
园艺学报 ›› 2021, Vol. 48 ›› Issue (6): 1123-1134.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2020-0806
张贺翠, 王玉奎, 左同鸿, 刘倩莹, 张以忠, 胡燈科, 谢琴琴, 朱利泉( )
)
收稿日期:2021-02-04
修回日期:2021-03-02
出版日期:2021-06-25
发布日期:2021-07-07
通讯作者:
朱利泉
E-mail:zhuliquan@swu.edu.cn
基金资助:
ZHANG Hecui, WANG Yukui, ZUO Tonghong, LIU Qianying, ZHANG Yizhong, HU Dengke, XIE Qinqin, ZHU Liquan( )
)
Received:2021-02-04
Revised:2021-03-02
Online:2021-06-25
Published:2021-07-07
Contact:
ZHU Liquan
E-mail:zhuliquan@swu.edu.cn
摘要:
在通过酵母双杂交文库获得了与钙响应蛋白BoSPx相互作用蛋白BoPID的基础上,对BoPID的编码基因进行了克隆、时空特异性表达分析及筛选与其互作的蛋白,以期为BoSPx通过BoPID参与自交不亲和性分子过程提供依据。结果表明,BoPID包含2个外显子和1个内含子,编码439个氨基酸。激酶磷酸化预测分析显示具有激酶活性;系统进化和共线性分析显示BoPID具有较强的植物种属特异性,与芜菁、拟南芥和甘蓝型油菜等十字花科植物聚类在一起,BoPID与AtPID在染色体水平上高度同源。组织特异性表达分析显示BoPID在柱头中的表达量高于花器官中的其他部位。荧光定量PCR分析表明BoPID在甘蓝柱头自花授粉15 min显著上调表达,而后下调表达。启动子元件分析发现BoPID含有ABA、IAA、脱落酸、茉莉酸、水杨酸和胁迫响应等多个应答元件。BoPID蛋白定位于细胞膜和细胞质中,可能是一种泊位于膜上并突触于胞质中的双栖蛋白。酵母双杂交和GST-Pull down结果表明BoPID与BoCML12、BoCaM2、BoPIN1能够发生相互作用。BoPID可能是BoSPx与BoCML12、BoCaM2之间相互作用的桥梁蛋白,共同通过生长素调节钙响应的方式参与了自交不亲和分子过程。
中图分类号:
张贺翠, 王玉奎, 左同鸿, 刘倩莹, 张以忠, 胡燈科, 谢琴琴, 朱利泉. 甘蓝BoPID基因的克隆与分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2021, 48(6): 1123-1134.
ZHANG Hecui, WANG Yukui, ZUO Tonghong, LIU Qianying, ZHANG Yizhong, HU Dengke, XIE Qinqin, ZHU Liquan. Cloning and Expression Analysis of BoPID in Brassica oleracea[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2021, 48(6): 1123-1134.
| 用途 Fuction | 引物名称 Primer name | 引物序列 Sequence | 退火温度/℃ Tm |
|---|---|---|---|
| 酵母双杂交载体 Yeast two-hybrid vector | BK-F BK-R AD-BoCML12-F AD-BoCML12-R AD-BoCaM2-F AD-BoCaM2-R AD-PIN1-F AD-PIN1-R | TCAGAGGAGGACCTGCATATGTTACGAGAATCAGACGGTGAG TCGACGGATCCCCGGGAATTCAAAGAAATCGAACGCCGCT GTACCAGATTACGCTCATATGTTACGAGAATCAGACAGTGAGAT ATGCCCACCCGGGTGGAATTCCGCTGGTTTGTTACTTCTACCAC GTACCAGATTACGCTCATATGATGGCGGATCAGCTGACC ATGCCCACCCGGGTGGAATTCCTTAGCCATCATGACTTTAACGAA GTACCAGATTACGCTCATGCTTTGCCTCAAGGAATTGTACC ATGCCCACCCGGGTGGAATTC GTAGTAGAGAAGGGTTATGGGC | 58 58 60 60 |
