/genes10050360 URL |
| [5] | Devaiah B N, Karthikeyan A S, Raghothama K G. 2007. WRKY75 transcription factor is a modulator of phosphate acquisition and root development in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiology, 143(4):89-1801. |
| [6] | Diao Wei-ping, Wang Shu-bin, Liu Jin-bing, Pan Bao-gui, Guo Guang-jun, Ge Wei. 2015. Genome-wide analysis of the WRKY transcription factor family in pepper. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 42(11):2183-2196. (in Chinese) |
| 刁卫平, 王述彬, 刘金兵, 潘宝贵, 郭广君, 戈伟. 2015. 辣椒全基因组WRKY转录因子的分析. 园艺学报, 42(11):2183-2196. | |
| [7] | Garrido G, Arnao M B, Acosta M, Sánchez-Bravo J. 2003. Polar transport of indole-3-acetic acid in relation to rooting in carnation cuttings:influence of cold storage duration and cultivar. Biologia Plantarum, 47(4):481-485. |
| [8] |
Guo C, Guo R, Xu X, Gao M, Li X, Song J, Zheng Y, Wang X. 2014. Evolution and expression analysis of the grape(Vitis vinifera L.)WRKY gene family. Journal of Experimental Botany, 65(6):1513-1528.
doi: 10.1093/jxb/eru007 URL |
| [9] |
He Z, Zhang H, Gao S, Lercher M J, Chen W H, Hu S. 2016. Evolview v2:an online visualization and management tool for customized and annotated phylogenetic trees. Nucleic Acids Research, 44(W1):W236-W241.
doi: 10.1093/nar/gkw370 URL |
| [10] |
Huang X, Li K, Xu X, Yao Z, Jin C, Zhang S. 2015. Genome-wide analysis of WRKY transcription factors in white pear(Pyrus bretschneideri)reveals evolution and patterns under drought stress. BMC genomics, 16(1):1-14.
doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-16-1 URL |
| [11] |
Ishiguro S, Nakamura K. 1994. Characterization of a cDNA encoding a novel DNA-binding protein,SPF1,that recognizes SP8 sequences in the 5′ upstream regions of genes coding for sporamin and β-amylase from sweet potato. Molecular and General Genetics MGG, 244(6):563-571.
doi: 10.1007/BF00282746 URL |
| [12] |
Janiak A, Kwasniewski M, Sowa M, Kuczyńska A, Mikołajczak K, Ogrodowicz P, Szarejko I. 2019. Insights into barley root transcriptome under mild drought stress with an emphasis on gene expression regulatory mechanisms. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(24):6139.
doi: 10.3390/ijms20246139 URL |
| [13] |
Jiang C, Shen Q J, Wang B, He B, Xiao S, Chen L, Yu T, Ke X, Zhong Q, Fu J, Chen Y, Wang L, Yin F, Zhang D, Ghidan W, Huang X, Cheng Z. 2017. Transcriptome analysis of WRKY gene family in Oryza officinalis Wall ex Watt and WRKY genes involved in responses to Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae stress. PLoS One, 12(11):e0188742.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0188742 URL |
| [14] |
Justamante M S, Acosta-Motos J R, Cano A, Villanova J, Birlanga V, Albacete A, Cano E Á, Acosta M, Pérez-Pérez J M. 2019. Integration of phenotype and hormone data during adventitious rooting in carnation(Dianthus caryophyllus L.)stem cuttings. Plants, 8(7):226.
doi: 10.3390/plants8070226 URL |
| [15] |
Li D, Liu P, Yu J, Wang L, Dossa K, Zhang Y, Zhou R, Wei X, Zhang X. 2017. Genome-wide analysis of WRKY gene family in the sesame genome and identification of the WRKY genes involved in responses to abiotic stresses. BMC Plant Biology, 17(1):1-19.
doi: 10.1186/s12870-016-0951-9 URL |
| [16] | Li Xiaoying, Xu Hongxia, Chen Junwei. 2019. Identification and expression analysis of WRKY transcription factors in Eriobotrya japonica. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 46(5):939-954. (in Chinese) |
| 李晓颖, 徐红霞, 陈俊伟. 2019. 枇杷WRKY转录因子鉴定与表达分析. 园艺学报, 46(5):939-954. | |
| [17] |
Li M Y, Xu Z S, Tian C, Huang Y, Wang F, Xiong A S. 2016. Genomic identification of WRKY transcription factors in carrot(Daucus carota)and analysis of evolution and homologous groups for plants. Scientific Reports, 6(1):1-17.
