
园艺学报 ›› 2021, Vol. 48 ›› Issue (1): 83-95.doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2020-0042
荐红举1, 万梦圆1, 付毅1, 丁艺1, 琚熙三1, 尚丽娜1, 李辉1, 王季春1, 胡柏耿2, 吕典秋1,**( )
)
收稿日期:2020-03-30
修回日期:2020-06-02
出版日期:2021-01-25
发布日期:2021-01-29
通讯作者:
吕典秋
E-mail:smallpotatoes@126.com
基金资助:
JIAN Hongju1, WAN Mengyuan1, FU Yi1, DING Yi1, JU Xisan1, SHANG Lina1, LI Hui1, WANG Jichun1, HU Bogeng2, LÜ Dianqiu1,**( )
)
Received:2020-03-30
Revised:2020-06-02
Online:2021-01-25
Published:2021-01-29
Contact:
Lü Dianqiu
E-mail:smallpotatoes@126.com
摘要:
利用拟南芥几丁质酶(Chitinase,CHI)基因家族蛋白序列在马铃薯基因组内进行BlastP分析,获得马铃薯CHI家族成员,并对其进行基因结构分析、motif预测、进化树构建、顺式作用元件和组织表达分析。共有26个马铃薯CHI基因成员得到鉴定,其所有成员均含有较少的内含子,其中motif 1 ~ motif 6均含有具有催化功能的GH19结构域。一共检测到166个胁迫或激素响应元件。进化树分析显示,CHI分为6个亚家族。马铃薯几丁质酶基因在不同组织中差异表达并且在水杨酸或茉莉酸处理后诱导表达,暗示水杨酸和茉莉酸对几丁质酶家族有不同的调控作用。
中图分类号:
荐红举, 万梦圆, 付毅, 丁艺, 琚熙三, 尚丽娜, 李辉, 王季春, 胡柏耿, 吕典秋. 马铃薯CHI家族基因鉴定及其对外源水杨酸和茉莉酸的响应分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2021, 48(1): 83-95.
JIAN Hongju, WAN Mengyuan, FU Yi, DING Yi, JU Xisan, SHANG Lina, LI Hui, WANG Jichun, HU Bogeng, LÜ Dianqiu. Genome-wide Identification and Expression Analysis of Chitinase Gene Family in Potato and Its Response to Exogenous Salicylic Acid and Jasmonic Acid[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2021, 48(1): 83-95.
| 基因名称 Gene | 引物序列(5′-3′) Primer sequence |
|---|---|
| StuEFLa | F:ATTGGAAACGGATATGCTCCA;R:TCCTTACCTGAACGCCTGTCA |
| StuChi7 | F:CGAATACATTGAACAAAACGCG;R:GTATCATTCTTCGTTGGCTTCC |
| StuChi11 | F:CGTCATCTCAAATTCCGTGTTT;R:CAGTAGTGTTTTGGGAGGTTTG |
| StuChi17 | F:CTAAACGACTTCCTGGTTTTGG;R:CATTGAGTCAACATCACCTTGG |
| StuChi21 | F:ACTTCCCATGAAACTACTGGAG;R:TGCTCTCTAAGGAAGCAGTAAC |
表1 引物序列
Table 1 Primer sequences
| 基因名称 Gene | 引物序列(5′-3′) Primer sequence |
|---|---|
| StuEFLa | F:ATTGGAAACGGATATGCTCCA;R:TCCTTACCTGAACGCCTGTCA |
| StuChi7 | F:CGAATACATTGAACAAAACGCG;R:GTATCATTCTTCGTTGGCTTCC |
| StuChi11 | F:CGTCATCTCAAATTCCGTGTTT;R:CAGTAGTGTTTTGGGAGGTTTG |
| StuChi17 | F:CTAAACGACTTCCTGGTTTTGG;R:CATTGAGTCAACATCACCTTGG |
| StuChi21 | F:ACTTCCCATGAAACTACTGGAG;R:TGCTCTCTAAGGAAGCAGTAAC |
| 基因 Gene | 基因编号 Gene ID | 位置 Location | 氨基酸数 Number of amino acid | 分子量/D MW | pI | 外显子数Exon No. | 亚细胞定位Subcellular location | 分类 Subgroup | 亚家族Subfamily |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| StuChi1 | PGSC0003DMG400000073 | chr01: 72805788-72807273 | 298 | 31 990.93 | 4.5 | 1 | 细胞外 Outside | C | GH18 |
| StuChi2 | PGSC0003DMG400000074 | chr01: 72808827-72810061 | 298 | 31 821.89 | 4.6 | 1 | 细胞外 Outside | C | GH18 |
| StuChi3 | PGSC0003DMG400000078 | chr01: 72833577-72842485 | 302 | 32 363.59 | 5.9 | 1 | 细胞外 Outside | C | GH18 |
| StuChi4 | PGSC0003DMG400001528 | chr02: 38744461-38745679 | 252 | 27 535.83 | 5.9 | 3 | 细胞外 Outside | F | GH19 |
| StuChi5 | PGSC0003DMG400001529 | chr02: 38749197-38750328 | 254 | 27 389.43 | 4.7 | 3 | 细胞外 Outside | F | GH19 |
| StuChi6 | PGSC0003DMG400003191 | chr07: 334428-335534 | 368 | 41 516.91 | 7.1 | 1 | 细胞外 Outside | A | GH18 |
| StuChi7 | PGSC0003DMG400004593 | chr12: 59618049-59621290 | 327 | 36 260.51 | 7.0 | 3 | 细胞外 Outside | D | GH19 |
