
园艺学报 ›› 2021, Vol. 48 ›› Issue (7): 1304-1316.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2021-0151
张双双, 苏维, 刘阳, 王海平, 宋江萍, 阳文龙, 贾会霞, 张晓辉*( ), 李锡香
), 李锡香
收稿日期:2021-03-23
修回日期:2021-05-21
出版日期:2021-07-25
发布日期:2021-08-10
通讯作者:
张晓辉
E-mail:zhangxiaohui01@caas.cn
基金资助:
ZHANG Shuangshuang, SU Wei, LIU Yang, WANG Haiping, SONG Jiangping, YANG Wenlong, JIA Huixia, Zhang Xiaohui*( ), LI Xixiang
), LI Xixiang
Received:2021-03-23
Revised:2021-05-21
Online:2021-07-25
Published:2021-08-10
Contact:
Zhang Xiaohui
E-mail:zhangxiaohui01@caas.cn
摘要:
以白菜(Brassica rapa ssp. chinensis,AA基因组)为母本,以起源于非洲对黑腐病免疫的埃塞俄比亚芥(Brassica carinata,BBCC基因组)为父本进行远缘杂交,通过胚挽救方法获得ABC基因组杂种植株。杂种植株营养体粗壮高大,杂种优势明显。分子标记和流式细胞检测确定是真杂种。F1代植株初期无花粉,组培继代多代后育性逐渐恢复。与埃塞俄比亚芥回交的后代株系育性恢复速度高于与白菜回交的后代。流式细胞分析发现杂种染色质含量介于白菜和埃塞俄比亚芥之间,并且存在染色体和非整倍体加倍现象。花粉母细胞染色体压片显示减数分裂中存在染色体不减数、染色体滞后、染色体非对称分离、染色体粘贴和染色体桥等现象。从人工合成ABC植株与白菜回交的群体中筛选出高抗或免疫黑腐病的株系,抗性可以遗传。
中图分类号:
张双双, 苏维, 刘阳, 王海平, 宋江萍, 阳文龙, 贾会霞, 张晓辉, 李锡香. 白菜与埃塞俄比亚芥远缘杂交种质创制及黑腐病抗性转育[J]. 园艺学报, 2021, 48(7): 1304-1316.
ZHANG Shuangshuang, SU Wei, LIU Yang, WANG Haiping, SONG Jiangping, YANG Wenlong, JIA Huixia, Zhang Xiaohui, LI Xixiang. Germplasm Innovation and Black Rot Resistance Transferring in Brassica rapa ssp. chinensis Through Interspecific Hybridization with Brassica carinata[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2021, 48(7): 1304-1316.
| 分子标记编号 | 上游引物(5′-3′) | 下游引物(5′-3′) |
|---|---|---|
| Molecular marker ID | Forward primer | Reverse primer |
| 1A | GAGAAAACTCGGTGGGATCA | TCCCATACGCTCTCCTTCAC |
| 1B | GCAACACTTGCTGTTTTGGA | GCTGAGGTAGGAAGGGAAGG |
| 2A2 | GATCGACCTTCCATCACGTC | CCTTGTGCAAGAAGGTGTTG |
| 2B | GCTTTGTGGGTTTGAGCTTG | GCCATTTTGAACCATGAACC |