| 启动子表达 Promoter expression | GUS-F GUS-R | CAAGCTTGGCTGCAGGTCGACAGACAAGCGAATACTTTTAGGG GGTGGACTCCTCTTAGAATTCGAACATAACGTGGGAAGAGAGTA | 60 |
| qRT-PCR | qRT-PCR-F qRT-PCR-R | ATGGCCACTGATTCAGCAAT ATACCGGCCGTATTCCTCCT | 60 |
| RT-PCR | RT-PCR-F RT-PCR-R | ATGGCCACTGATTCAGCAAT GACGGCATAAGTAAACTGTTCCGATG | 60 |
| 亚细胞定位 Subcellular localization | 1300-GFP-F 1300-GFP-R | GAGAACACGGGGGACTCTAGAATGGCGTCTCCTAAATCCTCA GAGCTTTTGCTCCATGAGCTCAAAGAAATCGAACGCCGCT | 60 |
表1 本研究中所用的基因引物
Table 1 Gene primer used in this study
| 用途 Fuction | 引物名称 Primer name | 引物序列 Sequence | 退火温度/℃ Tm |
|---|---|---|---|
| 酵母双杂交载体 Yeast two-hybrid vector | BK-F BK-R AD-BoCML12-F AD-BoCML12-R AD-BoCaM2-F AD-BoCaM2-R AD-PIN1-F AD-PIN1-R | TCAGAGGAGGACCTGCATATGTTACGAGAATCAGACGGTGAG TCGACGGATCCCCGGGAATTCAAAGAAATCGAACGCCGCT GTACCAGATTACGCTCATATGTTACGAGAATCAGACAGTGAGAT ATGCCCACCCGGGTGGAATTCCGCTGGTTTGTTACTTCTACCAC GTACCAGATTACGCTCATATGATGGCGGATCAGCTGACC ATGCCCACCCGGGTGGAATTCCTTAGCCATCATGACTTTAACGAA GTACCAGATTACGCTCATGCTTTGCCTCAAGGAATTGTACC ATGCCCACCCGGGTGGAATTC GTAGTAGAGAAGGGTTATGGGC | 58 58 60 60 |
| 启动子表达 Promoter expression | GUS-F GUS-R | CAAGCTTGGCTGCAGGTCGACAGACAAGCGAATACTTTTAGGG GGTGGACTCCTCTTAGAATTCGAACATAACGTGGGAAGAGAGTA | 60 |
| qRT-PCR | qRT-PCR-F qRT-PCR-R | ATGGCCACTGATTCAGCAAT ATACCGGCCGTATTCCTCCT | 60 |
| RT-PCR | RT-PCR-F RT-PCR-R | ATGGCCACTGATTCAGCAAT GACGGCATAAGTAAACTGTTCCGATG | 60 |
| 亚细胞定位 Subcellular localization | 1300-GFP-F 1300-GFP-R | GAGAACACGGGGGACTCTAGAATGGCGTCTCCTAAATCCTCA GAGCTTTTGCTCCATGAGCTCAAAGAAATCGAACGCCGCT | 60 |
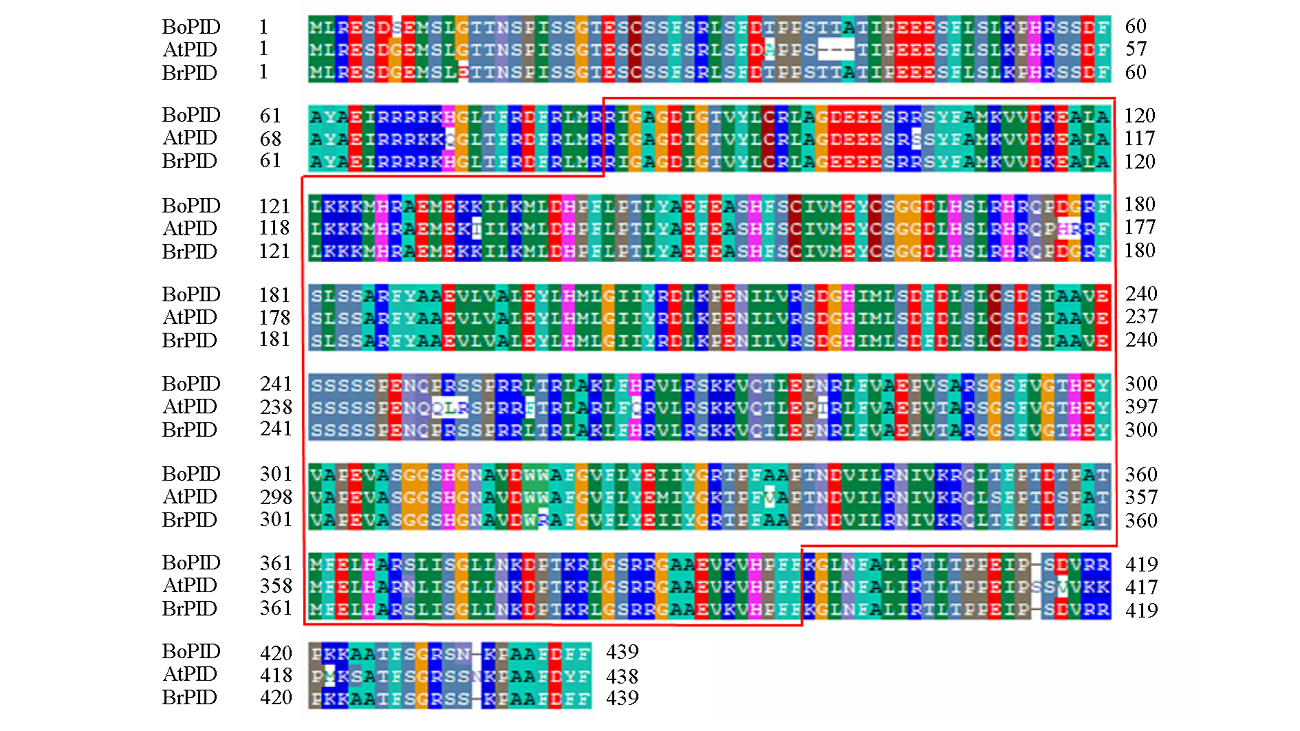
图3 甘蓝BoPID、蛋白与AtPID和BrPID同源蛋白序列多重比对分析
Fig. 3 Multiple alignment analysis of BoPID protein and homologous AtPID and BrPID protein sequences in Brassica oleracea
| 启动子顺式作用元件 Promotercis-acting element | 元件序列 Element sequence | 功能 Function | 位置/aa Location |
|---|---|---|---|
| TGA-box | TGACGTAA | 生长素响应元件 Auxin response element | -86 |