| StuChi8 | PGSC0003DMG400006591 | chr03: 44670486-44671710 | 294 | 32 248.04 | 9.3 | 1 | 质膜Plasma membrane | C | GH18 |
| StuChi9 | PGSC0003DMG400008673 | chr02: 19537307-19539201 | 264 | 28 748.54 | 8.8 | 3 | 细胞外 Outside | F | GH19 |
| 基因 Gene | 基因编号 Gene ID | 位置 Location | 氨基酸数 Number of amino acid | 分子量/D MW | pI | 外显子数Exon No. | 亚细胞定位Subcellular location | 分类 Subgroup | 亚家族Subfamily |
| StuChi10 | PGSC0003DMG400008796 | chr00: 25050182-25052792 | 323 | 35 031.61 | 6.5 | 3 | 细胞外 Outside | F | GH19 |
| StuChi11 | PGSC0003DMG400008797 | chr00: 25056603-25057931 | 280 | 29 350.85 | 8.5 | 4 | 细胞外 Outside | F | GH19 |
| StuChi12 | PGSC0003DMG400011836 | chr07: 292990-294141 | 383 | 41 627.01 | 4.8 | 1 | 过氧化物酶体 Microbody (Peroxisome) | B | GH18 |
| StuChi13 | PGSC0003DMG400011842 | chr07: 294672-296216 | 355 | 39 811.97 | 9.2 | 2 | 过氧化物酶体 Microbody (Peroxisome) | B | GH18 |
| StuChi14 | PGSC0003DMG400011843 | chr07: 303868-306084 | 372 | 42 305.99 | 9.3 | 3 | 线粒体基质 Mitochondrial matrix space | A | GH18 |
| StuChi15 | PGSC0003DMG400016302 | chr06: 39116330-39117653 | 285 | 31 468.23 | 5.9 | 2 | 细胞外 Outside | E | GH19 |
| StuChi16 | PGSC0003DMG400016302 | chr06: 39116330-39117653 | 136 | 15 182.02 | 5.4 | 1 | 细胞质 Cytoplasm | E | GH19 |
| StuChi17 | PGSC0003DMG400021602 | chr09: 61360398-61361921 | 323 | 35 986.30 | 7.9 | 3 | 细胞外 Outside | D | GH19 |
| StuChi18 | PGSC0003DMG400025063 | chr04: 61242553-61244259 | 276 | 29 982.95 | 4.6 | 2 | 细胞外 Outside | E | GH19 |
| StuChi19 | PGSC0003DMG400025063 | chr04: 61242553-61244259 | 136 | 14 988.53 | 4.3 | 1 | 细胞质 Cytoplasm | E | GH19 |
| StuChi20 | PGSC0003DMG400026853 | chr00: 21407639-21408792 | 316 | 34 091.35 | 5.2 | 3 | 质膜Plasma membrane | F | GH19 |
| StuChi21 | PGSC0003DMG400026854 | chr00: 21415307-21416600 | 320 | 34 117.04 | 6.2 | 3 | 细胞外 Outside | F | GH19 |
| StuChi22 | PGSC0003DMG400026855 | chr00: 21419777-21420932 | 332 | 35 506.90 | 8.4 | 3 | 细胞外 Outside | F | GH19 |
| StuChi23 | PGSC0003DMG400033882 | chr05: 44304719-44306659 | 292 | 30 945.16 | 7.5 | 2 | 细胞外 Outside | C | GH18 |
| StuChi24 | PGSC0003DMG400037480 | chr07: 347182-349354 | 435 | 49 224.80 | 6.7 | 4 | 质膜Plasma membrane | A | GH18 |
| StuChi25 | PGSC0003DMG400040317 | chr00: 21299520-21300925 | 279 | 29 606.22 | 8.4 | 2 | 细胞外 Outside | F | GH19 |
| StuChi26 | PGSC0003DMG402001531 | chr02: 38760083-38761491 | 263 | 28 819.75 | 9.2 | 3 | 细胞外 Outside | F | GH19 |
表2 马铃薯几丁质酶基因全基因组鉴定与分子特征分析
Table 2 Genome-wide identification and molecular characterization of chitinase gene family in potato
| 基因 Gene | 基因编号 Gene ID | 位置 Location | 氨基酸数 Number of amino acid | 分子量/D MW | pI | 外显子数Exon No. | 亚细胞定位Subcellular location | 分类 Subgroup | 亚家族Subfamily |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| StuChi1 | PGSC0003DMG400000073 | chr01: 72805788-72807273 | 298 | 31 990.93 | 4.5 | 1 | 细胞外 Outside | C | GH18 |
| StuChi2 | PGSC0003DMG400000074 | chr01: 72808827-72810061 | 298 | 31 821.89 | 4.6 | 1 | 细胞外 Outside | C | GH18 |
| StuChi3 | PGSC0003DMG400000078 | chr01: 72833577-72842485 | 302 | 32 363.59 | 5.9 | 1 | 细胞外 Outside | C | GH18 |