doi: 10.1038/s41598-016-0001-8 URL |
| [18] |
Liu C, Xie T, Chen C, Luan A, Long J, Li C, Ding Y, He Y. 2017. Genome-wide organization and expression profiling of the R2R3-MYB transcription factor family in pineapple(Ananas comosus). BMC Genomics, 18(1):1-16.
doi: 10.1186/s12864-016-3406-7 URL |
| [19] |
Ma Q, Xia Z, Cai Z, Li L, Cheng Y, Liu J, Nian H. 2019. GmWRKY16 enhances drought and salt tolerance through an ABA-mediated pathway in Arabidopsis thaliana. Frontiers in Plant Science, 9:1979.
doi: 10.3389/fpls.2018.01979 URL |
| [20] |
Nan H, Gao L. 2019. Genome-wide analysis of WRKY genes and their response to hormone and mechanic stresses in carrot. Frontiers in Genetics, 10:363.
doi: 10.3389/fgene.2019.00363 URL |
| [21] |
Rushton P J, Somssich I E, Ringler P, Shen Q J. 2010. WRKY transcription factors. Trends in Plant Science, 15(5):247-258.
doi: 10.1016/j.tplants.2010.02.006 URL pmid: 20304701 |
| [22] |
Tan X L, Fan Z Q, Li L L, Wu Y, Kuang J F, Lu W J, Chen J Y. 2016. Molecular characterization of a leaf senescence-related transcription factor BRWRKY75 of chinese flowering cabbage. Horticultural Plant Journal, 2(5):272-278.
doi: 10.1016/j.hpj.2017.01.003 URL |
| [23] |
van Verk M C, Pappaioannou D, Neeleman L, Bol J F, Linthorst H J M. 2008. A novel WRKY transcription factor is required for induction of PR-1a gene expression by salicylic acid and bacterial elicitors. Plant Physiology, 146(4):1983-1995.
doi: 10.1104/pp.107.112789 URL |
| [24] |
Villacorta-Martín C, Sánchez-García A B, Villanova J, Cano A, Pérez-Pérez J M. 2015. Gene expression profiling during adventitious root formation in carnation stem cuttings. BMC Genomics, 16(1):1-18.
doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-16-1 URL |
| [25] |
Wang P, Xu X, Tang Z, Zhang W, Huang X Y, Zhao F J. 2018. OsWRKY28 regulates phosphate and arsenate accumulatio,root system architecture and fertility in rice. Frontiers in Plant Science, 9:1330.
doi: 10.3389/fpls.2018.01330 URL |
| [26] |
Wang Z, Feng R, Zhang X, Su Z, Wei J, Liu J. 2019. Characterization of the Hippophae rhamnoides WRKY gene family and functional analysis of the role of the HrWRKY21 gene in resistance to abiotic stresses. Genome, 62(10):689-703.
doi: 10.1139/gen-2019-0024 URL |
| [27] | Waqas M, Azhar M T, Rana I A, Azeem F, Ali M A, Nawaz M A, Chung G, Atif R M. 2019. Genome-wide identification and expression analyses of WRKY transcription factor family members from chickpea(Cicer arietinum L.)reveal their role in abiotic stress-responses. Genes & Genomics, 41(4):467-481. |
| [28] |
Xie Z, Zhang Z L, Zou X, Huang J, Ruas P, Thompson D, Shen Q. J. 2005. Annotations and functional analyses of the rice WRKY gene superfamily reveal positive and negative regulators of abscisic acid signaling in aleurone cells. Plant Physiology, 137(1):176-189.
doi: 10.1104/pp.104.054312 URL |
| [29] |
Xu H, Watanabe K A, Zhang L, Shen Q J. 2016. WRKY transcription factor genes in wild rice Oryza nivara. DNA Research, 23(4):311-323.
doi: 10.1093/dnares/dsw025 URL |
| [30] | Xu Rui-rui, Zhang Shi-zhong, Cao Hui, Shu Huai-rui. 2012. Bioinformatics analysis of WRKY transcription factor genes family in apple. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 39(10):2049-2060. (in Chinese) |
| 许瑞瑞, 张世忠, 曹慧, 束怀瑞. 2012. 苹果WRKY转录因子家族基因生物信息学分析. 园艺学报, 39(10):2049-2060. | |
| [31] |
Yue H, Chang X, Zhi Y, Wang L, Xing G, Song W, Nie X. 2019. Evolution and identification of the WRKY gene family in quinoa(Chenopodium quinoa). Genes, 10(2):131.