| AAGAA-motif | GTAAAGAAA | 脱落酸响应元件 Abscisic acid response element | -339、-203 |
| ABRE | TACGGTC | -110、-132、-199、 -856 | |
| DRE | GCCGAC | -129 | |
| G-box | CACGTG | -73 | |
| ACE | GACACGTATG | -54、-1 356 | |
| ARE | AAACCA | 厌氧诱导元件 Anaerobic induction element | -487、-224 |
| G-BOX | CACGTG | 光响应元件 Light responsive element | -69、-110 |
| AE-box | AGAAACAA | -100 | |
| GT1-motif | GGTTAA | -517 | |
| GTGGC-motif | CATCGTGTGGC | -102 | |
| TCT-motif | TCTTAC | -120 | |
| CGTCA-motif | CGTCA | -320 | |
| ERE | ATTTCATA | 乙烯响应元件 Ethylene-responsive element | -676、-868、-1 399 |
| TGACG-motif | TGACG | 茉莉酸响应元件MeJA-responsiveness | -305 |
| AT-rich element | ATAGAAATCAA | 水杨酸响应元件 Salicylic acid response element | -837 |
| MBS | CAACTG | MYB结合位点 MYB binding site | -149 |
| MYC | CATTTG | 胁迫响应元件 Stress response element | -404 |
| STRE | AGGGG | -612、-713 |
表2 BoPID启动子顺式作用元件
Table 2 cis-Acting elements of the BoPID promoter
| 启动子顺式作用元件 Promotercis-acting element | 元件序列 Element sequence | 功能 Function | 位置/aa Location |
|---|---|---|---|
| TGA-box | TGACGTAA | 生长素响应元件 Auxin response element | -86 |
| AAGAA-motif | GTAAAGAAA | 脱落酸响应元件 Abscisic acid response element | -339、-203 |
| ABRE | TACGGTC | -110、-132、-199、 -856 | |
| DRE | GCCGAC | -129 | |
| G-box | CACGTG | -73 | |
| ACE | GACACGTATG | -54、-1 356 | |
| ARE | AAACCA | 厌氧诱导元件 Anaerobic induction element | -487、-224 |
| G-BOX | CACGTG | 光响应元件 Light responsive element | -69、-110 |
| AE-box | AGAAACAA | -100 | |
| GT1-motif | GGTTAA | -517 | |
| GTGGC-motif | CATCGTGTGGC | -102 | |
| TCT-motif | TCTTAC | -120 | |
| CGTCA-motif | CGTCA | -320 | |
| ERE | ATTTCATA | 乙烯响应元件 Ethylene-responsive element | -676、-868、-1 399 |
| TGACG-motif | TGACG | 茉莉酸响应元件MeJA-responsiveness | -305 |
| AT-rich element | ATAGAAATCAA | 水杨酸响应元件 Salicylic acid response element | -837 |
| MBS | CAACTG | MYB结合位点 MYB binding site | -149 |