| StuChi4 | PGSC0003DMG400001528 | chr02: 38744461-38745679 | 252 | 27 535.83 | 5.9 | 3 | 细胞外 Outside | F | GH19 |
| StuChi5 | PGSC0003DMG400001529 | chr02: 38749197-38750328 | 254 | 27 389.43 | 4.7 | 3 | 细胞外 Outside | F | GH19 |
| StuChi6 | PGSC0003DMG400003191 | chr07: 334428-335534 | 368 | 41 516.91 | 7.1 | 1 | 细胞外 Outside | A | GH18 |
| StuChi7 | PGSC0003DMG400004593 | chr12: 59618049-59621290 | 327 | 36 260.51 | 7.0 | 3 | 细胞外 Outside | D | GH19 |
| StuChi8 | PGSC0003DMG400006591 | chr03: 44670486-44671710 | 294 | 32 248.04 | 9.3 | 1 | 质膜Plasma membrane | C | GH18 |
| StuChi9 | PGSC0003DMG400008673 | chr02: 19537307-19539201 | 264 | 28 748.54 | 8.8 | 3 | 细胞外 Outside | F | GH19 |
| 基因 Gene | 基因编号 Gene ID | 位置 Location | 氨基酸数 Number of amino acid | 分子量/D MW | pI | 外显子数Exon No. | 亚细胞定位Subcellular location | 分类 Subgroup | 亚家族Subfamily |
| StuChi10 | PGSC0003DMG400008796 | chr00: 25050182-25052792 | 323 | 35 031.61 | 6.5 | 3 | 细胞外 Outside | F | GH19 |
| StuChi11 | PGSC0003DMG400008797 | chr00: 25056603-25057931 | 280 | 29 350.85 | 8.5 | 4 | 细胞外 Outside | F | GH19 |
| StuChi12 | PGSC0003DMG400011836 | chr07: 292990-294141 | 383 | 41 627.01 | 4.8 | 1 | 过氧化物酶体 Microbody (Peroxisome) | B | GH18 |
| StuChi13 | PGSC0003DMG400011842 | chr07: 294672-296216 | 355 | 39 811.97 | 9.2 | 2 | 过氧化物酶体 Microbody (Peroxisome) | B | GH18 |
| StuChi14 | PGSC0003DMG400011843 | chr07: 303868-306084 | 372 | 42 305.99 | 9.3 | 3 | 线粒体基质 Mitochondrial matrix space | A | GH18 |
| StuChi15 | PGSC0003DMG400016302 | chr06: 39116330-39117653 | 285 | 31 468.23 | 5.9 | 2 | 细胞外 Outside | E | GH19 |
| StuChi16 | PGSC0003DMG400016302 | chr06: 39116330-39117653 | 136 | 15 182.02 | 5.4 | 1 | 细胞质 Cytoplasm | E | GH19 |
| StuChi17 | PGSC0003DMG400021602 | chr09: 61360398-61361921 | 323 | 35 986.30 | 7.9 | 3 | 细胞外 Outside | D | GH19 |
| StuChi18 | PGSC0003DMG400025063 | chr04: 61242553-61244259 | 276 | 29 982.95 | 4.6 | 2 | 细胞外 Outside | E | GH19 |
| StuChi19 | PGSC0003DMG400025063 | chr04: 61242553-61244259 | 136 | 14 988.53 | 4.3 | 1 | 细胞质 Cytoplasm | E | GH19 |
| StuChi20 | PGSC0003DMG400026853 | chr00: 21407639-21408792 | 316 | 34 091.35 | 5.2 | 3 | 质膜Plasma membrane | F | GH19 |
| StuChi21 | PGSC0003DMG400026854 | chr00: 21415307-21416600 | 320 | 34 117.04 | 6.2 | 3 | 细胞外 Outside | F | GH19 |
| StuChi22 | PGSC0003DMG400026855 | chr00: 21419777-21420932 | 332 | 35 506.90 | 8.4 | 3 | 细胞外 Outside | F | GH19 |
| StuChi23 | PGSC0003DMG400033882 | chr05: 44304719-44306659 | 292 | 30 945.16 | 7.5 | 2 | 细胞外 Outside | C | GH18 |
| StuChi24 | PGSC0003DMG400037480 | chr07: 347182-349354 | 435 | 49 224.80 | 6.7 | 4 | 质膜Plasma membrane | A | GH18 |
| StuChi25 | PGSC0003DMG400040317 | chr00: 21299520-21300925 | 279 | 29 606.22 | 8.4 | 2 | 细胞外 Outside | F | GH19 |
| StuChi26 | PGSC0003DMG402001531 | chr02: 38760083-38761491 | 263 | 28 819.75 | 9.2 | 3 | 细胞外 Outside | F | GH19 |
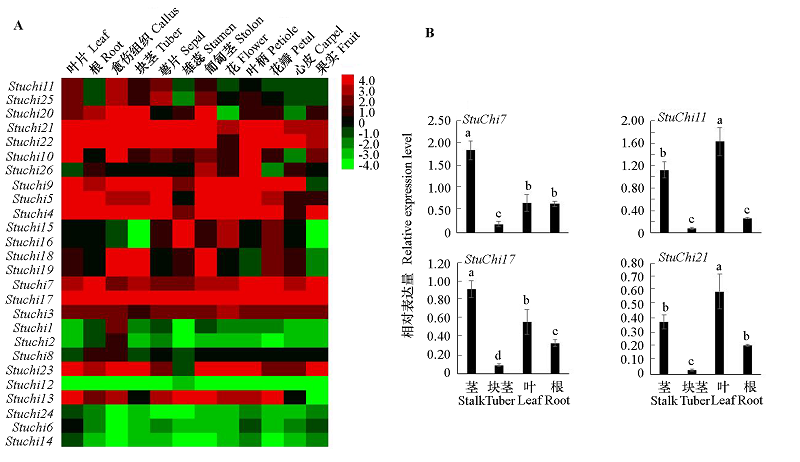
图3 马铃薯几丁质酶基因的组织表达特异性 图中不同小写字母表示在0.05水平差异显著。
Fig. 3 Tissues-specific expression analysis of StuChi genes Small letters in the figure showed significant difference at the level of 0.05.