| 3A | ATAACGCTGAACTGGCGAAG | TTGATTGTCACACCGGAGAA |
| 3B | CCGGACCATAAATTATCGCA | GCTCCTCCTCCTCCATCTTC |
| 3B2 | CCTCCGCTAAGGTAAATCTCG | GCCGGAAGAAGAGATCAGTTT |
| 5B2 | TTCTTGTCAGTCCTGTCCCC | TCCCGAGGTACTTCACTTGC |
| 6D2 | GCTTCATTGGATCCCACATC | GGGTTCGTGATTGATGGTAAA |
| 7A2 | TGCCCTCCAAAATCCAATTA | CAGAAGCTCGGGAAGACATC |
| 7C | GGGAAAATTAAACCAAGCCA | GAACACATGGTGGACACAGC |
| 7D | GGAGAAGAAAACAGCGATGC | GGAATAGCTCTTGACGCTCG |
| 8B2 | TGCTGCTAAGTCTAGTCCACAA | CCTCAAGATCCACAATGCCT |
| 9D | TGACAGCATATGAAGCCTGC | GATCCTGCCACAAGAATTTGA |
表1 分子标记引物及序列
Table 1 The primer sequences of the molecular markers
| 分子标记编号 | 上游引物(5′-3′) | 下游引物(5′-3′) |
|---|---|---|
| Molecular marker ID | Forward primer | Reverse primer |
| 1A | GAGAAAACTCGGTGGGATCA | TCCCATACGCTCTCCTTCAC |
| 1B | GCAACACTTGCTGTTTTGGA | GCTGAGGTAGGAAGGGAAGG |
| 2A2 | GATCGACCTTCCATCACGTC | CCTTGTGCAAGAAGGTGTTG |
| 2B | GCTTTGTGGGTTTGAGCTTG | GCCATTTTGAACCATGAACC |
| 3A | ATAACGCTGAACTGGCGAAG | TTGATTGTCACACCGGAGAA |
| 3B | CCGGACCATAAATTATCGCA | GCTCCTCCTCCTCCATCTTC |
| 3B2 | CCTCCGCTAAGGTAAATCTCG | GCCGGAAGAAGAGATCAGTTT |
| 5B2 | TTCTTGTCAGTCCTGTCCCC | TCCCGAGGTACTTCACTTGC |
| 6D2 | GCTTCATTGGATCCCACATC | GGGTTCGTGATTGATGGTAAA |
| 7A2 | TGCCCTCCAAAATCCAATTA | CAGAAGCTCGGGAAGACATC |
| 7C | GGGAAAATTAAACCAAGCCA | GAACACATGGTGGACACAGC |
| 7D | GGAGAAGAAAACAGCGATGC | GGAATAGCTCTTGACGCTCG |
| 8B2 | TGCTGCTAAGTCTAGTCCACAA | CCTCAAGATCCACAATGCCT |
| 9D | TGACAGCATATGAAGCCTGC | GATCCTGCCACAAGAATTTGA |
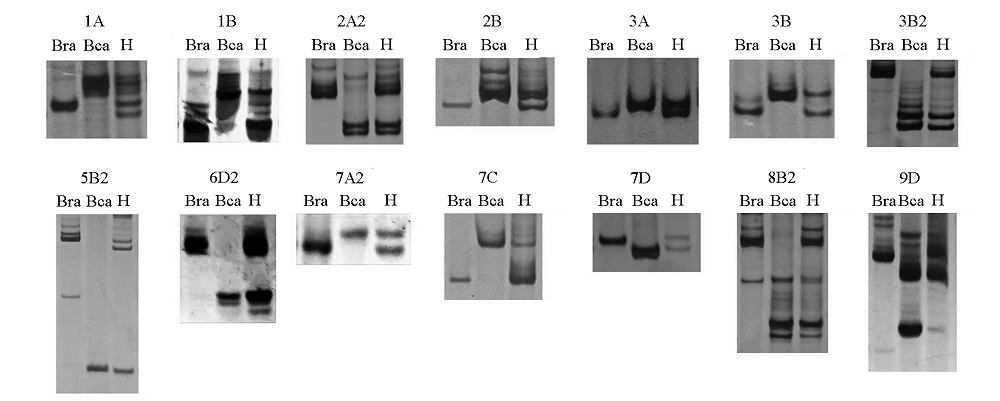
图2 分子标记鉴定白菜(Bra)与埃塞俄比亚芥(Bca)杂交F1代(H)植株 1A ~ 9D:分子标记编号。
Fig. 2 Analysis of the F1 hybrid(H)of Brassica rapa ssp. chinensis(Bra)and B. carinata(Bca)with molecular markers 1A-9D:Marker ID.