| MYC | CATTTG | 胁迫响应元件 Stress response element | -404 |
| STRE | AGGGG | -612、-713 |
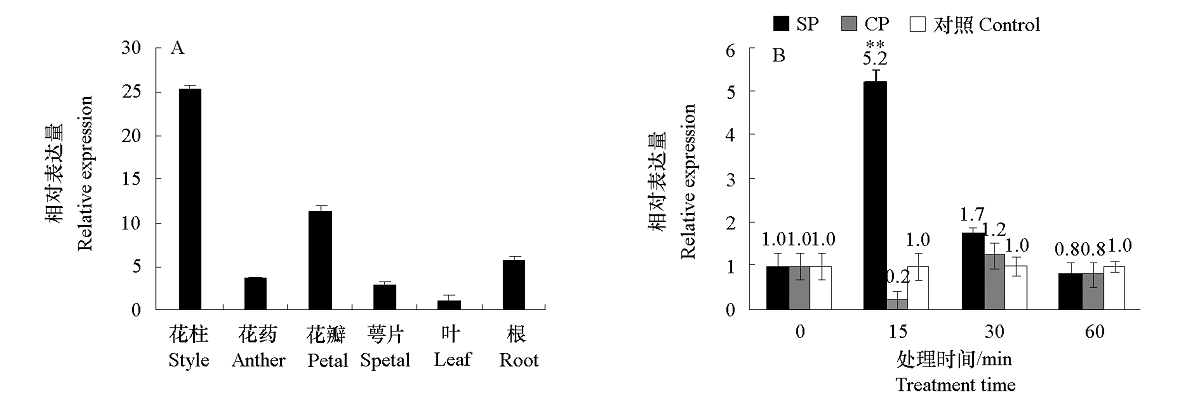
图6 甘蓝BoPID在不同组织、自花(SP)和异花(CP)授粉后不同时间的表达分析
Fig. 6 Expression pattern of BoPID in different tissues,different times of self-flowering and cross-flowering in Brassica oleracea ** P < 0.001.
| 候选蛋白 Candidate protein | 蛋白名称 Protein name | 功能注释 Functional comment |
|---|---|---|
| BoCML12 | 类钙调蛋白12 Calciumodulin-like protein 12 | 编码类钙调蛋白12,含有6个EF-Hand结合基序,响应机械刺激反应表达 The calmodulin-like 12,which contains six EF-Hand binding motifs,is expressed in response to a mechanical stimulation response |
| BoCaM2 | 钙调蛋白2 Calmodulin 2 | 编码含有4个EF-Hand结合基序的钙结合蛋白2 Calcium binding protein 2 encoding four EF-Hand binding motifs |
| BoPIN1 | 生长素极性运输载体 Auxin efflux carrier 1 | pin1突变体的特征在于不引发任何花的花序分生组织,导致形成针状花序 The pin1mutant is characterized by not inducing any inflorescence meristem of the flower,resulting in the formation of needles |
表3 候选蛋白的功能注释分析
Table 3 Functional annotation analysis of candidate proteins
| 候选蛋白 Candidate protein | 蛋白名称 Protein name | 功能注释 Functional comment |
|---|---|---|
| BoCML12 | 类钙调蛋白12 Calciumodulin-like protein 12 | 编码类钙调蛋白12,含有6个EF-Hand结合基序,响应机械刺激反应表达 The calmodulin-like 12,which contains six EF-Hand binding motifs,is expressed in response to a mechanical stimulation response |
| BoCaM2 | 钙调蛋白2 Calmodulin 2 | 编码含有4个EF-Hand结合基序的钙结合蛋白2 Calcium binding protein 2 encoding four EF-Hand binding motifs |
| BoPIN1 | 生长素极性运输载体 Auxin efflux carrier 1 | pin1突变体的特征在于不引发任何花的花序分生组织,导致形成针状花序 The pin1mutant is characterized by not inducing any inflorescence meristem of the flower,resulting in the formation of needles |
| [1] | Barbez E, Kleine-Vehn J. 2013. Divide Et impera-cellular auxin compartmentalization. Current Opinion in Plant Biolog, 16 (1):78-84. |
| [2] |
Benjamins R, Ampudia C G, Hooykaas P J. 2003. PINOID-mediated signaling involves calcium-binding proteins. Plant Physiology, 132(3):1623-1630.