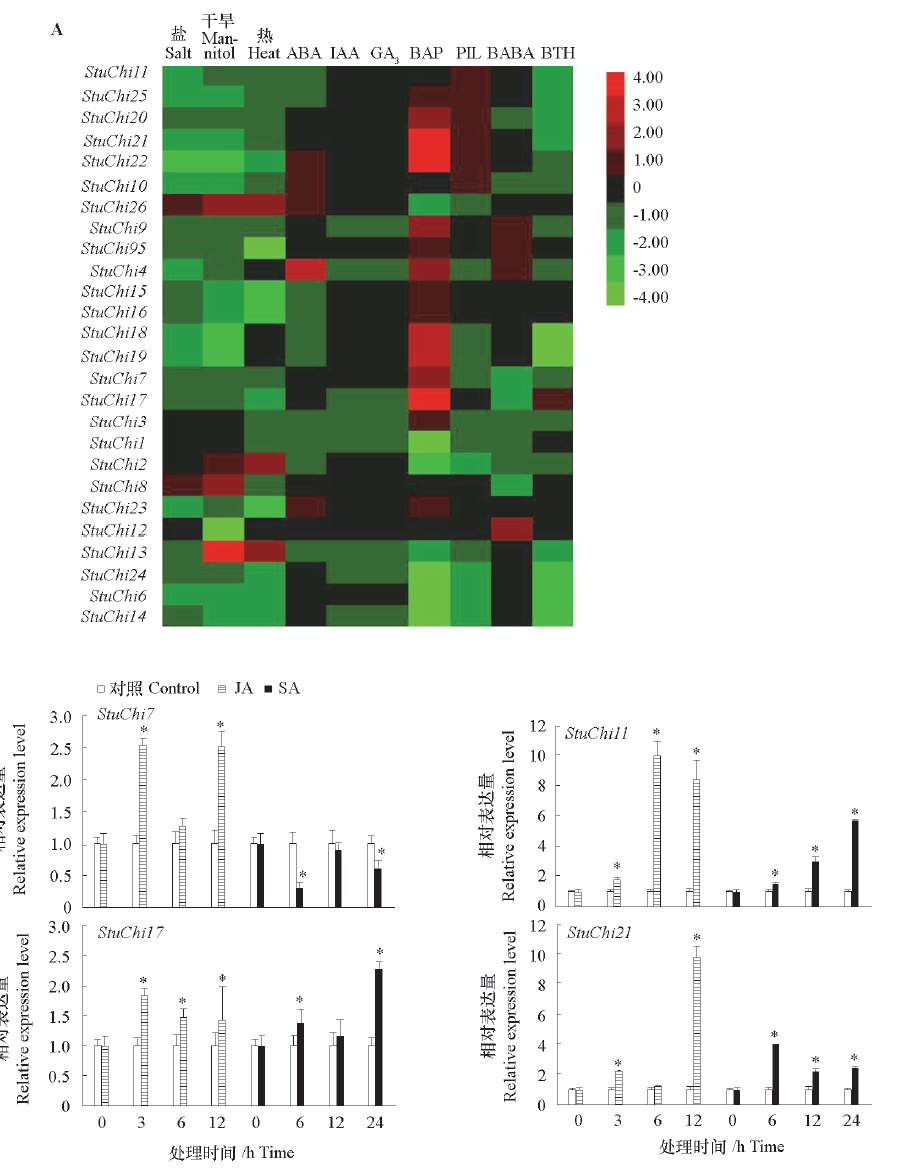
图4 基于转录组数据(A)和植物生长调节剂(B)分析马铃薯几丁质酶基因对环境胁迫的响应 *表示对照与处理在0.05水平差异显著。
Fig. 4 Environmental stresses response analysis of StuChi genes based on RNA-Seq data(A)and exogenous hormones(B) * notes significant differences between control and treatment at 0.05 level.
| [1] |
Backiyarani S, Uma S, Nithya S, Chandrasekar A, Saraswathi M S, Thangavelu R, Mayilvaganan M, Sundararaju P, Singh N K. 2015. Genome-wide analysis and differential expression of chitinases in banana against root lesion nematode(Pratylenchus coffeae)and eumusa leaf spot (Mycosphaerella eumusae) pathogens. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 175(8):3585-3598.
doi: 10.1007/s12010-015-1528-z pmid: 25820355 |
| [2] | Bishop J G, Dean A M, Mitchell-Olds T. 2000. Rapid evolution in plant chitinases:molecular targets of selection in plant-pathogen coevolution. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 97(10):5322-5327. |
| [3] |
Cao J, Li X, Lv Y. 2017. Dynein light chain family genes in 15 plant species:identification,evolution and expression profiles. Plant Science, 254:70-81.
doi: 10.1016/j.plantsci.2016.10.011 URL |
| [4] | Cao J, Tan X N. 2019. Comprehensive analysis of the chitinase family genes in tomato(Solanum lycopersicum). Plants-Basel, 8(3):52. |
| [5] |
Cao R, Liu X, Gao K, Mendgen K, Kang Z, Gao J, Dai Y, Wang X. 2009. Mycoparasitism of endophytic fungi isolated from reed on soilborne phytopathogenic fungi and production of cell wall-degrading enzymes in vitro. Current Microbiology, 59(6):584-592.