doi: 10.3390/genes10020131 URL |
| [32] |
Zhang H, Gao S, Lercher M J, Hu S, Chen W H. 2012. EvolView,an online tool for visualizing,annotating and managing phylogenetic trees. Nucleic Acids Research, 40(W1):569-572.
doi: 10.1093/nar/gkr753 URL |
| [33] |
Zhou Q Y, Tian A G, Zou H F, Xie Z M, Lei G, Huang J, Wang C M, Wang H W, Zhang J S, Chen S Y. 2008. Soybean WRKY-type transcription factor genes,GmWRKY13,GmWRKY21,and GmWRKY54,confer differential tolerance to abiotic stresses in transgenic Arabidopsis plants. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 6(5):486-503.
doi: 10.1111/pbi.2008.6.issue-5 URL |
| [1] | 王晓晨, 聂子页, 刘先菊, 段 伟, 范培格, 梁振昌, . 脱落酸对‘京香玉’葡萄果实单萜物质合成的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(2): 237-249. |
| [2] | 张 欣, 漆艳香, 曾凡云, 王艳玮, 谢培兰, 谢艺贤, 彭 军. 香蕉枯萎病菌Dicer-like基因的功能分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(2): 279-294. |
| [3] | 任 菲, 卢苗苗, 刘吉祥, 陈信立, 刘道凤, 眭顺照, 马 婧. 蜡梅胚胎晚期丰富蛋白基因CpLEA的表达及抗性分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(2): 359-370. |
| [4] | 于婷婷, 李 欢, 宁源生, 宋建飞, 彭璐琳, 贾竣淇, 张玮玮, 杨洪强. 苹果GRAS全基因组鉴定及其对生长素的响应分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(2): 397-409. |
| [5] | 翟含含, 翟宇杰, 田义, 张叶, 杨丽, 温陟良, 陈海江. 桃SAUR家族基因分析及PpSAUR5功能鉴定[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(1): 1-14. |
| [6] | 杨植, 张川疆, 杨芯芳, 董梦怡, 王振磊, 闫芬芬, 吴翠云, 王玖瑞, 刘孟军, 林敏娟. 枣与酸枣杂交后代果实遗传倾向及混合遗传分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(1): 36-52. |
| [7] | 崔建, 钟雄辉, 刘泽慈, 陈登辉, 李海龙, 韩睿, 乐祥庆, 康俊根, 王超. 结球甘蓝染色体片段替换系构建[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(1): 65-78. |
| [8] | 何成勇, 赵晓丽, 许腾飞, 高德航, 李世访, 王红清. 草莓病毒1山东分离物全基因组分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(1): 153-160. |
| [9] | 罗海林, 袁雷, 翁华, 闫佳会, 郭青云, 王文清, 马新明. 蚕豆萎蔫病毒2号青海辣椒分离物的鉴定与全基因组序列克隆[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(1): 161-169. |
| [10] | 忽靖宇, 阙开娟, 缪田丽, 吴少政, 王田田, 张磊, 董鲜, 季鹏章, 董家红. 侵染鸢尾的番茄斑萎病毒鉴定[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(1): 170-176. |
| [11] | 赵雪艳, 王琪, 王莉, 王方圆, 王庆, 李艳. 基于比较转录组的延胡索组织差异性表达分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(1): 177-187. |
| [12] | 蒋亚君, 陈佳佳, 谭彬, 郑先波, 王伟, 张郎郎, 程钧, 冯建灿. 桃PpIDD11调控花发育的功能研究[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(9): 1841-1852. |
| [13] | 王沙, 张心慧, 赵玉洁, 李变变, 招雪晴, 沈雨, 董建梅, 苑兆和. 石榴花青苷合成相关基因PgMYB111的克隆与功能分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(9): 1883-1894. |
| [14] | 黄玲, 胡先梅, 梁泽慧, 王艳平, 产祝龙, 向林. 郁金香花青素合成酶基因TgANS的克隆与功能鉴定[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(9): 1935-1944. |
| [15] | 李茂福, 杨媛, 王华, 范又维, 孙佩, 金万梅. 月季中R2R3-MYB基因RhMYB113c调控花青素苷合成[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(9): 1957-1966. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
版权所有 © 2012 《园艺学报》编辑部 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
编辑部地址: 北京市海淀区中关村南大街12号中国农业科学院蔬菜花卉研究所 邮编: 100081
电话: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
技术支持:北京玛格泰克科技发展有限公司