doi: 10.1104/pp.103.019943 URL |
| [3] | Cui Y N, Zhuang M, Wu J, Liu J S, Zhang Y Y, Zhang L K, Huang Y L, Cai X, Liang J L, Zhang K, Wang X W, Cheng F. 2020. Segmental translocation contributed to the origin of the Brassica S-locus Horticultural Plant Journal, 6 (3):167-178. |
| [4] |
Friml J, Vieten A, Sauer M, Weijers D, Schwarz H, Hamann T, Offringa R, Jürgens G. 2003. Efflux-dependent auxin gradients establish the apical-basal axis of Arabidopsis. Nature, 426(6963):147.
pmid: 14614497 |
| [5] |
Geldner N, Anders N, Wolters H, Keicher J, Kornberger W, Muller P, Delbarre A, Ueda T, Nakano A, Jurgens G. 2003. The Arabidopsis GNOM ARF-GEF mediates endosomal recycling,auxin transport,and auxin-dependent plant growth. Cell, 112:219-230.
pmid: 12553910 |
| [6] |
Grunewald W, Friml J. 2010. The march of the PINs: developmental plasticity by dynamic polar targeting in plant cells. The EMBO Journal, 29 (16):2700-2714.
doi: 10.1038/emboj.2010.181 pmid: 20717140 |
| [7] |
Indriolo E, Safavian D, Goring D R. 2014. The ARC1 E3 ligase promotes two different self-pollen avoidance traits in Arabidopsis. The Plant Cell, 26:1525-1543.
pmid: 24748043 |
| [8] |
Kramer E M, Bennett M J. 2006. Auxin transport: a field in flux. Trends in Plant Science, 11(8):382-386.
doi: 10.1016/j.tplants.2006.06.002 URL |
| [9] |
Křeček P, Skůpa P, Libus J, Naramoto S, Tejos R, Friml J. 2009. The PIN-FORMED(PIN)protein family of auxin transporters. Genome Biol, 10:249.
doi: 10.1186/gb-2009-10-12-249 URL |
| [10] |
Landoni M, Francesco A D, Galbiati M, Tonelli C. 2010. A loss-of-function mutation in Calmodulin 2 gene affects pollen germination in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Molecular Biology, 74(3):235-247.
doi: 10.1007/s11103-010-9669-5 URL |
| [11] |
Larsson E, Franks R G, Sundberg E. 2013. Auxin and the Arabidopsis thaliana gynoecium. Journal of Experimental Botany, 64(9):2619-2627.
doi: 10.1093/jxb/ert099 URL |
| [12] |
Lian X P, Zhang H C, Zeng J, Wang Y K, Bai X J, Liu Q Y, Zuo T H, Zhang Y Z, Converse R, Zhu L Q. 2020. C2H2-like zinc fnger protein 1 causes pollen and pistil malformation through the auxin pathway. Plant Growth Regulation, 90:505-518.
doi: 10.1007/s10725-019-00568-1 URL |
| [13] | Liu J, ZhangH C, Lian X P. 2015. Identification of interacting motifs between armadillo repeat containing 1(ARC1)and exocyst 70A1(Exo70A1) proteins in Brassica oleracea. Protein J,doi:10.1007/s10930-015-9644-8. |
| [14] |
Liu N N. 2019. Effects of IAA and ABA on the immature peach fruit development process. Horticultural Plant Journal, 5 (4):145-154.
doi: 10.1016/j.hpj.2019.01.005 URL |
| [15] |
Livak K J, Schmittgen T D. 2001. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2-ΔΔCt method. Methods, 25(4):402-408.