图4 白菜与埃塞俄比亚芥远缘杂交后代花、角果、种子的形态对比
Fig.4 Morphological comparison of flowers,siliques,seeds of progenies from interspecific hybridization between Brassica rapa ssp. chinensis and B. carinata
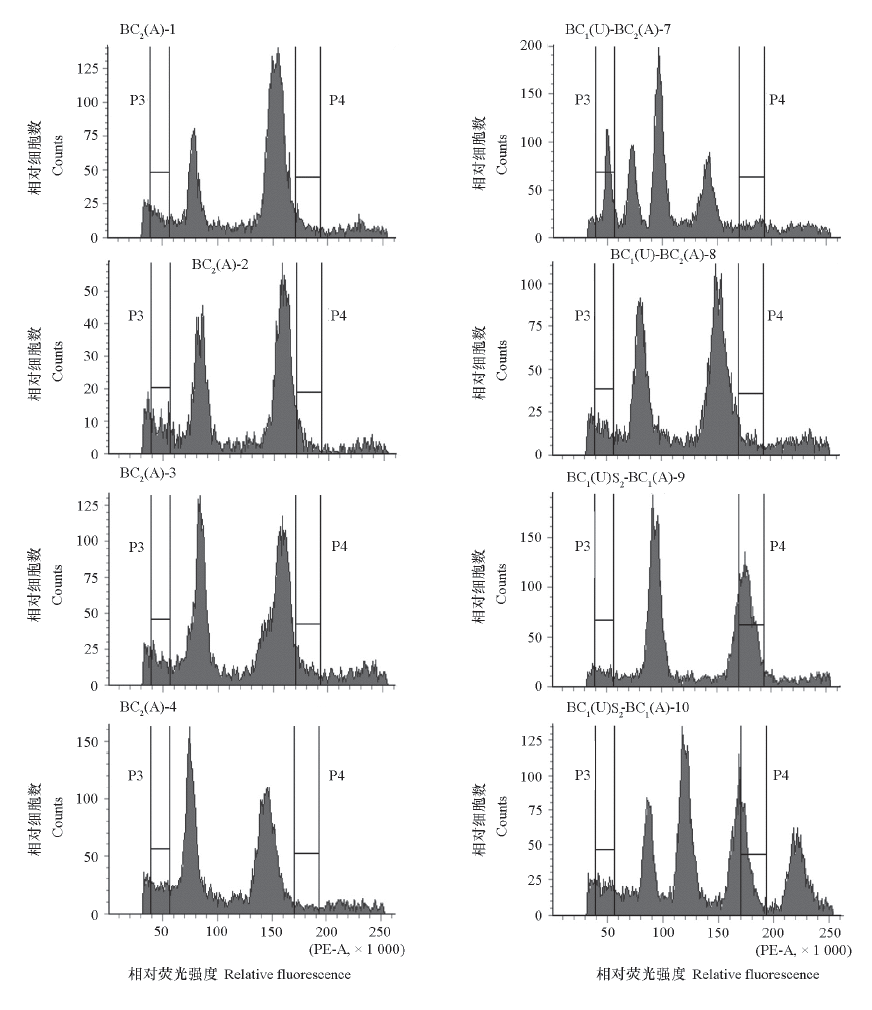
图6 白菜与埃塞俄比亚芥杂交后代幼嫩叶片细胞的染色质含量分布 BC2(A):与白菜回交2代;BC1(U):与埃塞俄比亚芥回交1代;BC1(U)-BC2(A):埃塞俄比亚芥回交1代,再与白菜回交2代;BC1(U)S2- BC1(A):与埃塞俄比亚芥回交1代,自交2代,再与白菜回交1代。
Fig.6 Chromatin content in cells from young leaf of the hybrid of Brassica rapa ssp. chinensis and Brassica carinata BC2(A):Second generation progenies of the inter-specific hybrid backcrossed with B. rapa ssp. chinensis;BC1(U):Progenies of the inter-specific hybrid backcrossed with B. carinata;BC1(U)-BC2(A):Inter-specific hybrid backcrossed with B. carinata for one generation and backcrossed with B. rapa ssp. chinensis for two generation;BC1(U)S2-BC1(A):Inter-specific hybrid backcrossed with B. carinata for one generation,followed by two generation of selfing,and then backcrossed with B. rapa ssp. chinensis for one generation.