doi: 10.1007/s00284-009-9477-9 URL |
| [6] |
Chen J, Piao Y, Liu Y, Li X, Piao Z. 2018. Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of chitinase gene family in Brassica rapa reveals its role in clubroot resistance. Plant Science, 270:257-267.
doi: 10.1016/j.plantsci.2018.02.017 URL |
| [7] |
Chen Q H G, Bleecker A B. 1995. Analysis of Ethylene signal-transduction kinetics associated with seedling-growth response and chitinase induction in wild-type and mutant Arabidopsis. Plant Physiology, 108(2):597-607.
doi: 10.1104/pp.108.2.597 URL |
| [8] |
Chye M L, Zhao K J, He Z M, Ramalingam S, Fung K L. 2005. An agglutinating chitinase with two chitin-binding domains confers fungal protection in transgenic potato. Planta, 220(5):717-730.
doi: 10.1007/s00425-004-1391-6 URL |
| [9] |
Cletus J, Balasubramanian V, Vashisht D, Sakthivel N. 2013. Transgenic expression of plant chitinases to enhance disease resistance. Biotechnology Letters, 35(11):1719-1732.
doi: 10.1007/s10529-013-1269-4 pmid: 23794096 |
| [10] |
Davis J M, Wu H, Cooke J E, Reed J M, Luce K S, Michler C H. 2002. Pathogen challenge,salicylic acid,and jasmonic acid regulate expression of chitinase gene homologs in pine. Molecular Plant-Microbe Interactions, 15(4):380-387.
doi: 10.1094/MPMI.2002.15.4.380 URL |
| [11] | Gregorova Z, Kovacik J, Klejdus B, Maglovski M, Kuna R, Hauptvogel P, Matusikova I. 2015. Drought-induced responses of physiology,metabolites,and PR proteins in Triticum aestivum. Journal of Agricultural & Food Chemistry, 63(37):8125-8133. |
| [12] |
Grover A. 2012. Plant chitinases:genetic diversity and physiological roles. Critical Reviews in Plant Sciences, 31:57-73.
doi: 10.1080/07352689.2011.616043 URL |
| [13] | Guo X L, Bai L R, Su C Q, Shi L R, Wang D W. 2013. Molecular cloning and expression of drought-induced protein 3(DIP3)encoding a class III chitinase in upland rice. Genetics & Molecular Research, 12(4):6860-6870. |
| [14] |
Hamel F, Bellemare G. 1995. Characterization of a class I chitinase gene and of wound-inducible,root and flower-specific chitinase expression in Brassica napus. Biochim Biophys Acta, 1263(3):212-220.
pmid: 7548207 |
| [15] |
Hou Z, Cao J. 2016. Comparative study of the P2X gene family in animals and plants. Purinergic Signal, 12(2):269-281.
doi: 10.1007/s11302-016-9501-z URL |
| [16] |
Jekel P A, Hartmann J B H, Beintema J J. 1991. The primary structure of hevamine,an enzyme with lysozyme chitinase activity from hevea-brasiliensis latex. European Journal of Biochemistry, 200(1):123-130.
pmid: 1879417 |
| [17] | Jiang C, Huang R F, Song J L, Huang M R, Xu L A. 2013. Genomewide analysis of the chitinase gene family in Populus trichocarpa. Journal of Northwest A & F University, 92(1):121-125. |
| [18] | Jiao Long, Bian Lei, Luo Zongxiu, Li Zhaoqun, Xin Zhaojun, Xiu Chunli, Cai Xiaoming, Chen Zongmao. 2020. Comparison of tea plant volatiles exogenously induced by jasmonates or salicylates elicitors. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 47(5):927-938. (in Chinese) |
| 焦龙, 边磊, 罗宗秀, 李兆群, 辛肇军, 修春丽, 蔡晓明, 陈宗懋. 2020. 茉莉酸、水杨酸类激发子外源诱导的茶树挥发物比较. 园艺学报, 47(5):927-938. | |
| [19] |
Kashyap P, Deswal R. 2017. A novel class I Chitinase from Hippophae rhamnoides:indications for participating in ICE-CBF cold stress signaling pathway. Plant Science, 259:62-70.
doi: 10.1016/j.plantsci.2017.03.004 URL |
| [20] | Kasprzewska A. 2003. Plant chitinases-regulation and function. Cellular & Molecular Biology Letters, 8(3):809-824. |
| [21] |
Kesari P, Patil D N, Kumar P, Tomar S, Sharma A K, Kumar P. 2015. Structural and functional evolution of chitinase-like proteins from plants. Proteomics, 15(10):1693-1705.
doi: 10.1002/pmic.201400421 pmid: 25728311 |
| [22] |
Kovacs G, Sagi L, Jacon G, Arinaitwe G, Busogoro J P, Thiry E, Strosse H, Swennen R, Remy S. 2013. Expression of a rice chitinase gene in transgenic banana(‘Gros Michel’,AAA genome group)confers resistance to black leaf streak disease. Transgenic Research, 22(1):117-130.
doi: 10.1007/s11248-012-9631-1 URL |
| [23] |
Lacombe-Harvey M E, Brzezinski R, Beaulieu C. 2018. Chitinolytic functions in actinobacteria:ecology,enzymes,and evolution. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 102(17):7219-7230.