pmid: 11846609 |
| [16] |
Michniewicz M, Zago M K, Abas L, Weijers D, Schweighofer A, Meskiene I, Heisler M G, Ohno C, Zhang J, Huang F, Schwab R, Weigel D, Meyerowitz E M, Luschnig C, Offringa R, Friml J. 2007. Antagonistic regulation of PIN phosphorylation by PP2A and PINOID directs auxin flux. Cell, 130:1044-1056.
pmid: 17889649 |
| [17] |
Nasrallah J B, Nasrallah M E. 2014. Robust self-incompatibility in the absence of a functional ARC1 gene in Arabidopsis thaliana. The Plant Cell, 26:3838-3841.
doi: 10.1105/tpc.114.129387 pmid: 25336507 |
| [18] | Nasrallah M E, Liu P, Nasrallah J B. 2002. Generation of self-incompatible Arabidopsis thaliana by transfer of two S locus genes from A. lyrata. Science, 297:247-249. |
| [19] | M A, Yee D, Haasen K E, Goring D R. 2008. ‘Self'pollen rejection through the intersection of two cellular pathways in the Brassicaceae: self-incompatibility and the compatible pollen response//Vernonica E, Self-incompatibility in flowering plants. Berlin,Heidelberg:Springer:173-191. |
| [20] |
Scandola S, Samuel M A. 2019. A flower-specific phospholipase D is a stigmatic compatibility factor targeted by the self-incompatibility response in Brassica napus. Current Biology, 29:1-7.
doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2018.11.016 URL |
| [21] | Tantikanjana T, Nasrallah J B. 2012. Non-cell-autonomous regulation of crucifer self-incompatibility by auxin response factor ARF3. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 109 (47):19468-19473. |
| [22] |
Vehn K J, Huang F, Naramoto S, Zhang J, Michniewicz M, Offringa R, Frim J. 2009. PIN auxin efflux carrier polarity is regulated by PINOID Kinase-mediated recruitment into GNOM-independent trafficking in Arabidopsis. The Plant Cell, 21:3839-3849.
doi: 10.1105/tpc.109.071639 URL |
| [23] |
Vieten A, Sauer M, Brewer P B, Friml J. 2007. Molecular and cellular aspects of auxin-transport-mediated development. Trends Plant Sci, 12:160-168.
pmid: 17369077 |
| [24] | Wang Yu-kui, Bai Xiao-jing, Lian Xiao-ping, Zhang He-cui, Luo Shao-lan, Pu Min, Zuo Tong-hong, Liu Qian-ying, Zhu Li-quan. 2018. Cloning and expression analysis of BoSPx in Brassica oleracea. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 51 (22):4328-4338. (in Chinese) |
| 王玉奎, 白晓璟, 廉小平, 张贺翠, 罗绍兰, 蒲敏, 左同鸿, 刘倩莹, 朱利泉. 2018. 甘蓝 BoSPx的克隆与表达分析. 中国农业科学, 51 (22):4328-4338. | |
| [25] | Wang Yu-kui, Zhang He-cui, Bai Xia-jing, Lian Xiao-ping, Shi Song-mei, Liu Qian-ying, Zuo Tong-hong, Zhu Li-quan. 2019. Characteristics and expression analysis of BoPINs family genes in Brassica oleracea. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 45 (8):1270-1278. ( in Chinese). |
| 王玉奎, 张贺翠, 白晓璟, 廉小平, 施松梅, 刘倩莹, 左同鸿, 朱利泉. 2019. 甘蓝 BoPINs家族基因的特征和表达分析, 作物学报, 45 (8):1270-1278. | |
| [26] | Yan Shuangshuang, Qiu Zhengkun, Yu Bingwei, Ming Fangyan, Chen Changming, Lei Jianjun, Cao Bihao. 2020. Advances in phytohormone auxin response to high temperature. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 47 (11):2238-2246. (in Chinese) |
| 颜爽爽, 邱正坤, 余炳伟, 明方艳, 陈长明, 雷建军, 曹必好. 2020. 植物生长素响应高温胁迫研究进展. 园艺学报, 47 (11):2238-2246. | |
| [27] | Zeng J, Mo Y L, Chen J J, Li C M, Zhao L, Liu Y H. 2020. Expression and interaction proteins analysis of BjuFKF 1 in stem mustard. Scientia Horticulturae,269,109430. |
| [28] |
Zhu Li-quan, Zhou Yan. 2015. Protein elements and signal transduction process of self-incompatibility in Brassica oleracea. Acta Agron Sin, 41 (1):1-14. ( in Chinese).
doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1006.2015.00001 URL |
| 朱利泉, 周燕. 2015. 甘蓝自交不亲和性信号传导元件与传导过程. 作物学报, 41 (1):1-14. |
| [1] | 韩 睿, 钟雄辉, 陈登辉, 崔 建, 乐祥庆, 颉建明, 康俊根, . 黑腐病菌效应因子XopR的甘蓝靶标基因BobHLH34的克隆及功能分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(2): 319-330. |
| [2] | 崔建, 钟雄辉, 刘泽慈, 陈登辉, 李海龙, 韩睿, 乐祥庆, 康俊根, 王超. 结球甘蓝染色体片段替换系构建[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(1): 65-78. |
| [3] | 吕红豪, 杨丽梅, 方智远, 张扬勇, 庄 木, 刘玉梅, 王 勇, 季家磊, 李占省, 韩风庆. 春甘蓝新品种‘中甘27’和‘中甘28’[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(S1): 63-64. |
| [4] | 周 娜, 陶伟林, 陆景伟, 郑 阳, 胡 燕, 潘晓雪. 甘蓝新品种‘渝园春印’[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(S1): 65-66. |
| [5] | 李强, 蔡玉梅, 苏彦宾, 王英, 顾丽嫱, 赵玉倩. 中早熟甘蓝新品种‘劲绿60’[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(8): 1835-1836. |
| [6] | 陈道宗, 刘镒, 沈文杰, 朱博, 谭晨. 白菜、甘蓝和甘蓝型油菜PAP1/2同源基因的鉴定及分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(6): 1301-1312. |
| [7] | 杨丽梅, 方智远. 中国甘蓝遗传育种研究60年[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(10): 2075-2098. |
| [8] | 吕红豪, 杨丽梅, 方智远, 张扬勇, 庄木, 刘玉梅, 王勇, 季家磊, 李占省, 韩风庆. 春甘蓝新品种'中甘26'[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(10): 2285-2286. |
| [9] | 吕红豪, 杨丽梅, 方智远, 张扬勇, 庄木, 刘玉梅, 孙培田, 王勇, 季家磊, 李占省, 韩风庆. 抗枯萎病早熟优质春甘蓝新品种‘YR中甘21’[J]. 园艺学报, 2021, 48(9): 1839-1840. |
| [10] | 董艺, 冯羽飞, 许忠民, 王世民, 唐鸿吕, 黄炜. SSR标记遗传距离与结球甘蓝杂种优势的关系分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2021, 48(5): 934-946. |
| [11] | 任文静, 于海龙, 陈立, 张斌, 陈文迪, 方智远, 杨丽梅, 庄木, 吕红豪, 王勇, 季家磊, 张扬勇. 甘蓝Ogura CMS育性恢复基因Rfo的传递效率解析及育种应用[J]. 园艺学报, 2021, 48(11): 2197-2210. |
| [12] | 杨丽梅, 方智远, 张扬勇, 庄 木, 吕红豪, 王 勇, 季家磊, 刘玉梅, 李占省, 韩风庆. 中国结球甘蓝抗病抗逆遗传育种近年研究进展[J]. 园艺学报, 2020, 47(9): 1678-1688. |
| [13] | 王五宏,汪精磊,李必元,魏庆镇,胡天华,胡海娇,包崇来*. 结球甘蓝抽薹性遗传规律和QTL定位分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2020, 47(5): 974-982. |
| [14] | 张扬勇,方智远*,杨丽梅,刘玉梅,庄 木,吕红豪,李占省,王 勇. 露地越冬甘蓝新品种‘中甘1305’[J]. 园艺学报, 2020, 47(3): 607-608. |
| [15] | 吕红豪,邢苗苗,杨丽梅,庄 木,张扬勇,王 勇,方智远*. 甘蓝抗芜菁花叶病毒育种研究进展[J]. 园艺学报, 2019, 46(9): 1765-1778. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
版权所有 © 2012 《园艺学报》编辑部 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
编辑部地址: 北京市海淀区中关村南大街12号中国农业科学院蔬菜花卉研究所 邮编: 100081
电话: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
技术支持:北京玛格泰克科技发展有限公司