图7 BC2(A)植株减数分裂时花粉母细胞的染色体异常情况 A:染色体不减数;B:染色体滞后;C:染色体3条聚集;D:染色体非对称分离;E、F:染色体粘贴和染色体桥。
Fig. 7 The abnormal chromosome behavior of pollen mother cells during meiosis in BC2(A)plants A:Chromosome non reduction;B:Chromosome lagging;C:Three chromosomes organized in a group;D:Asymmetric segregation;E,F:Chromosome stickiness and chromosome bridges.
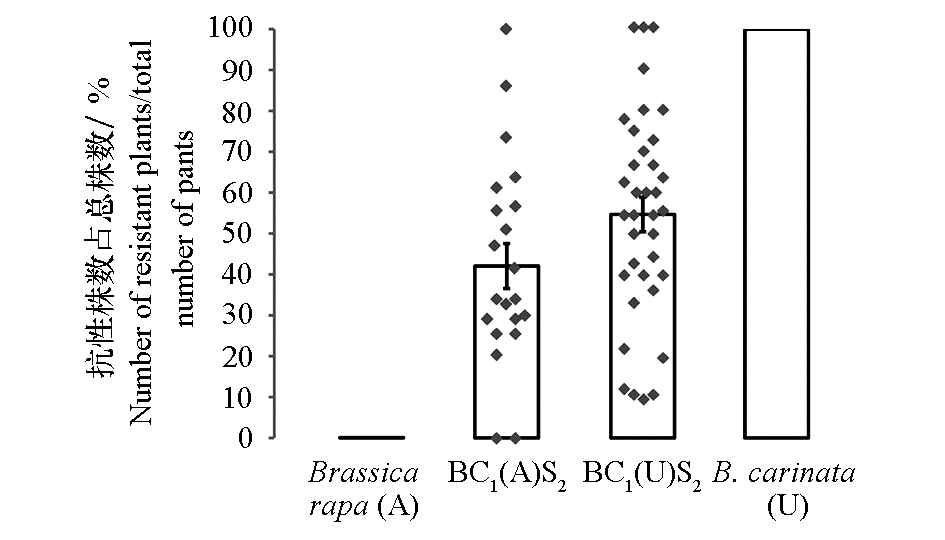
图8 白菜与埃塞俄比亚芥杂交后代的黑腐病抗性统计 BC1(A)S2是与白菜回交后自交2代,BC1(U)S2是与埃塞俄比亚芥回交后自交2代。
Fig.8 Black rot resistant assays of progenies from interspecific hybridization between Brassica rapa ssp. chinensis and B. carinata BC1(A)S2:Second generation selfing of plants backcrossed with B. rapa ssp. chinensis;BC1(U)S2:Second generation selfing of plants backcrossed with B. carinata.