doi: 10.1007/s00253-018-9149-4 pmid: 29931600 |
| [24] |
Lazar A, Coll A, Dobnik D, Baebler S, Bedina-Zavec A, Zel J, Gruden K. 2014. Involvement of potato(Solanum tuberosum L.)MKK6 in response to Potato virus Y. PLoS ONE, 9(8):e104553.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0104553 URL |
| [25] |
Lee C G, Da Silva C A, Dela Cruz C S, Ahangari F, Ma B, Kang M J, He C H, Takyar S, Elias J A. 2011. Role of chitin and chitinase/chitinase-like proteins in inflammation,tissue remodeling,and injury. Annual Review of Physiology, 73:479-501.
doi: 10.1146/annurev-physiol-012110-142250 URL |
| [26] |
Lee J H, Takei K, Sakakibara H, Cho H S, Kim D M, Kim Y S, Min S R, Kim W T, Sohn D Y, Lim Y P, Pai H S. 2003. CHRK1,a chitinase-related receptor-like kinase,plays a role in plant development and cytokinin homeostasis in tobacco. Plant Molecular Biology, 53(6):877-890.
doi: 10.1023/B:PLAN.0000023668.34205.a8 URL |
| [27] |
Li H, Greene L H. 2010. Sequence and structural analysis of the chitinase insertion domain reveals two conserved motifs involved in chitin-binding. PLoS ONE, 5(1):e8654.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0008654 URL |
| [28] | Li Qiang, Qi Jingjing, Dou Wanfu, Qin Xiujuan, He Yongrui, Chen Shanchun. 2020. Overexpression of CsNBS-LRR in citrus confers bacterial canker resistance by regulating SA signaling pathway. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 47(5):817-826. (in Chinese) |
| 李强, 祁静静, 窦万福, 秦秀娟, 何永睿, 陈善春. 2020. 柑橘超量表达CsNBS-LRR通过SA信号途径增强对溃疡病抗性. 园艺学报, 47(5):817-826. | |
| [29] | Lin W, Anuratha C S, Datta K, Potrykus I, Muthukrishnan S, Datta S K. 1995. Genetic-engineering of rice for resistance to sheath blight. Bio-Technology, 13(7):686-691. |
| [30] |
Liu Y, Wang L, Xing X, Sun L, Pan J, Kong X, Zhang M, Li D. 2013. ZmLEA3,a multifunctional group 3 LEA protein from maize(Zea mays L.),is involved in biotic and abiotic stresses. Plant and Cell Physiology, 54(6):944-959.
doi: 10.1093/pcp/pct047 URL |
| [31] | Liu Xia, Huang Xxun, Du Xia, Zhao Bin, Yang Yanli. 2019. The effect of salicylic acid on late blight resistance of different potato varieties. Enshi:China Potato Conference. (in Chinese) |
| 刘霞, 黄勋, 杜霞, 赵彬, 杨艳丽. 2019. 水杨酸对不同马铃薯品种晚疫病抗性的影响. 恩施:中国马铃薯大会. | |
| [32] |
Lopez R C, Gomez-Gomez L. 2009. Isolation of a new fungi and wound-induced chitinase class in corms of Crocus sativus. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 47(5):426-434.
doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2009.01.007 URL |
| [33] |
Ma H R, Wang F, Wang W J, Yin G Y, Zhang D Y, Ding Y Q, Timko M P, Zhang H B. 2016. Alternative splicing of basic chitinase gene PR3b in the low-nicotine mutants of Nicotiana tabacum L. cv. Burley 21. Journal of Experimental Botany, 67(19):5799-5809.
doi: 10.1093/jxb/erw345 URL |
| [34] |
Malolepszy A, Kelly S, Sorensen K K, James E K, Kalisch C, Bozsoki Z, Panting M, Andersen S U, Sato S, Tao K, Jesen D B, Vinter M, de Jong N, Madsen L H, Vmehara Y, Gysel K, Berentsen M V, Blaise M, Jensen K J, Thygesen M B, Sandal N, Andersen K R, Radutoiu S. 2018. A plant chitinase controls cortical infection thread progression and nitrogen-fixing symbiosis. Elife, 7:e38874.
doi: 10.7554/eLife.38874 URL |
| [35] |
Maksimov I V, Abizgildina P P, Sorokan’A V, Burkhanova G F. 2014. Regulation of peroxidase activity under the influence of signaling molecules and Bacillus subtilis 26D in potato plants infected with Phytophthora infestans. Applied Biochemistry and Microbiology, 50(2):173-8
doi: 10.1134/S0003683814020136 URL |
| [36] |
Margispinheiro M, Metzboutigue M H, Awade A, Detapia M, Leret M, Burkard G. 1991. Isolation of a complementary-DNA encoding the bean Pr4 chitinase-an acidic enzyme with an amino-terminus cysteine-rich domain. Plant Molecular Biology, 17(2):243-253.
doi: 10.1007/BF00039499 URL |
| [37] |
Neuhaus J M, Fritig B, Linthorst H J M, Meins F, Mikkelsen J D, Ryals J. 1996. A revised nomenclature for chitinase genes. Plant Molecular Biology Reporter, 14(2):102-104.