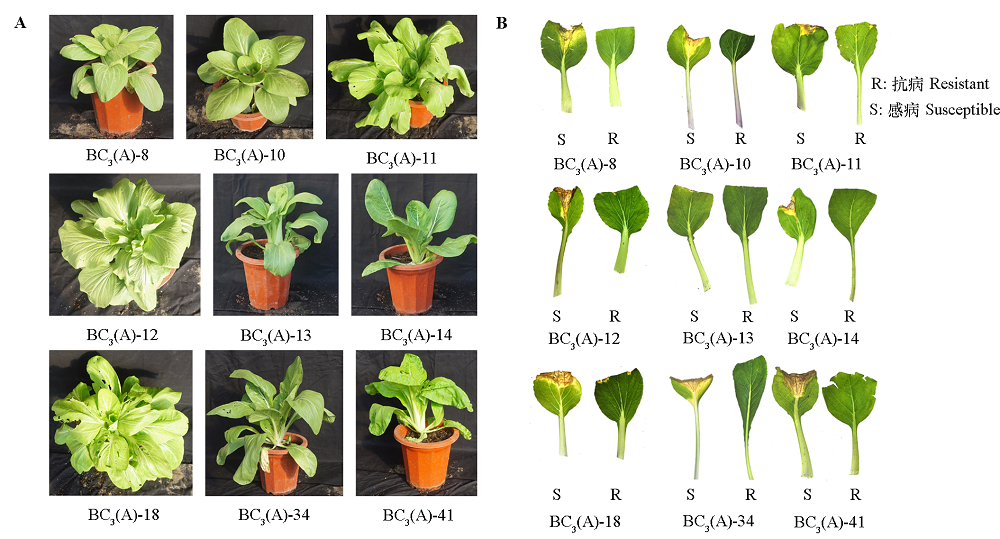
图9 与白菜回交BC3代植株的表型(A)和接种抗性鉴定(B)
Fig.9 The phenotype(A)and black rot resistant identification(B)of the BC3 plants with Brassica rapa ssp. chinensis as recurrent parent

图10 转育的抗病株系BC3(A)-S2与白菜亲本接种黑腐病菌鉴定
Fig.10 The disease resistant BC3(A)-S2 line and the original pakchoi inoculated with Xanthomonas campestris pv. Campestris
| [1] |
da Silva A L B R, Candian J S, do Rego E R, Coolong T, Dutta B. 2020. Screening cabbage cultivars for resistance to black rot under field conditions. Horttechnology, 30:448-455.
doi: 10.21273/HORTTECH04481-19 URL |
| [2] |
da Silva F P, Xavier A D S, Bruckner F P, de Rezende R R, Vidigal P M P, Alfenas-Zerbini P. 2019. Biological and molecular characterization of a bacteriophage infecting Xanthomonas campestris pv. campestris,isolated from Brassica fields. Arch Virol, 164:1857-1862.
doi: 10.1007/s00705-019-04263-4 URL |
| [3] |
Gong Q, Dai C Y, Zhang X H, Wang X L, Huang Z, Xu A X, Dong J G, Yu C Y. 2020. Towards breeding of rapeseed(Brassica napus)with alien cytoplasm and powdery mildew resistance from Ethiopian mustard(Brassica carinata). Breeding Science, 70:387-395.
doi: 10.1270/jsbbs.20017 URL |
| [4] |
Hu D, Zhang W, Zhang Y, Chang S, Chen L, Chen Y, Shi Y, Shen J, Meng J, Zou J. 2019. Reconstituting the genome of a young allopolyploid crop,Brassica napus,with its related species. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 17:1106-1118.
doi: 10.1111/pbi.2019.17.issue-6 URL |
| [5] |
Khedikar Y, Clarke W E, Chen L, Higgins E E, Kagale S, Koh C S, Bennett R, Parkin I A P. 2020. Narrow genetic base shapes population structure and linkage disequilibrium in an industrial oilseed crop,Brassica carinata A. Braun. Scientific Reports, 10:12629.
doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-69255-w URL |
| [6] |
Mason A S, Nelson M N, Takahira J, Cowling W A, Alves G M, Chaudhuri A, Chen N, Ragu M E, Dalton-Morgan J, Coriton O, Huteau V, Eber F, Chèvre A M, Batley J. 2014. The fate of chromosomes and alleles in an allohexaploid Brassica population. Genetics, 197:273-283.
doi: 10.1534/genetics.113.159574 URL |
| [7] |
Mason A S, Takahira J, Atri C, Samans B, Hayward A, Cowling W A, Batley J, Nelson M N. 2015. Microspore culture reveals complex meiotic behaviour in a trigenomic Brassica hybrid. BMC Plant Biology, 15:173.
doi: 10.1186/s12870-015-0555-9 URL |
| [8] |
Navabi Z K, Stead K E, Pires J C, Xiong Z, Sharpe A G, Parkin I A, Rahman M H, Good A G. 2011. Analysis of B-genome chromosome introgression in interspecific hybrids of Brassica napus × B. carinata. Genetics, 187:659-673.
doi: 10.1534/genetics.110.124925 URL pmid: 21196520 |
| [9] |
Sakudo A, Haritani M, Furusaki K, Onishi R, Onodera T. 2020. Electrically charged disinfectant containing calcium hydrogen carbonate mesoscopic crystals as a potential measure to control Xanthomonas campestris pv. campestris on cabbage seeds. Microorganisms, 8:1606.
doi: 10.3390/microorganisms8101606 URL |
| [10] |
Raman R, Qiu Y, Coombes N, Song J, Kilian A, Raman H. 2017. Molecular diversity analysis and genetic mapping of pod shatter resistance loci in Brassica carinata L. Frontiers in Plant Science, 8:1765.
doi: 10.3389/fpls.2017.01765 pmid: 29250080 |
| [11] |
Sharma B B, Kalia P, Singh D, Sharma T R. 2017. Introgression of black rot resistance from Brassica carinata to cauliflower(Brassica oleracea botrytis Group)through embryo rescue. Frontiers in Plant Science, 8:1255.
doi: 10.3389/fpls.2017.01255 pmid: 28769959 |
| [12] |
Sharma B B, Kalia P, Yadava D K, Singh D, Sharma T R. 2016. Genetics and molecular mapping of black rot resistance locus Xca1bc on chromosome B-7 in Ethiopian mustard(Brassica carinata A. Braun). PLoS ONE, 11:e0152290.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0152290 URL |
| [13] |
Sheng X G, Branca F, Zhao Z Q, Wang J S, Yu H F, Shen Y S, Gu H H. 2020. Identification of black rot resistance in a wild Brassicas pecies and its potential transferability to cauliflower. Agronomy, 10:1400.
doi: 10.3390/agronomy10091400 URL |
| [14] |
Singh A, Gautam V, Singh S, Sarkar Das S, Verma S, Mishra V, Mukherjee S, Sarkar A K. 2018. Plant small RNAs:advancement in the understanding of biogenesis and role in plant development. Planta, 248:545-558.
doi: 10.1007/s00425-018-2927-5 URL |
| [15] |
Taylor J D, Conway J, Roberts S J, Astley D, Vicente J G. 2002. Sources and origin of resistance to Xanthomonas campestris pv. campestris in Brassica genomes. Phytopathology, 92:105-111.
doi: 10.1094/PHYTO.2002.92.1.105 pmid: 18944146 |
| [16] |
Teklehaymanot T, Wang H J, Liang J L, Wu J, Lin R M, Zhou Z, Cai X, Wang X W. 2019. Variation in plant morphology and sinigrin content in Ethiopian mustard(Brassica carinata L.). Hortic Plant J, 5(5):205-212.
doi: 10.1016/j.hpj.2019.07.005 URL |
| [17] | Tu Yu-qin, Tang Jie, Zhang Yang, Xin Jia-jia, Tu Wei-feng, Ji Hong-li, Dai Xing-lin. 2020. Innovation of new determinate infloresence germplasm via hybridization between Brassica napus and Brassica carinata. Journal of Plant Genetic Resoures, 21(1):74-82. (in Chinese) |
| 涂玉琴, 汤洁, 张洋, 辛佳佳, 涂伟凤, 姬红利, 戴兴临. 2020. 甘蓝型油菜与埃塞俄比亚芥杂交创制有限花序新种质. 植物遗传资源学报, 21(1):74-82 | |
| [18] |
Vicente J G, Holub E B. 2013. Xanthomonas campestris pv. campestris(cause of black rot of crucifers)in the genomic era is still a worldwide threat to brassica crops. Mol Plant Pathol, 14:2-18.