doi: 10.1007/BF02684897 URL |
| [38] | Nishizawa Y, Nishio Z, Nakazono K, Soma M, Nakajima E, Ugaki M, Hibi T. 1999. Enhanced resistance to blast(Magnaporthe grisea)in transgenic Japonica rice by constitutive expression of rice chitinase. Theoretical & Applied Genetics, 99(3-4):383-390. |
| [39] |
Ohnuma T, Sorlie M, Fukuda T, Kawamoto N, Taira T, Fukamizo T. 2011. Chitin oligosaccharide binding to a family GH19 chitinase from the moss Bryum coronatum. The Febs Journal, 278(21):3991-4001.
doi: 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2011.08301.x URL |
| [40] |
Passarinho P A, Van Hengel A J, Fransz P F, de Vries S C. 2001. Expression pattern of the Arabidopsis thaliana AtEP3/Atchit IV endochitinase gene. Planta, 212(4):556-567.
pmid: 11525512 |
| [41] |
Petit A N, Baillieul F, Vaillant-Gaveau N, Jacquens L, Conreux A, Jeandet P, Clement C, Fontaine F. 2009. Low responsiveness of grapevine flowers and berries at fruit set to UV-C irradiation. Journal of Experimental Botany, 60(4):1155-1162.
doi: 10.1093/jxb/ern361 URL |
| [42] | Punja Z K, Zhang Y Y. 1993. Plant chitinases and their roles in resistance to fungal diseases. Journal of Nematology, 25(4):526-540. |
| [43] | Ren Yajuan, Wang Haixia, Li Yajun, Chen Yanlin, Wang Jing, Tian Zhendong. 2015. An early β-a minobutyric acid responsive gene StWRKY5 confers resistance to late blight in potato. Molecular Plant Breeding,(6):1207-1213. (in Chinese) |
| 任亚娟, 王海霞, 李亚军, 陈艳林, 王静, 田振东. 2015. β-氨基丁酸早期诱导表达基因StWRKY5参与马铃薯晚疫病抗性. 分子植物育种,(6):1207-1213. | |
| [44] |
Renner T, Specht C D. 2012. Molecular and functional evolution of class I chitinases for plant carnivory in the caryophyllales. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 29(10):2971-2985.
pmid: 22490823 |
| [45] |
Shinya T, Hanai K, Galis I, Suzuki K, Matsuoka K, Matsuoka H, Saito M. 2007. Characterization of NtChitIV,a class IV chitinase induced by beta-1,3-,1,6-glucan elicitor from Alternaria alternata 102:antagonistic effect of salicylic acid and methyl jasmonate on the induction of NtChitIV. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 353(2):311-317.
doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2006.12.009 URL |
| [46] |
Shoresh M, Harman G E. 2008. Genome-wide identification,expression and chromosomal location of the genes encoding chitinolytic enzymes in Zea mays. Molecular Genetics and Genomics, 280(2):173-185.
doi: 10.1007/s00438-008-0354-1 URL |
| [47] |
Su Y, Xu L, Fu Z, Yang Y, Guo J, Wang S, Que Y. 2014. ScChi,encoding an acidic class III chitinase of sugarcane,confers positive responses to biotic and abiotic stresses in sugarcane. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 15(2):2738-2760.
doi: 10.3390/ijms15022738 URL |
| [48] |
Su Y, Xu L, Wang S, Wang Z, Yang Y, Chen Y, Que Y. 2015. Identification,phylogeny,and transcript of chitinase family genes in sugarcane. Scientific Reports, 5:10708.
doi: 10.1038/srep10708 URL |
| [49] |
Suginta W, Sirimontree P, Sritho N, Ohnuma T, Fukamizo T. 2016. The chitin-binding domain of a GH-18 chitinase from Vibrio harveyi is crucial for chitin-chitinase interactions. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 93:1111-1117.
doi: S0141-8130(16)31678-6 pmid: 27667544 |
| [50] | Takashima T, Numata T, Taira T, Fukamizo T, Ohnuma T. 2018. Structure and enzymatic properties of a two-domain family GH19 chitinase from Japanese cedar(Cryptomeria japonica) pollen. Journal of Agricultural & Food Chemistry, 66(22):5699-5706. |
| [51] |
Takenaka Y, Nakano S, Tamoi M, Sakuda S, Fukamizo T. 2009. Chitinase gene expression in response to environmental stresses in Arabidopsis thaliana:chitinase inhibitor allosamidin enhances stress tolerance. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem, 73(5):1066-1071.
doi: 10.1271/bbb.80837 URL |
| [52] |
van der Holst P P, Schlaman H R, Spaink H P. 2001. Proteins involved in the production and perception of oligosaccharides in relation to plant and animal development. Current Opinion in Structural Biology, 11(5):608-616.
doi: 10.1016/S0959-440X(00)00255-4 URL |
| [53] |
Wang L Y, Wang Y S, Cheng H, Zhang J P, Yeok F S. 2015. Cloning of the Aegiceras corniculatum class I chitinase gene(AcCHII)and the response of AcCHII mRNA expression to cadmium stress. Ecotoxicology, 24(7-8):1705-1713.
doi: 10.1007/s10646-015-1502-0 URL |
| [54] |
White R F, Rybicki E P, Vonwvhmar M B, Dekker J L, Antoniw J F. 1987. Detection of PR-1 type proteins in Amaranthaceae,Cheuopodiaceae,Graminae and Solanaceae by immunoelectroblotting. Journal of General Virology, 68:2043-2048.
doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-68-7-2043 URL |
| [55] |
Wu J, Wang Y, Kim S T, Kim S G, Kang K Y. 2013. Characterization of a newly identified rice chitinase-like protein(OsCLP)homologous to xylanase inhibitor. BMC Biotechnology, 13:4.