doi: 10.1111/j.1364-3703.2012.00833.x URL pmid: 23051837 |
| [19] |
Vicente J G, Taylor J D, Sharpe A G, Parkin I A, Lydiate D J, King G J. 2002. Inheritance of race-specific resistance to Xanthomonas campestris pv. campestris in Brassica genomes. Phytopathology, 92:1134-1141.
doi: 10.1094/PHYTO.2002.92.10.1134 pmid: 18944224 |
| [20] |
Wang R, Zou J, Meng J, Wang J. 2018. Integrative analysis of genome-wide lncRNA and mRNA expression in newly synthesized Brassica hexaploids. Ecology and Evolution, 8:6034-6052.
doi: 10.1002/ece3.2018.8.issue-12 URL |
| [21] | Wei Z, Wang M, Chang S, Wu C, Liu P, Meng J, Zou J. 2016. Introgressing subgenome components from Brassica rapa and B. carinata to B. juncea for broadening its genetic base and exploring intersubgenomic heterosis. Frontiers in Plant Science, 7:1677. |
| [22] | Xie Yong-mei. 2008. Identification of black rot on cruciferous vegetables and the resistance of Chinese cabbage varieties in Shandong Province[M. D. Dissertation]. Tai’an:Shandong Agricultural University. (in Chinese) |
| 解永梅. 2008. 山东省十字花科蔬菜黑腐病菌的鉴定及大白菜品种抗病性研究[硕士论文]. 泰安:山东农业大学. | |
| [23] | Yu Yang-jun, Chen Guang, Xu Jia-bing, Zhang Feng-lan, Sun Ji-zhi, Zhao Xiu-yun, Zhang De-shuang. 2005. A new Chinese cabbage F1 hybrid-‘Jingchun 99’. China Vegetables, (10/11):8-9. (in Chinese) |
| 余阳俊, 陈广, 徐家炳, 张凤兰, 孙继志, 赵岫云, 张德双. 2005. 春大白菜新品种京春99的选育. 中国蔬菜, (10/11):8-9. | |
| [24] | Yuan Shi-feng, Qi Cun-kou. 2007. Inheritance of additional chromosomes in Brassica napus carinata disamic additional line 92I1096. Jiangsu Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 23(4):289-294. (in Chinese) |
| 袁世峰, 戚存扣. 2007. 甘蓝型油菜埃芥二体附加系92I1096附加染色体的遗传分析. 江苏农业学报, 23(4):289-294. | |
| [25] | Zhang Feng-lan. 1994. Indoor identification of resistance of Chinese cabbage to black rot and selection of resistant sources. Beijing Agricultural Sciences, 12(4):28-29. (in Chinese) |
| 张凤兰. 1994. 白菜对黑腐病抗性的室内鉴定方法及抗源筛选. 北京农业科学, 12(4):28-29. | |
| [26] |
Zhang W, Hu D, Raman R, Guo S, Wei Z, Shen X, Meng J, Raman H, Zou J. 2017. Investigation of the genetic diversity and quantitative trait loci accounting for important agronomic and seed quality traits in Brassica carinata. Frontiers in Plant Science, 8:615.
doi: 10.3389/fpls.2017.00615 URL |
| [27] |
Zhang X, Liu T, Li X, Duan M, Wang, Qiu Y, Wang H, Song J, Shen D. 2016. Interspecific hybridization,polyploidization,and backcross of Brassica oleracea var. alboglabra with B. rapa var. purpurea morphologically recapitulate the evolution of Brassica vegetables. Scientific Reports, 6:18618.