doi: 10.1186/1472-6750-13-4 URL |
| [56] |
Xu F, Fan C, He Y. 2007. Chitinases in Oryza sativa ssp. japonica and Arabidopsis thaliana. Journal of Genetics and Genomics, 34(2):138-150.
doi: 10.1016/S1673-8527(07)60015-0 URL |
| [57] | Xu J, Xu X, Tian L, Wang G, Zhang X, Wang X, Guo W. 2016. Discovery and identification of candidate genes from the chitinase gene family for Verticillium dahliae resistance in cotton. Science Reports, 6:29022. |
| [58] | Yang J, Zhang K Q. 2019. Chitin synthesis and degradation in fungi biology and enzymes. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology, 1142:153-167. |
| [59] | Yang Yanli. 2010. Preliminary study of exogenous jasmonic acid effects on potato resistance to late blight[Ph. D. Dissertation]. Changsha:Hunan Agricultural University. (in Chinese) |
| 杨艳丽. 2010. 外源茉莉酸影响马铃薯对晚疫病抗性的初步研究[博士论文]. 长沙:湖南农业大学. | |
| [60] |
Zhang C, Zhang L, Wang D, Ma H, Liu B, Shi Z, Ma X H, Chen Y, Chen Q. 2018. Evolutionary history of the glycoside hydrolase 3(GH3)family based on the sequenced genomes of 48 plants and identification of jasmonic acid-related GH3 proteins in Solanum tuberosum. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(7):1850.
doi: 10.3390/ijms19071850 URL |
| [1] | 王晓晨, 聂子页, 刘先菊, 段 伟, 范培格, 梁振昌, . 脱落酸对‘京香玉’葡萄果实单萜物质合成的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(2): 237-249. |
| [2] | 张 欣, 漆艳香, 曾凡云, 王艳玮, 谢培兰, 谢艺贤, 彭 军. 香蕉枯萎病菌Dicer-like基因的功能分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(2): 279-294. |
| [3] | 任 菲, 卢苗苗, 刘吉祥, 陈信立, 刘道凤, 眭顺照, 马 婧. 蜡梅胚胎晚期丰富蛋白基因CpLEA的表达及抗性分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(2): 359-370. |
| [4] | 于婷婷, 李 欢, 宁源生, 宋建飞, 彭璐琳, 贾竣淇, 张玮玮, 杨洪强. 苹果GRAS全基因组鉴定及其对生长素的响应分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(2): 397-409. |
| [5] | 翟含含, 翟宇杰, 田义, 张叶, 杨丽, 温陟良, 陈海江. 桃SAUR家族基因分析及PpSAUR5功能鉴定[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(1): 1-14. |
| [6] | 杨植, 张川疆, 杨芯芳, 董梦怡, 王振磊, 闫芬芬, 吴翠云, 王玖瑞, 刘孟军, 林敏娟. 枣与酸枣杂交后代果实遗传倾向及混合遗传分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(1): 36-52. |
| [7] | 崔建, 钟雄辉, 刘泽慈, 陈登辉, 李海龙, 韩睿, 乐祥庆, 康俊根, 王超. 结球甘蓝染色体片段替换系构建[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(1): 65-78. |
| [8] | 何成勇, 赵晓丽, 许腾飞, 高德航, 李世访, 王红清. 草莓病毒1山东分离物全基因组分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(1): 153-160. |
| [9] | 罗海林, 袁雷, 翁华, 闫佳会, 郭青云, 王文清, 马新明. 蚕豆萎蔫病毒2号青海辣椒分离物的鉴定与全基因组序列克隆[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(1): 161-169. |
| [10] | 忽靖宇, 阙开娟, 缪田丽, 吴少政, 王田田, 张磊, 董鲜, 季鹏章, 董家红. 侵染鸢尾的番茄斑萎病毒鉴定[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(1): 170-176. |
| [11] | 赵雪艳, 王琪, 王莉, 王方圆, 王庆, 李艳. 基于比较转录组的延胡索组织差异性表达分析[J]. 园艺学报, 2023, 50(1): 177-187. |
| [12] | 王 宽, 祁利潘, 吴桂丽, 冯 琰, 王 磊, 尹 江, 罗亚婷, 王 燕, 刘 畅, 龚学臣, 王海军. 中早熟马铃薯新品种‘北方002’[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(S2): 141-142. |
| [13] | 祁利潘, 冯 琰, 王 磊, 尹 江, 王 宽, 罗亚婷, 龚学臣, 刘 畅, 王 燕. 马铃薯新品种‘北方004’[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(S2): 143-144. |
| [14] | 李燕山, 隋启君, 蒋 伟, 杨琼芬, 白建明. 鲜食、淀粉兼用型马铃薯新品种‘云薯113’[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(S2): 145-146. |
| [15] | 邹 雪, 丁 凡, 刘丽芳, 余韩开宗, 陈年伟, 饶莉萍. 紫色马铃薯新品种‘绵紫芋1号’[J]. 园艺学报, 2022, 49(S1): 93-94. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
版权所有 © 2012 《园艺学报》编辑部 京ICP备10030308号-2 国际联网备案号 11010802023439
编辑部地址: 北京市海淀区中关村南大街12号中国农业科学院蔬菜花卉研究所 邮编: 100081
电话: 010-82109523 E-Mail: yuanyixuebao@126.com
技术支持:北京玛格泰克科技发展有限公司