doi: 10.1038/srep18618 URL |
| [28] |
Zhao Q, Zou J, Meng J, Mei S, Wang J. 2013. Tracing the transcriptomic changes in synthetic trigenomic allohexaploids of Brassica using an RNA-seq approach. PLoS ONE, 8:e68883.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0068883 URL |
| [29] |
Zou J, Hu D, Mason A S, Shen X, Wang X, Wang N, Grandke F, Wang M, Chang S, Snowdon R J, Meng J. 2018. Genetic changes in a novel breeding population of Brassica napus synthesized from hundreds of crosses between B. rapa and B. carinata. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 16:507-519.
doi: 10.1111/pbi.2018.16.issue-2 URL |
| [1] | 韩书辉, 韩彩锋, 韩书荣, 韩彩梅, 韩 旭. 秋大白菜新品种‘胶研秋宝’[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(S2): 83-84. |
| [2] | 汪维红, 张凤兰, 余阳俊, 张德双, 赵岫云, 于拴仓, 苏同兵, 李佩荣, 辛晓云. 秋大白菜新品种‘京秋1518’[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(S2): 85-86. |
| [3] | 余阳俊, 汪维红, 苏同兵, 张凤兰, 张德双, 赵岫云, 于拴仓, 李佩荣, 辛晓云, 王 姣. 抗根肿病耐抽薹大白菜新品种‘京春CR3’[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(S2): 87-88. |
| [4] | 王丽丽, 王 鑫, 吴海东, 温 蔷, 杨晓飞. 抗根肿病大白菜新品种‘辽白28’[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(S2): 89-90. |
| [5] | 余阳俊, 苏同兵, 张凤兰, 张德双, 赵岫云, 于拴仓, 汪维红, 李佩荣, 辛晓云, 王 姣, 武长见. 紫色苗用型大白菜新品种‘京研紫快菜’[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(S2): 91-92. |
| [6] | 黄 鹂, 陈财志, 余小林, 姚祥坦, 曹家树, . 早中熟普通白菜新品种‘浙大青’[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(S2): 93-94. |
| [7] | 余文迪, 姜贵芸, 刘娟旭, 余义勋, . 报春苣苔属新品种‘仙女棒’[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(S2): 185-186. |
| [8] | 何智宏, 何丽霞, 张延东, 杨国州, 李 睿, 徐晶晶, 瞿 丹, 李京璟. 牡丹新品种‘余霞散绮’[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(S2): 219-220. |
| [9] | 徐立功, 韩太利, 孙继峰, 杨晓东, 谭金霞. 苗用大白菜新品种‘锦绿2号’[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(S1): 67-68. |
| [10] | 邵贵荣, 朱 彬, 林 晓, 曹 萍, 方 勇, 崔 田, 蒋 鹏, 林咏铭, 林 魁, 林志滔. 白菜新品种‘金品008’[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(S1): 69-70. |
| [11] | 姜悦悦, 王田田, 赵 阳, 汪承刚, 侯金锋, 袁凌云. 白菜新品种‘皖绿2号’[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(S1): 71-72. |
| [12] | 王钰, 张雪, 张学颖, 张思雨, 闻婷婷, 王迎君, 甘彩霞, 庞文星. 抗毒素Camalexin对大白菜抗根肿病的作用研究[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(8): 1689-1698. |
| [13] | 张鲁刚, 卢倩倩, 何琼, 薛一花, 马晓敏, 马帅, 聂姗姗, 杨文静. 紫橙色大白菜新种质的创制[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(7): 1582-1588. |
| [14] | 陈道宗, 刘镒, 沈文杰, 朱博, 谭晨. 白菜、甘蓝和甘蓝型油菜PAP1/2同源基因的鉴定及分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(6): 1301-1312. |
| [15] | 王光鹏, 刘同坤, 徐新凤, 李竹帛, 高瞻远, 侯喜林. 大白菜LEA家族基因的鉴定及其部分成员在低温胁迫下的表达分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(2): 304-318. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
版权所有 © 2012 《园艺学报》编辑部 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
编辑部地址: 北京市海淀区中关村南大街12号中国农业科学院蔬菜花卉研究所 邮编: 100081
电话: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
技术支持:北京玛格泰克科技发展有限公司